Unit 5b - Land Use and Sustainability
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

91 Terms
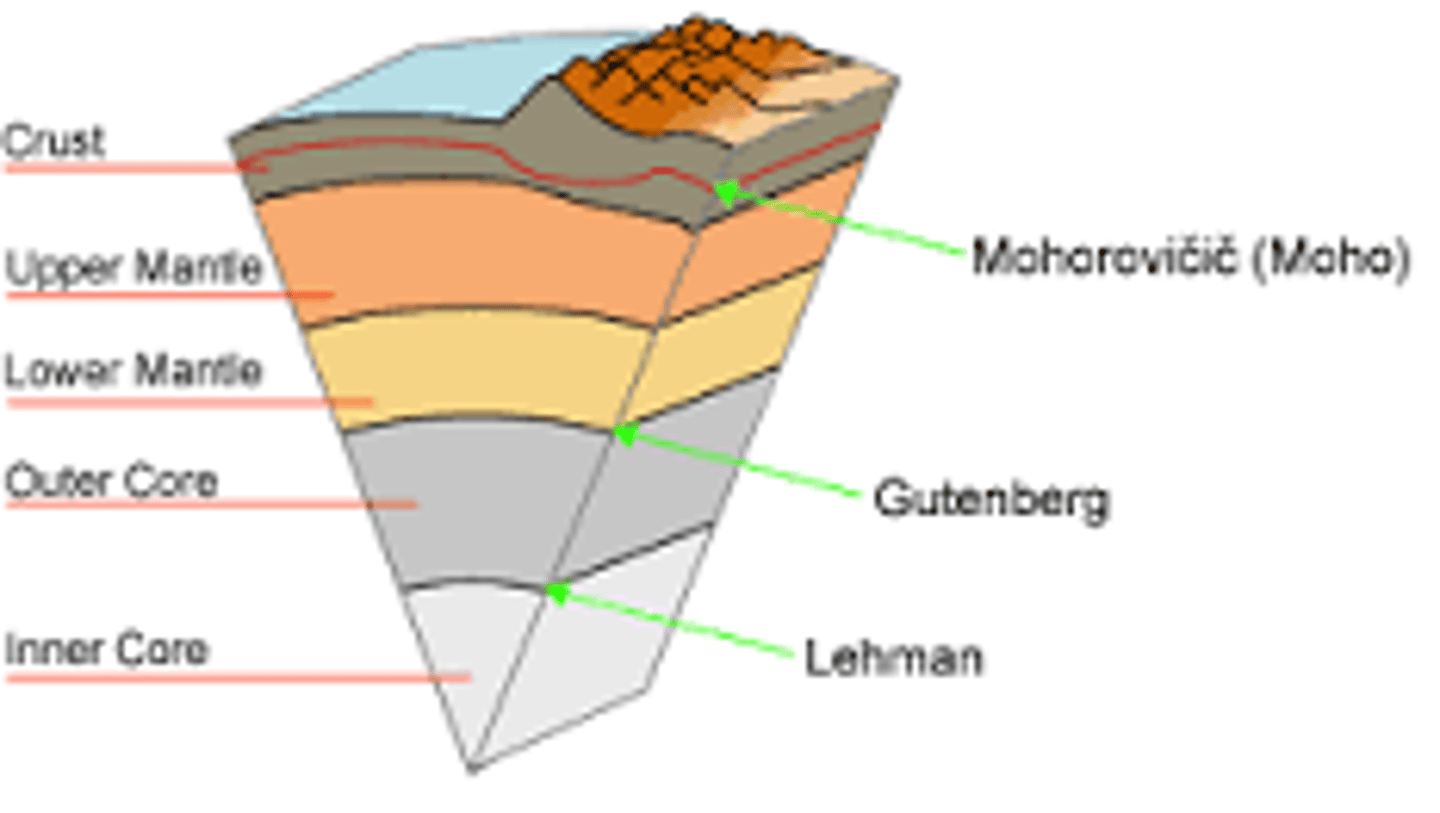
Lithosphere
Earth's crust, 35km to 100km thick.
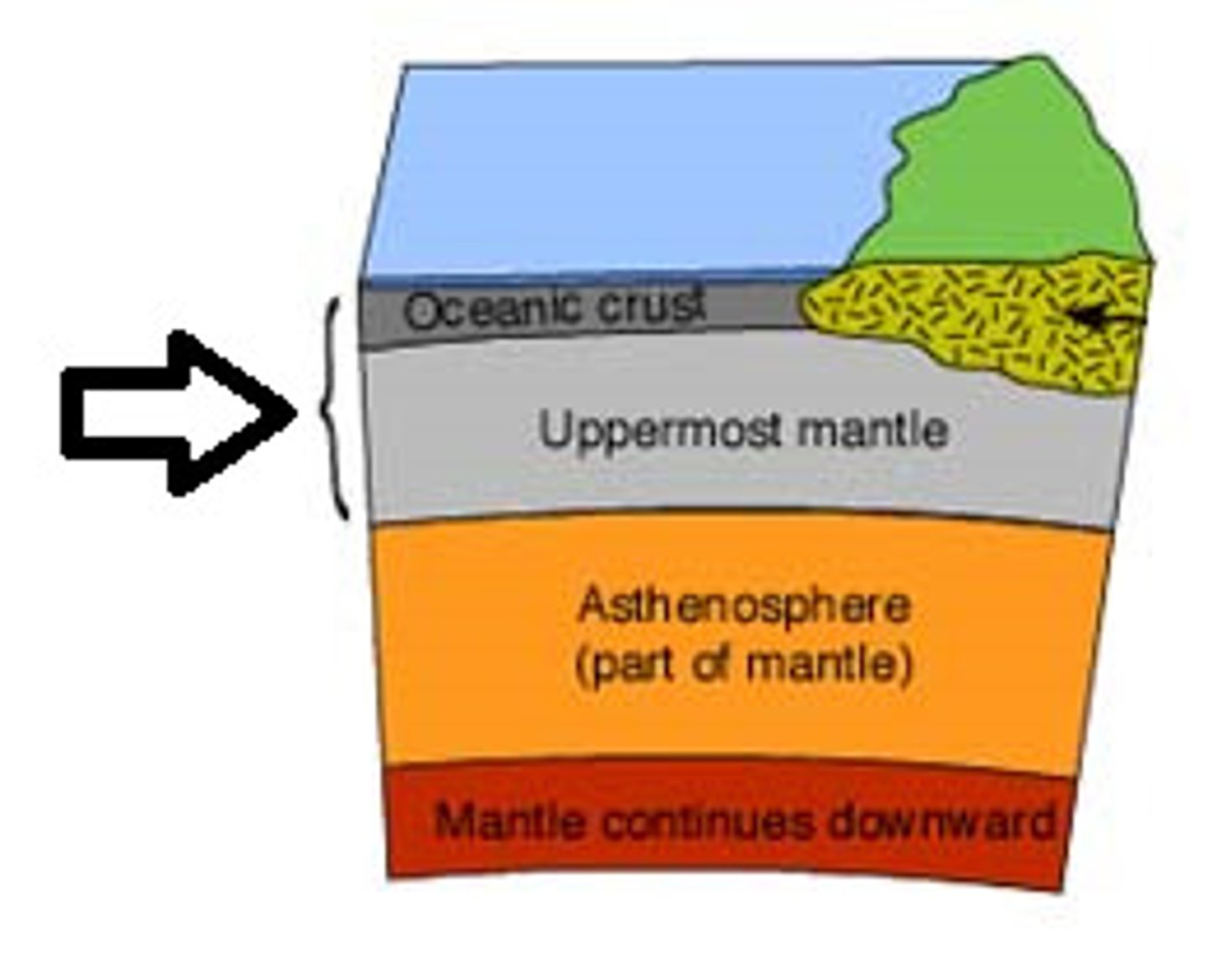
Mantle
Layer acting like fluid rock due to pressure.
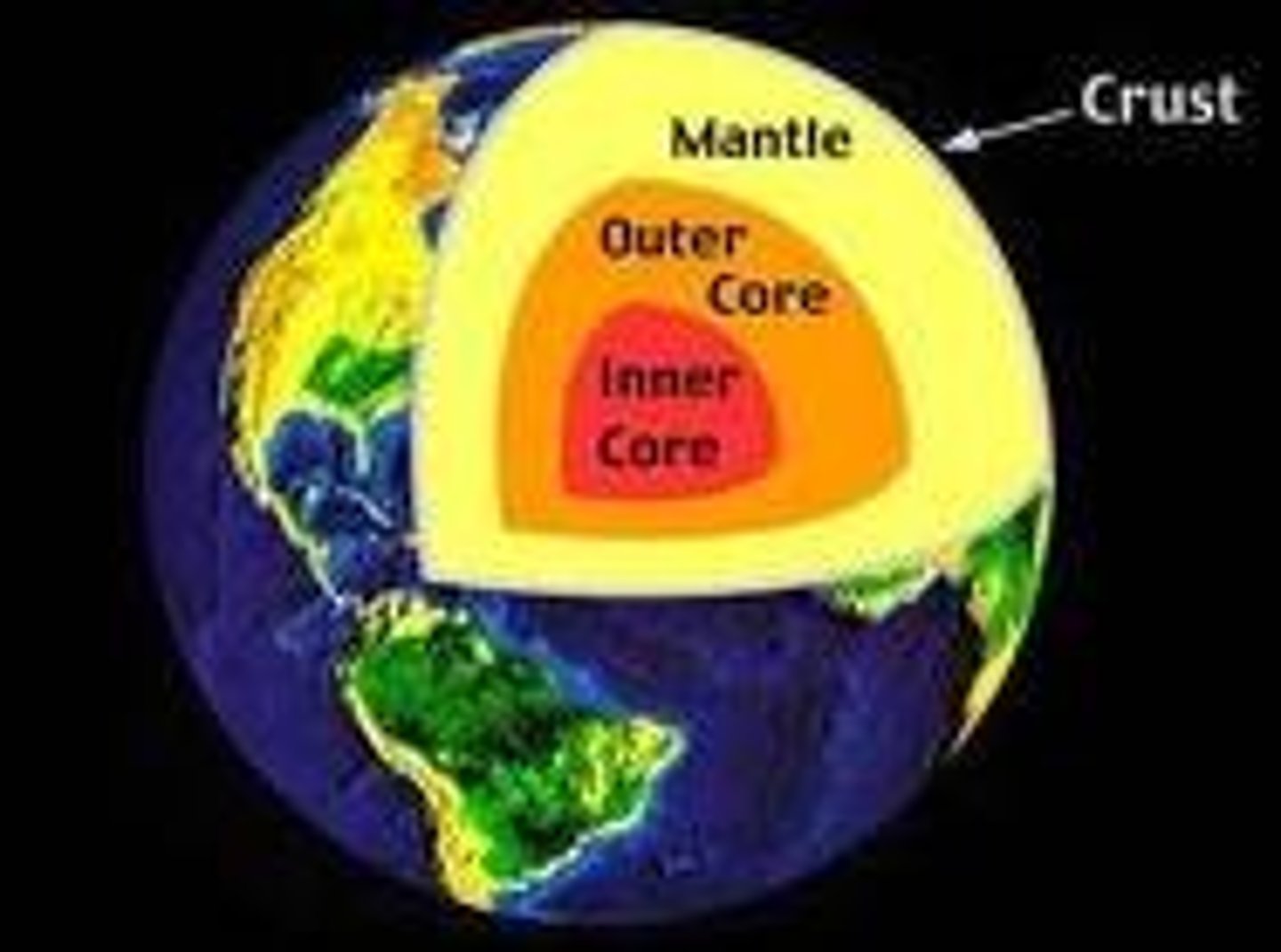
Inner Core
Solid iron, hottest layer under immense pressure.
