506: The Eye
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
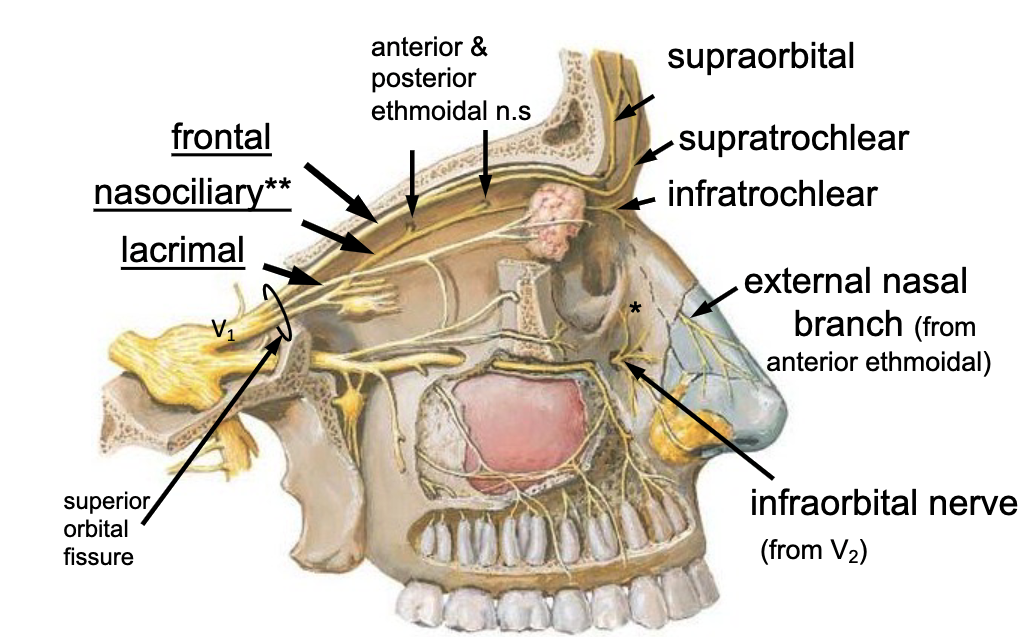
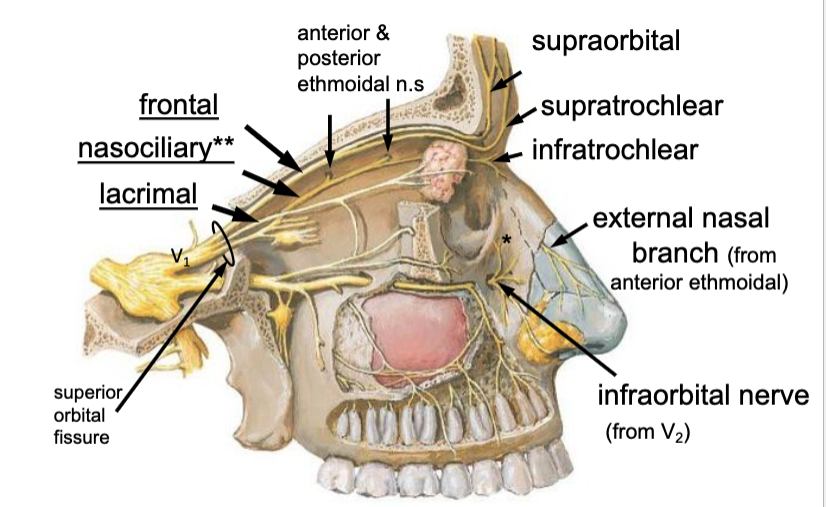
lacrimal n.
frontal n.
nasociliary n.
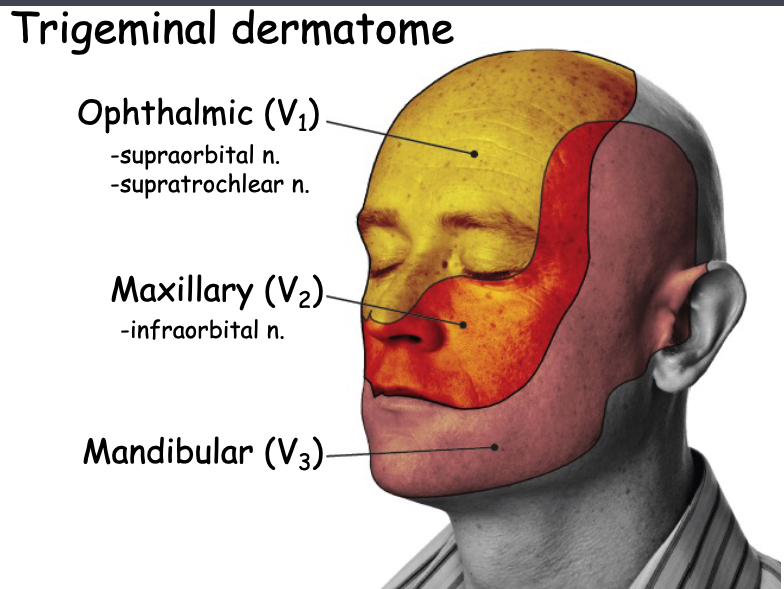
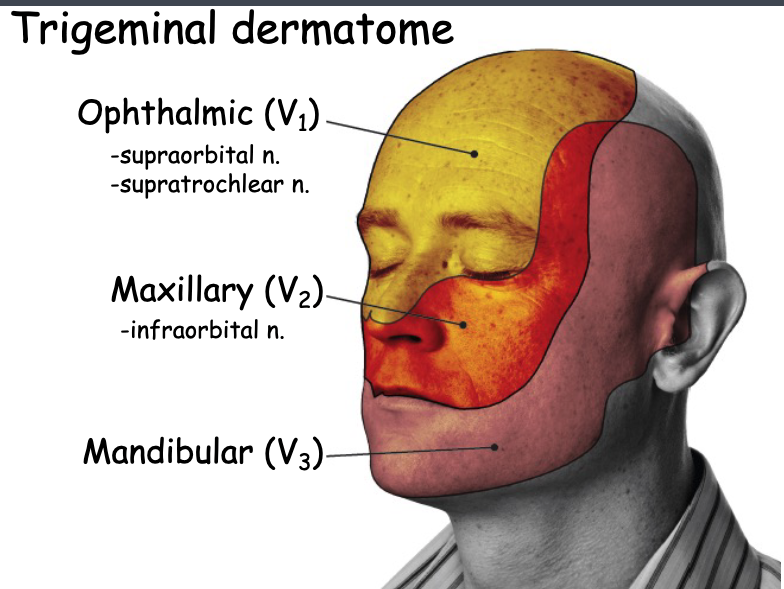
what are the 3 main branches of the opthalmic branch of CN V?
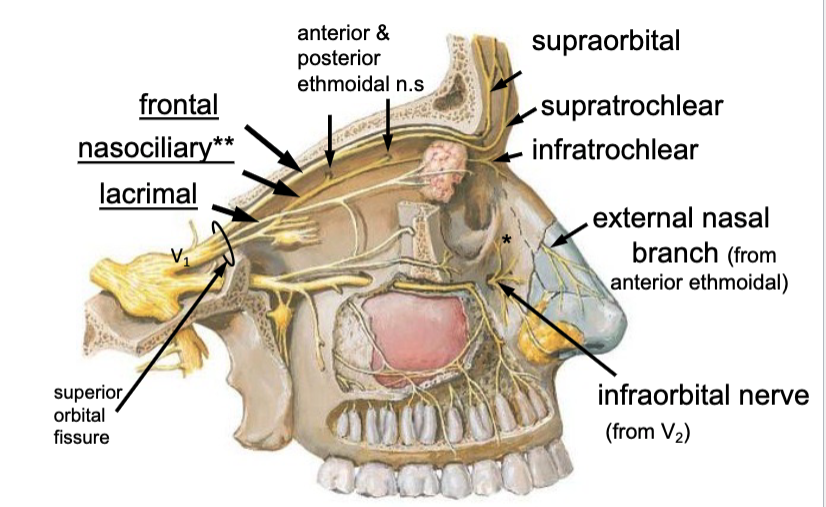
frontal n.
the supraorbital n. is a branch of the:
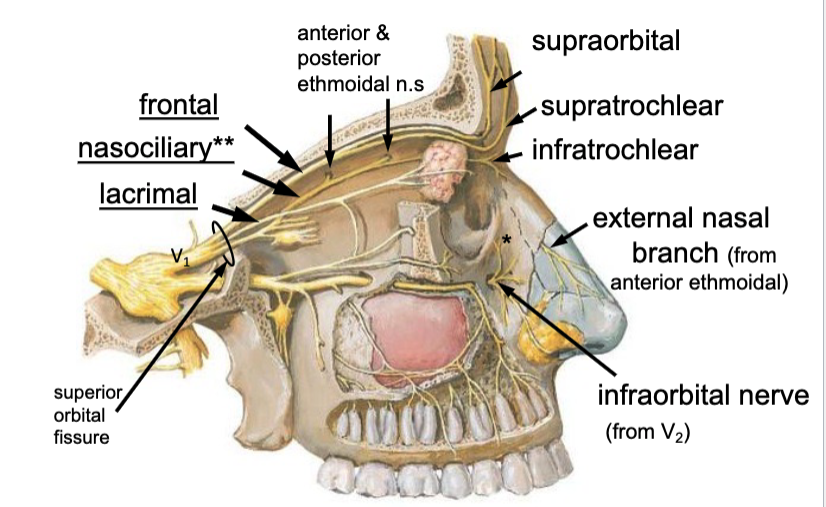
frontal n.
the supratrochlear n. is a branch of the:
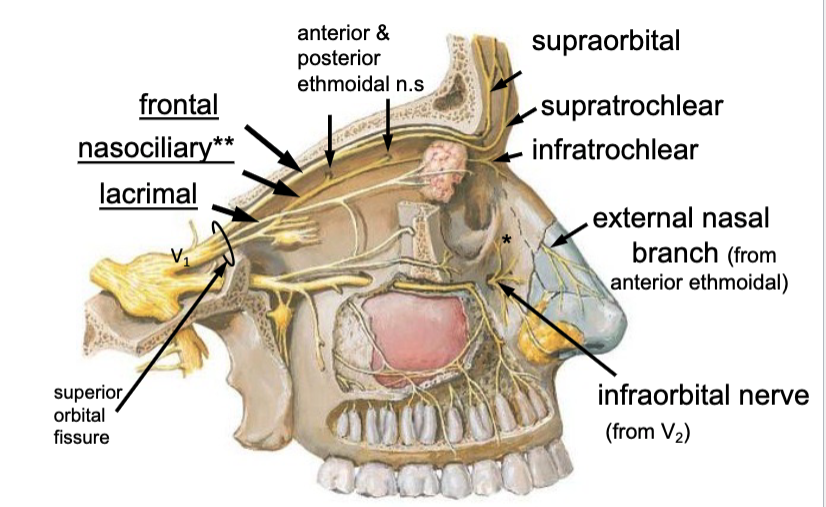
anterior ethmoidal n.
posterior ethmoidal n.
what are the two branches of the nasociliary n.?
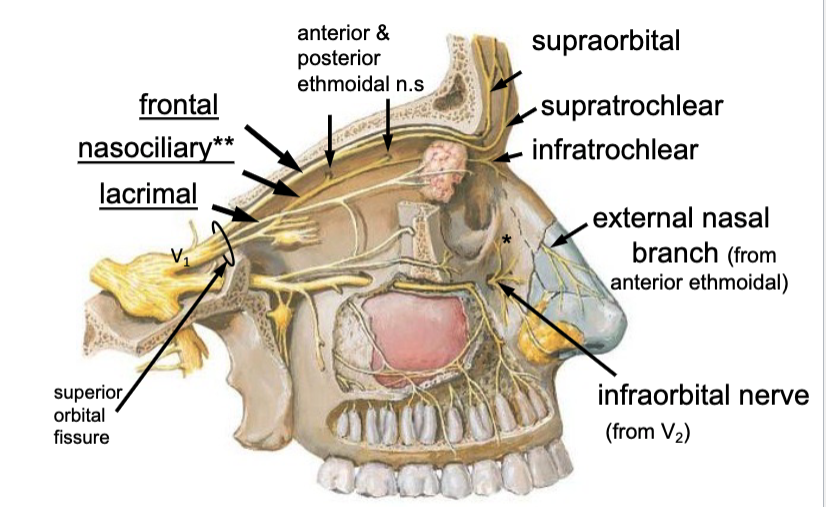
nasociliary n.
the anterior ethmoidal n. is a branch of the:
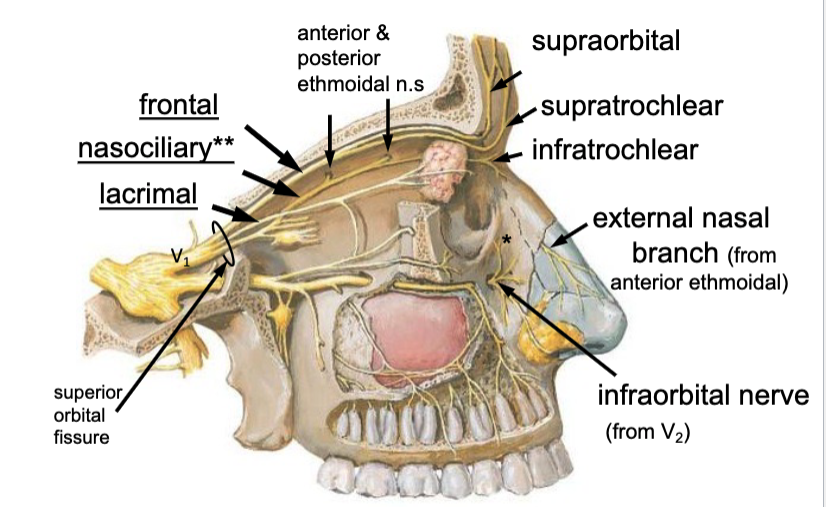
nasociliary n.
