AP Biology Review Unit I - Chemistry of Life
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Antiparellel
referring to the arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix
alpha helix
A coiled region constituting one form of the secondary structure of proteins, arising from a specific pattern of hydrogen bonding between atoms of the polypeptide backbone (not the side chains).
amino acids
monomers of proteins
amino group
A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms
beta pleated sheet
One form of the secondary structure of proteins in which the polypeptide chain folds back and forth, or where two regions of the chain lie parallel to each other and are held together by hydrogen bonds.
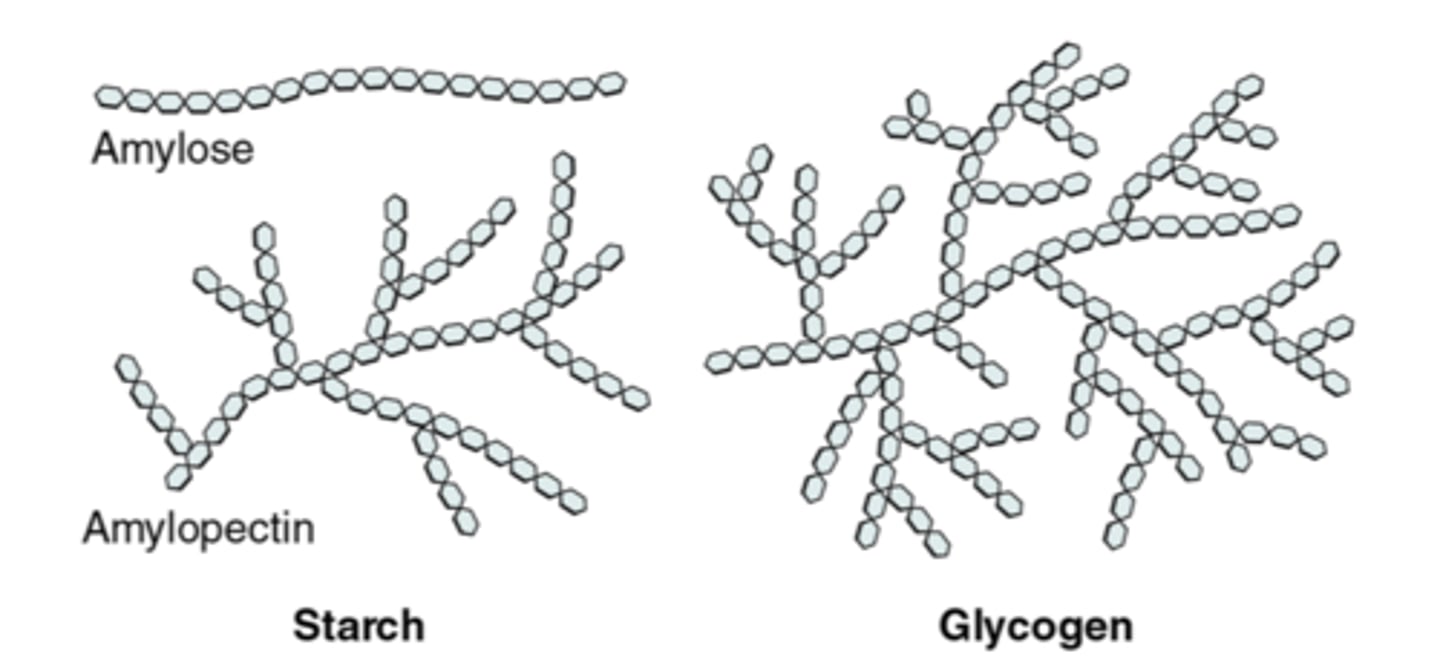
branched carbohydrate
Examples: amylopectin, glycogen
Calorie
Amount of energy needed to raise temperature 1 gram of water 1 degree C
carbohydrate
Energy-rich organic compound, such as a sugar or a starch, that is made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Carbon
an element that can bond with many elements and form unlimited chains, 4 bonding sites
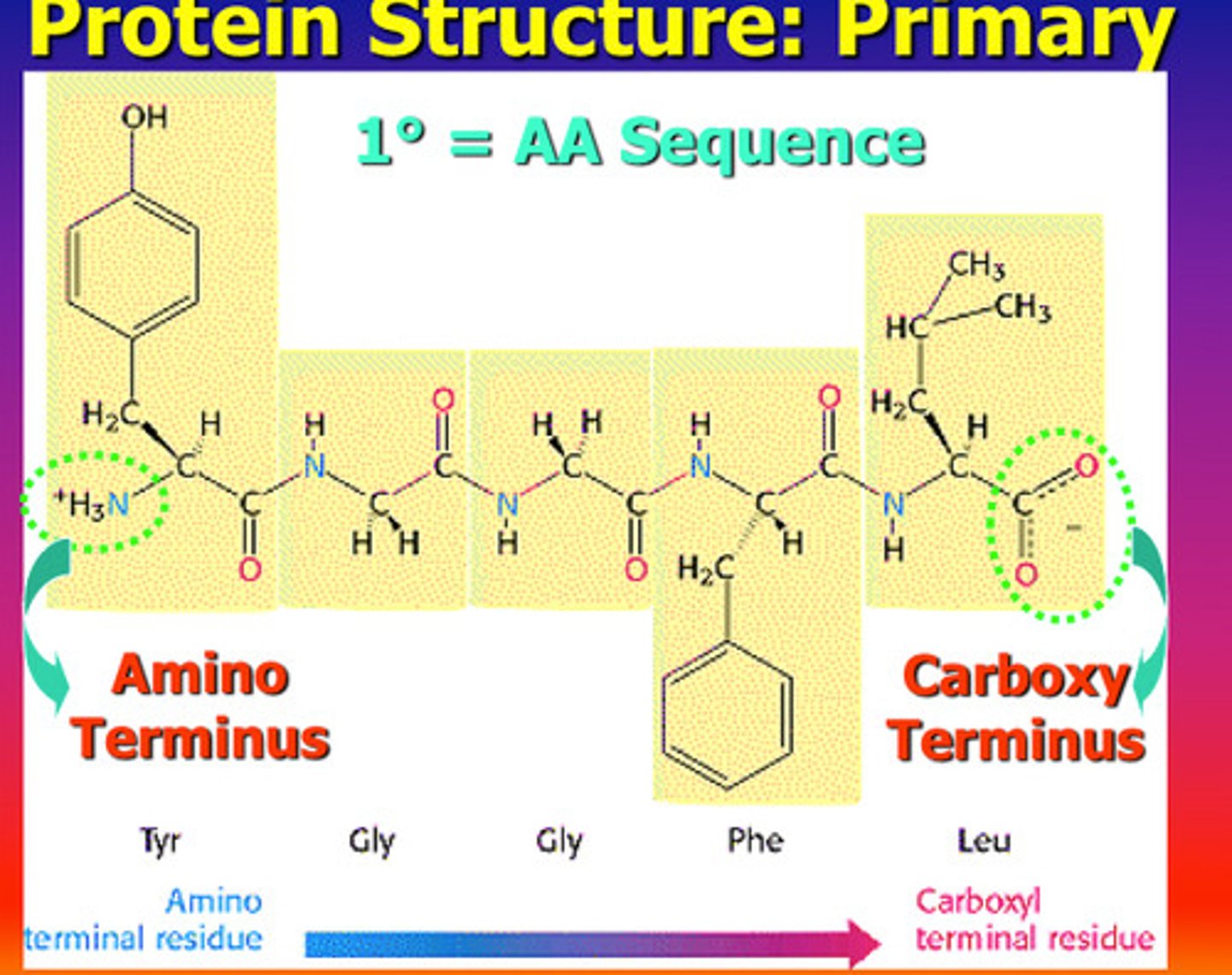
carboxyl terminus
the free carboxyl group at one end of a polypeptide
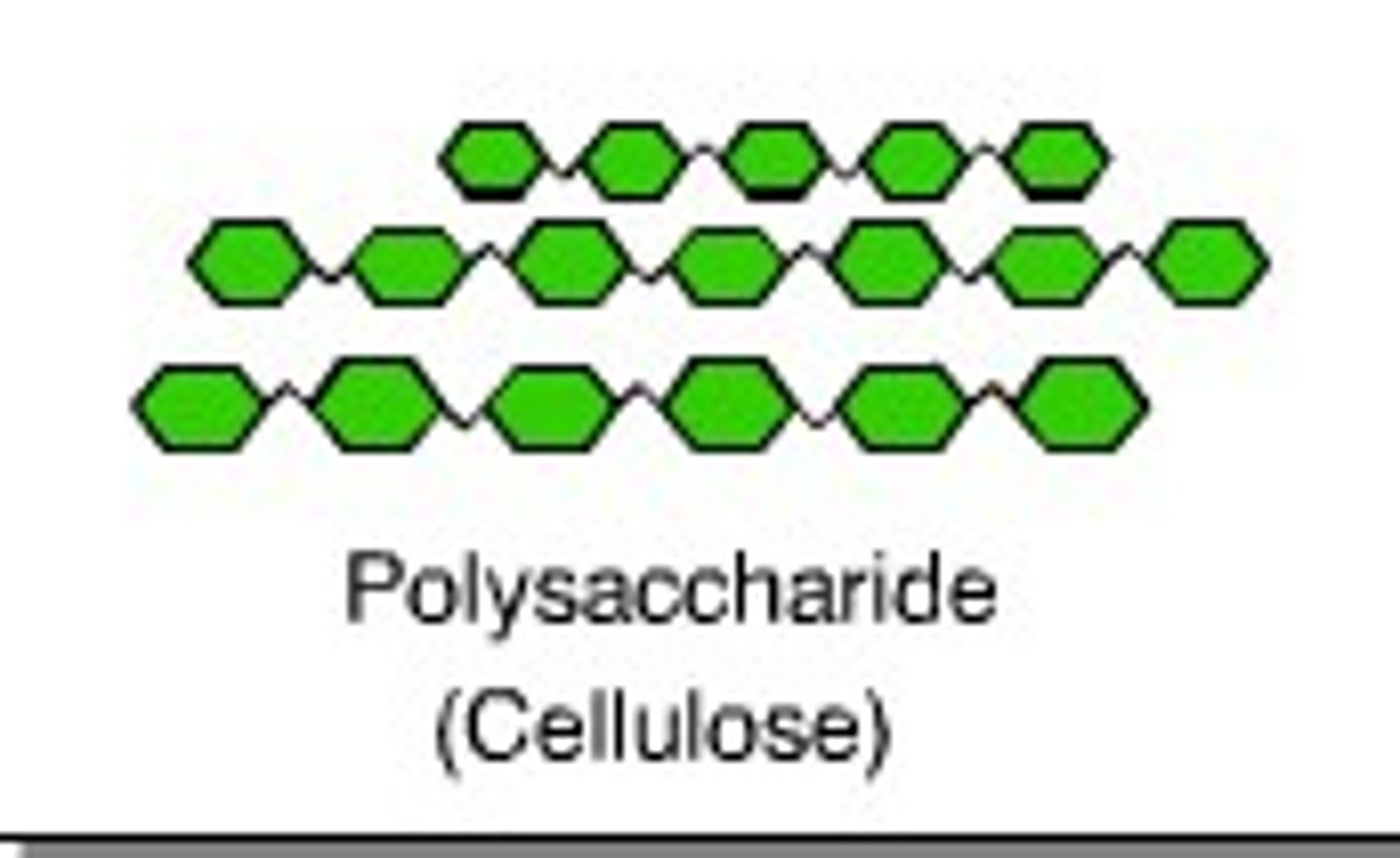
Cellulose
polysaccharide consisting of glucose monomers that reinforces plant-cell walls
Chitin
A structural polysaccharide, consisting of amino sugar monomers, found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthropods.