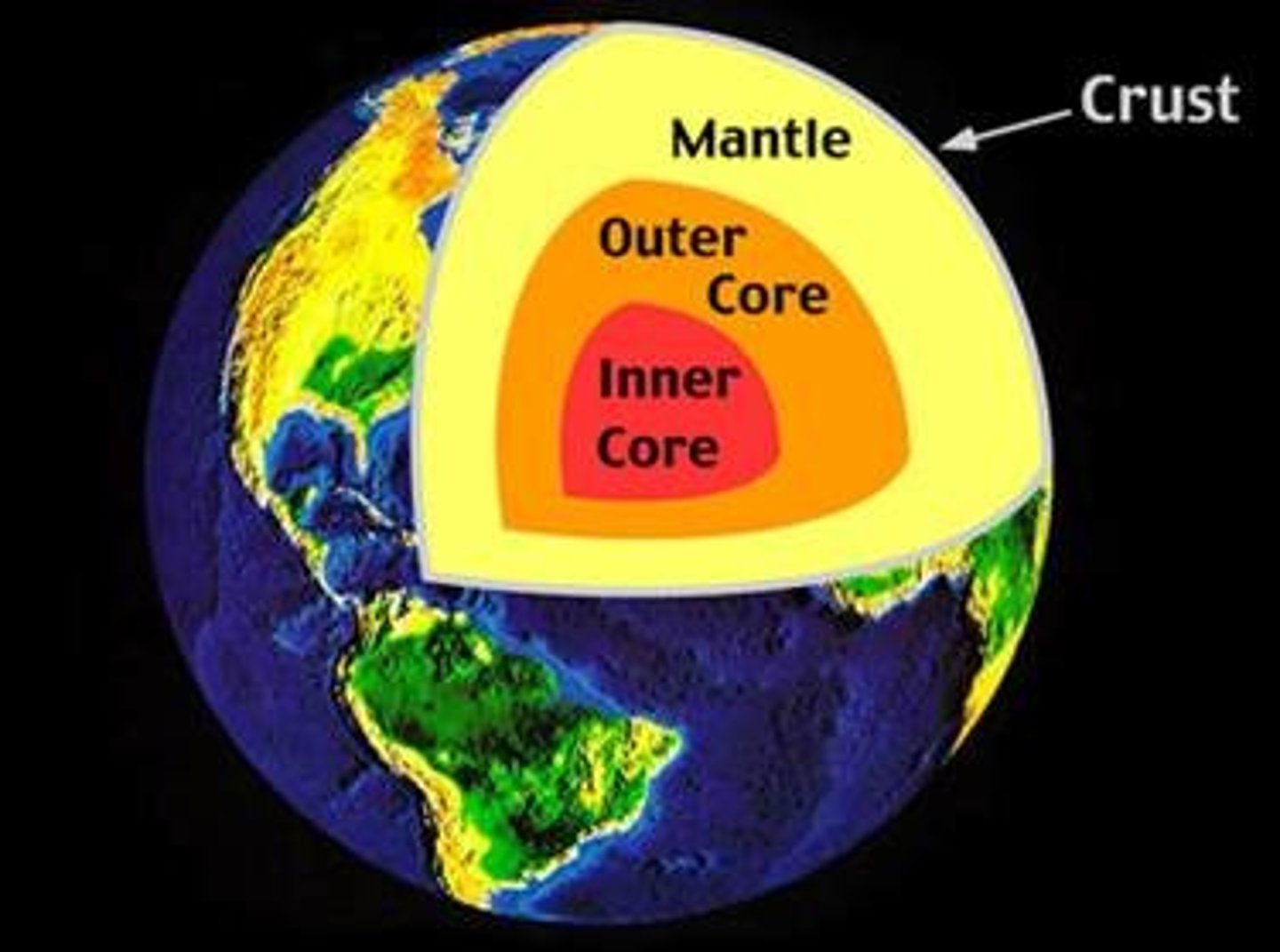
Outer Core
Liquid iron layer surrounding the inner core.
Mohorovicic Discontinuity
Boundary between crust and molten mantle.
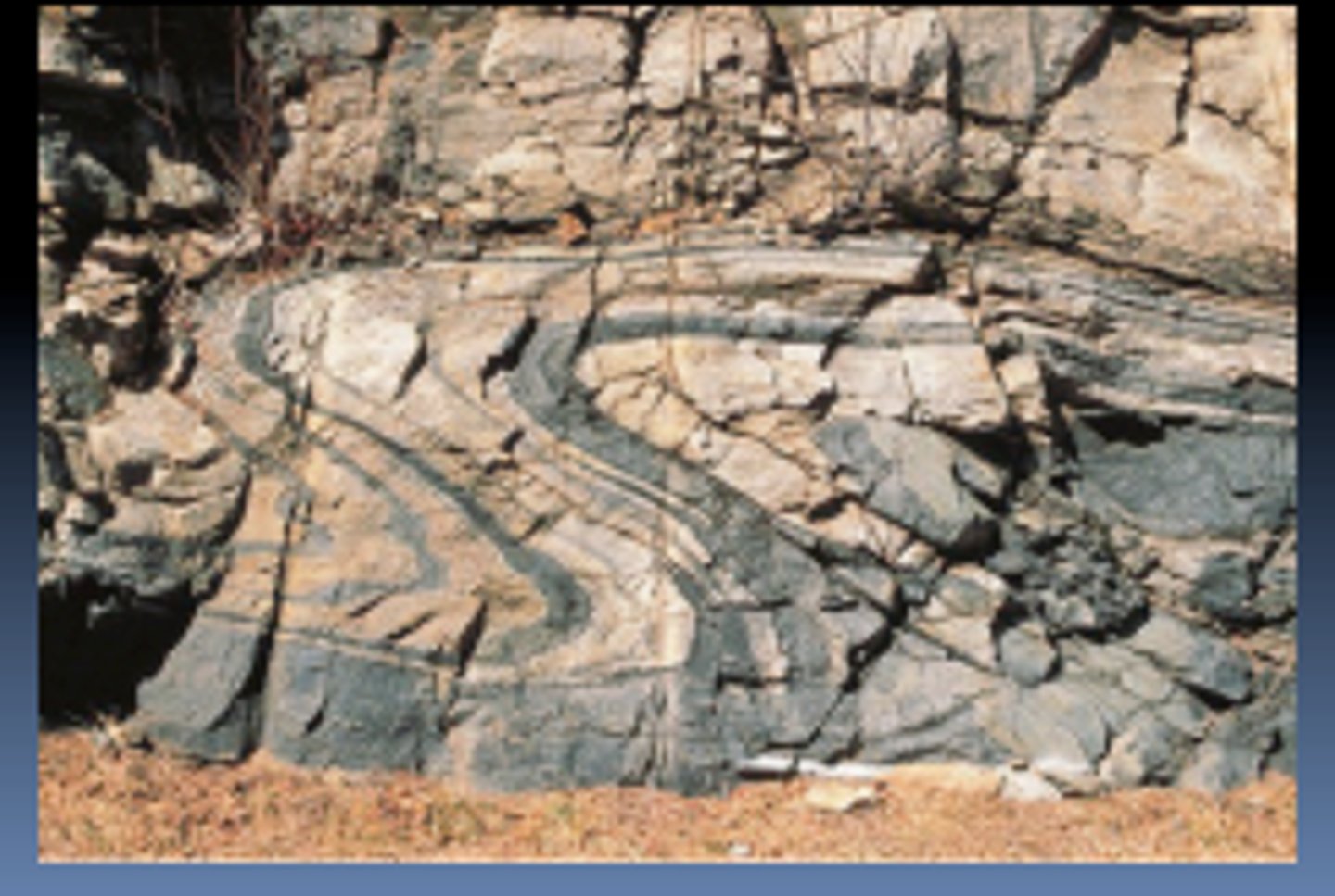
Plastic Rock
Rock in mantle that can be shaped easily.

Convection Currents
Movement of molten rock causing tectonic plate motion.
