Knowt 12 - Premodern Humans
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Primer, "Heidi," and the Neanderthals
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Pleistocene (4 Info)
"Ice Age"
Middle Pleistocene: 780 – 125 ka
Later Pleistocene: 125 – 10 ka
Glacial & interglacial periods
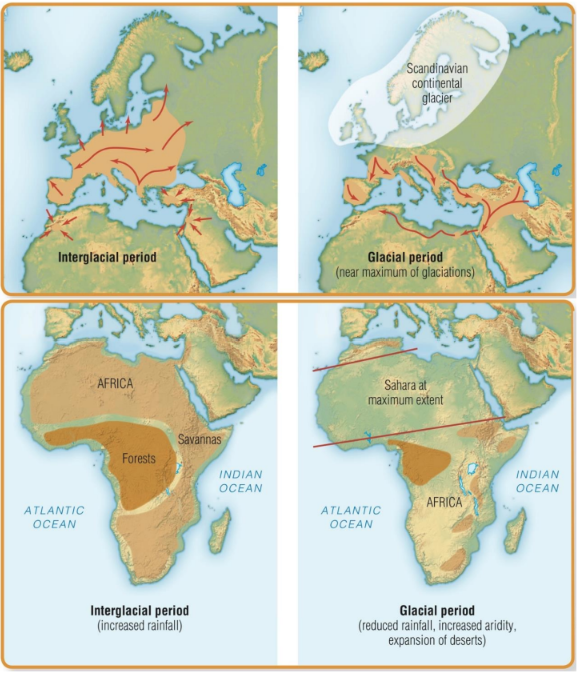
Glacial Periods (4 Info)
Colder temperatures
Sea levels drop
Europe: glaciers advance
Africa: deserts expand
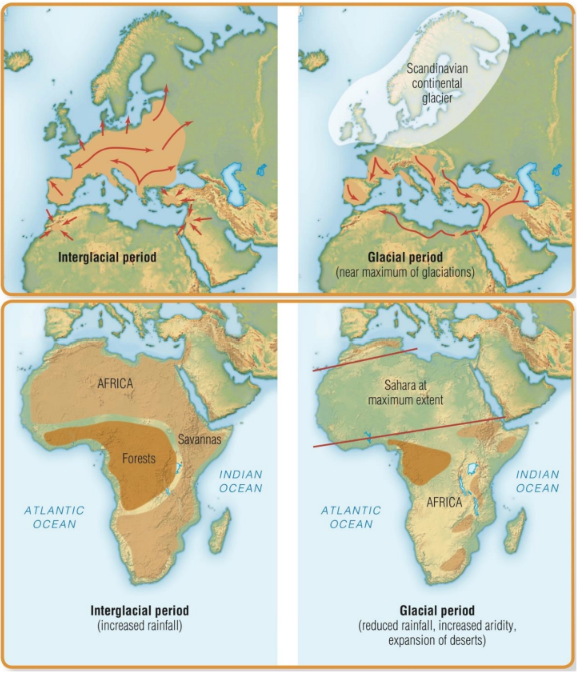
Interglacial Periods (4 Info)
Warmer temperatures
Sea levels rise
Europe: glaciers retreat
Africa: savannahs expand
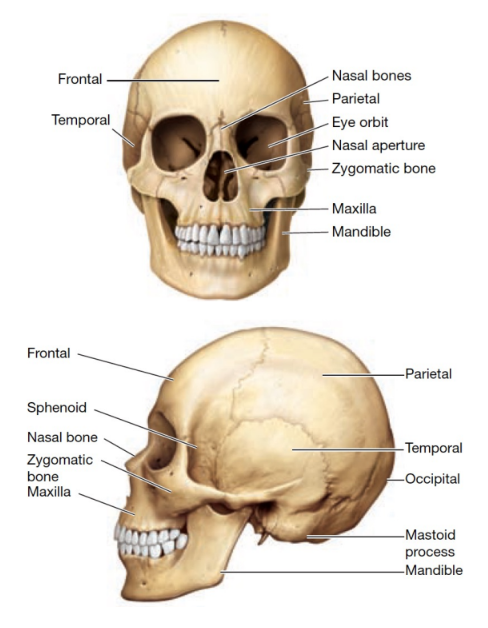
Anatomically Modern Humans (9 Info)
cranial capacity: 1350cc (avg)
high braincase
rounded occipital bone
small, flat face
projecting nasal bones
small brow ridge
protruding chin
parabolic dental arcade
Small teeth
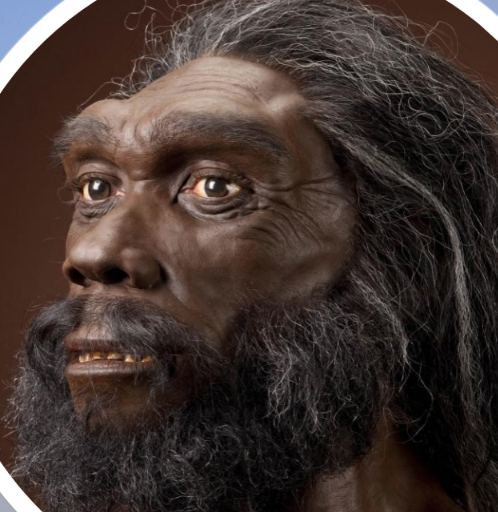
Premodern Humans - Characteristics (7 Info)
Dramatic encephalization
Longer, but slightly higher braincase