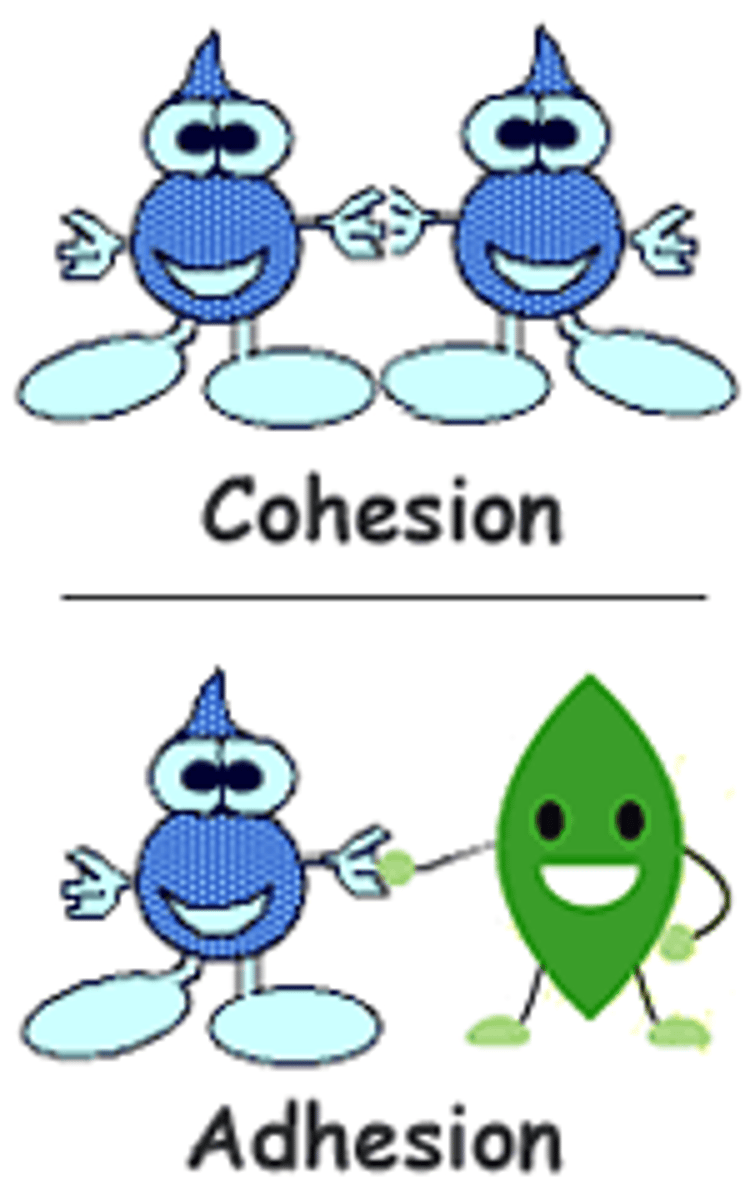
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Covalent bonds form when
electrons are shared between two atoms
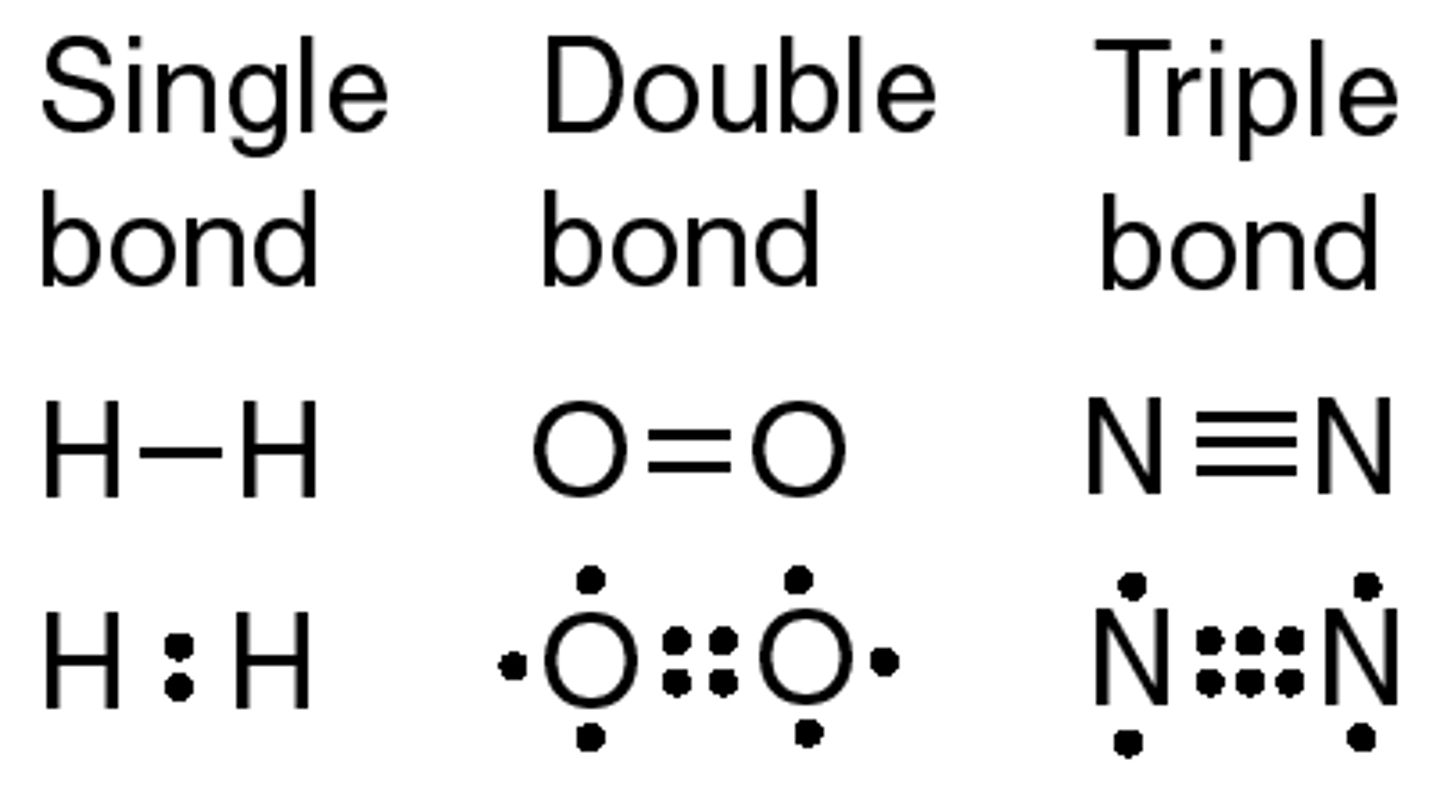
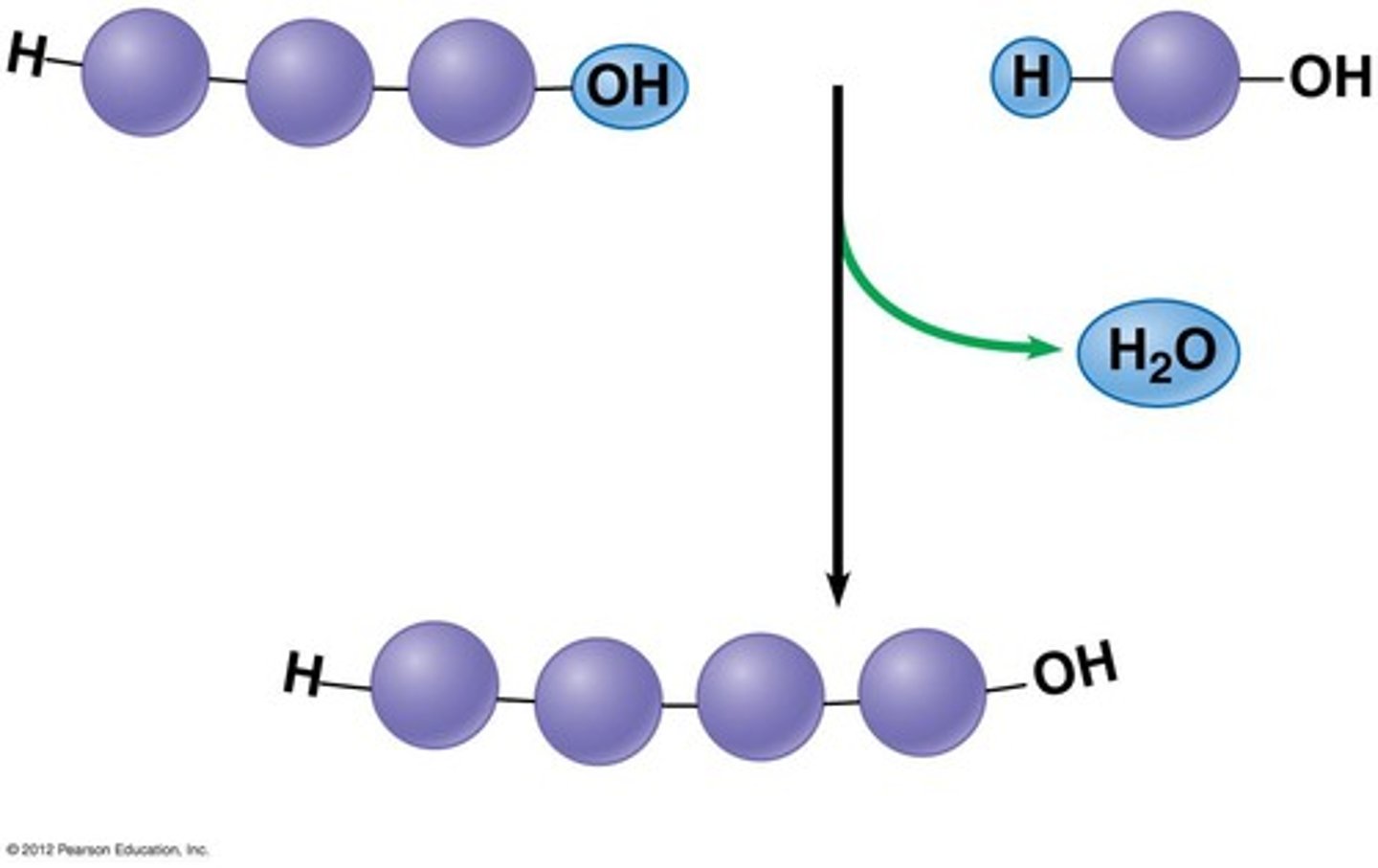
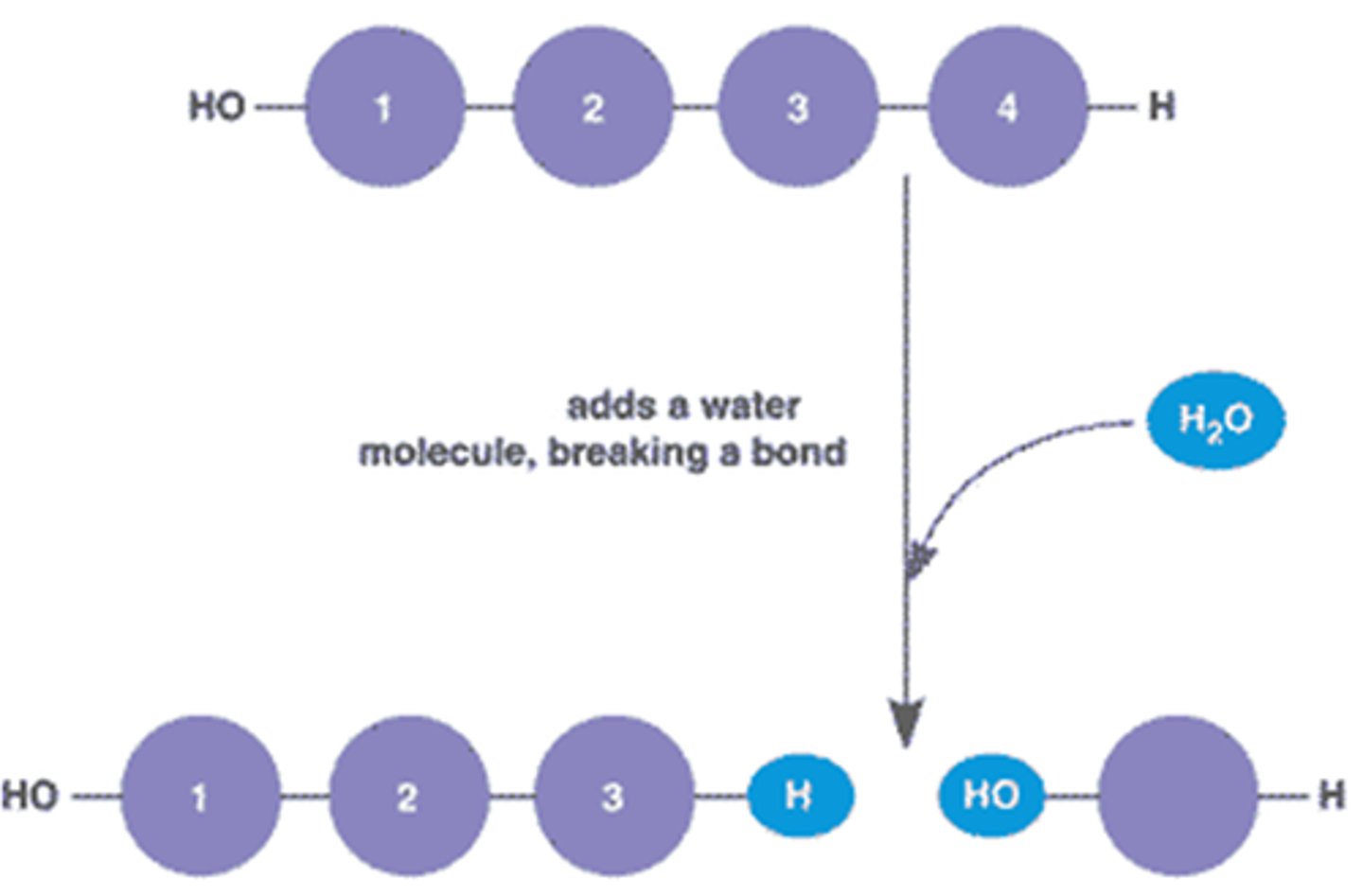
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
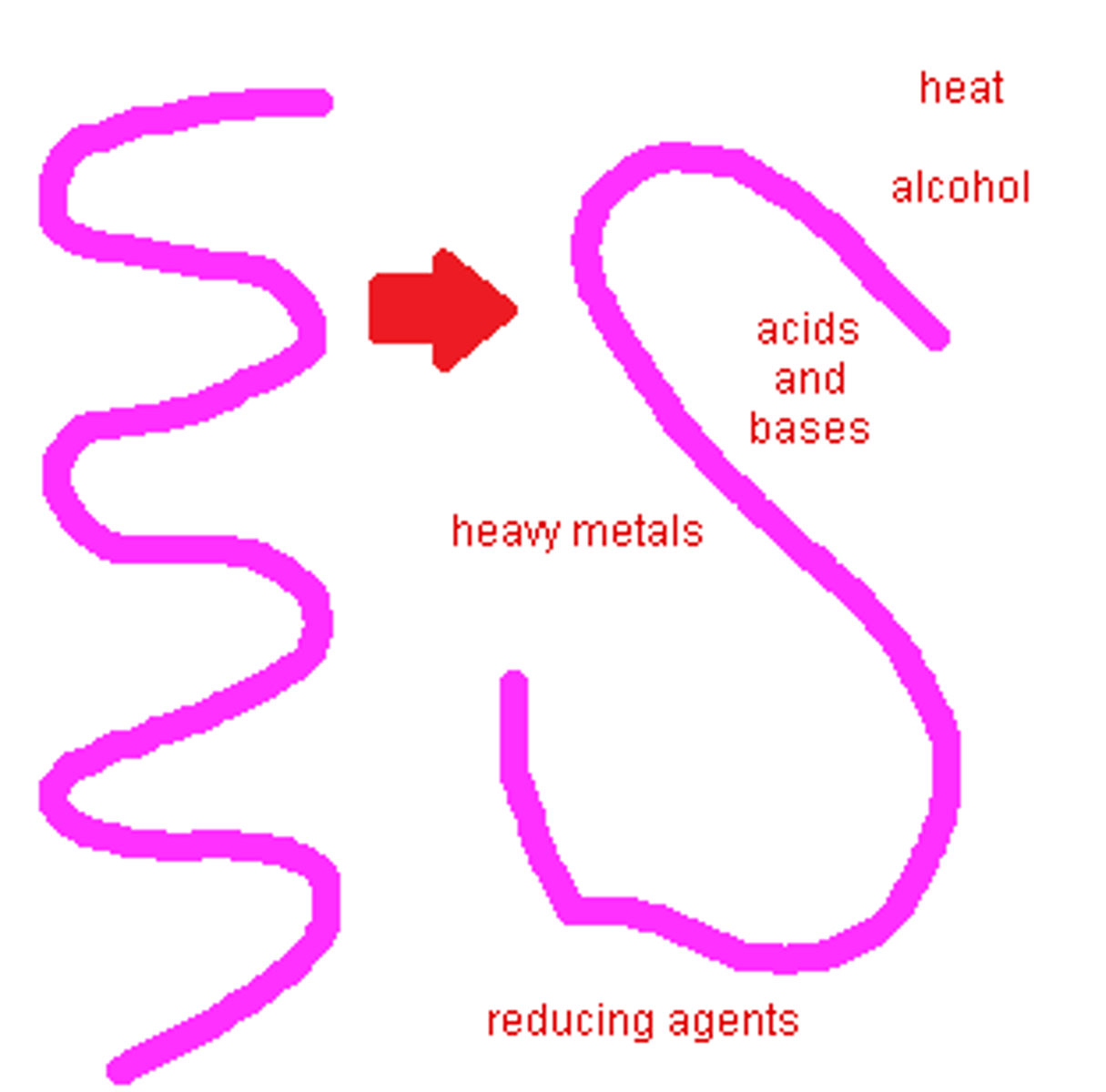
Denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat or other factor