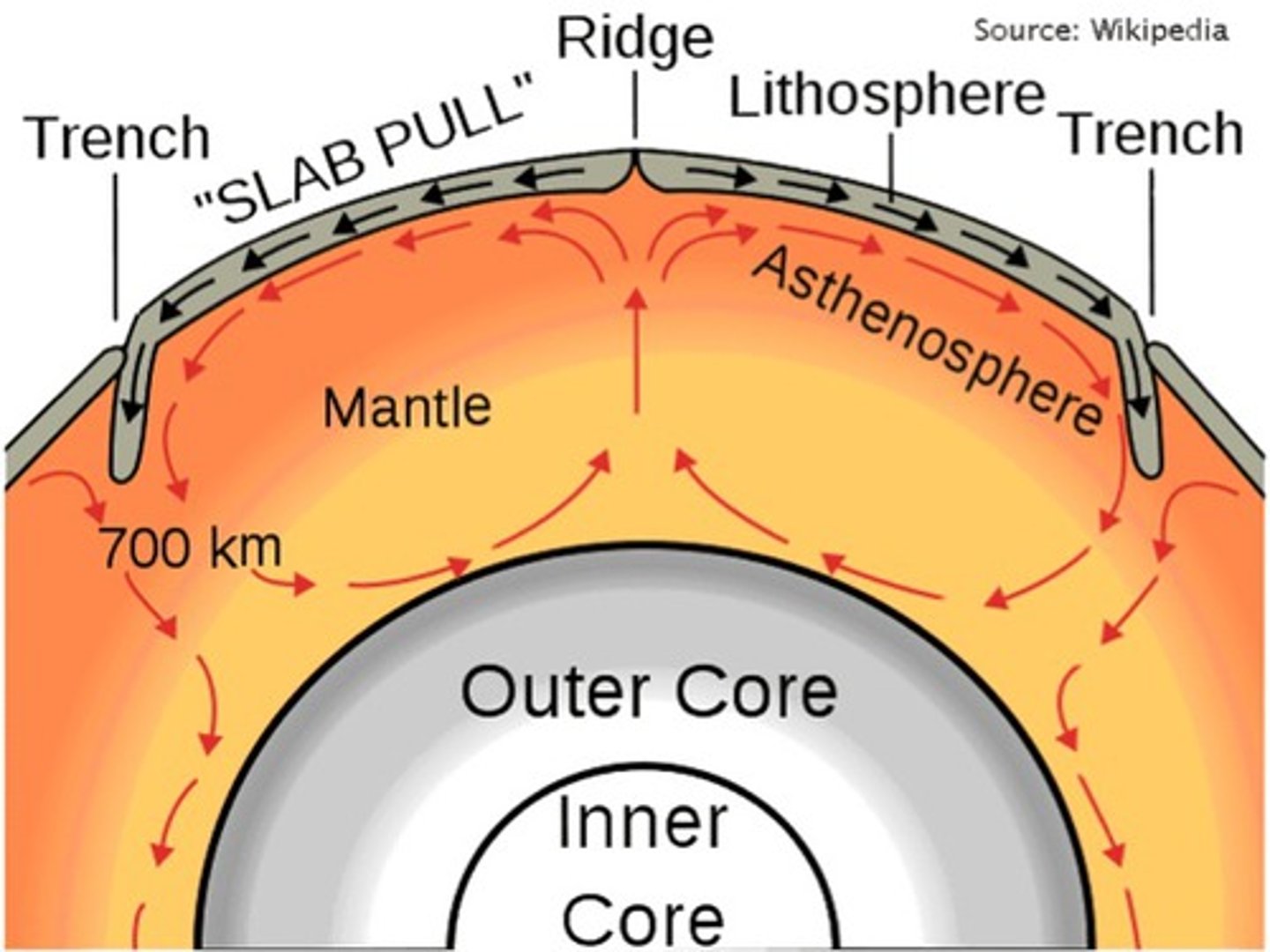
Asthenosphere
Upper mantle where tectonic plates move.
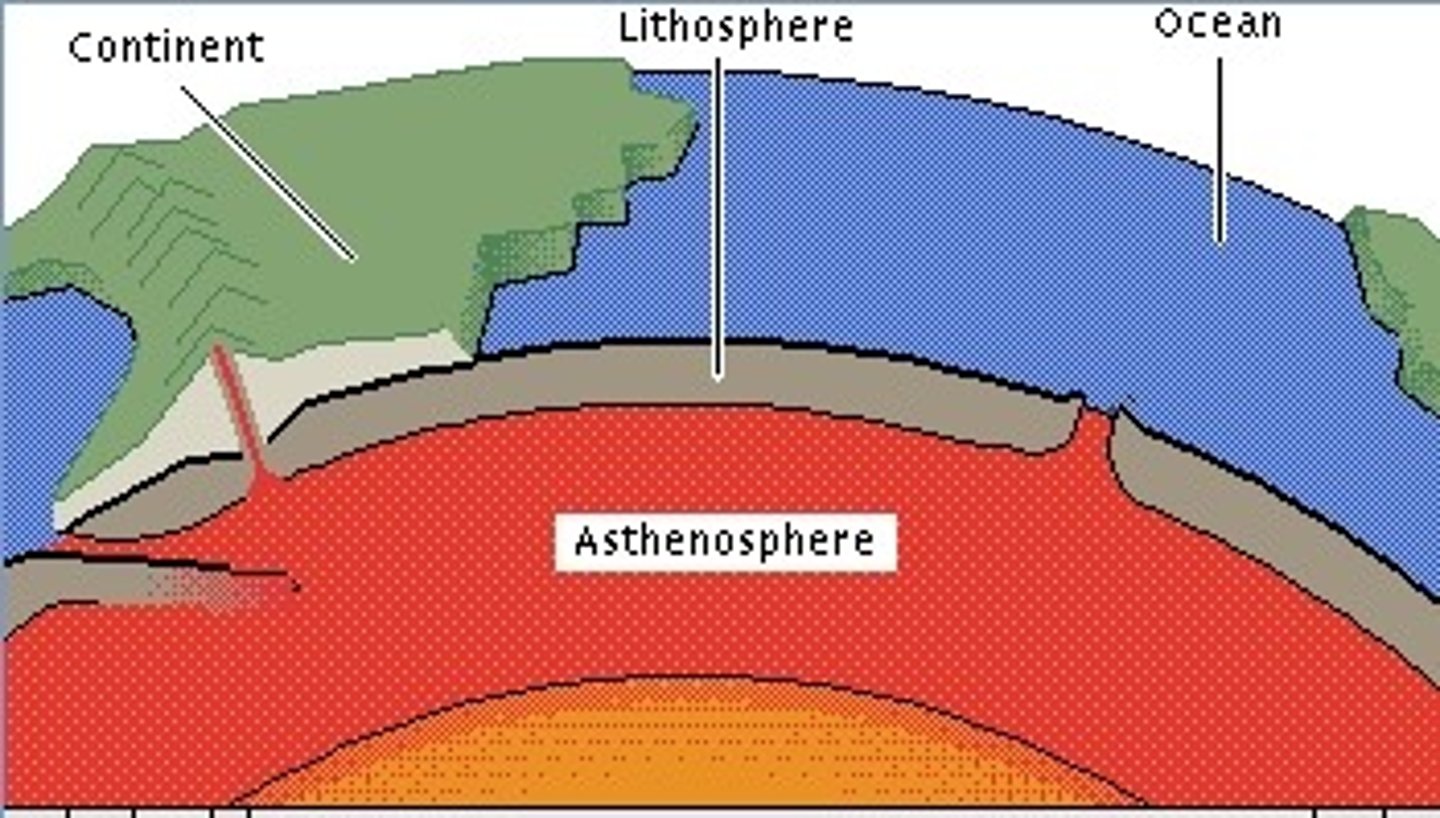
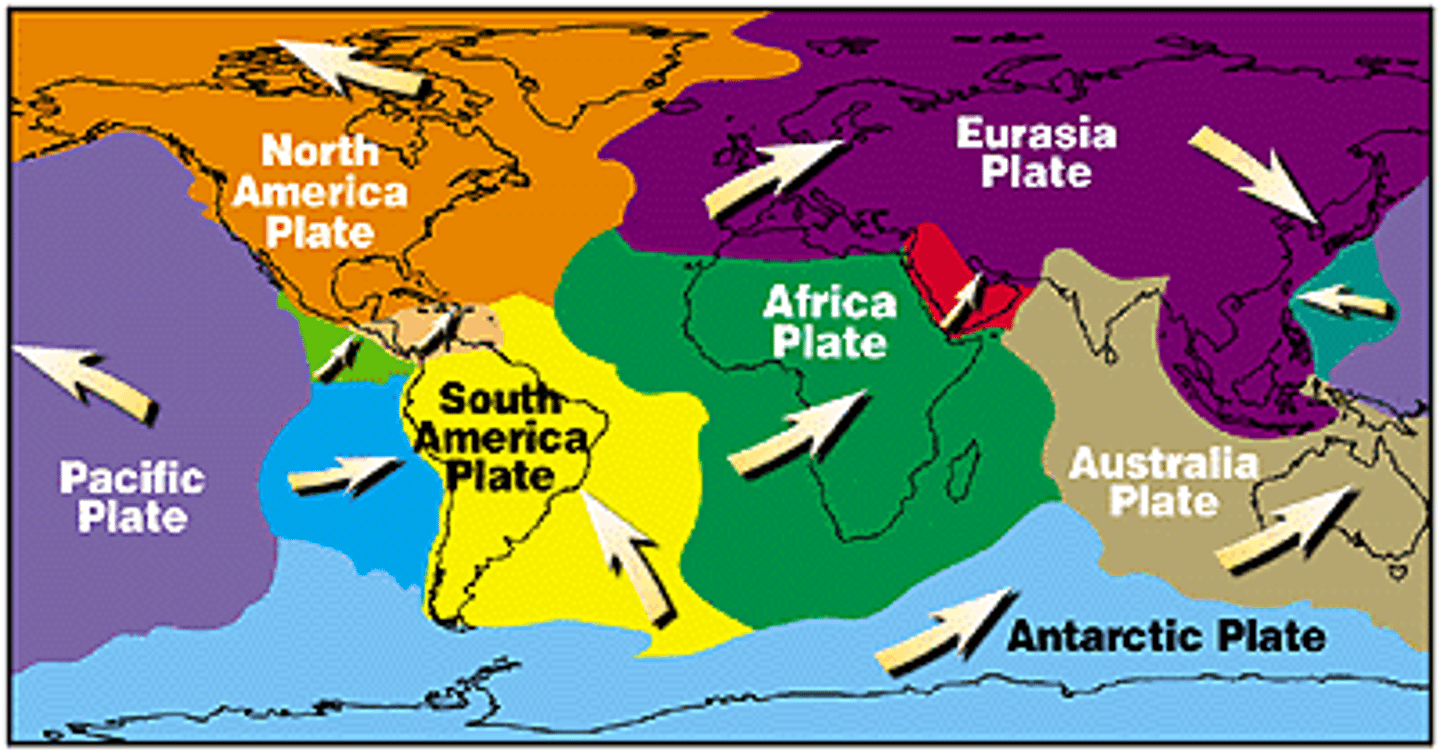
Tectonic Plates
Solid lithospheric pieces moving on asthenosphere.
Convergent Boundaries
Plates move towards each other, forming mountains.