the posterior ethmoidal n. is a branch of the:
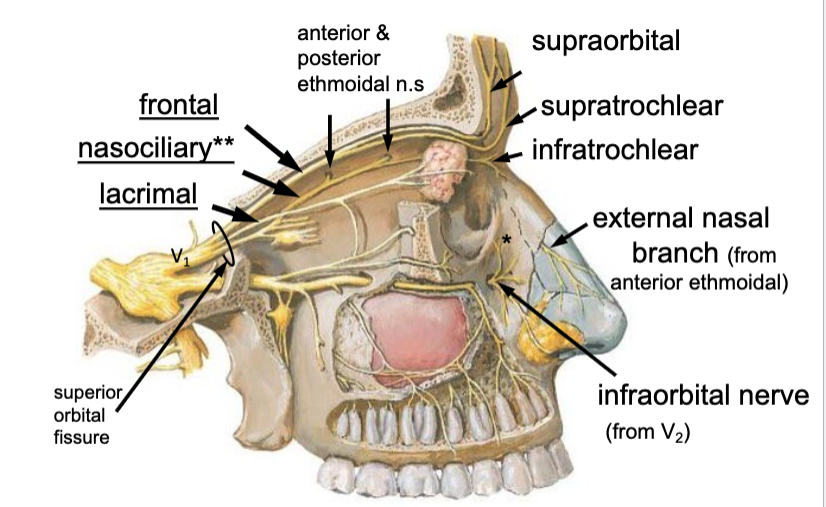
anterior ethmoidal n.
the external nasal n. branch is a branch of the:
V2
the inferior eyelid's sensory innervation comes from:
V1
the superior eyelid's sensory innervation comes from:
nasociliary n.
which branch of V2 is the only nerve that supplies the sensory info to the eyeball?
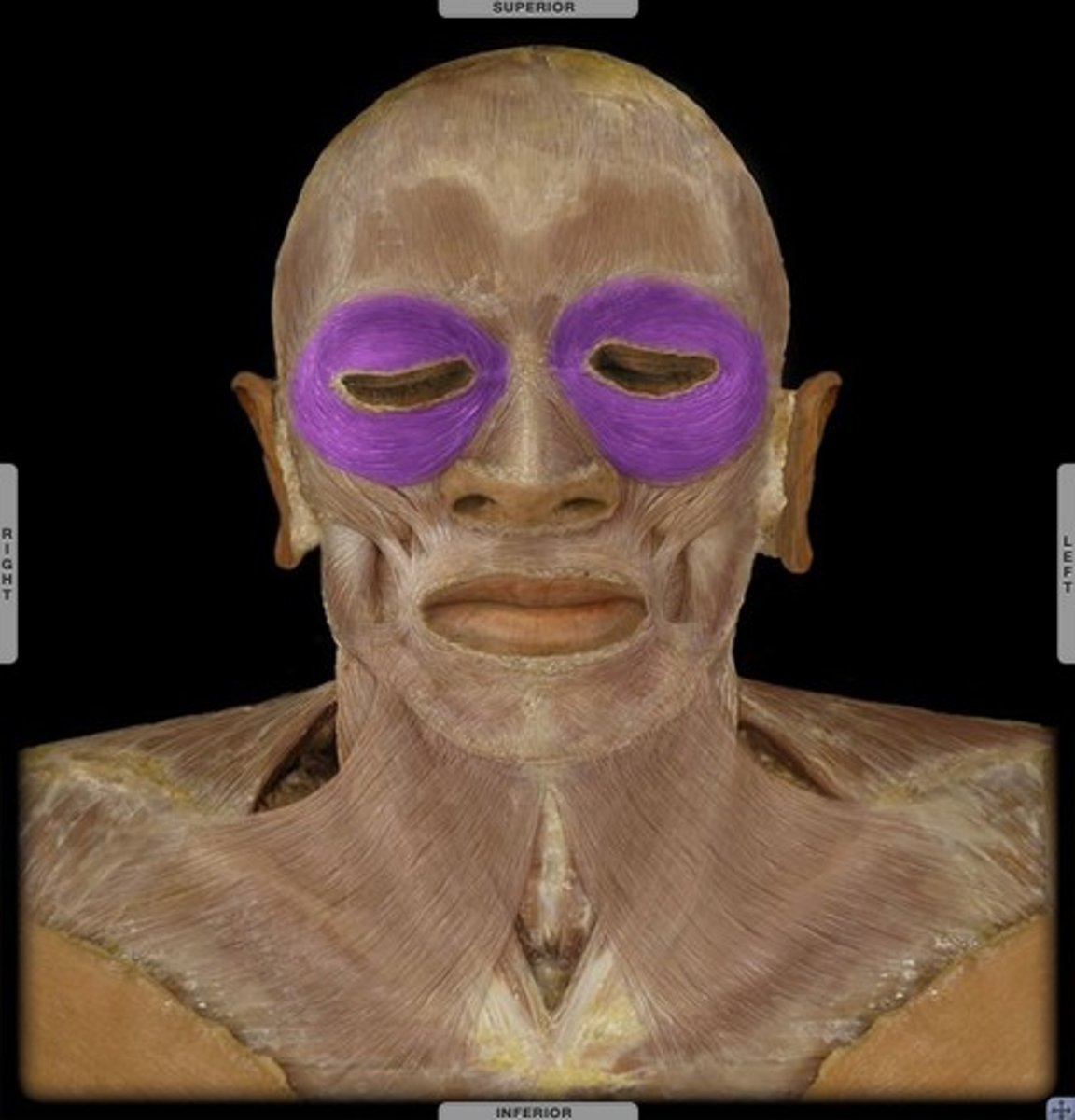
obicularis oculi m.
identify the structure:
medial palpebral ligament
identify the structure:
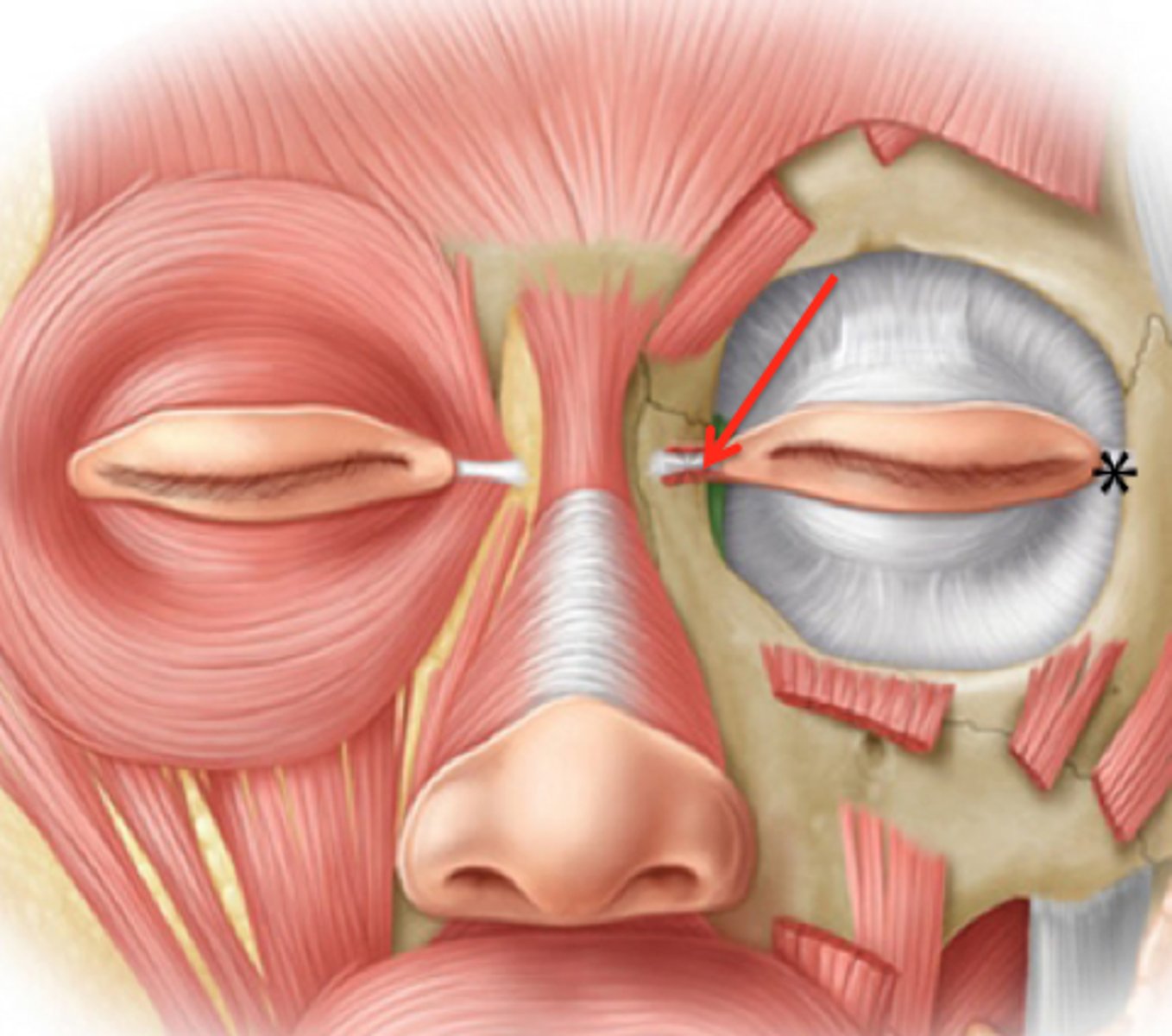
lateral palpebral ligament
CN VII to orbicularis oculi (palpebral part)
CN V1 (nasociliary)
CN II (visual threat or bright light)
CN VIII (sudden sounds)
motor control for the blink reflex is done by…?
sensory control is done by…?
V1
sensory innervation to activate the blink reflex triggered by touch is done by:
CN II
sensory innervation to activate the blink reflex triggered by visual threat or bright light is done by:
CN VIII
sensory innervation to activate the blink reflex triggered by sudden sounds is done by:
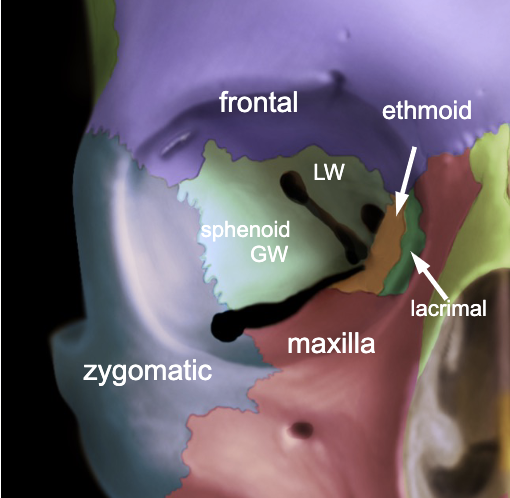
frontal
maxilla
zygomatic
lacrimal
ethmoid
sphenoid
name the 6 bones that make up the orbit:
superior orbital fissure
V1 enters the orbit via the:
frontal bone
the supraorbital foramen is located on the:
maxilla bone
the infraorbital foramen is located on the:
orbital blowout fracture
what is the diangosis?