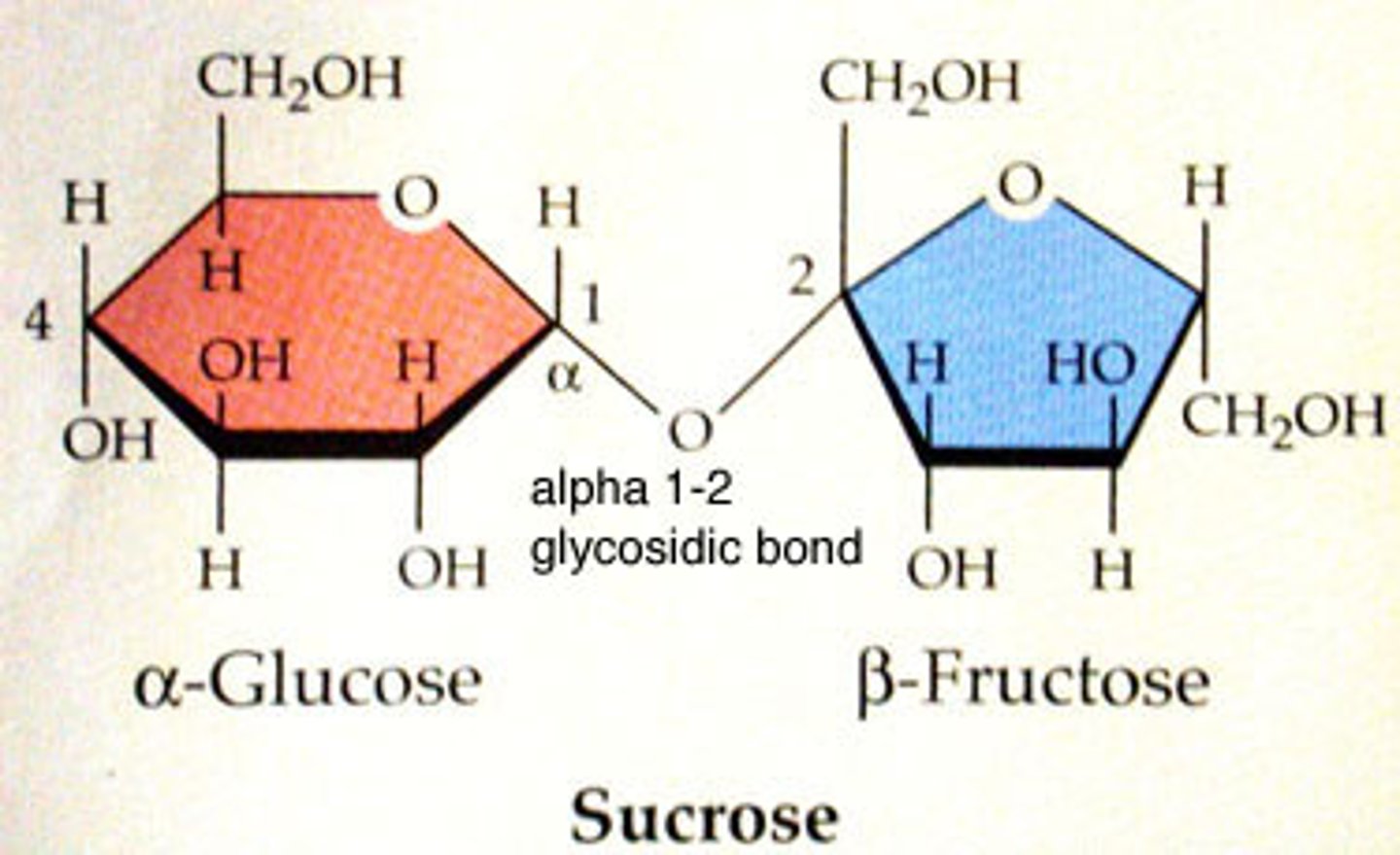
disaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of two monosaccharides, sucrose, lactose maltose
disulfide bonds
Strong chemical side bonds formed when the sulfur atoms in two adjacent protein chains are joined together.
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
fatty acids
unbranched carbon chains that make up most lipids