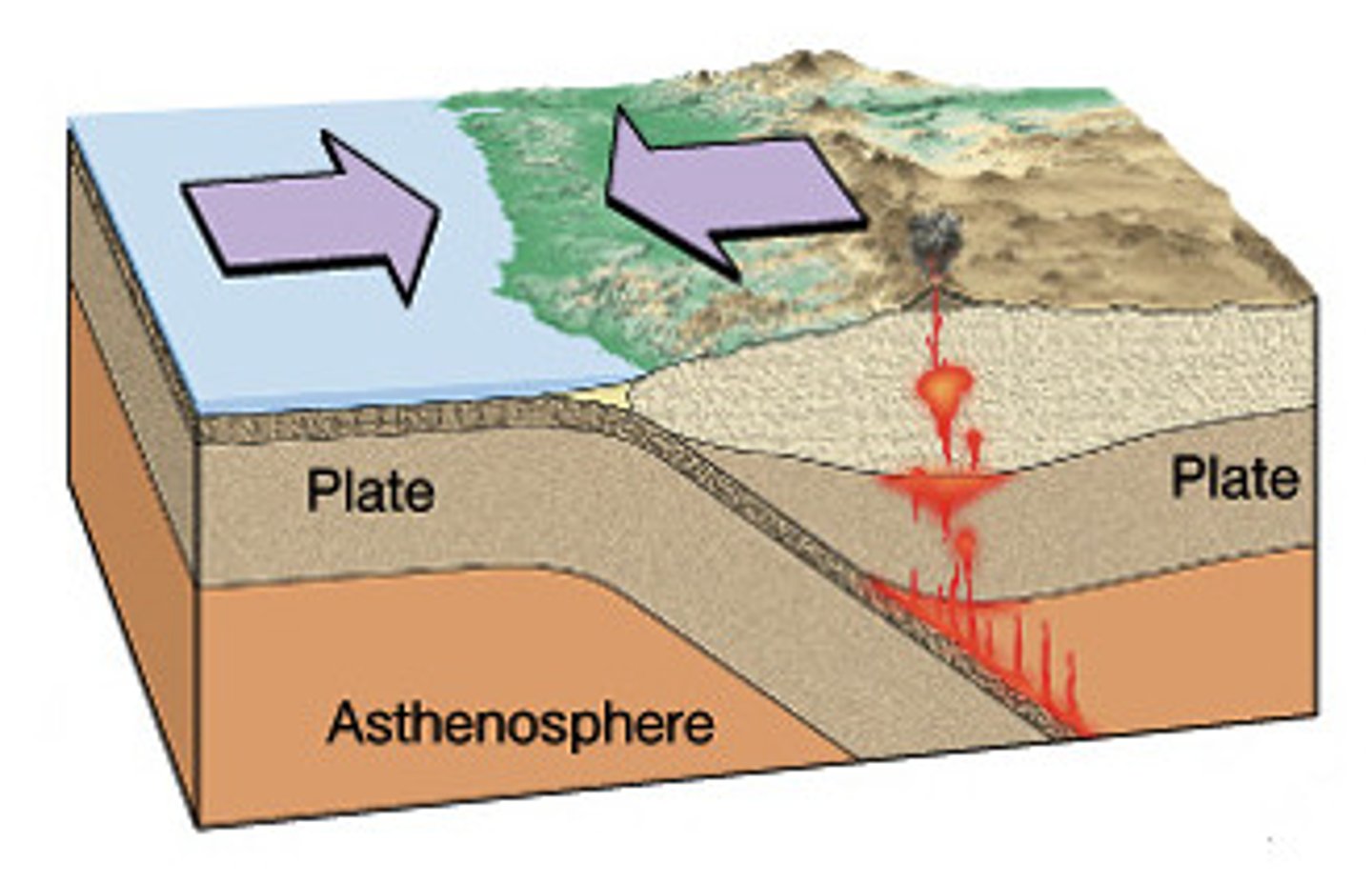
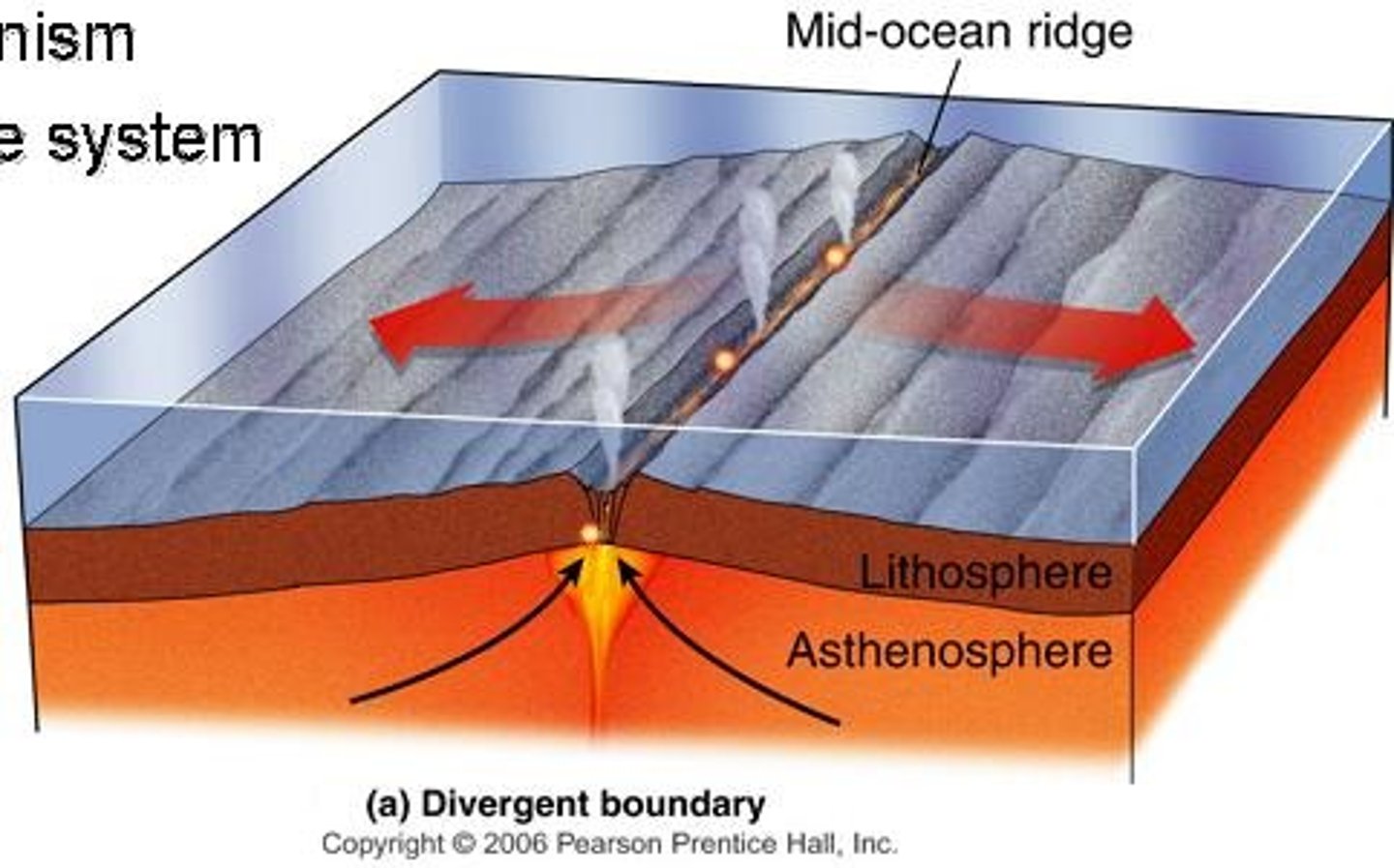
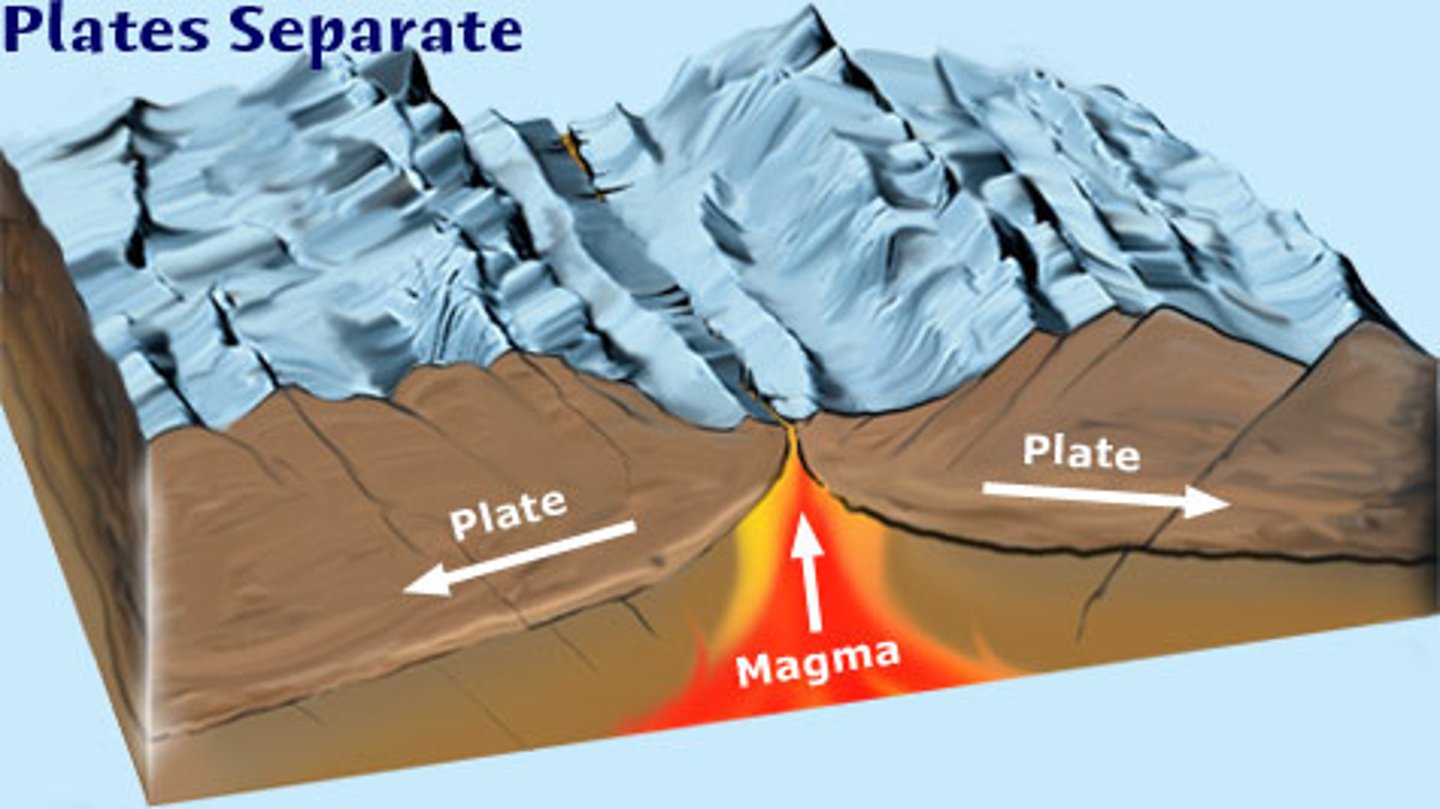
Divergent Boundaries
Plates move apart, creating new land from magma.