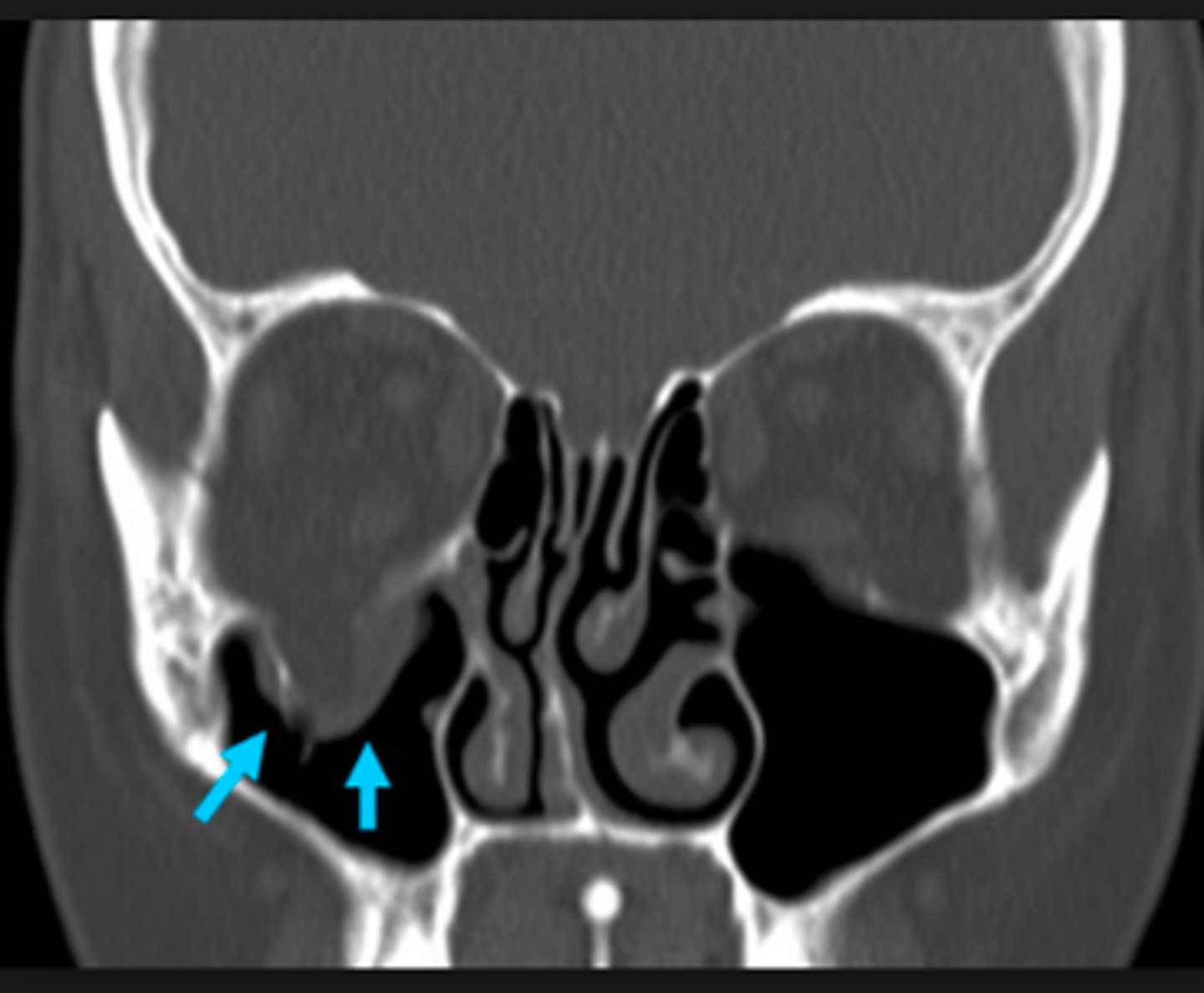
diplopia (if both eyes don’t track equally)
infraorbital nerve damage (facial numbness)
infections
complications with orbital blowout fractures involve?
CSF
what causes the pressure exerted on the optic nerve in papilledema?
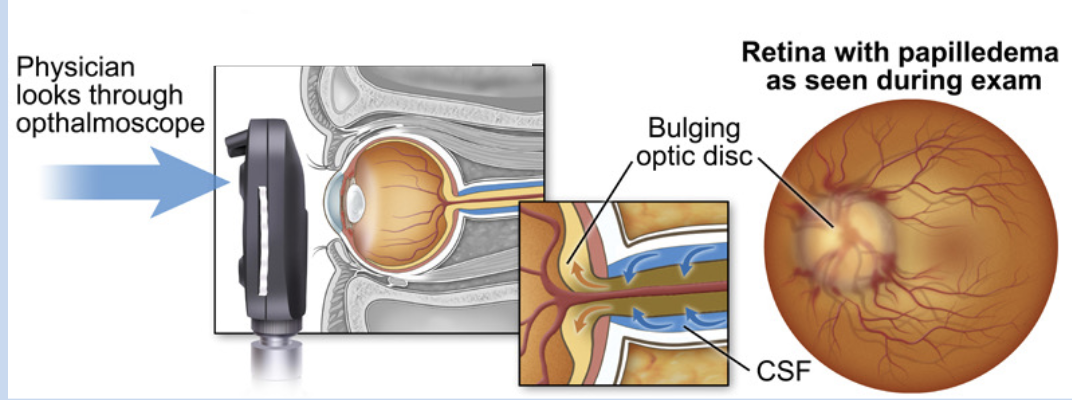
papilledema
patient presents with bilateral blurred vision. An eye exam was done and displays bulging of the optic disc. what is the diagnosis?
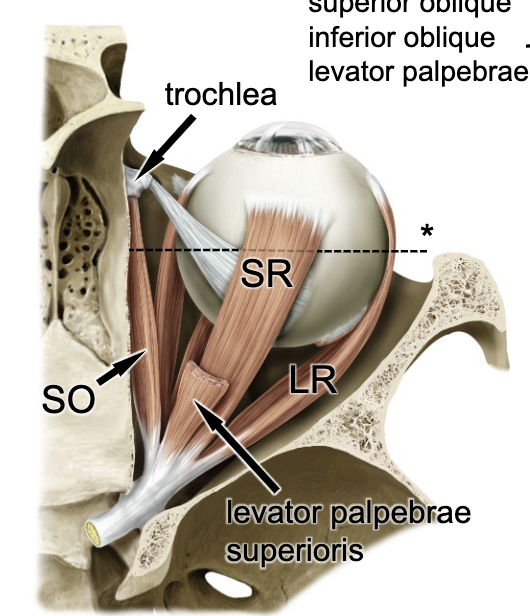
anterior
the rectus muscles of the eye insert onto the eyeball on the _______ aspect
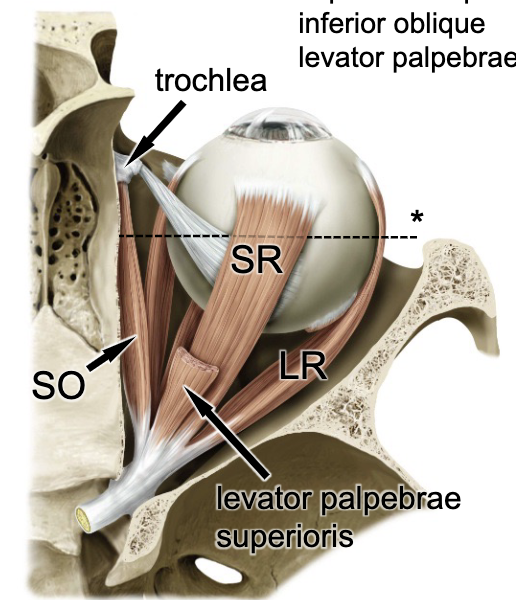
posterior
the oblique muscles of the eye insert onto the eyeball on the _______ aspect
superior rectus m.
identify the structure:
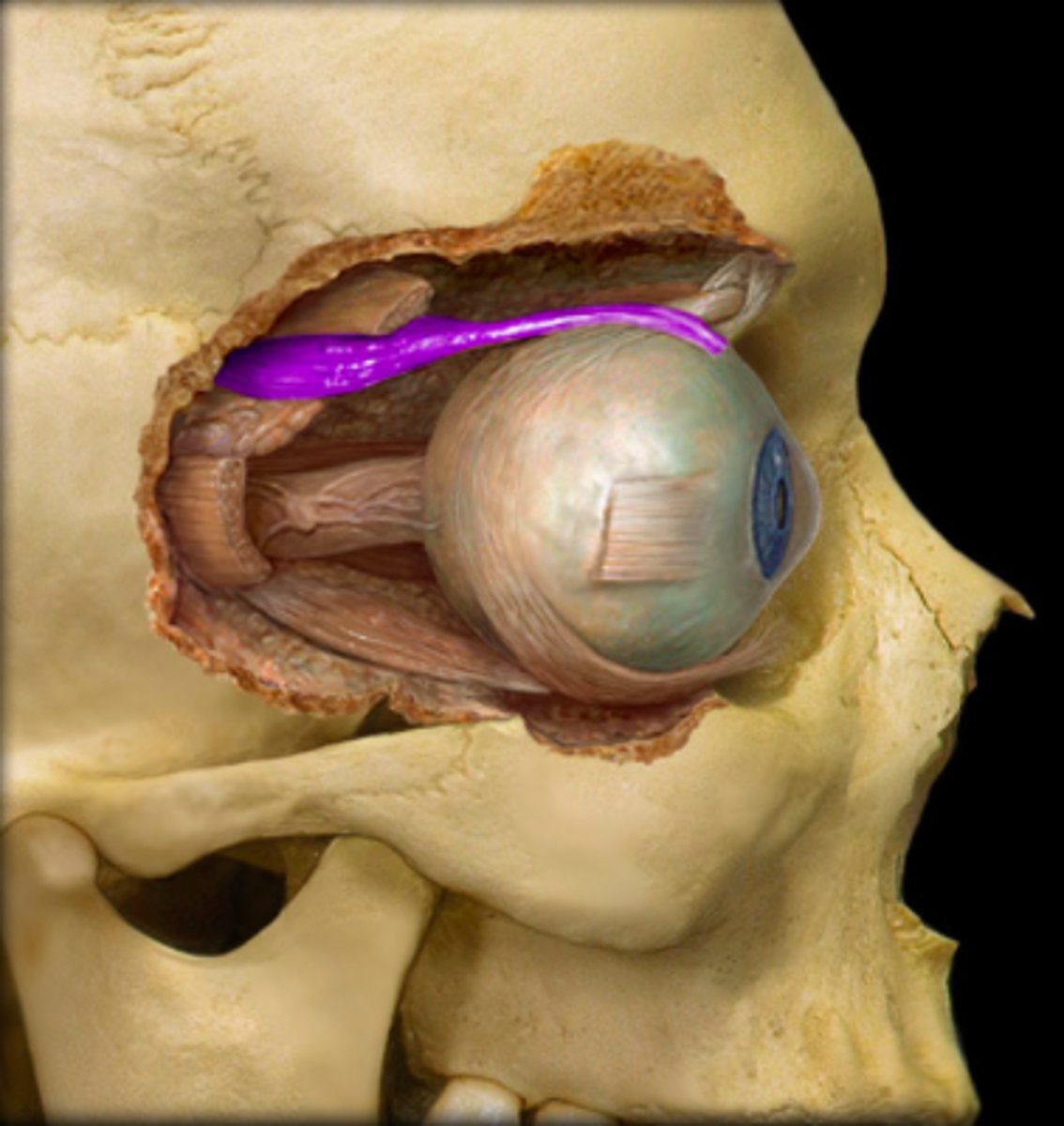
medial rectus m.
identify the structure:
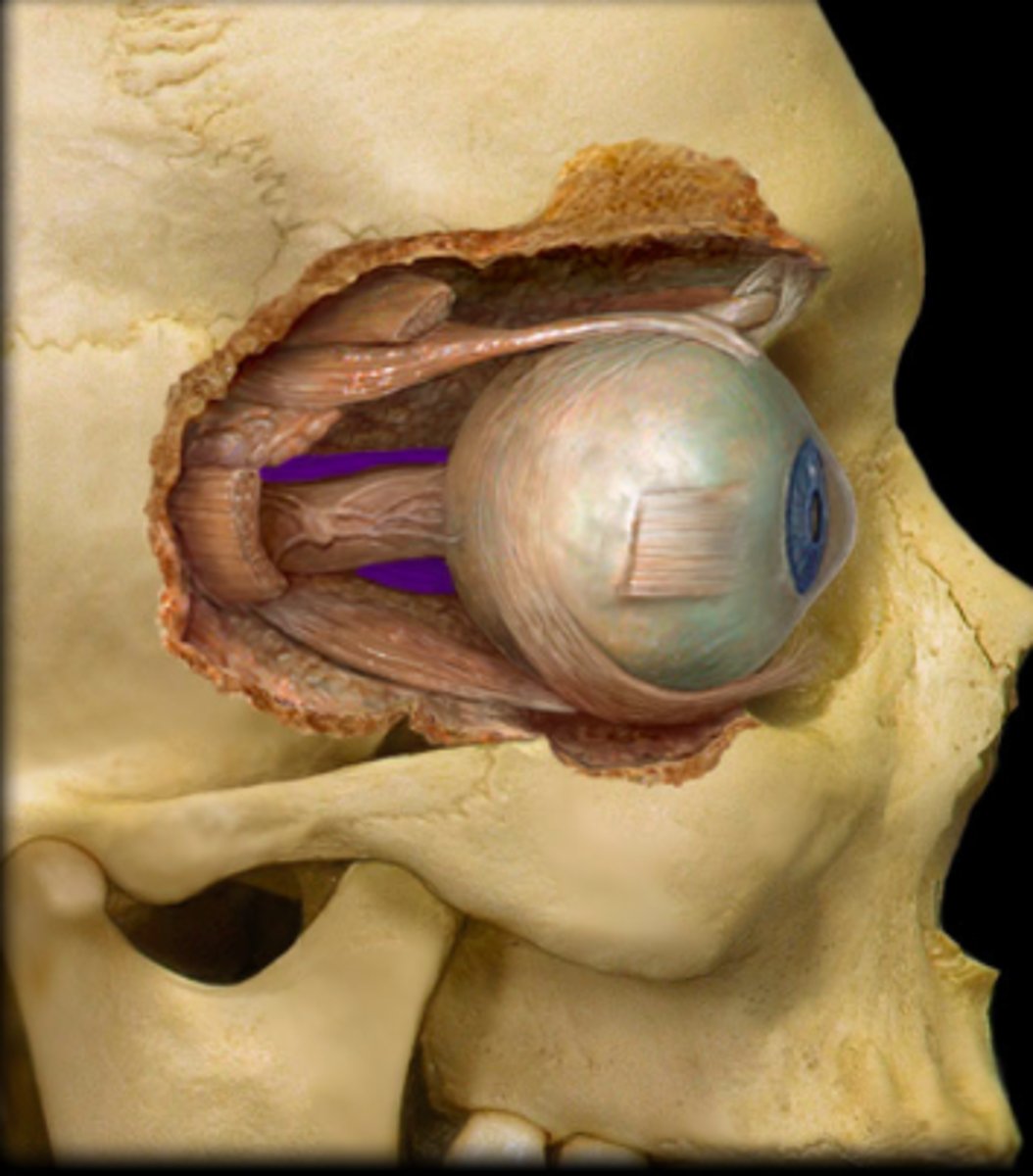
inferior rectus m.