Fibrous proteins (structural proteins)
Extended and strand-like proteins. Examples: keratin, elastin, collagen, and contractile fibers

globular proteins
these are compact, generally rounded, and soluble in water.
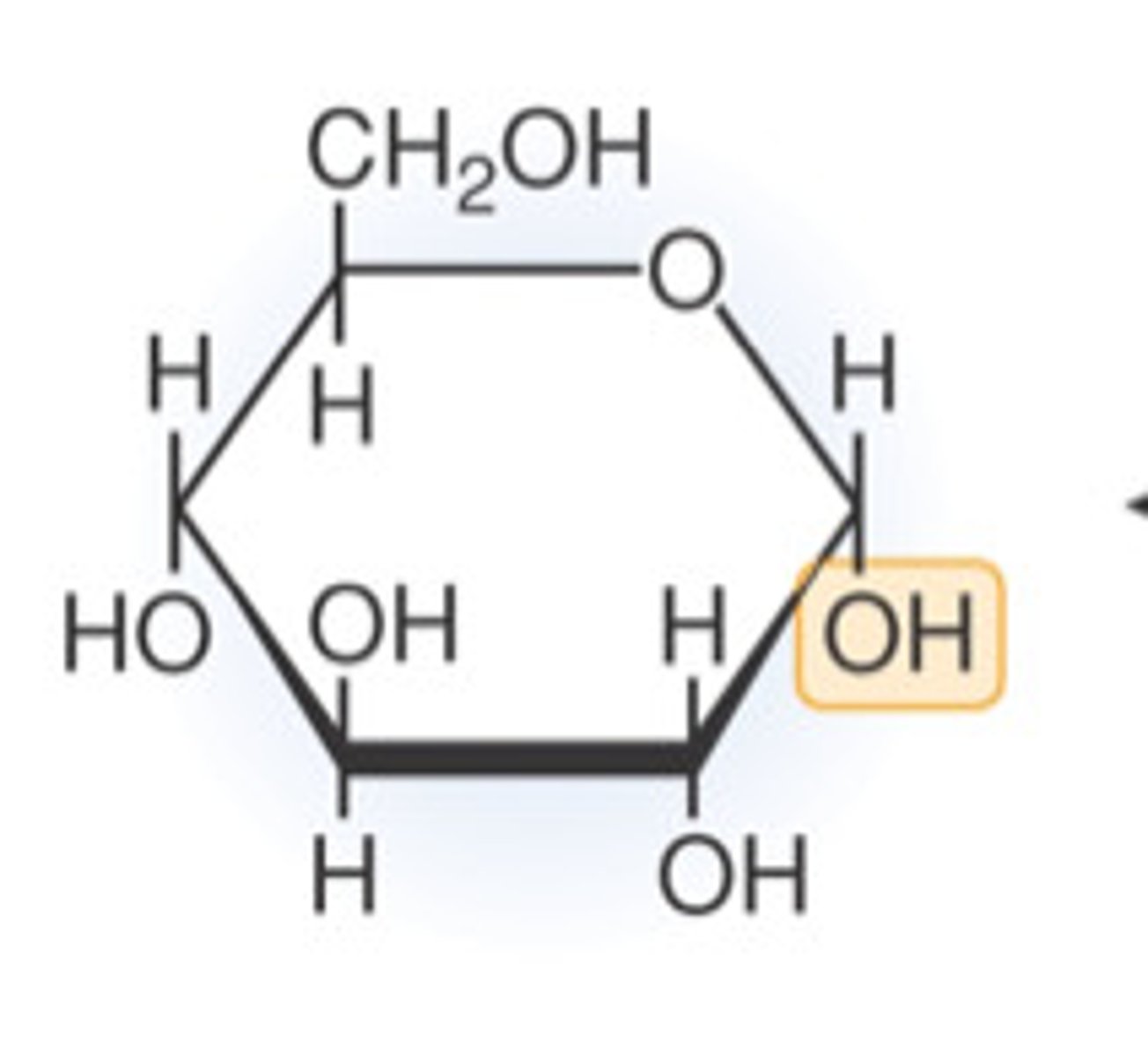
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy.
glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol to which fatty acids are covalently bonded to make fats and oils.
Glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
heat
The energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
Hydrogen Group
H
Hydrolysis
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
Hydrophobic
Having an aversion to water; tending to coalesce and form droplets in water.
Hydrophilic
Having an affinity for water.
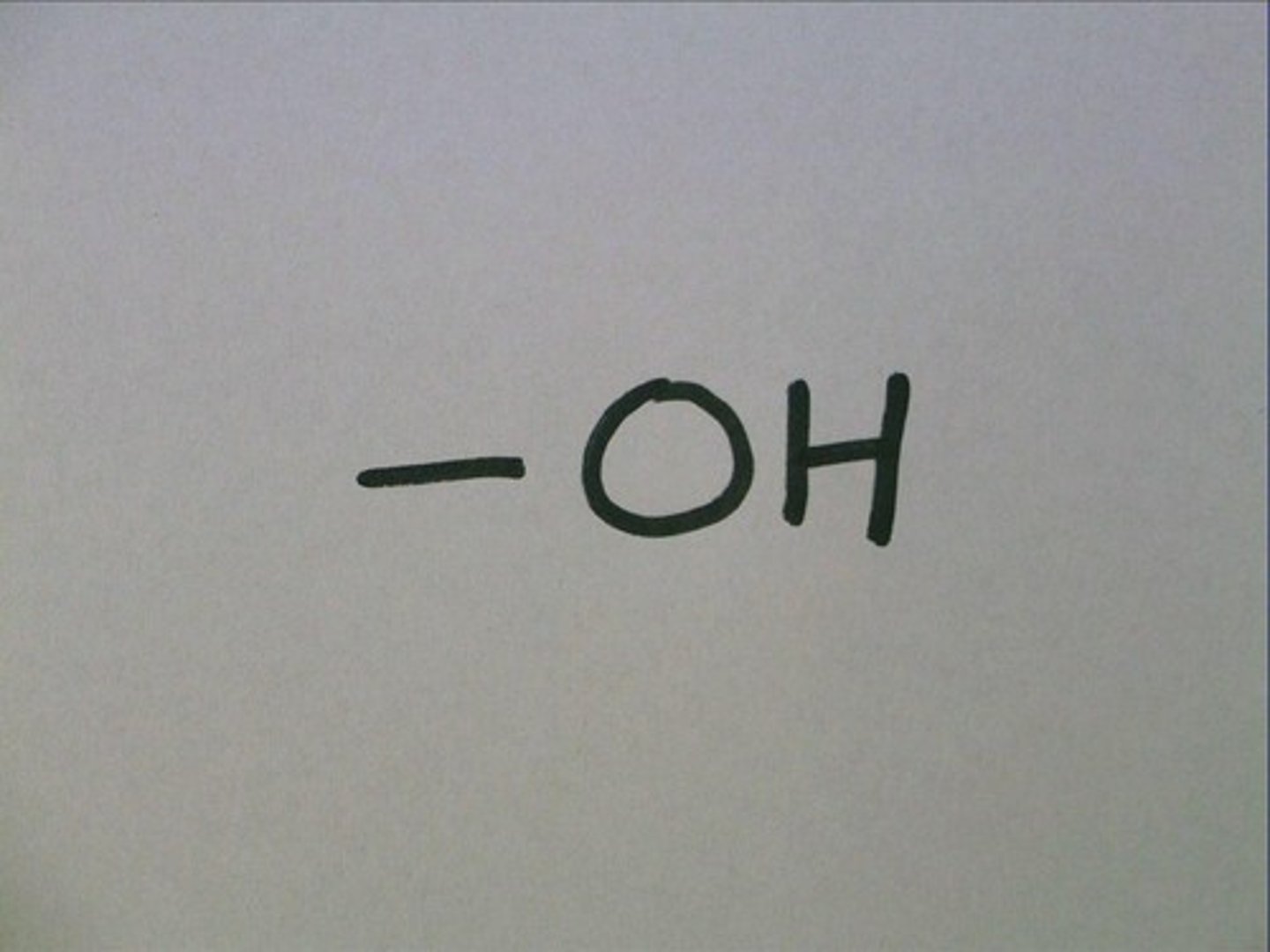
hydroxyl group
A chemical group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom.
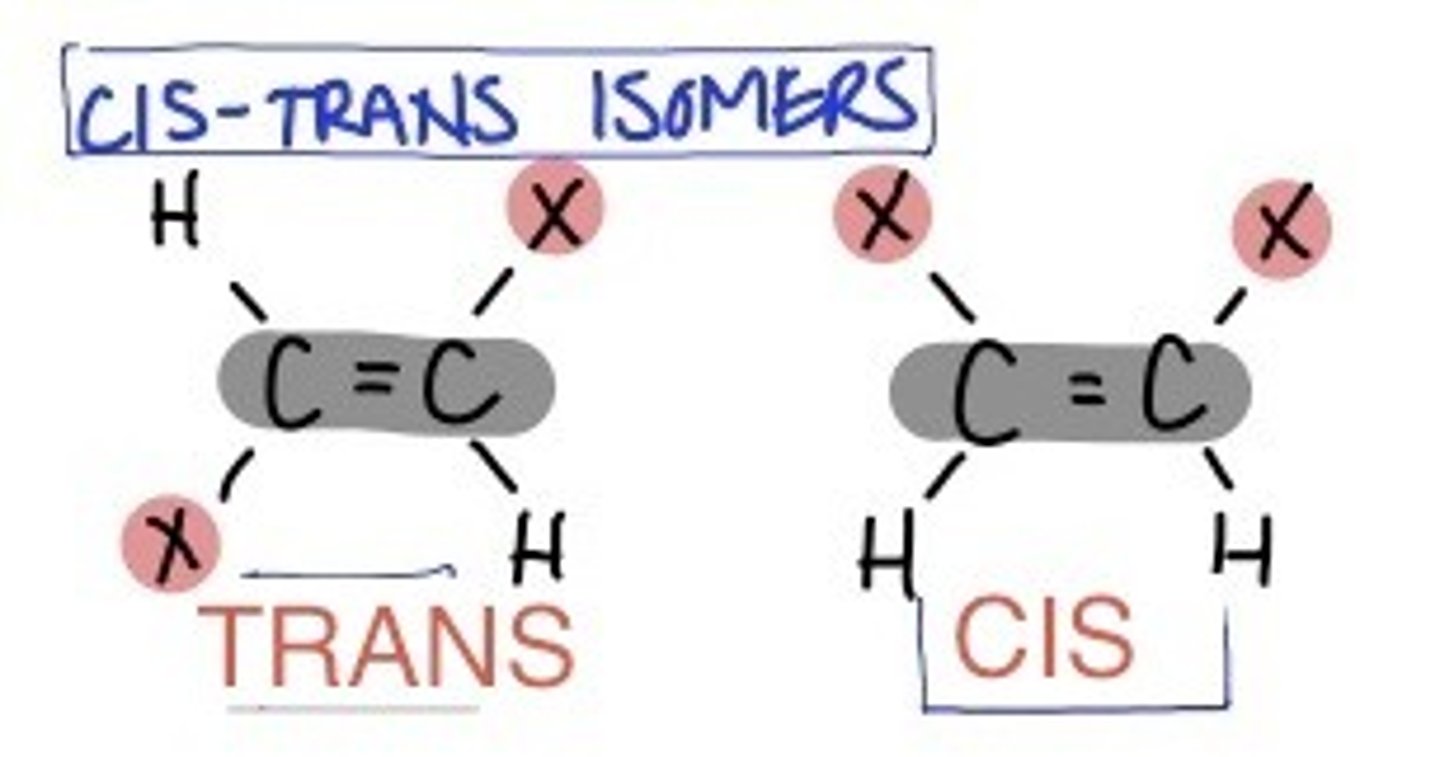
Isomer
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
kilocalorie (kcal)
A quantity of heat equal to 1,000 calories. Used to measure the energy content of food, it is usually called a "Calorie."
kinetic energy
the energy an object has due to its motion
Lactose
glucose + galactose (milk sugar)
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules
Monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
Nitrogen
Most abundant gas in the atmosphere
nitrogenous base
is a carbon ring structure that contains one or more atoms of nitrogen. In DNA, Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine.
nonpolar
No partial charges. Do not mix with water.