Larger brow ridge
Bigger, projecting face
Projecting occipital bone
Larger teeth
No chin
Premodern Humans - Species (2 Species)
Homo Heidelbergensis
Homo Neanderthalensis
Premodern Humans - Dispersal (4 Places)
Africa
Eurasia
Asia
Europe
Premodern Humans - Subspecies (3 Subspecies)
Homo sapiens heidelbergensis
Homo sapiens neanderthalensis
Homo sapiens sapiens
“Heidi” - Homo Heidelbergensis (6 Info)
700 - 200 ka
Range: Africa, Europe, Eurasia, Asia
Ancestral Characters
Derived Characters: 1300 cc (Avg), Higher max cranial width, Canine Fossa
Continued general evolutionary trend
Intermediate Robusticity

Bodo, Ethiopia (3 Info)
600 ka
Description: Adult Male, 1250 cc, Wide Nasal Opening
Significance: Earliest confirmed evidence of H. Heidelbergensis, signs of de-fleshing
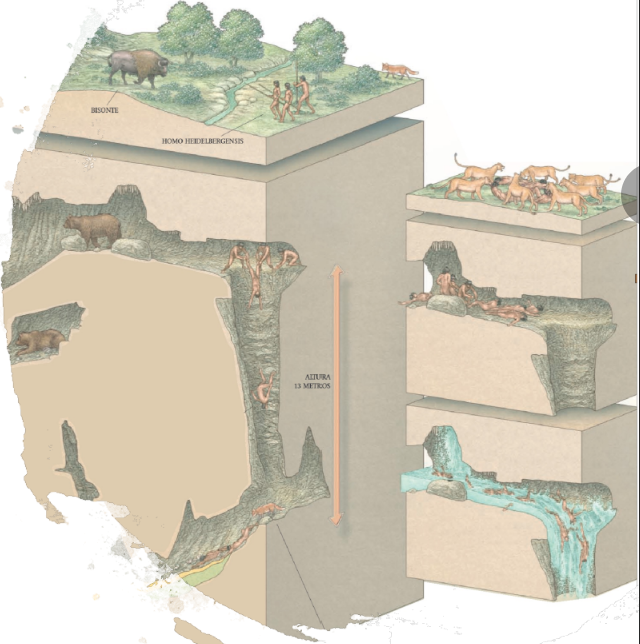
Sima de los Huesos (3 Info)
Sierra de Atapuerca, Spain
430 ka
Significance: 1000s of hominin fossils, 34 individuals, 80% of hominin remains, DNA shows Neanderthal relationship, Intentional Burial?