identify the structure:
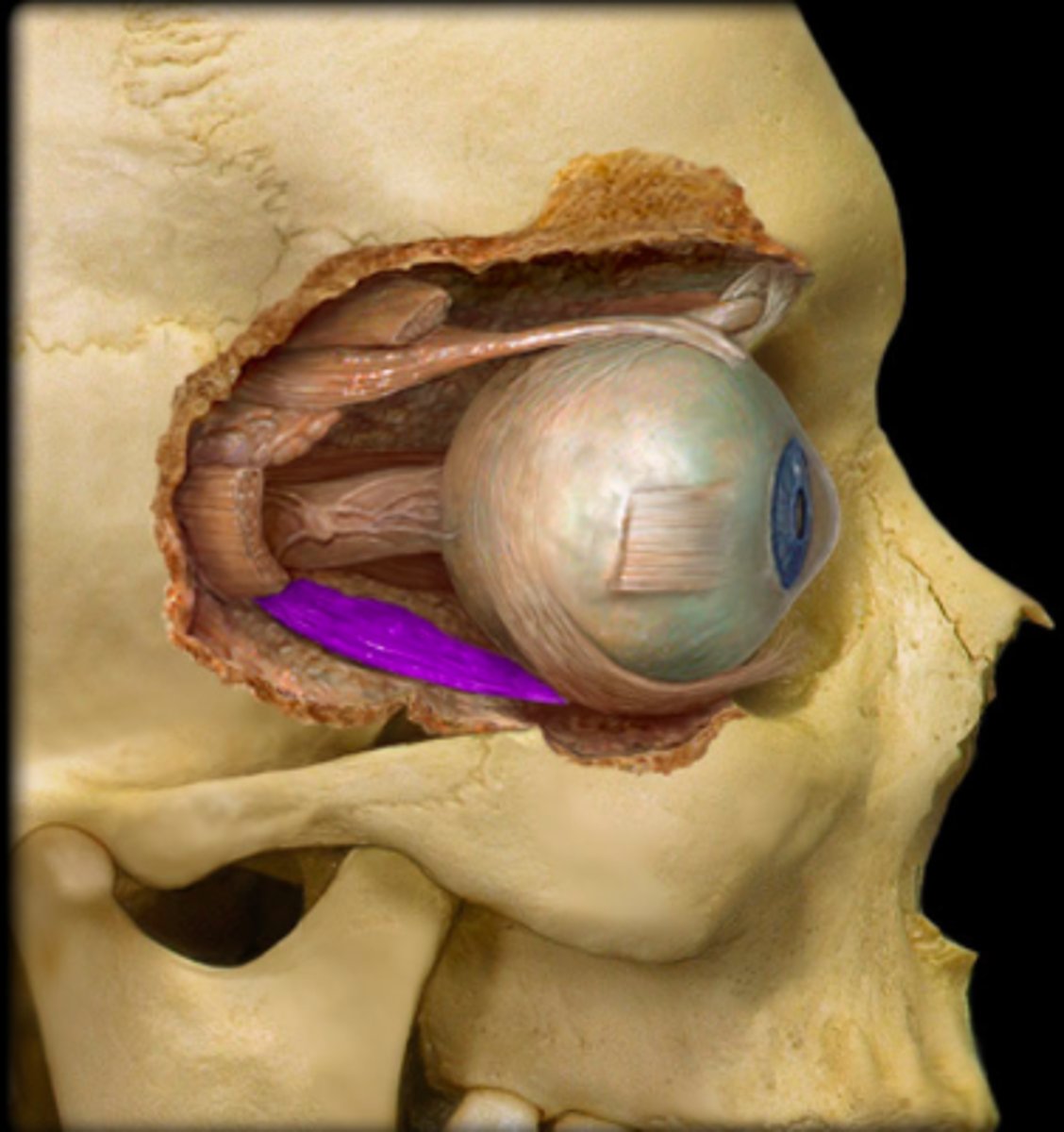
lateral rectus m.
identify the structure:
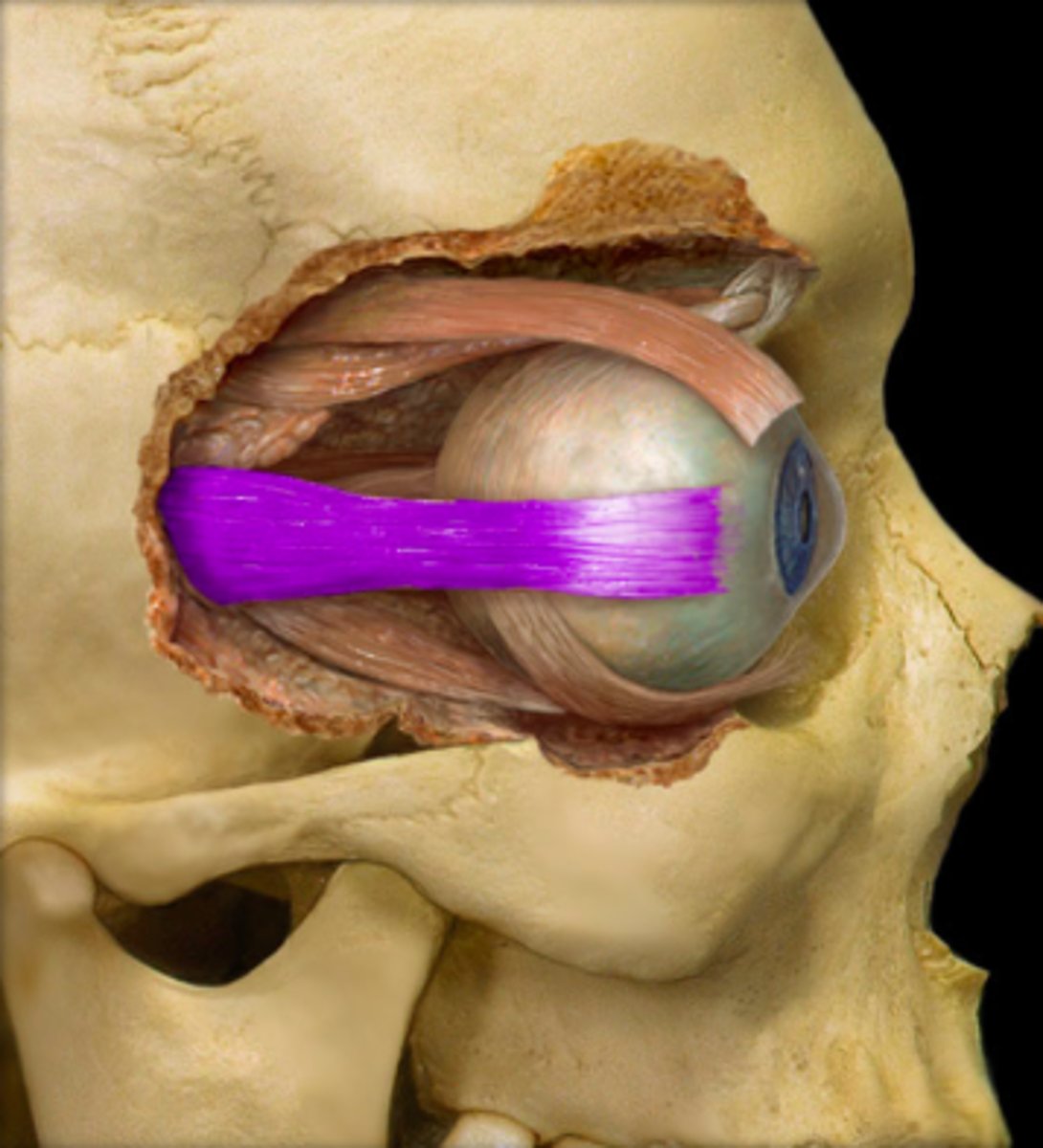
superior oblique m.
identify the structure:
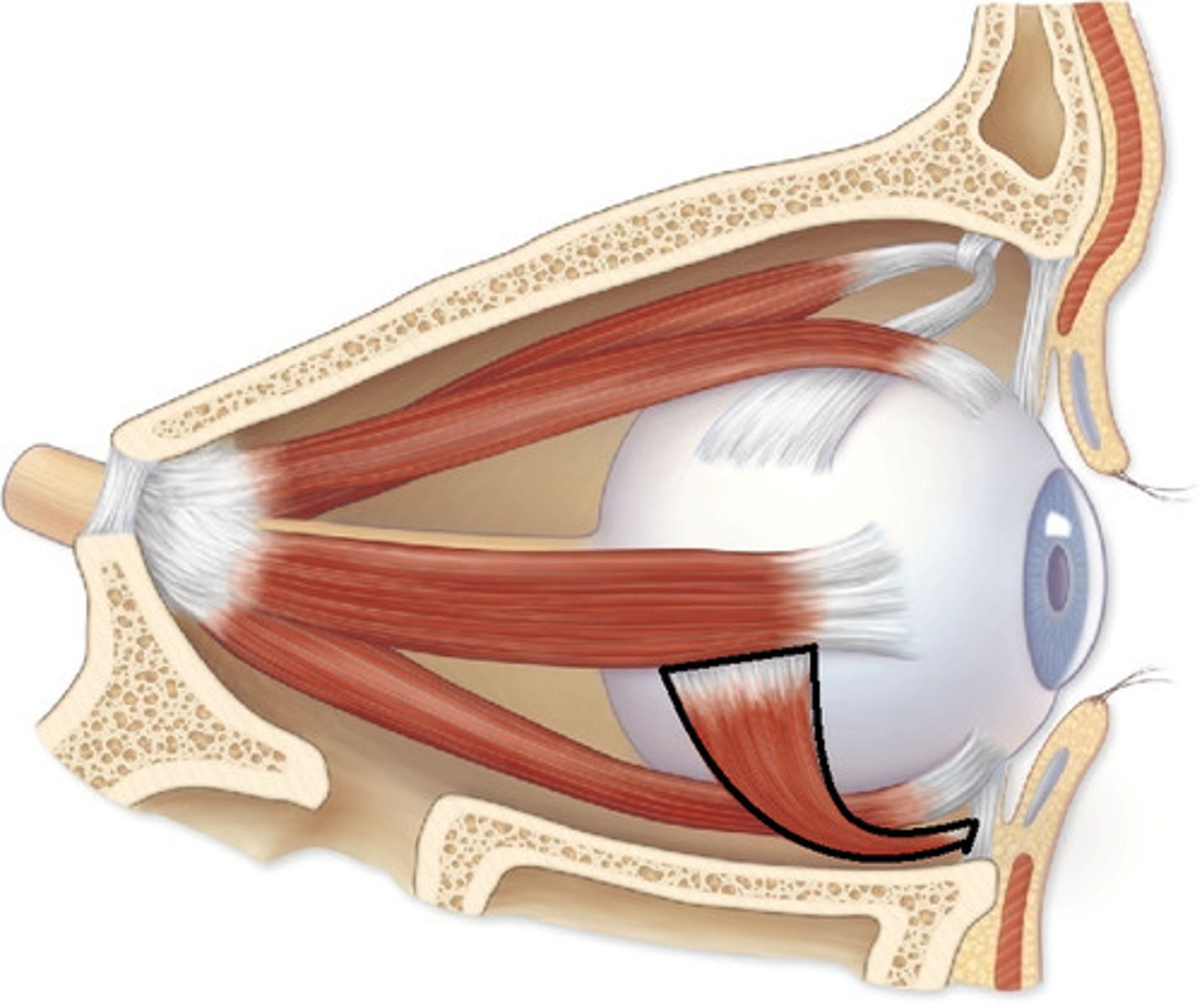
inferior oblique m.