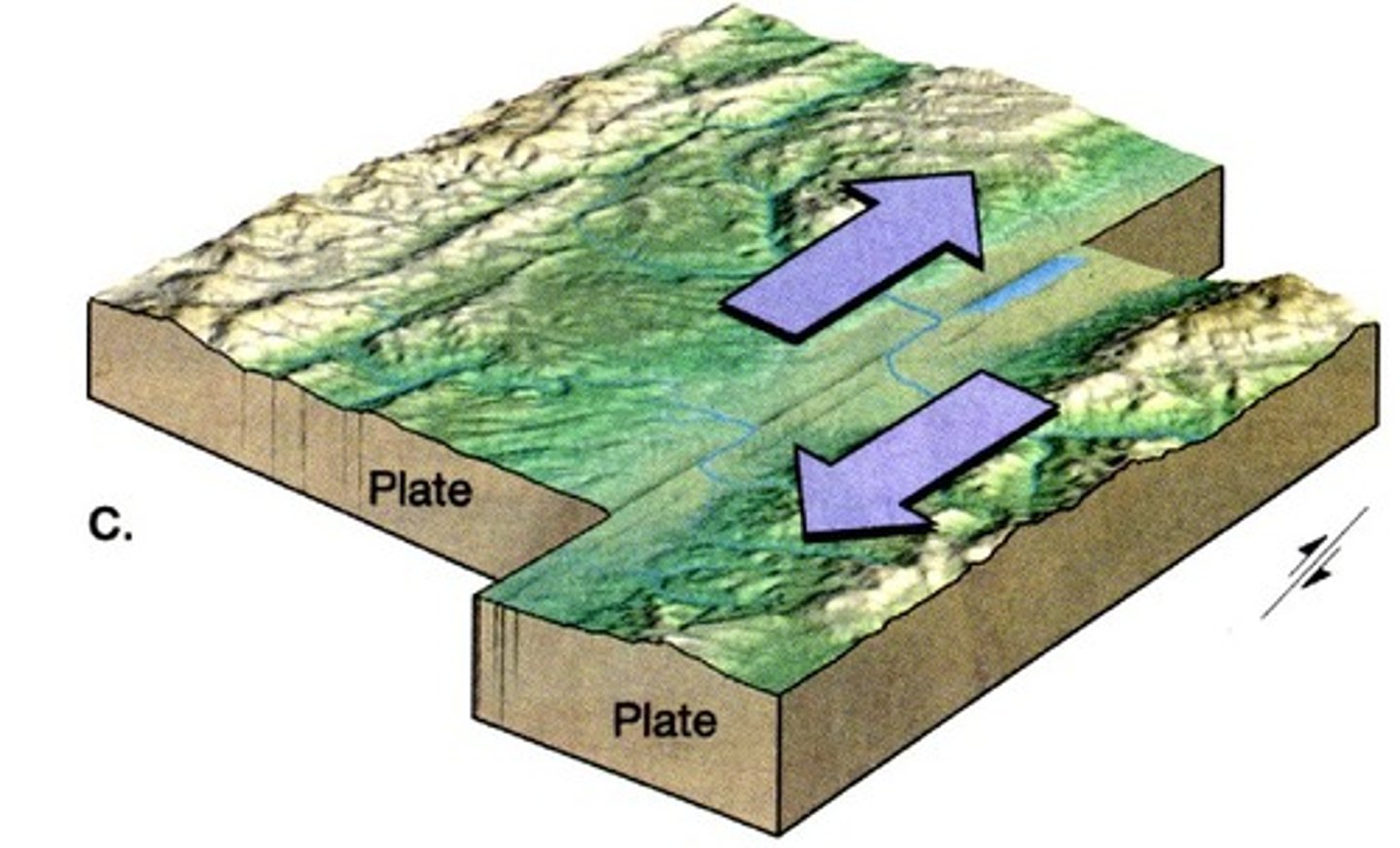
Transform Boundaries
Plates slide past each other, causing friction.
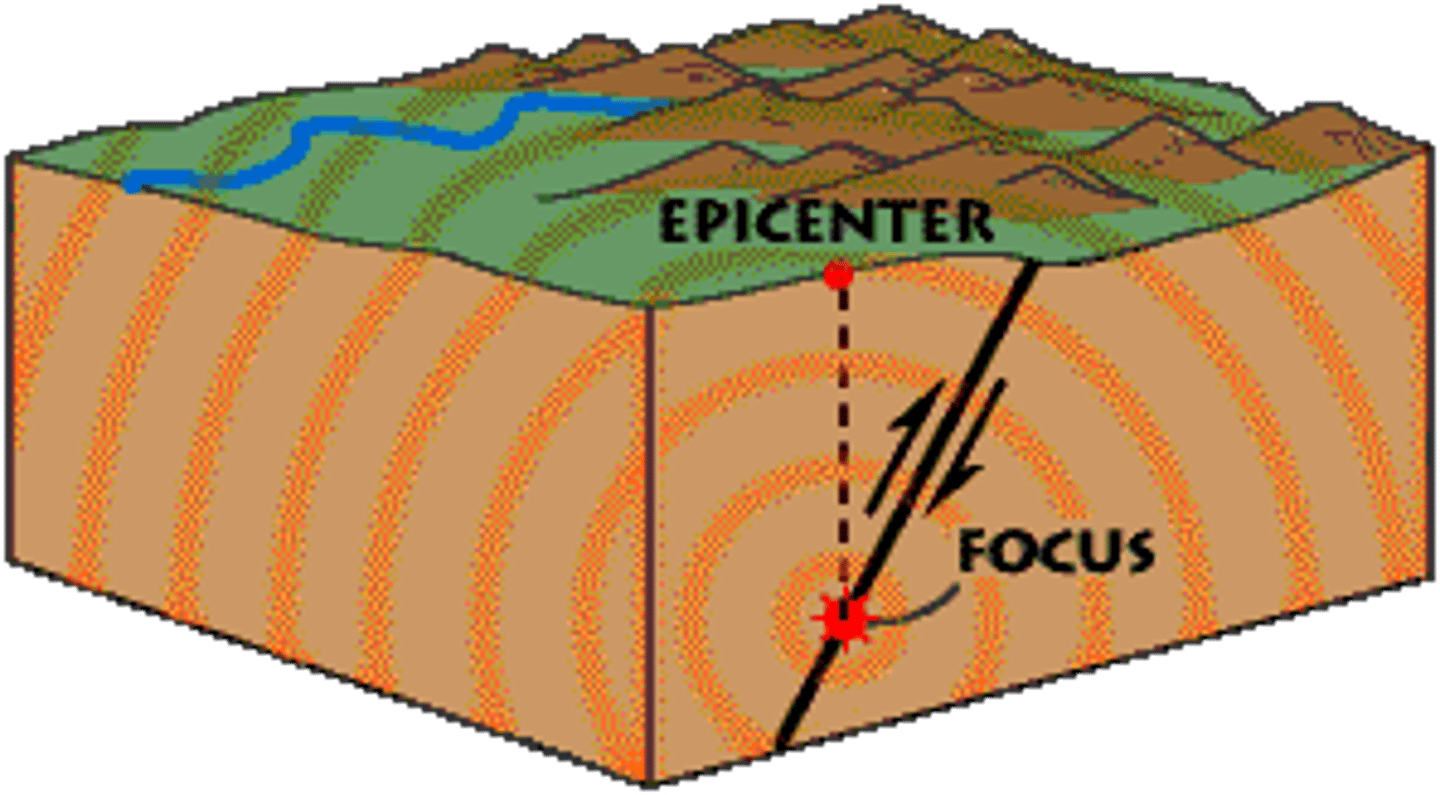
Focus
Point where plates contact during an earthquake.
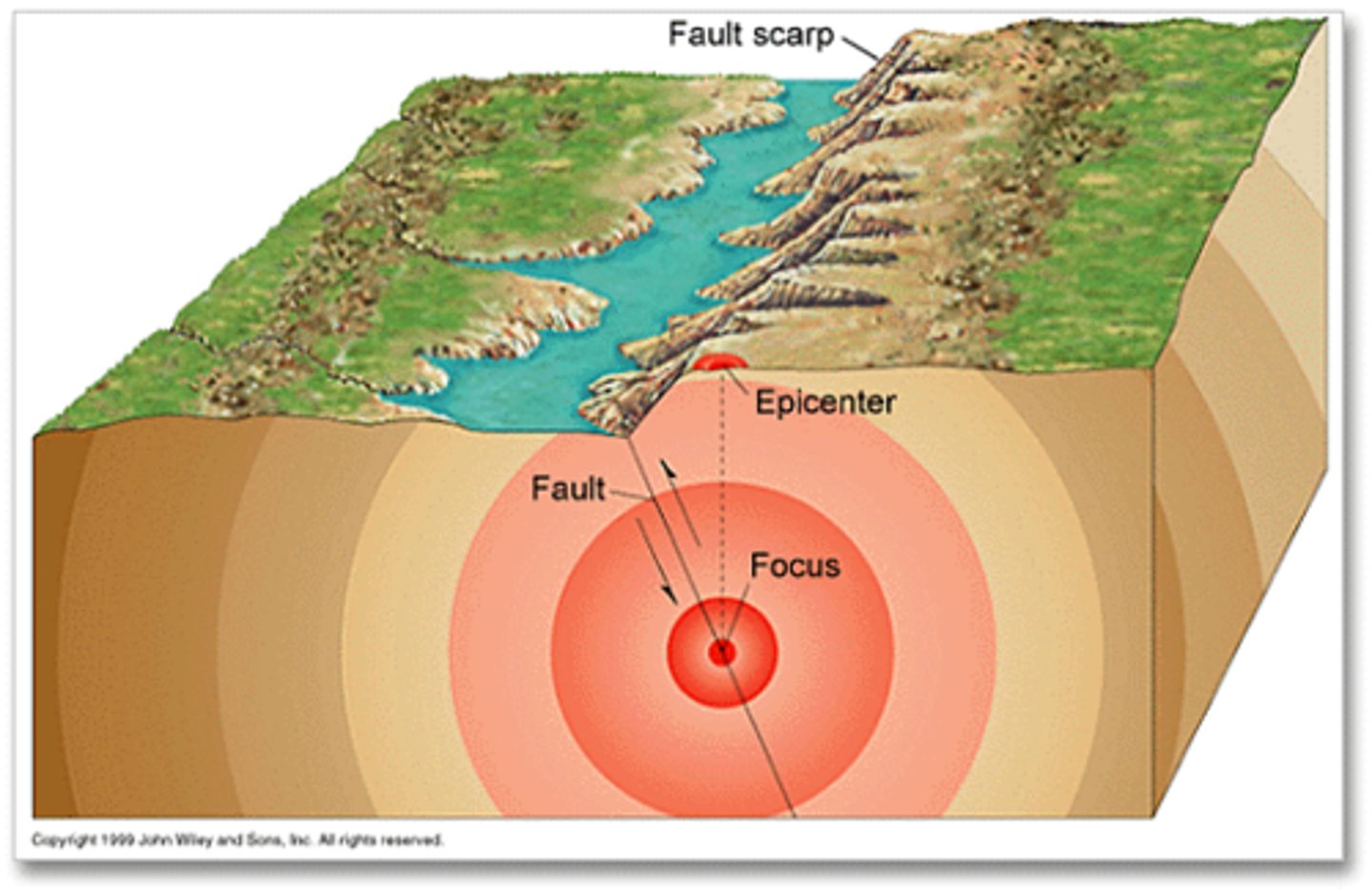
Epicenter
Point on surface directly above earthquake focus.