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
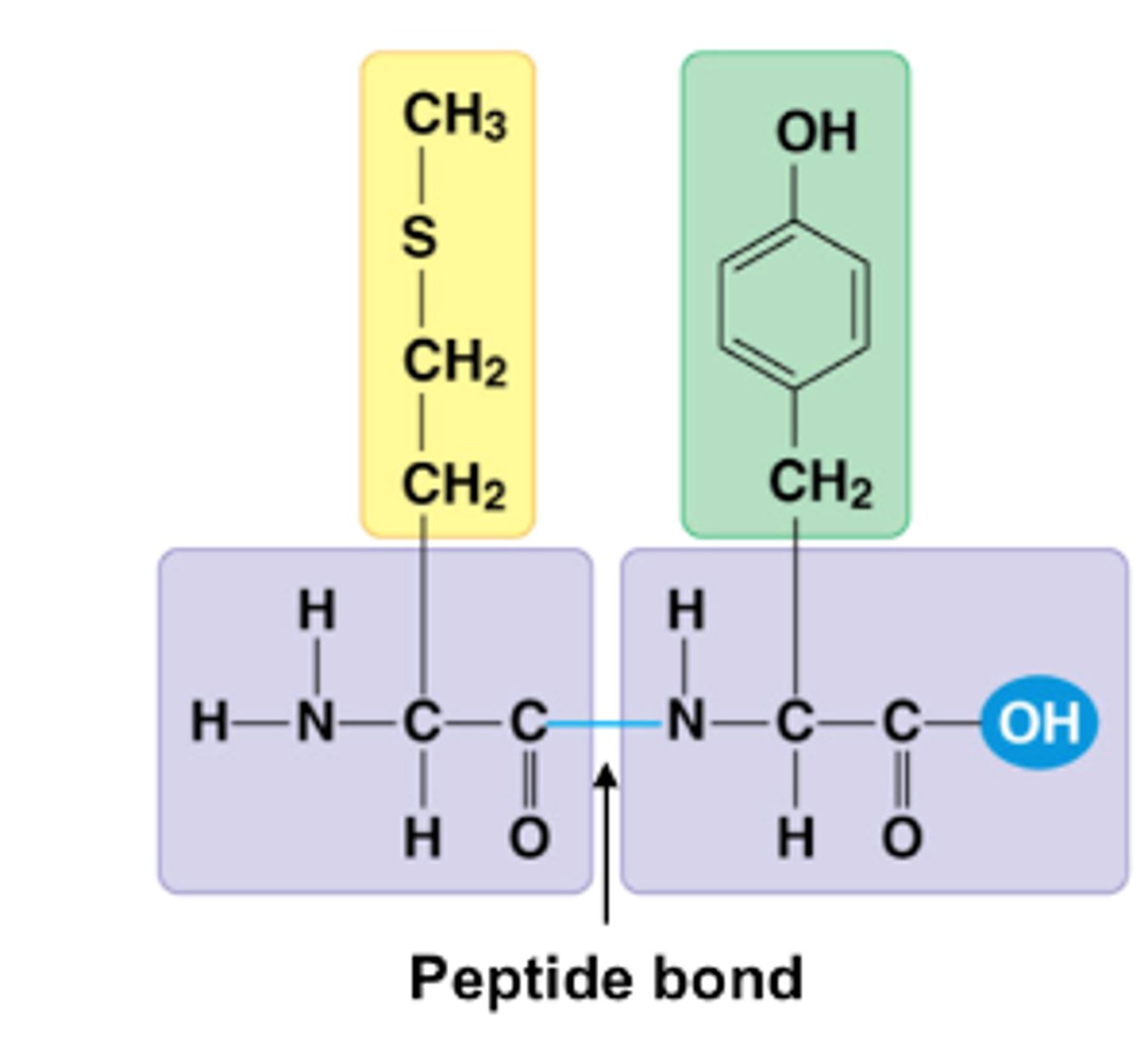
peptide
Short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids C-N
phosphate group
A chemical group consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms; important in energy transfer.
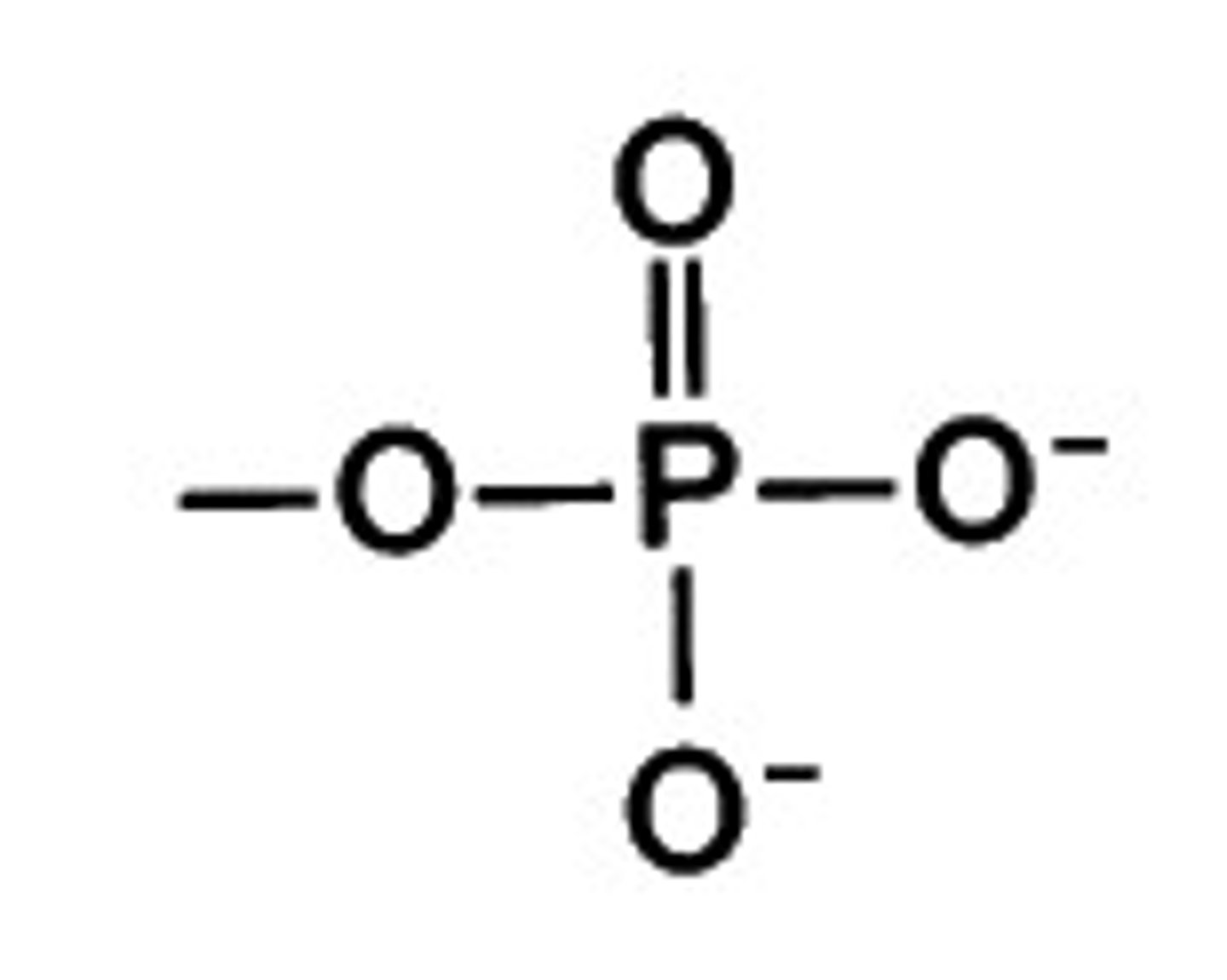
phosphate
element found in nucleic acids, phospholipids
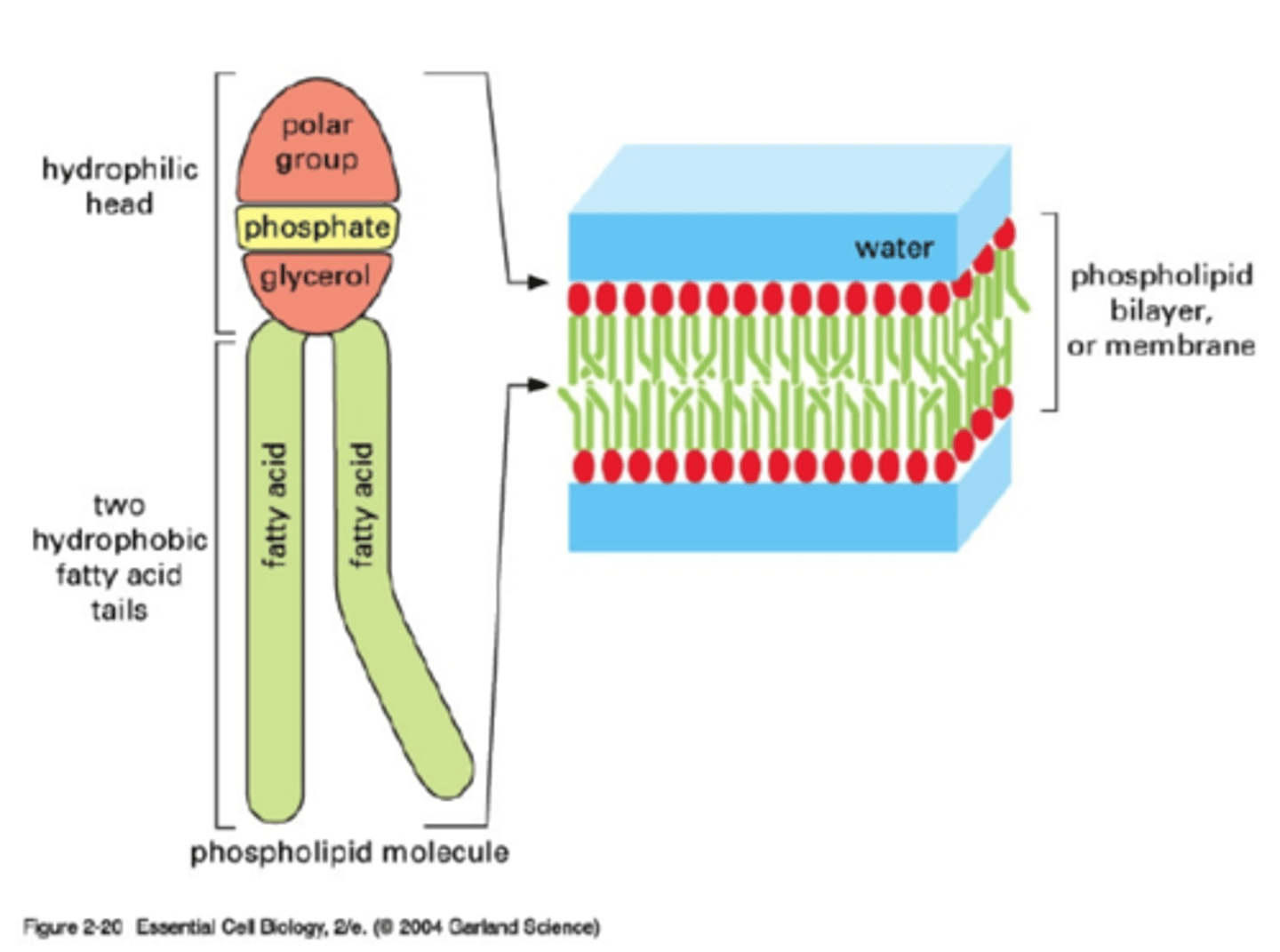
Phopholipids
They serve as a major structural component of most biological membranes. They form the lipid bilayer in cell membranes of organisms.