identify the structure:
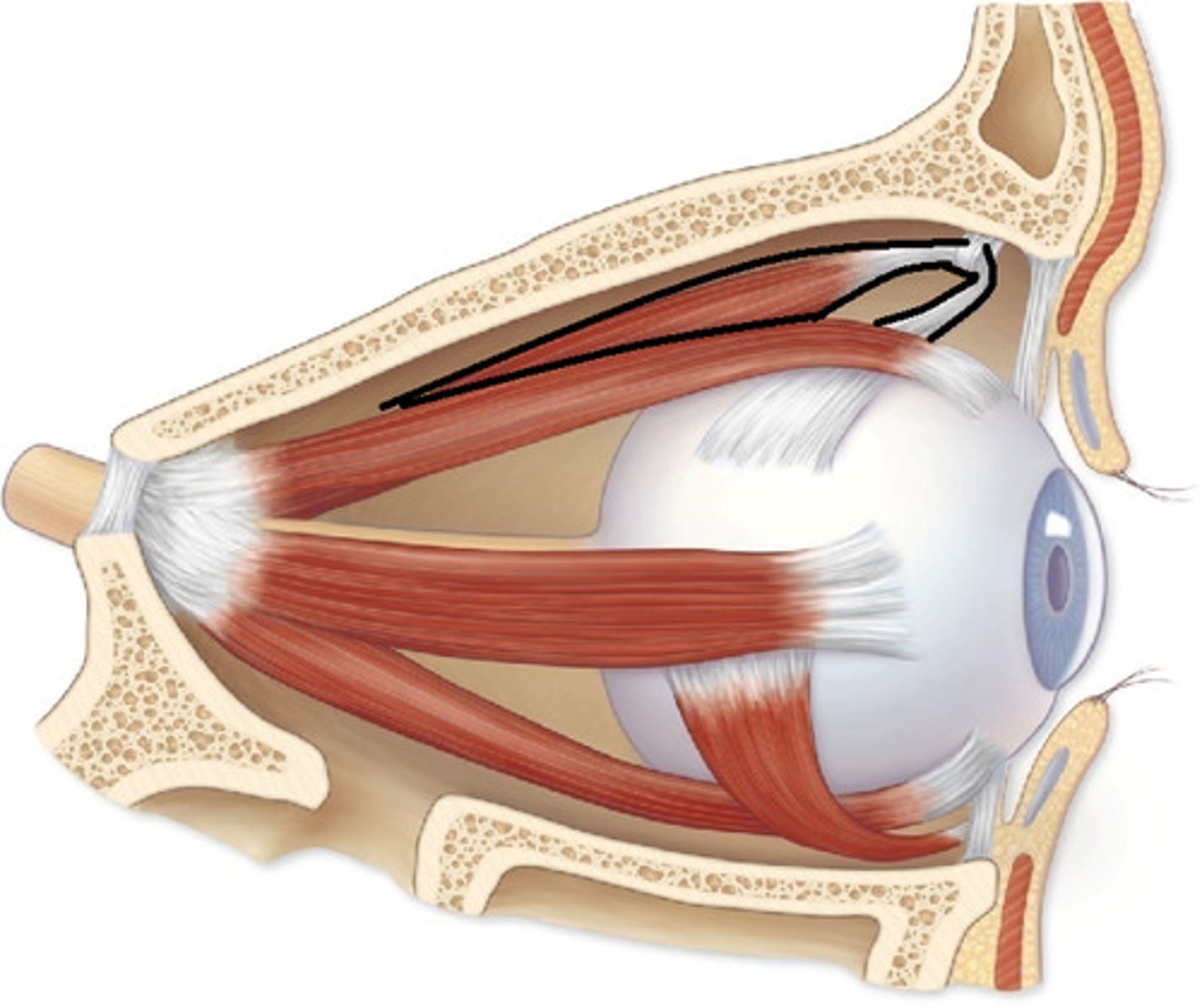
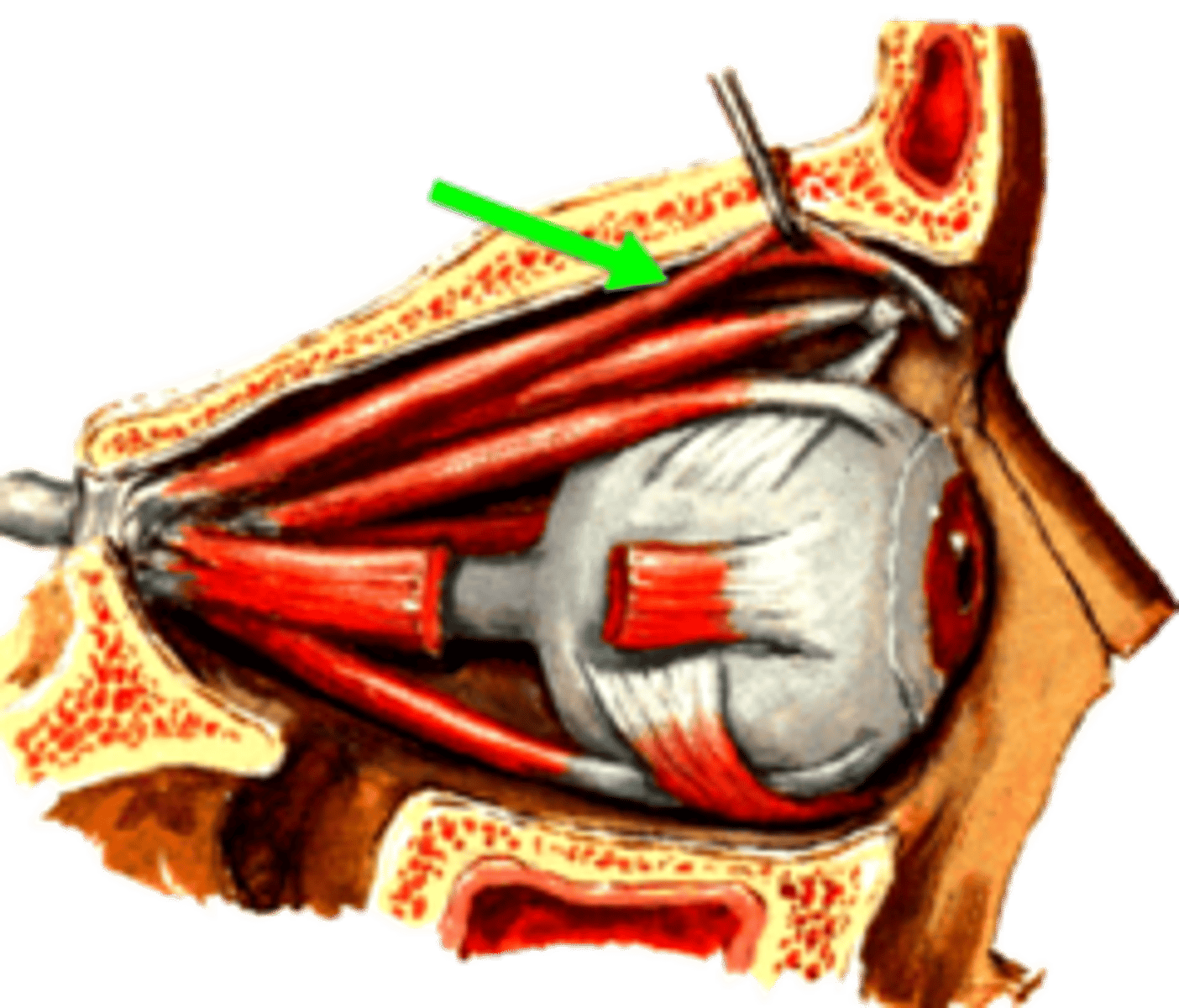
levator palpebrae superioris m.
identify the structure:
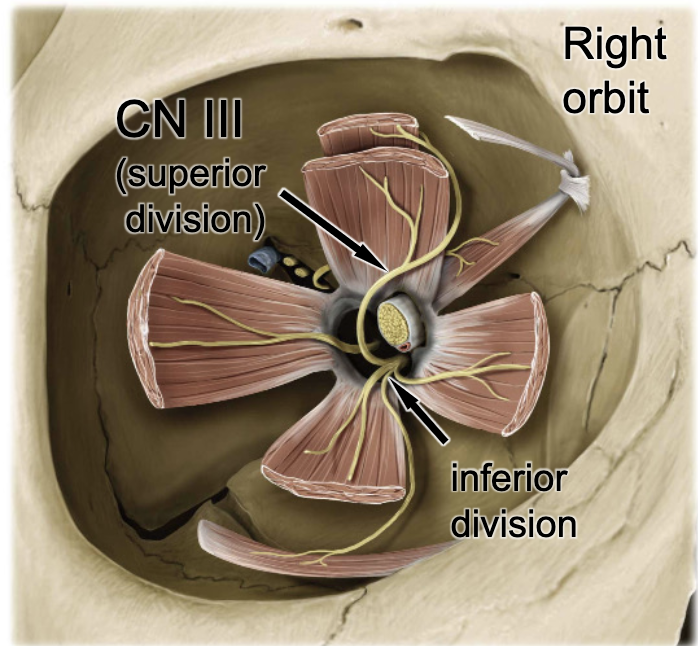
CN III
the superior rectus m. is innervated by:
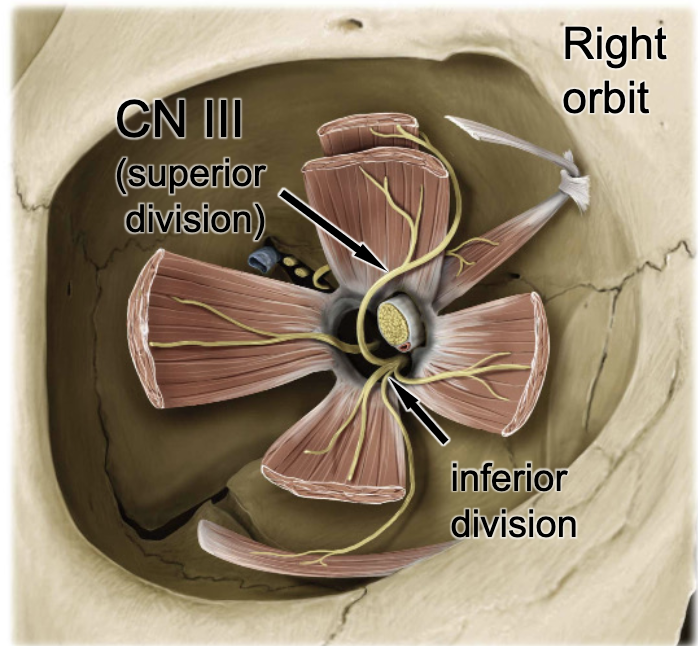
CN III
the medial rectus m. is innervated by:
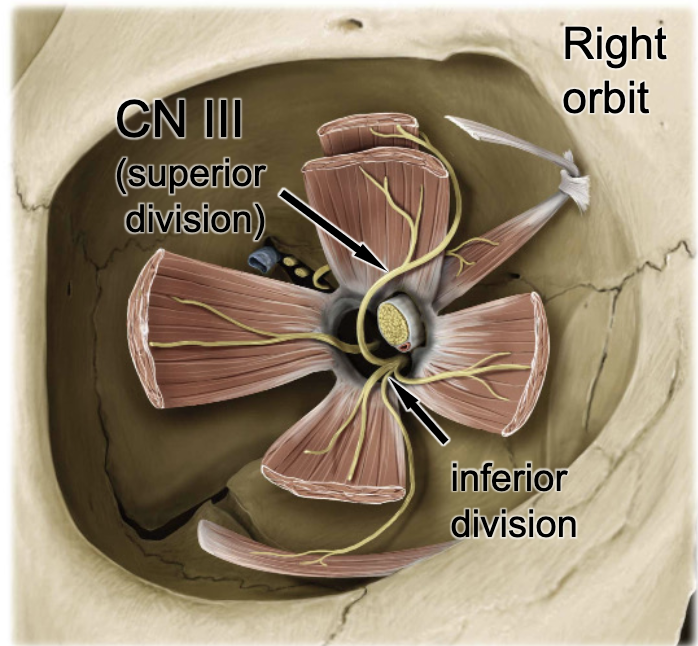
CN III
the inferior rectus m. is innervated by:
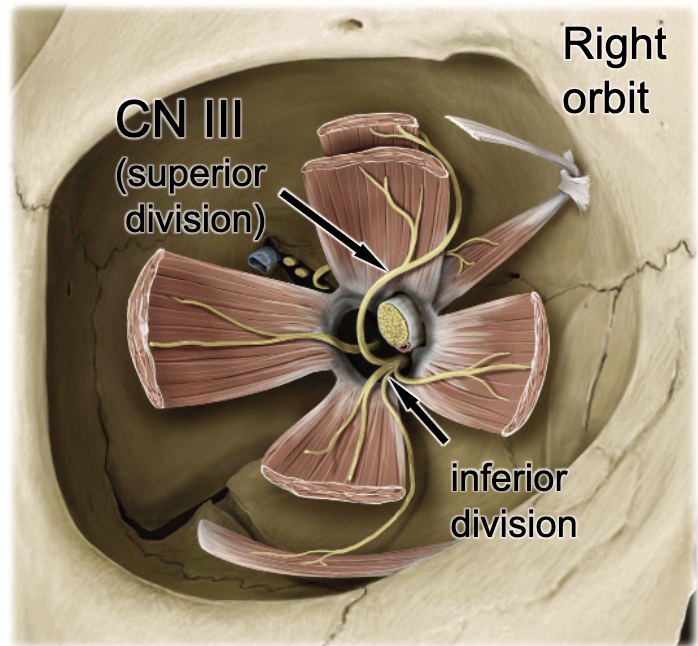
CN III
the inferior oblique m. is innervated by:
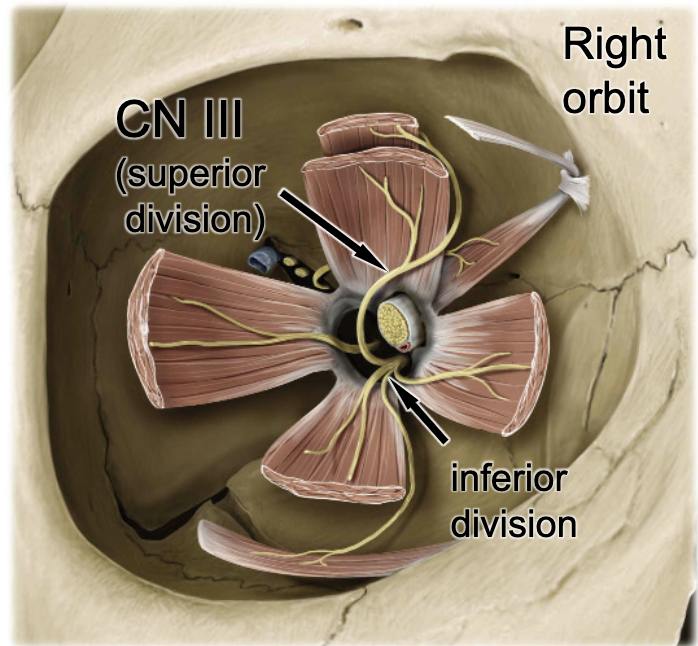
CN III
the levator palpebrae superioris m. is innervated by:
CN IV
the superior oblique m. is innervated by:
CN VI
the lateral rectus m. is innervated by:
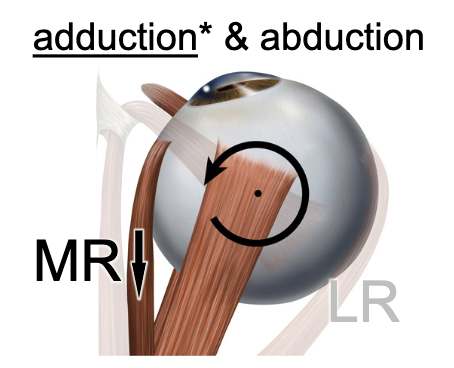
medial rectus m.
muscle action: adducts the eye:
lateral rectus m.
muscle action: ABducts the eye:
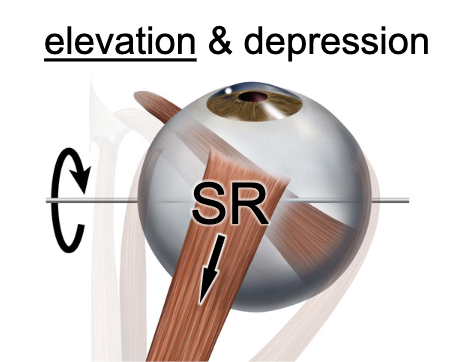
superior rectus m.
muscle action: elevates and adducts the eye:
inferior rectus m.
muscle action: depresses and adducts the eye:
superior oblique m.
muscle action: depresses and abducts the eye:
inferior oblique m.
muscle action: elevates and abducts the eye:
medial and lateral rectus mm.
which two muscles actually move in the exact direction they indicated?