Seismic Waves
Energy released during an earthquake.
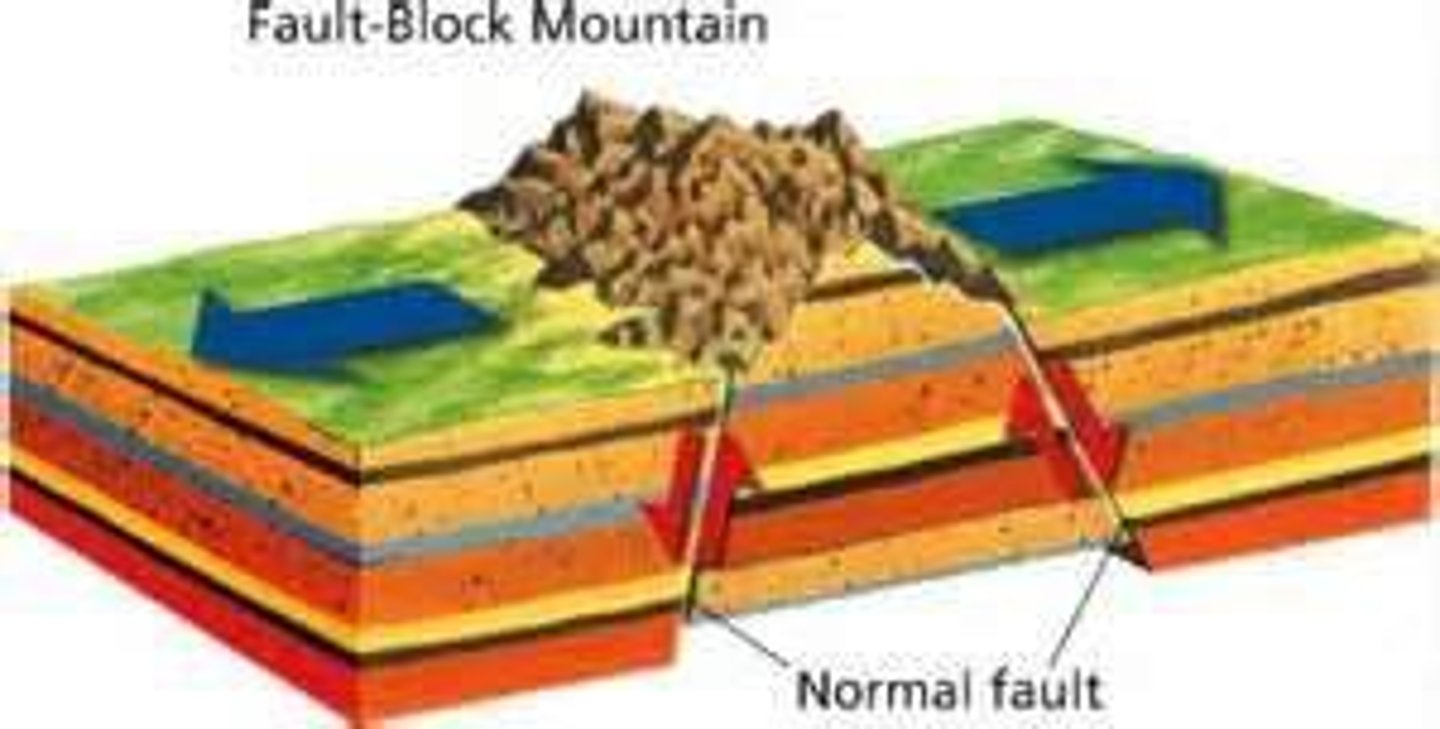
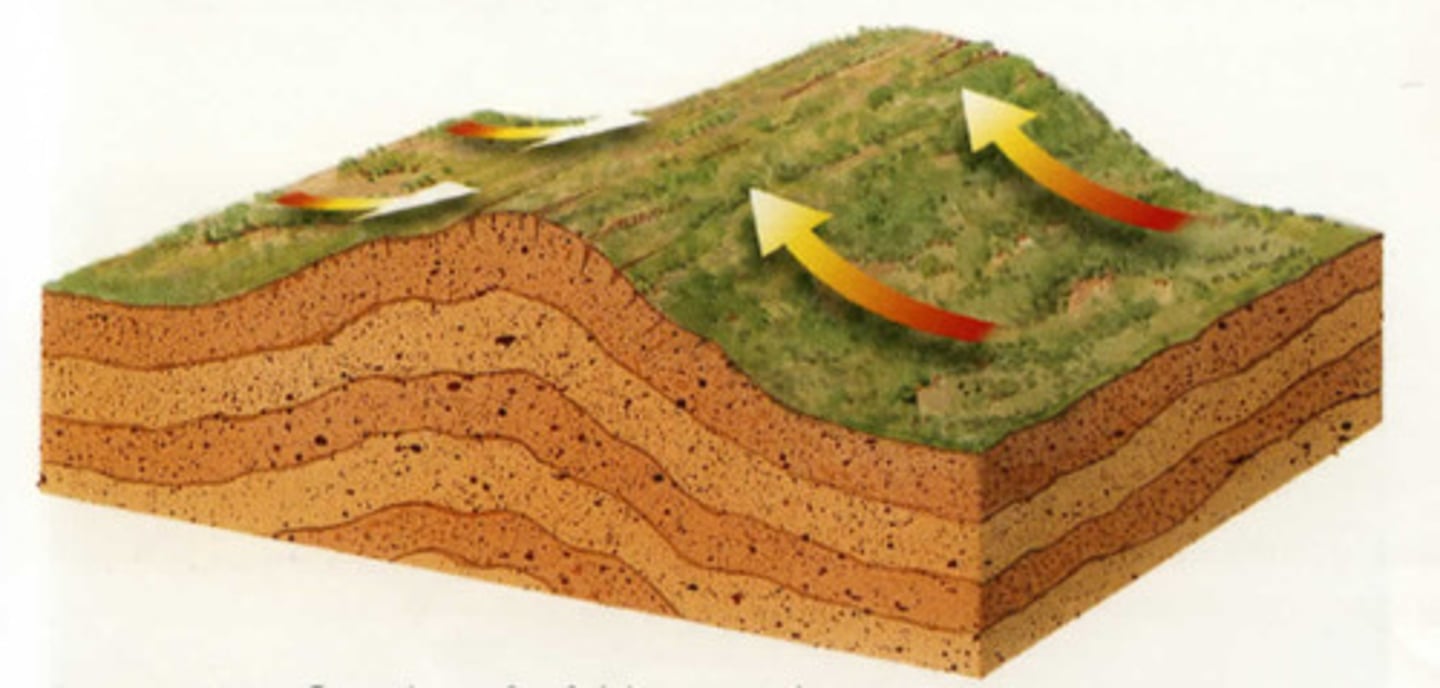
Fault-block Mountains
Mountains formed by upward force of tectonic plates.
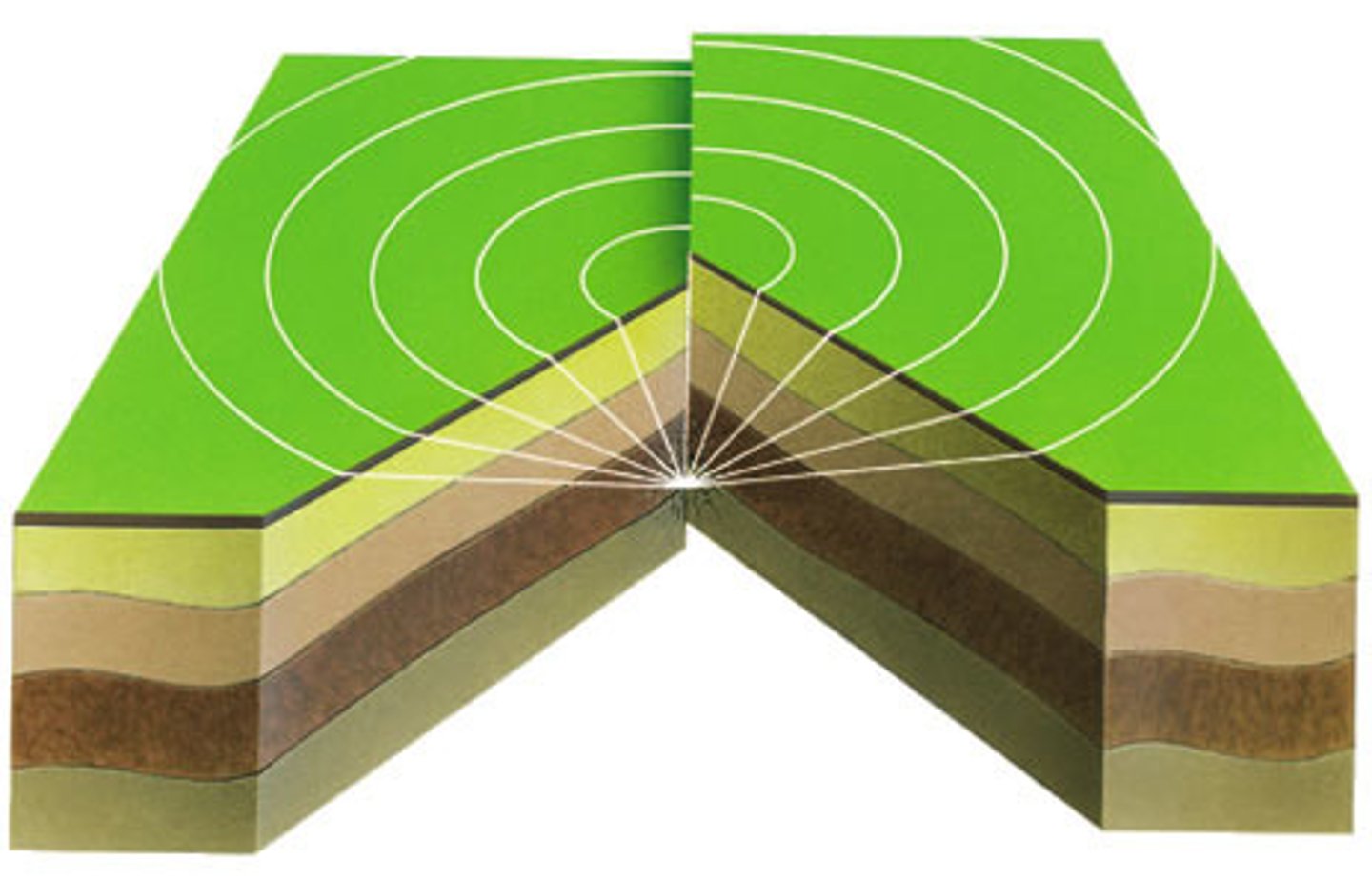
Folded Mountains
Mountains formed by bending of tectonic plates.