Schöningen, Germany (2 Info)
300 ka
Significance: Clear Evidence of hunting, 11 wooden weapons, 10,000+ Faunal remains
Tools, Culture, Lifestyle (5 Info)
used the "Levallois Technique"
regional hunter-gatherers
control of fire and cooking
built temporary structures
varied diet; first to exploit marine life
The Neanderthals (5 Info)
Discovery: 1856
Location: Neander Valley, Germany
Dates: Early Neanderthals": 400/300 - 130 ka; "Classic Neanderthals": 130 – 40 ka
Range: Europe and Asia
Pronunciation: neander-TAL, not –thal.

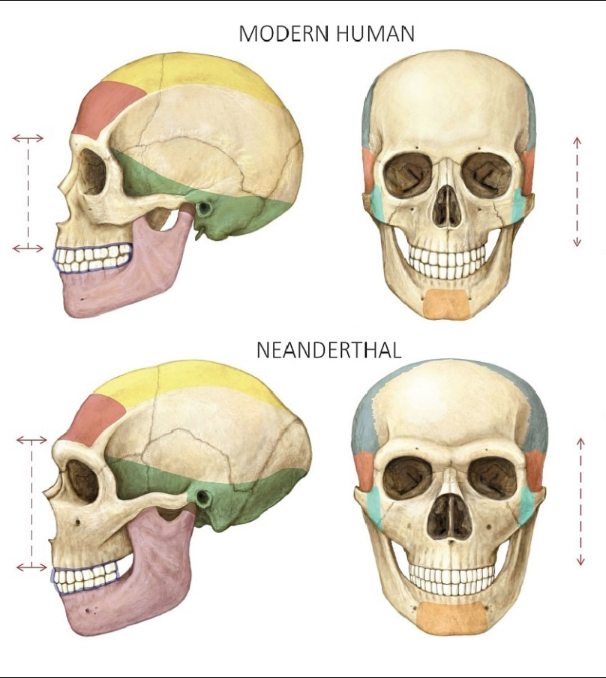
The Neanderthals - Characteristics (7 Info)
1410 – 1520 cc (avg)
long, low cranium w/ sloping forehead
"occipital bun"
retromoral space
large, wide nasal aperture/cavity
projecting midface
widely set orbits
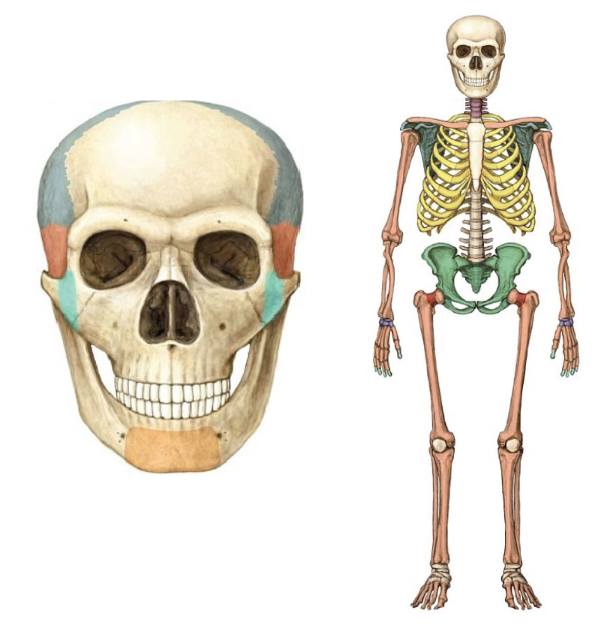
The Neanderthals - Aberration or Adaptation? (6 Info)
wide nasal aperture/cavity
wide, short trunk
short tibias
large infraorbital foramina