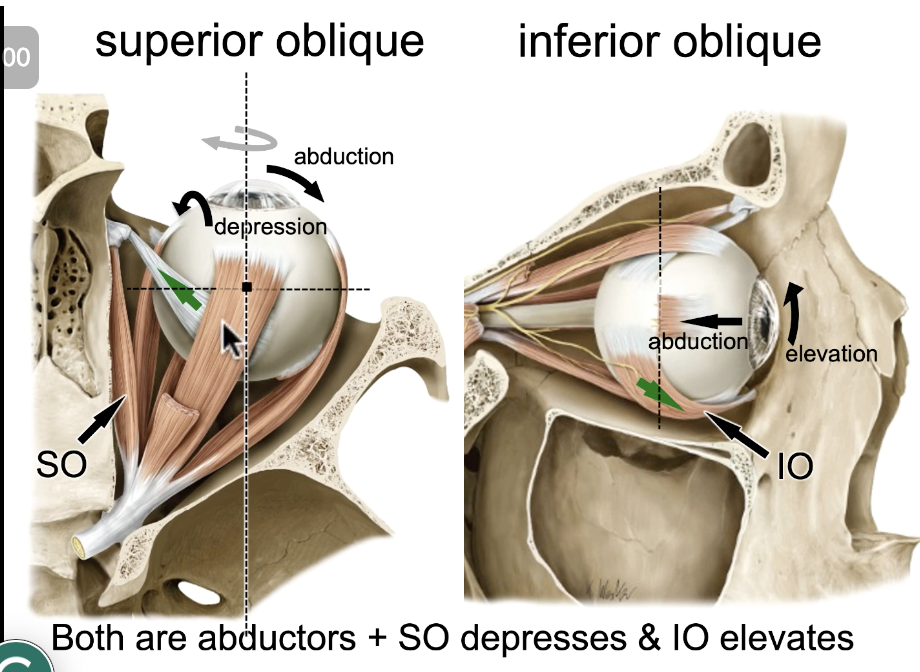
inferior rectus & superior oblique
Vertical depression of the eyeball requires what muscles:
superior rectus & inferior oblique
vertical elevation of the eyeball requires what muscles:
parasympathetic
the ciliary muscle is under __________ control
sympathetic
the dilator pupillae muscle is under __________ control
parasympathetic
the sphincter pupullae muscle is under __________ control
parasympathetic (pupillary constriction)
patient presents with trauma to the head from a car accident. Patient is unconscious. You shine a light in the eye to check for what type of function?
CN III (pupillary constriction)
patient presents with trauma to the head from a car accident. Patient is unconscious. You shine a light in the eye to check for what nerve function?
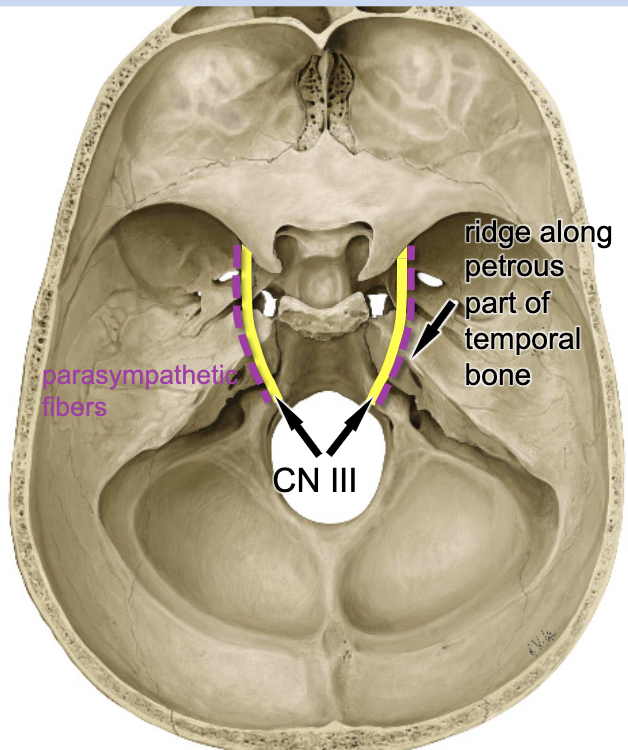
ridge along petrous part of temporal bone
what part of the middle cranial fossa can compress CN III during a traumatic event?
constriction of both pupils
if you shine a light in one eye, what is your baseline expectation?
contraction of the eye you shine the light to
if you shine a light in the left eye but there is damage to CN III at the ridge along petrous part of temporal bone on the right, what reaction will resent?
contraction of the eye opposite that you shine the light to
if you shine a light in the left eye but there is damage to CN III at the ridge along petrous part of temporal bone on the left, what reaction will resent?
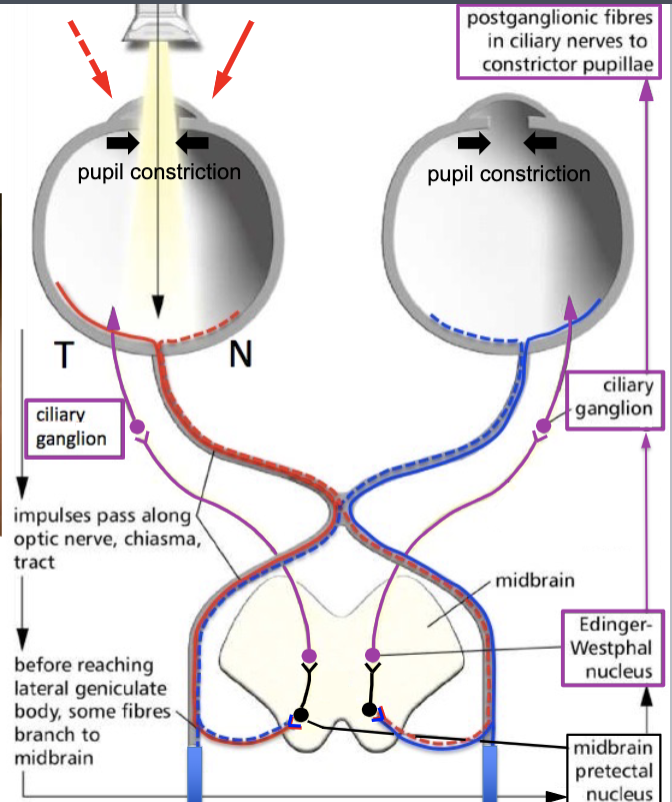
lateral geniculate nucleus
sensory fibers that receive light input travel to the:
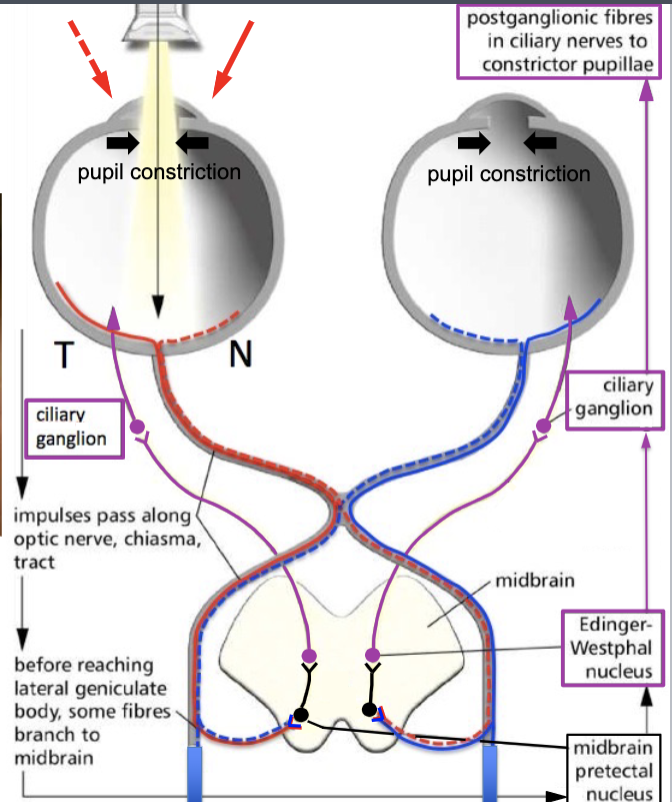
midbrain pretectal nucleus
some sensory fibers that receive light input will travel straight to the parasympathetic reflex. They synapse at the:
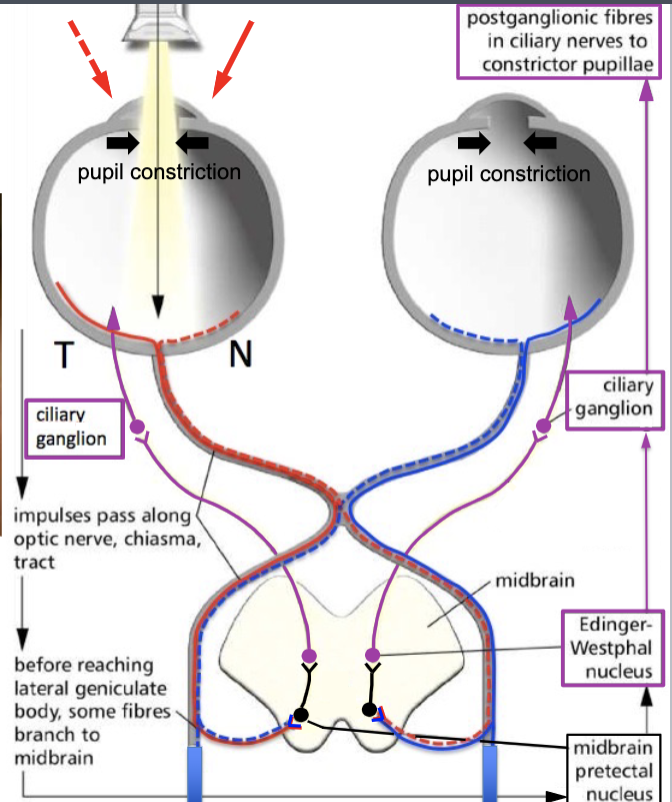
Edinger-Westphal nucleus
the cell bodies of presynaptic parasympathetic fibers for the eyes are located at the:
left abducent nerve palsy (CN VI affected which immobilizes lateral rectus m.)
patient presents with the following eye movement. You recognize that this is…?