Volcano Formation
Occurs when magma escapes through crust cracks.
Earthquake Effects
Can cause landslides, tsunamis, and surface damage.
Mid-Ocean Ridge
Underwater mountains formed by divergent plate movement.
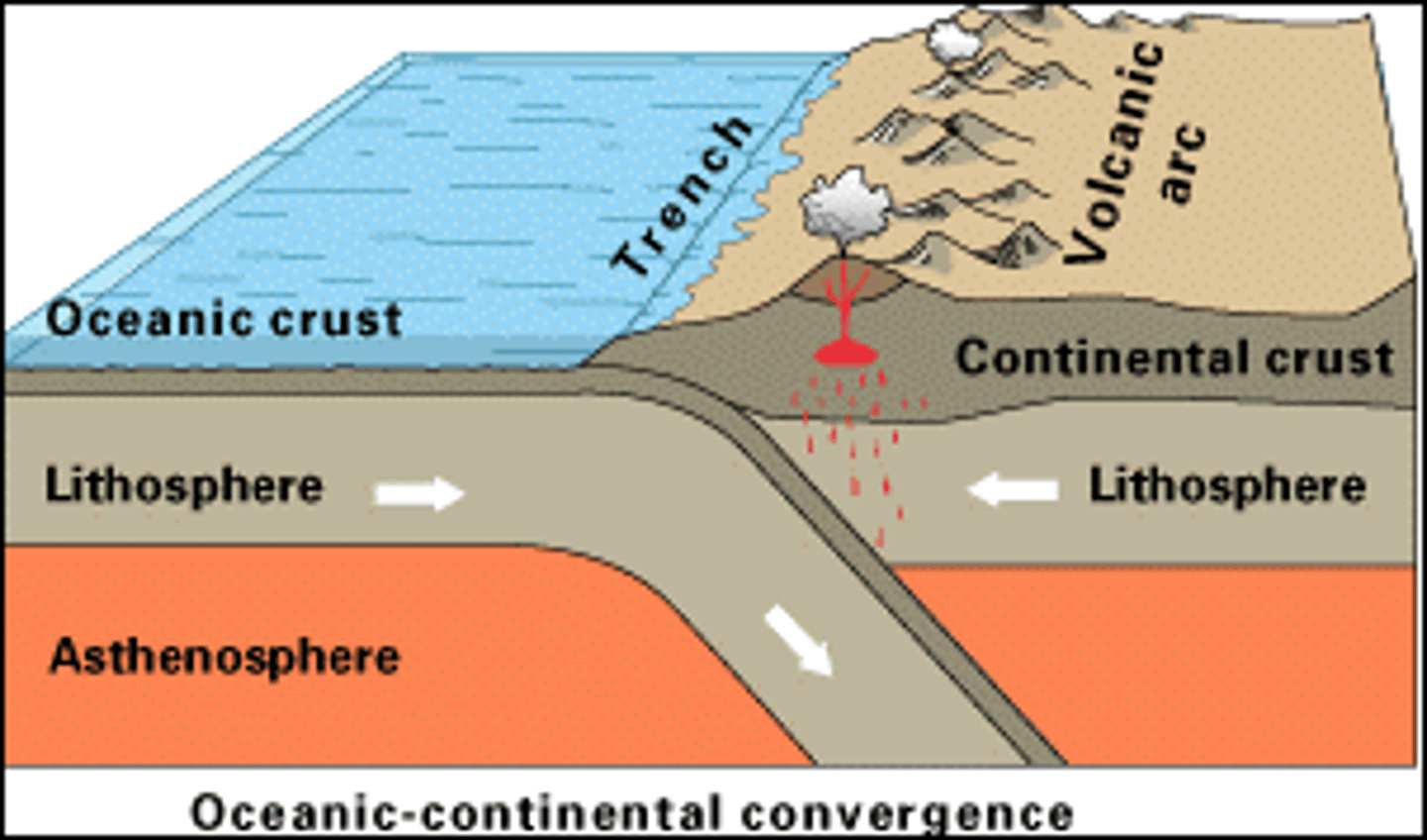
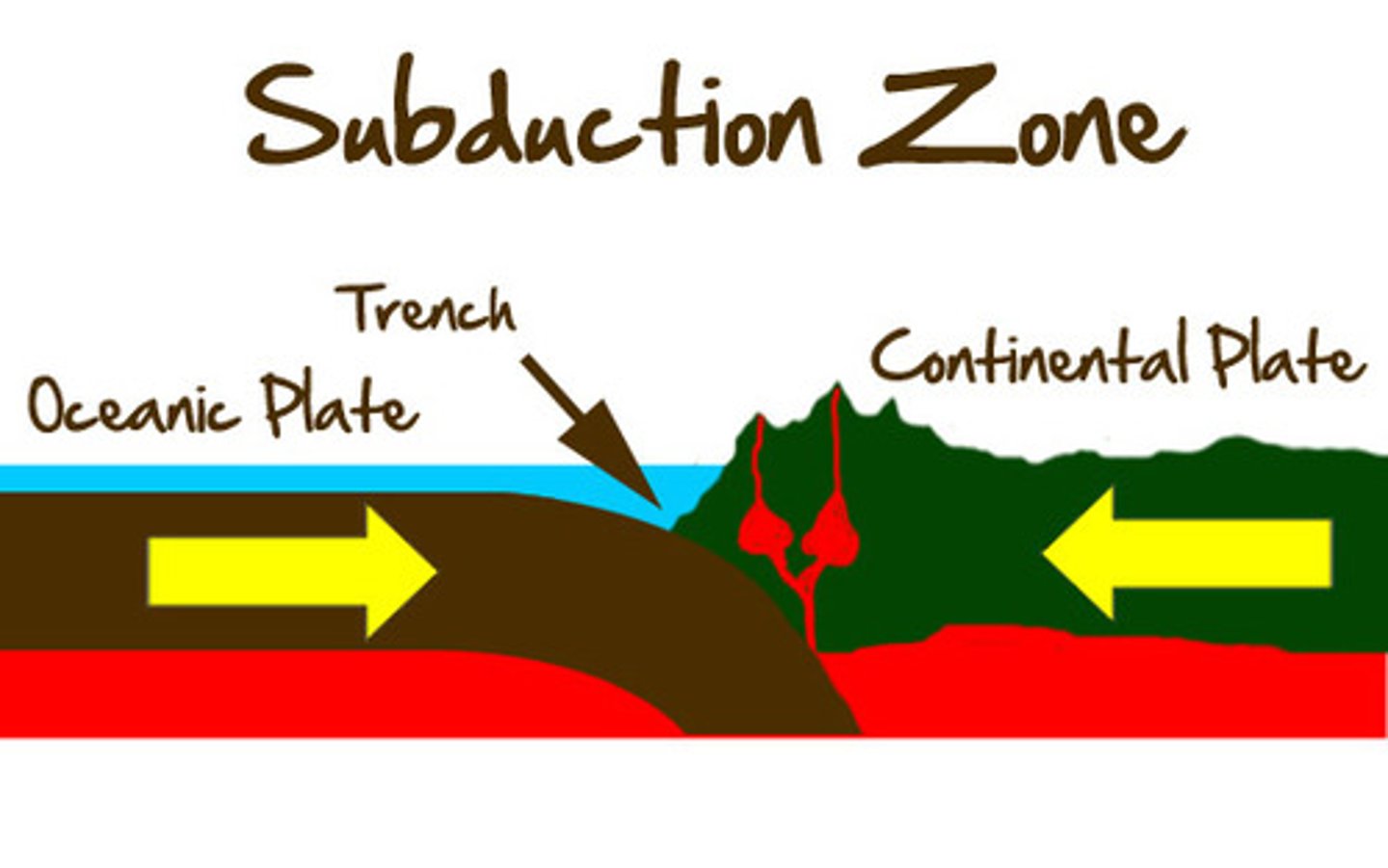
Subduction
Denser oceanic plate forced under another plate.