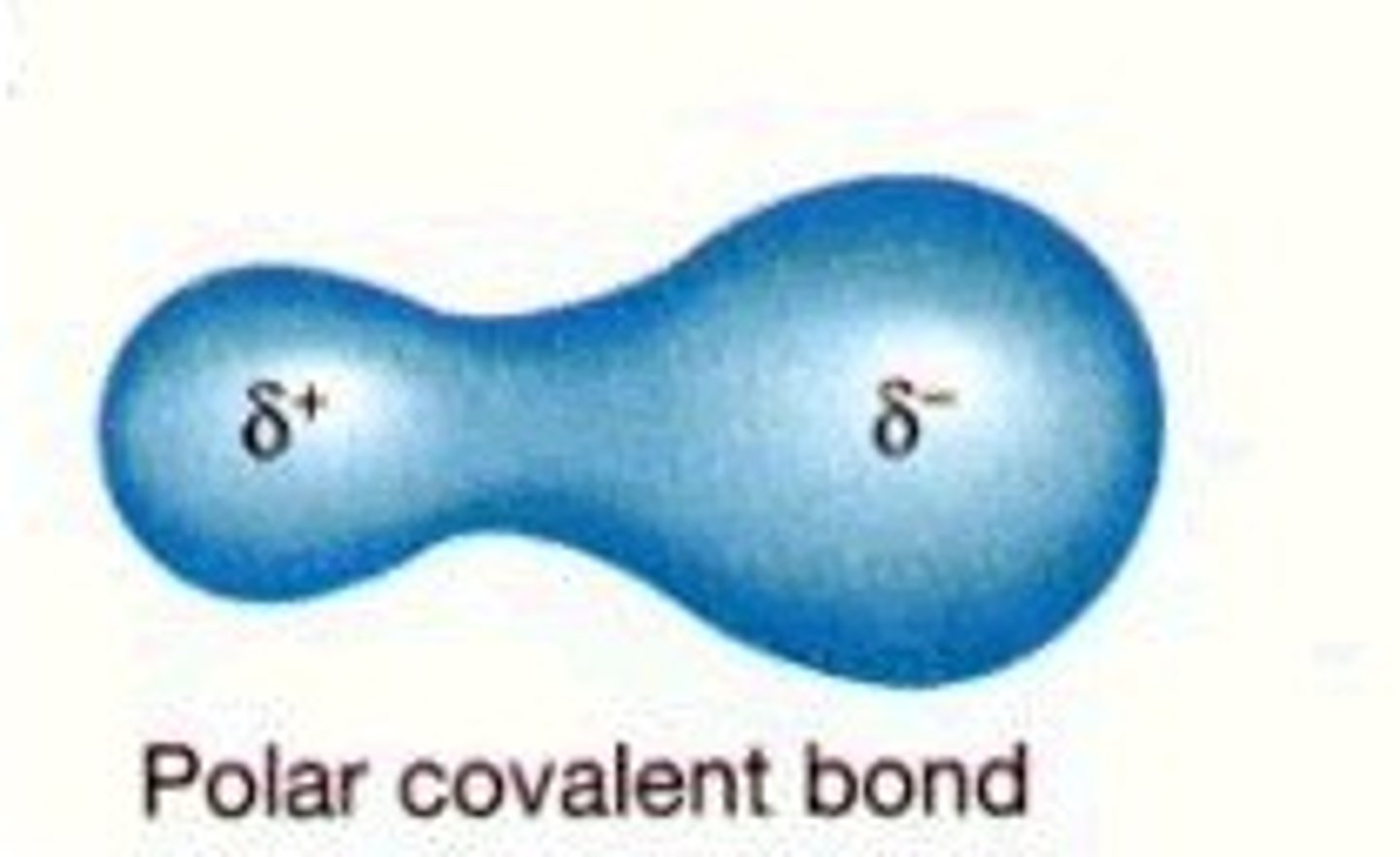
polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
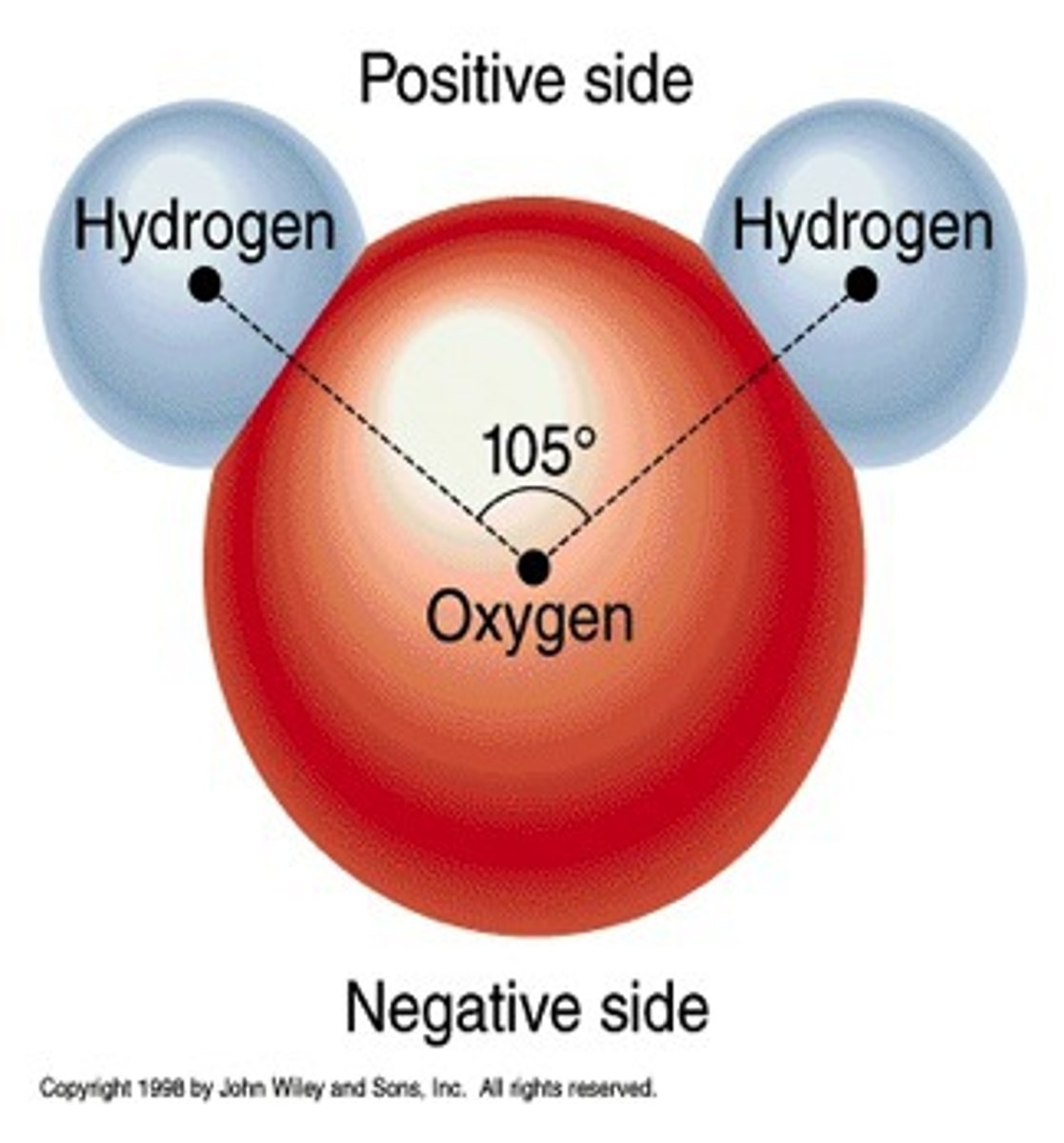
polar molecule
A molecule that has electrically charged areas.