large cranial capacity
Glacial Period 225-125 at -6o C
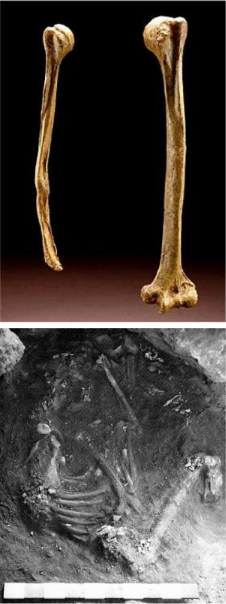
The Neanderthals - Burying (3 Info)
They buried their dead: Shanidar Cave, Iraq, 50-45 ka, 4 intentional burials
They took care of their injured: Shanidar 1 sustained significant injuries
They used “medicine”: pollen of plants with curative effects
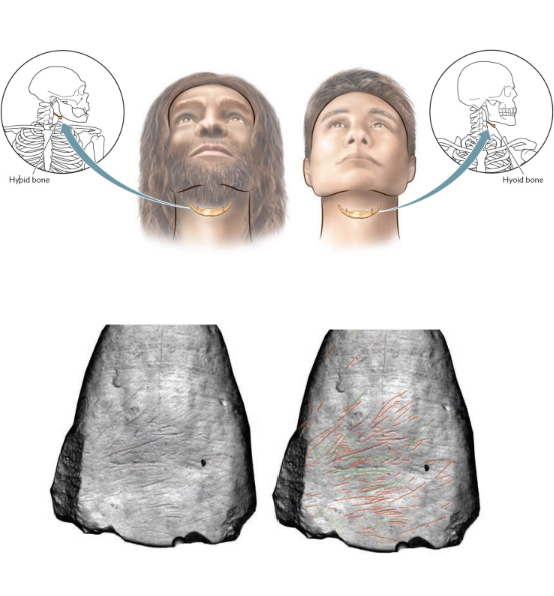
The Neanderthals - Speaking (2 Indo)
They likely Spoke: Kebara Cave, Israel; 60 ka; hyroid bone
Evidence of brain lateralization: In Teeth?
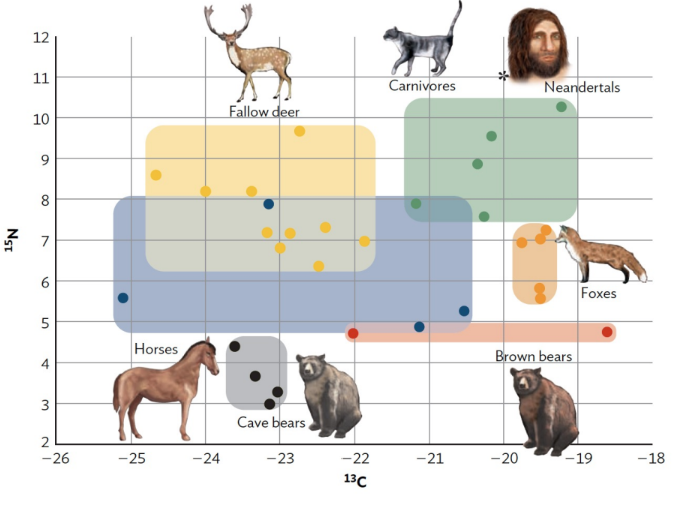
The Neanderthals - hunting (3 Info)
Abundance of processed faunal remains
Bone chemistry/stable isotope analysis
Tooth plaque
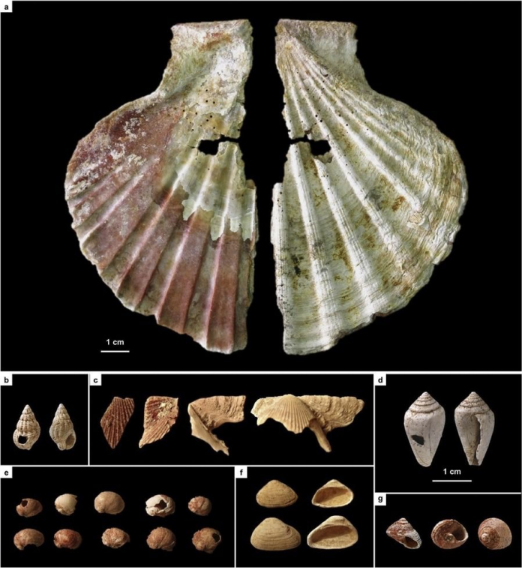
The Neanderthals - Symbolism (3 Info)
Cuevo de los Aviones, Spain
50 ka
Description: dyed, perforated shells

The Neanderthals - Genetics (2 Info)
mtDNA: difference of 200 - 105 base pairs (out of 16,569!)
nDNA: 99.7% the same