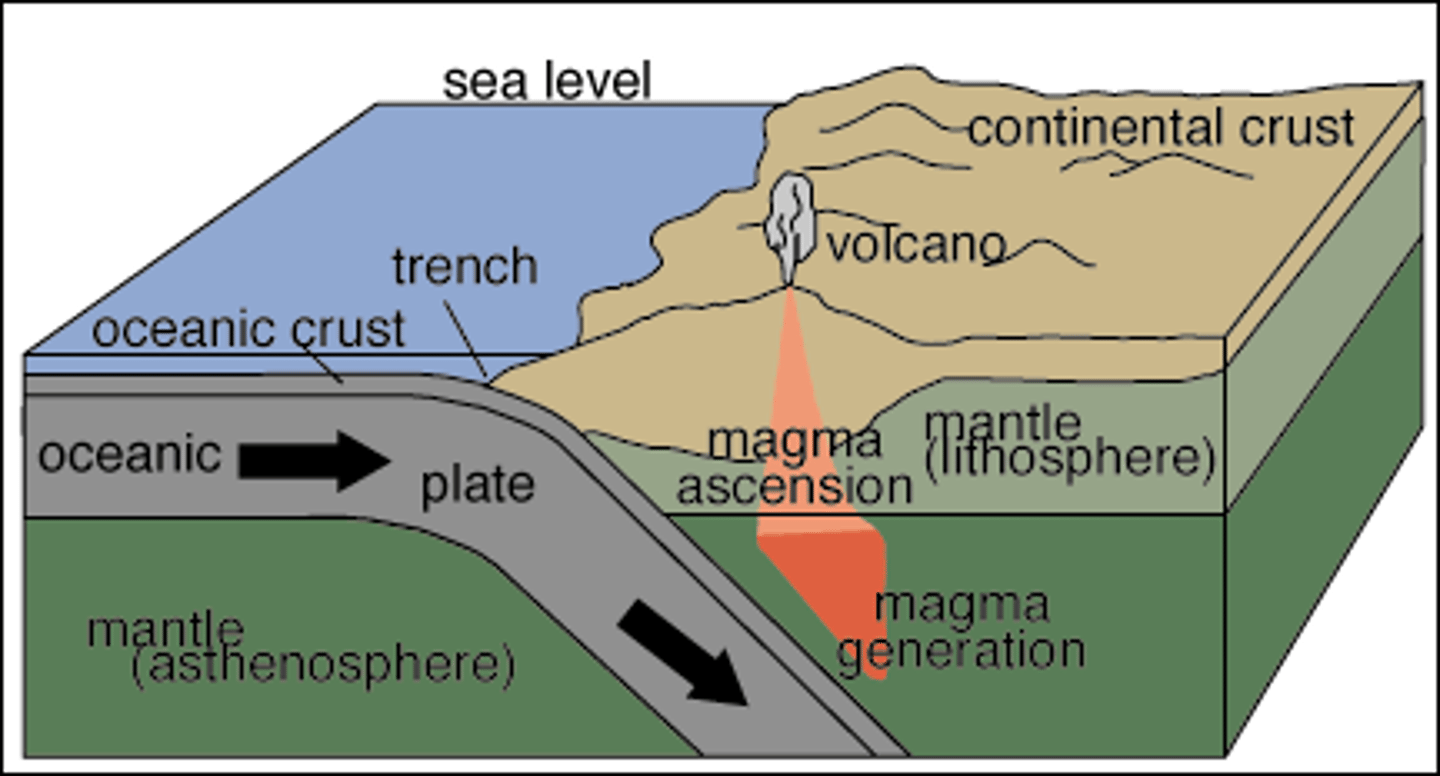
Rift
Less forceful separation of tectonic plates.
Volcano
An opening in Earth's crust for magma.
Magma
Molten rock beneath Earth's surface.
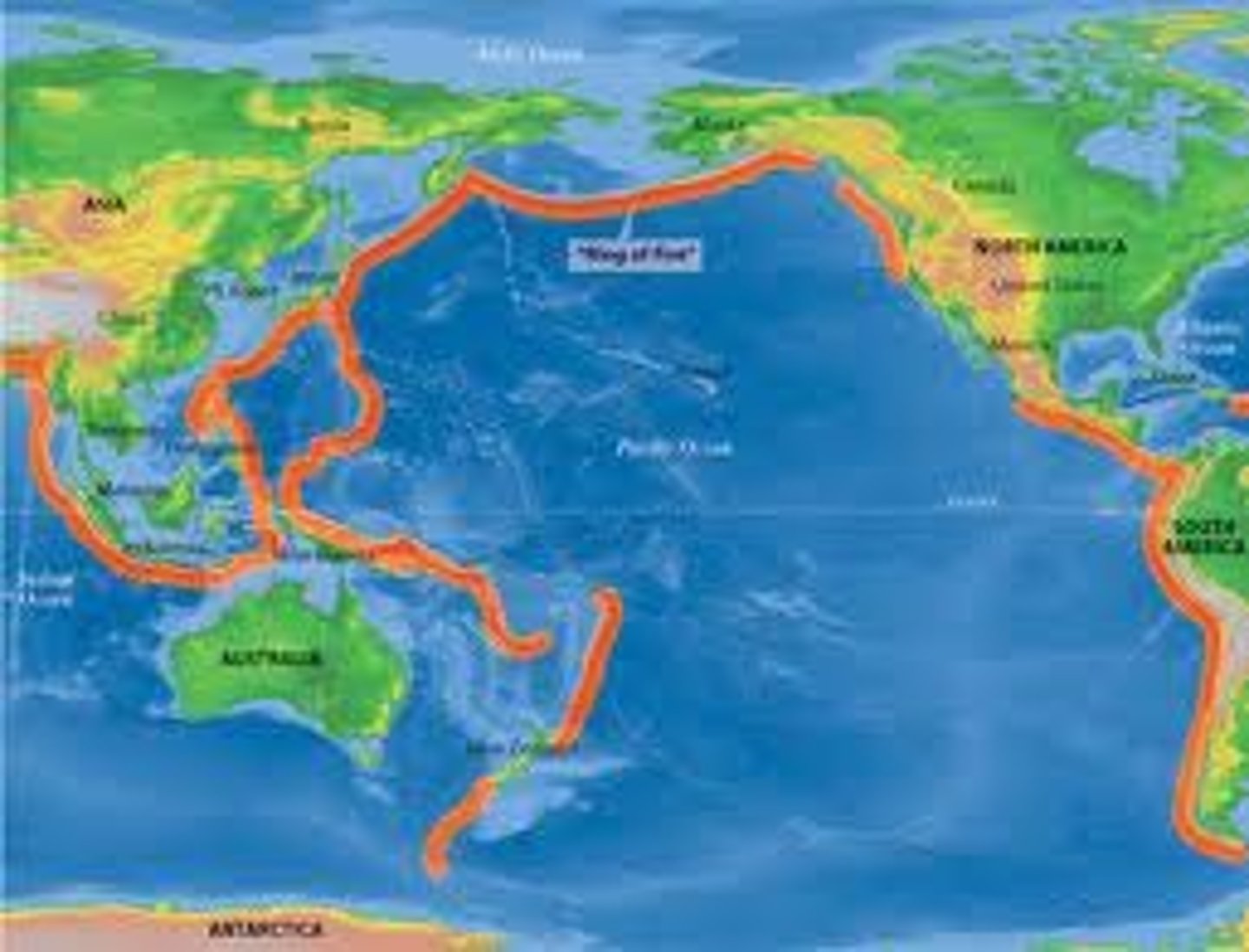
Ring of Fire
Pacific region with many volcanoes and earthquakes.
Subducting Plates
Tectonic plates moving under each other.
Tectonic Plates
Massive sections of Earth's crust that move.
Urbanization
Population concentration in urban areas.
Land Use
Human activities related to land management.
Zoning Codes
Regulations governing land use and development.
Residential Land Use
Primary land use in U.S. cities.
Commercial Land Use
Land designated for business activities.
Industrial Land Use
Land used for manufacturing and factories.
Mixed-Use Land
Combines residential, commercial, and industrial uses.
Euclidean Zoning
Land use separation by type in cities.
Traffic Congestion
Overcrowding of vehicles on roadways.
Pollution
Contamination of air, water, or land.
Climate Change Emissions
Gases contributing to global warming.
Agricultural Advancements
Improvements in farming techniques and outputs.
Irrigation
Artificial application of water to crops.
Biodiversity Loss
Decline in variety of species in ecosystems.
Heat Islands
Urban areas significantly warmer than surroundings.
Push Factors
Reasons driving migration from rural to urban.
Pull Factors
Attractions drawing people to urban areas.
Vertical Forest
Building design incorporating trees for air quality.
Hurricanes
Severe storms causing destruction and displacement.
Wildfires
Uncontrolled fires in forests or grasslands.
Floods
Overflow of water onto normally dry land.
Pull Factors
Attractions that draw people to cities.
Entertainment
Activities that provide enjoyment and leisure.
Infrastructure
Physical structures supporting urban development.
Education
Systematic instruction for knowledge and skills.
Job Availability
Presence of employment opportunities in cities.
Push Factors
Reasons causing people to leave rural areas.
Sustainability
Development meeting present needs without future compromise.
Excessive Consumption
Overuse of resources beyond sustainable limits.
Climate Change
Long-term alteration of temperature and weather patterns.
Ecosystem Health
Well-being of biological communities and their environments.
Biodiversity
Variety of life in a particular habitat.
Pollution
Contamination of the environment by harmful substances.
Three E's
Environment, Economy, Equity for sustainability.
Natural Air Filters
Trees absorb pollutants, improving air quality.
Flood Defense
Trees prevent floods and landslides effectively.
Forest Industry Jobs
1.6 billion people depend on forestry employment.
Carbon Absorption
Trees absorb 1 ton of carbon in 40 years.
Deforestation
Clearing forests for agriculture or development.
Reforestation
Planting trees to restore forested areas.
Wildlife Corridors
Connect patches of forest for animal movement.
Habitat Fragmentation
Disruption of habitats affecting ecosystem stability.
Deforestation
Clearing forests, impacting biodiversity and emissions.
Reforestation
Planting trees to restore forest ecosystems.
Green Revolution
Agricultural transformation increasing crop yields globally.
Norman Borlaug
Agricultural scientist known for wheat cross-breeding.
Selective Plant Breeding
Choosing plants with desirable traits for reproduction.
Lodging
Wheat heads falling over due to size.
Sustainable Practices
Methods reducing environmental impact in agriculture.
Cover Crops
Crops grown post-harvest to improve soil health.
Strip Cropping
Alternating crops to reduce soil erosion.
Contour Farming
Planting along land contours to minimize runoff.
Crop Rotation
Changing crops annually to maintain soil nutrients.
Livestock Grazing Rotation
Moving livestock to prevent pasture overgrazing.
Organic Farming
Farming without synthetic fertilizers or GMOs.
Manure Use
Natural fertilizer alternative to synthetic options.
Biosolids
Treated sewage not allowed in organic farming.
Organic Food Health
Organic foods have minimal nutritional advantages.
Vertical Farming
Growing crops in stacked layers for efficiency.
LED Technology
Energy-efficient lighting reducing vertical farming costs.
Precision Agriculture
Using technology for targeted farming interventions.
Environmental Impact Reduction
Minimizing agriculture's negative effects on ecosystems.
Pesticide Regulation
Strict rules governing pesticide use in farming.
Future Farming Techniques
Innovative methods enhancing sustainability in agriculture.