Polymers
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
Polypeptide
long chain of amino acids that makes proteins
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids
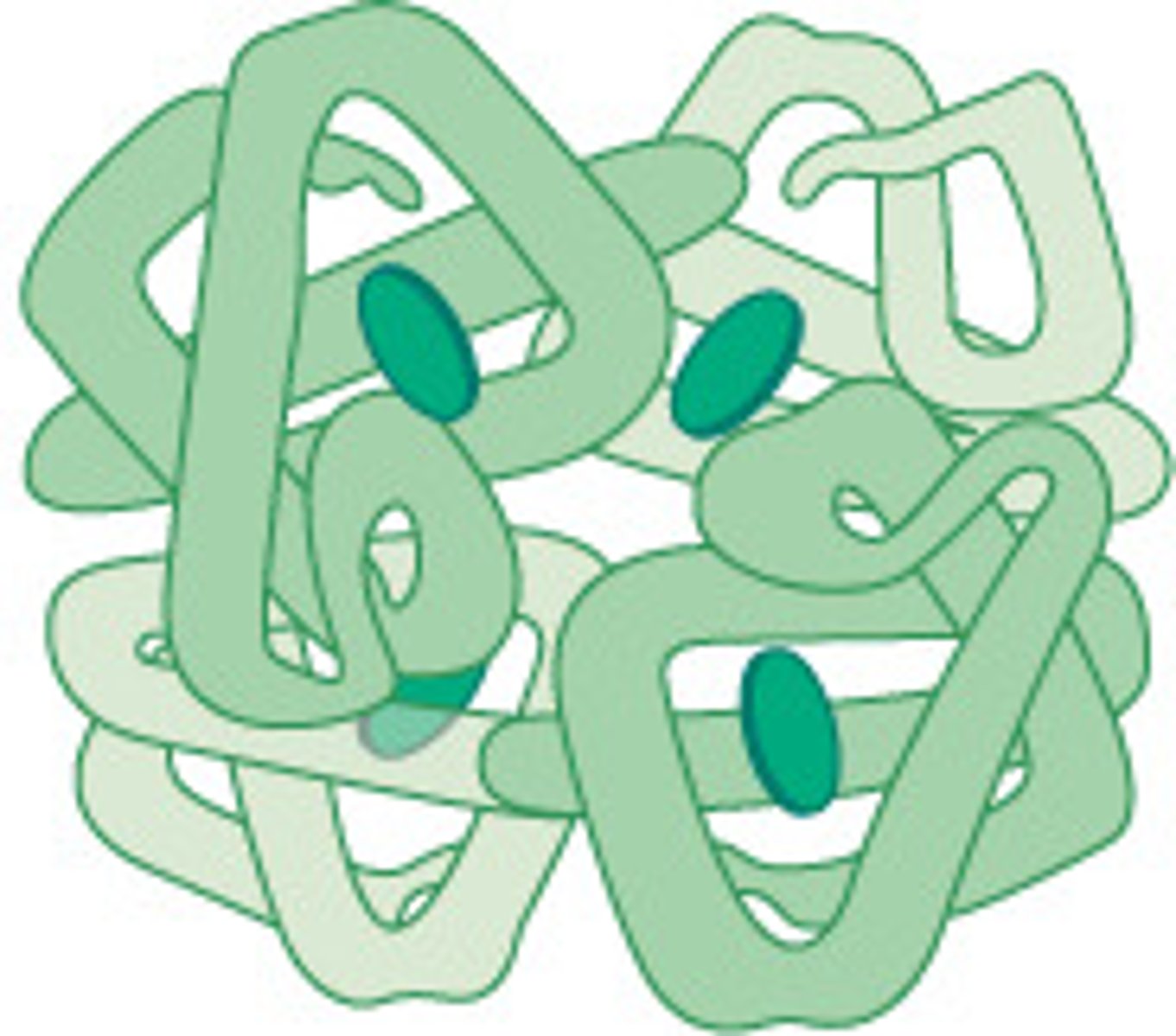
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
function of proteins
essential for the growth, development, and repair of all body tissues
function of carbohydrates
provide energy
function of lipids
long term energy storage
function of nucleic acids
store and transmit genetic information
Ribose
A five-carbon sugar present in RNA
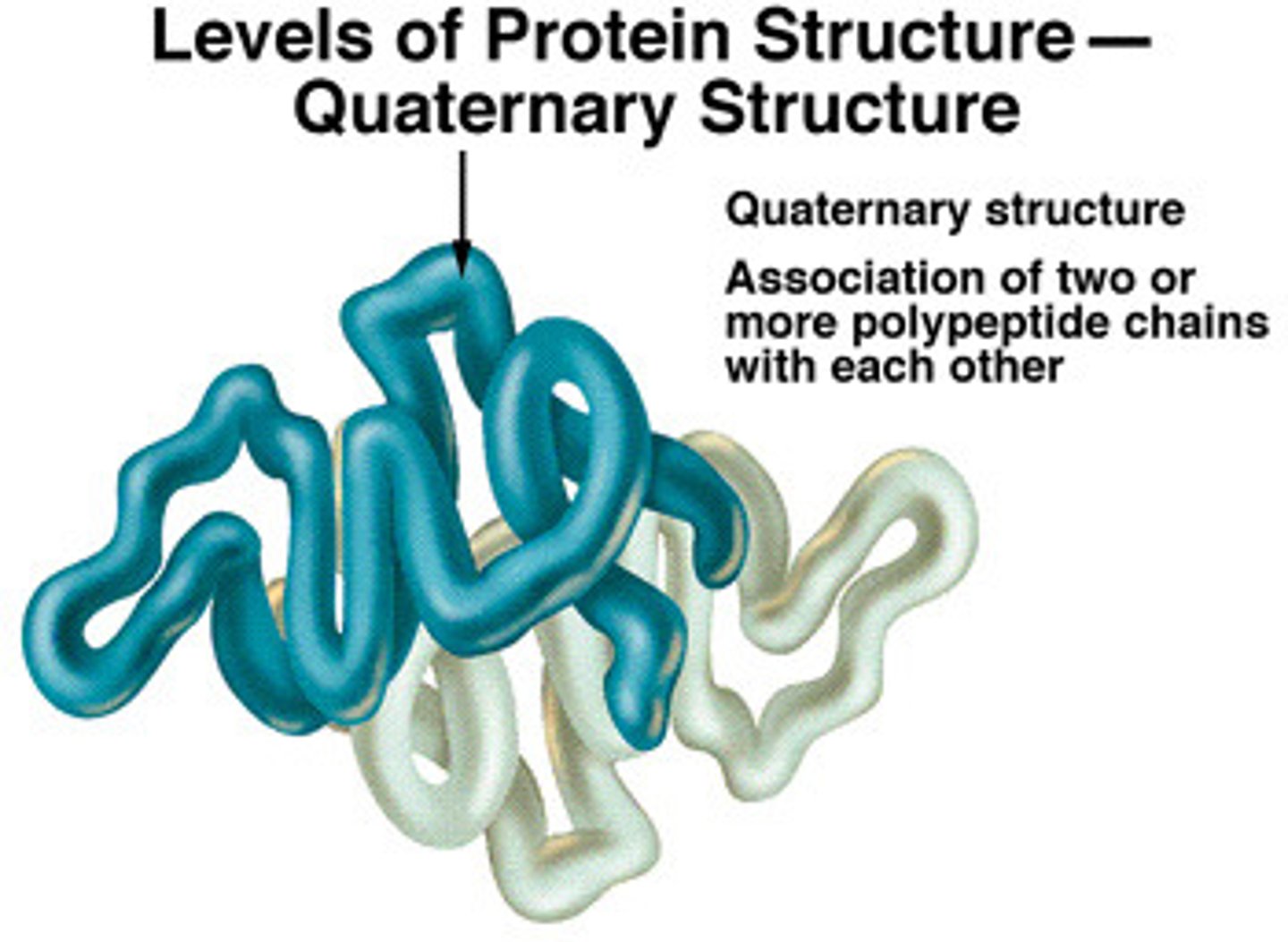
quaternary structure
Union of 2+ polypeptide subunits
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
saturated fats
fats that are solid at room temperature and saturated with hydrogen. Butter
secondary structure of protein
protein structure is formed by folding and twisting of amino acid chain
specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
Sucrose
table sugar, disaccharide
surface tension
the uneven forces acting on the particles on the surface of a liquid

Temperature
A measure of the average energy of motion of the particles of a substance.
tertiary structure
Results from interactions between side chains.
thermal energy
The total energy of all the particles of an object.
unsaturated fats
fats that remain liquid at room temperature