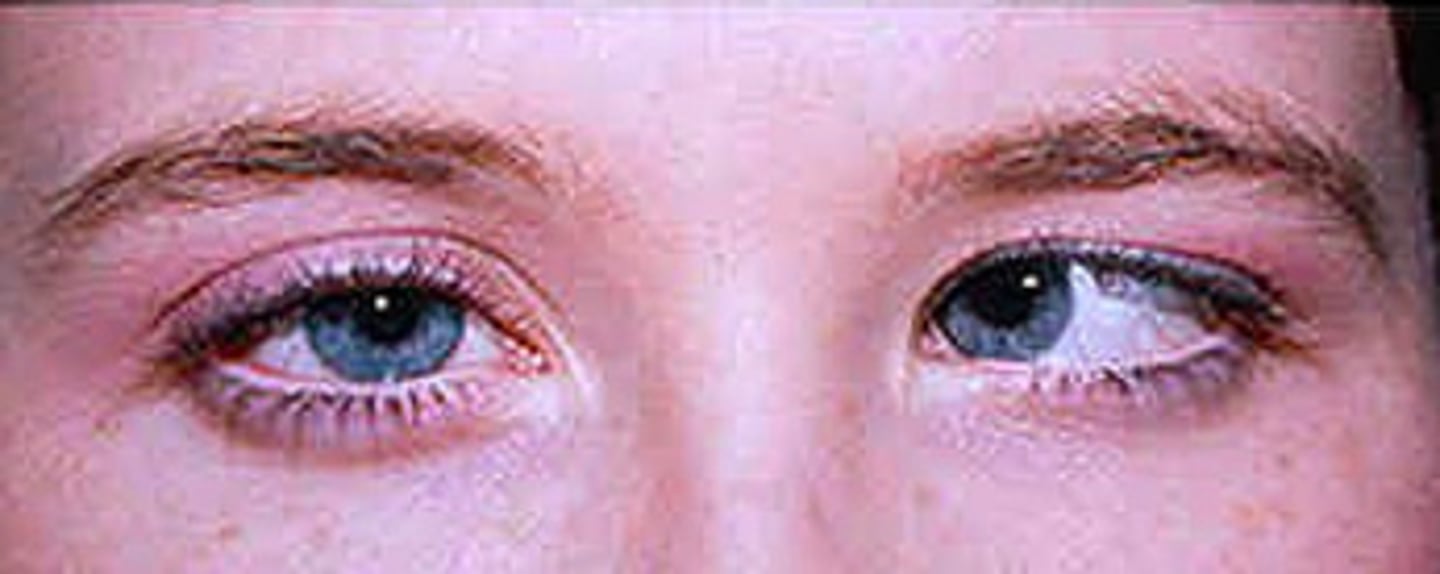
CN VI
which nerve in the cavernous sinus is deepest and most at risk for infection and pathology?
left oculomotor n. palsy
patient presents with the following eye movement. You recognize that this is
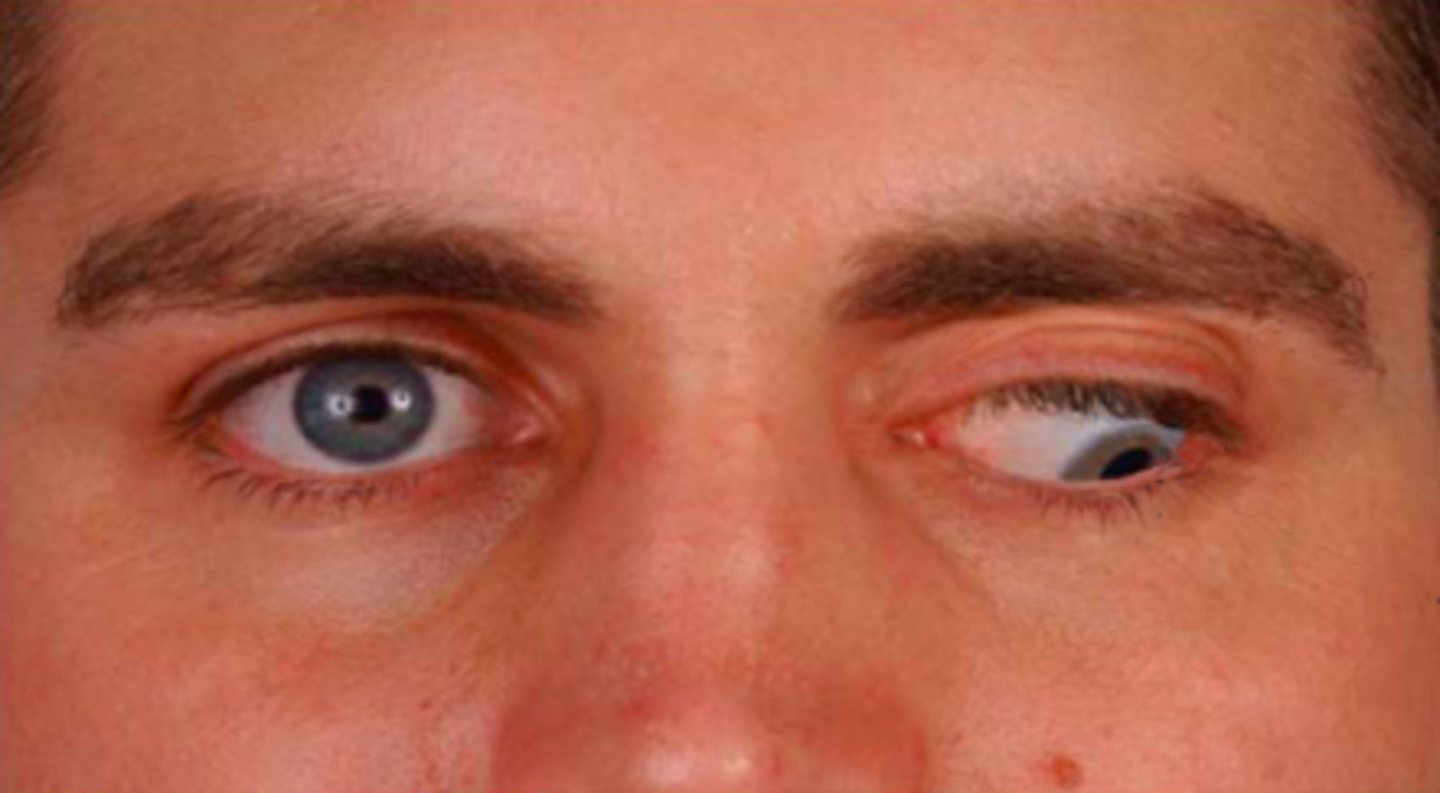

ptosis
drooping of the eyelid:
miosis
pupil constriction:
CN VII (secretomotor fibers)
tear production and secretion is innervated by:
lacrimal glands
meibomian glands
conjunctival glands (goblet cells)
what glands are involved in tear production?
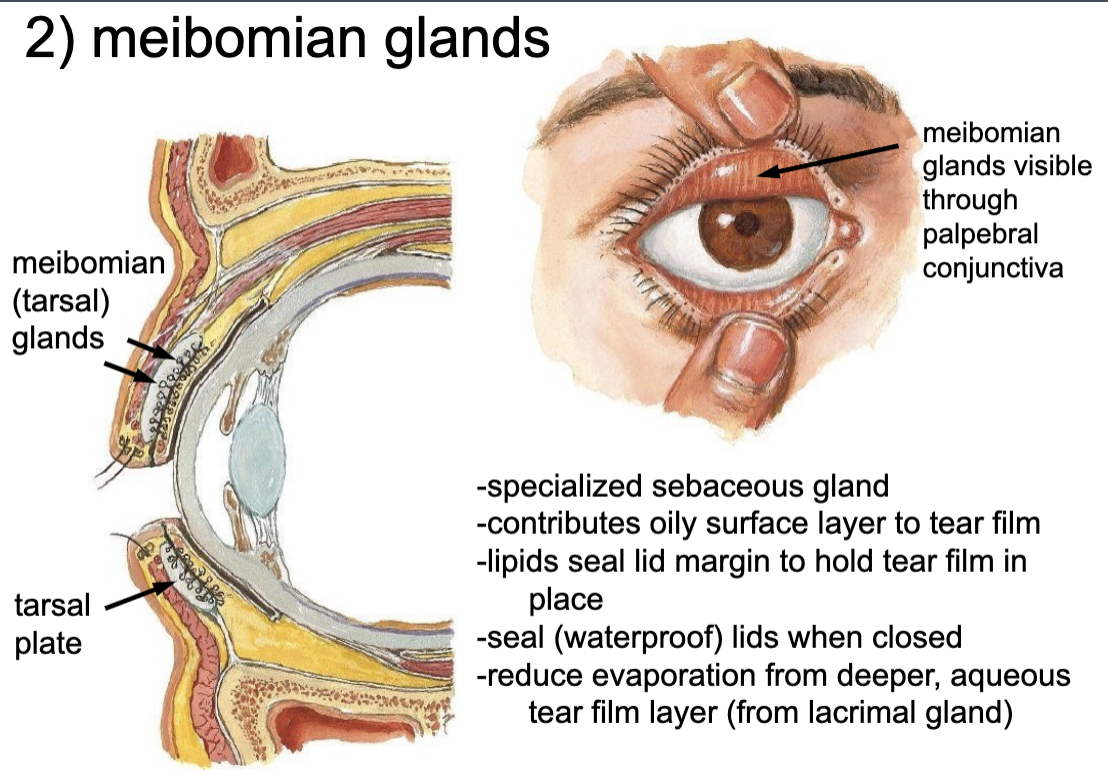
meibomian glands
-specialized sebaceous gland
-contributes oily surface layer to tear film
-lipids seal lid margin to hold tear film in place
-seal (waterproof) lids when closed
-reduce evaporation from deeper, aqueous tear film layer (from lacrimal gland)
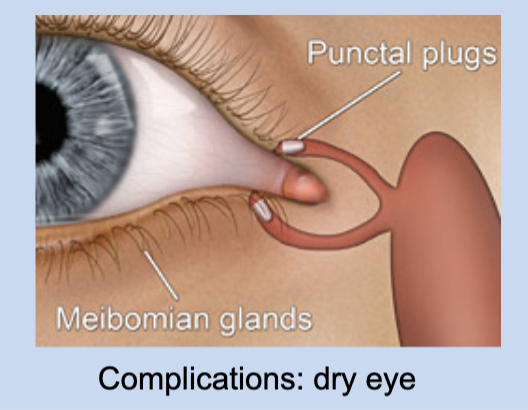
dry eyes from defective film layer (Tx: using punctal silicon plugs to lessen drainage of tears)
what is a complication that can arise with meibomian glands?
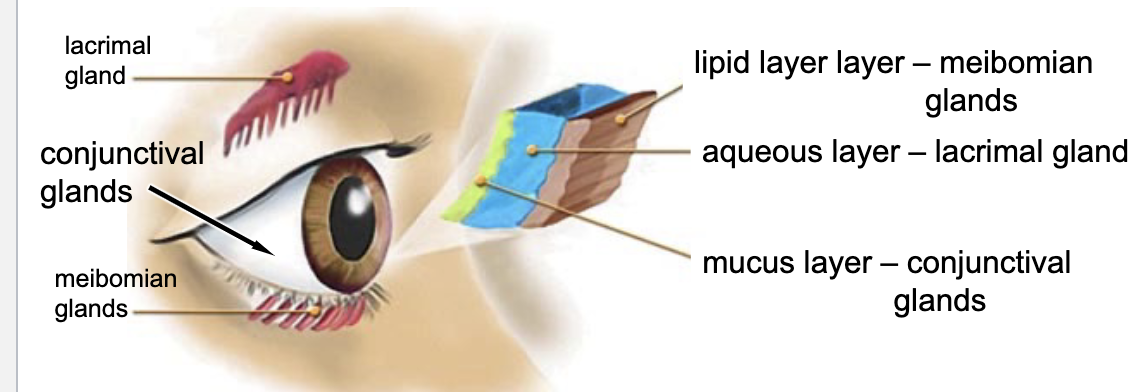
conjunctival glands
-flushes debris from ocular surface
-protects cornea from drying
-provides oxygen and nutrients to cornea
-contains antibacterial enzymes (e.g. lysozyme)
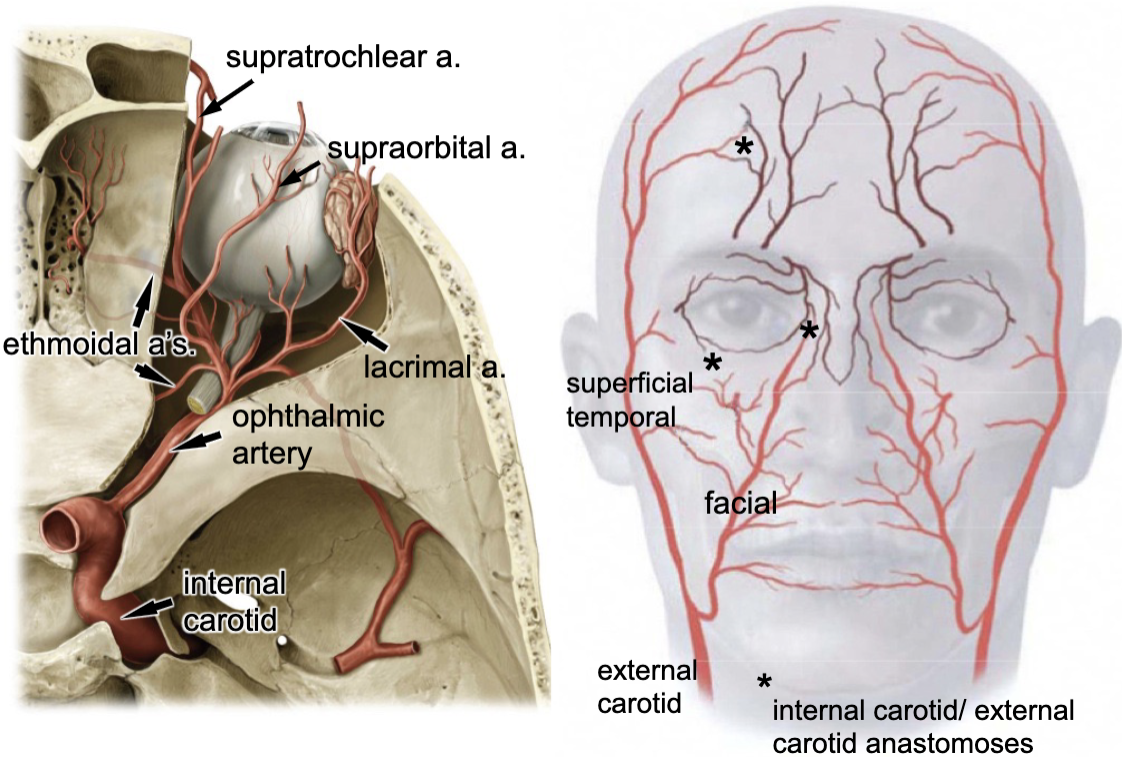
internal carotid a.
the opthalmic artery is a branch of the:
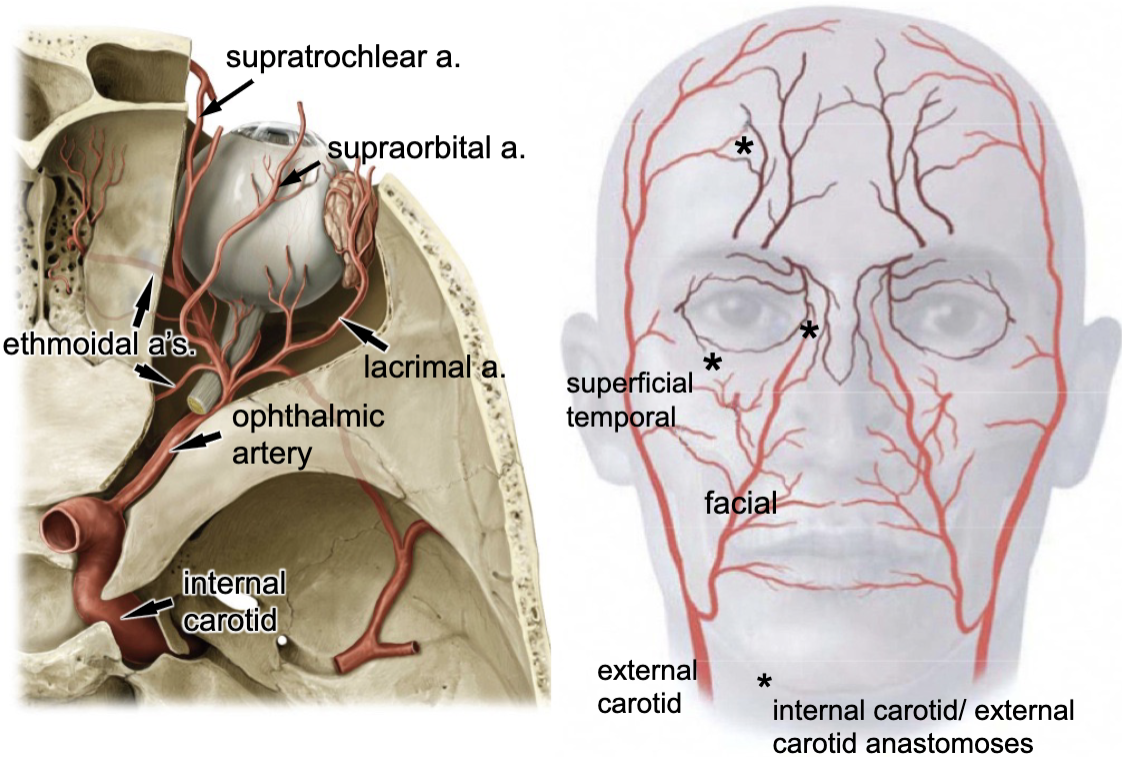
optic canal
opthalmic a. enters the orbit via the:
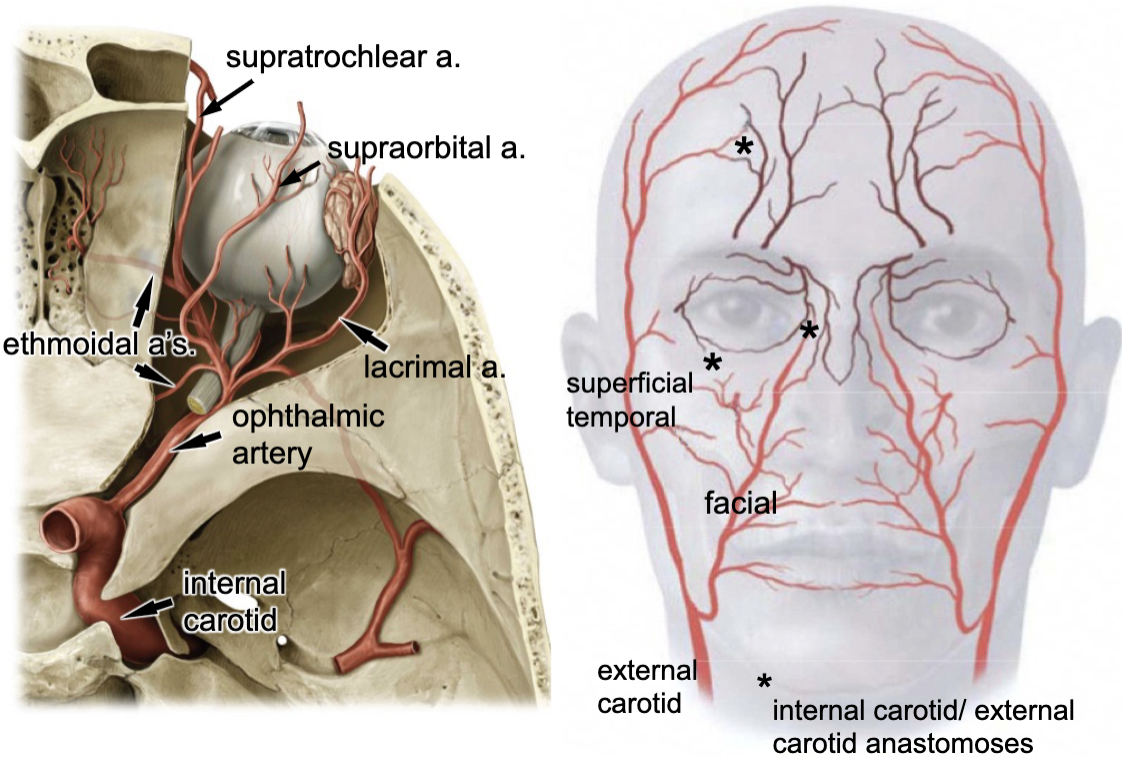
lacrimal a.
supraorbital a.
supratrochlear a.
3 branches of the opthalmic artery:
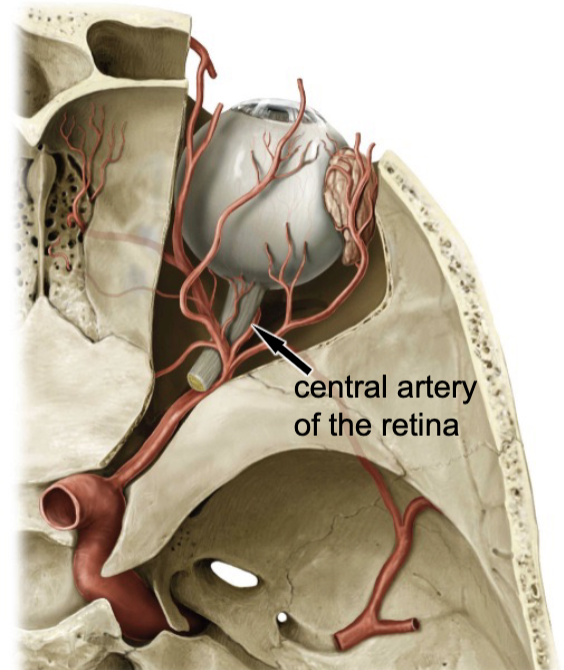
central artery of the retina
which artery travels with the optic nerve?
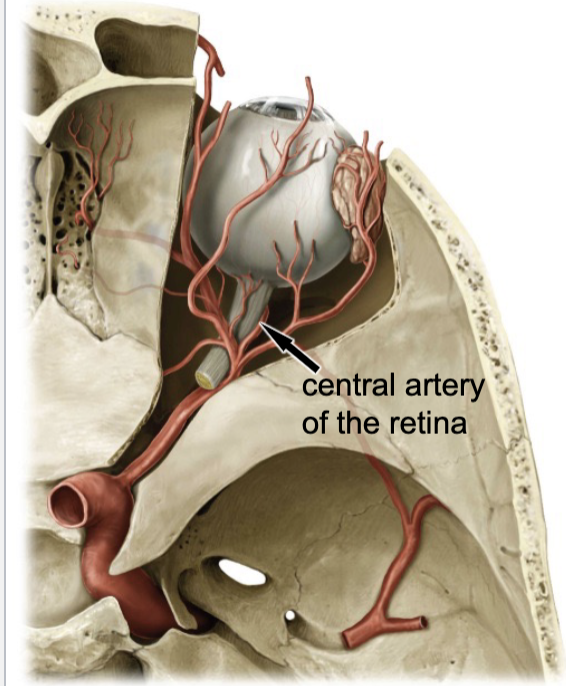
central artery of the retina
blood supply for the inner aspect of the retina:
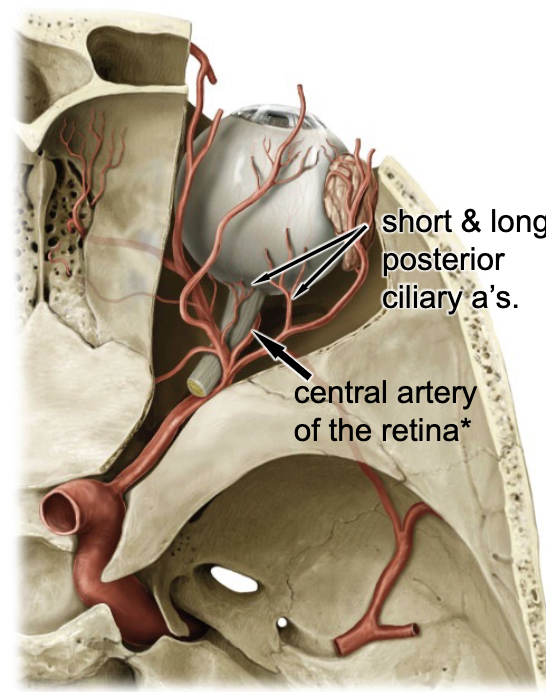
long ciliary aa.
blood supply for the ciliary muscle and iris:
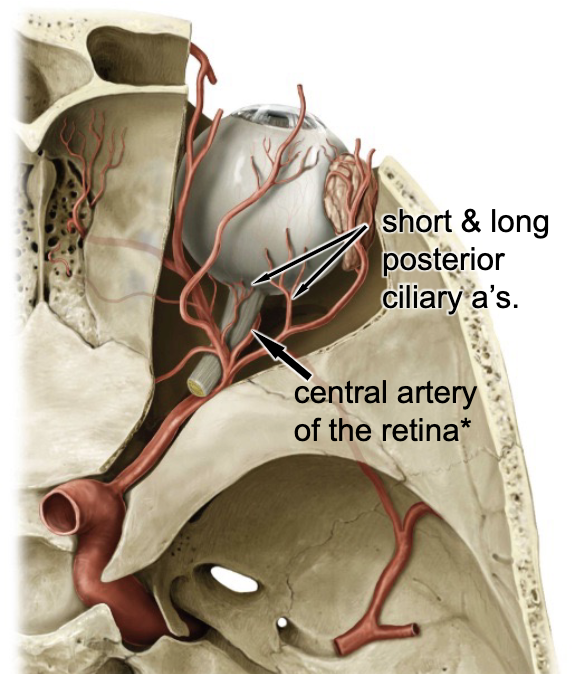
short ciliary aa.
blood supply for the outer retina, form the:
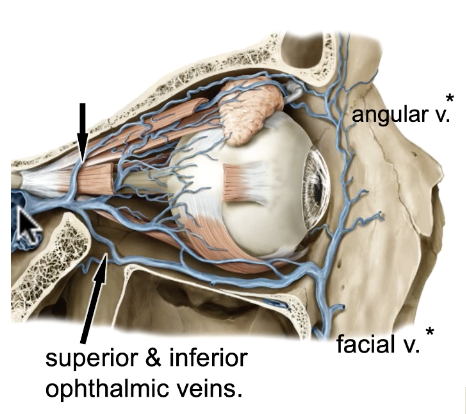
superior & inferior ophthalmic veins connected to facial v./angular v/ and cavernous sinus
what veins are involved in the eyeball venous drainage
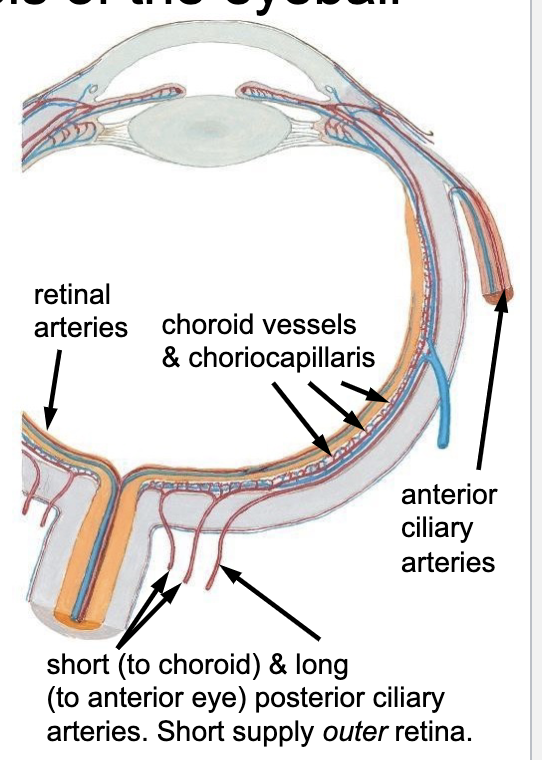
choroid vessels and choriocapillaries (dense bundle of capillaries)
the “red eye” effect is due to what?