Blood pressure/circulation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
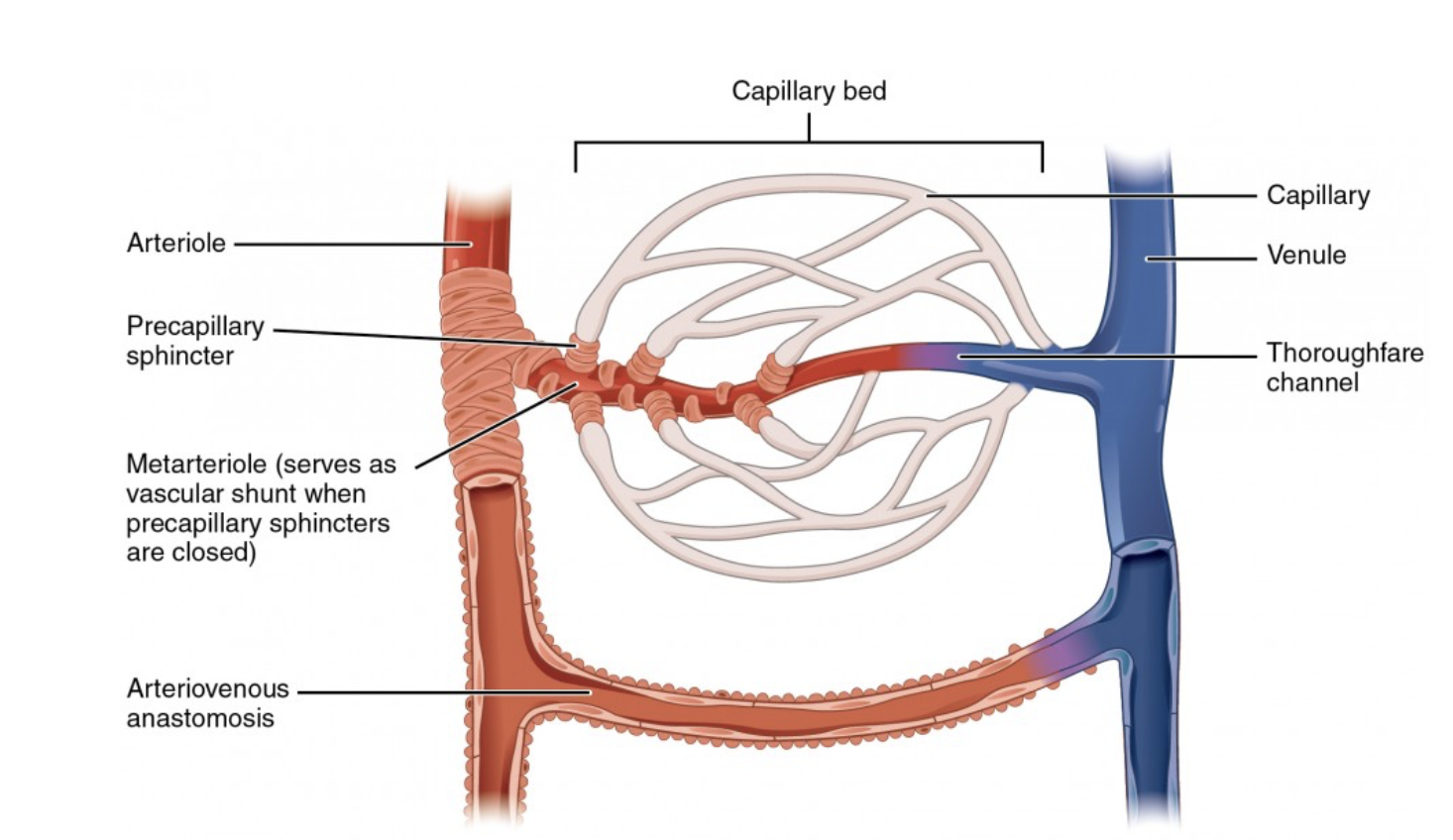
Which of the following best describes the primary role of arterioles in the circulatory system?
To operate as control valves that regulate blood distribution to capillary beds-they have muscular walls that can contract or relax allowing them to precisely control amount of blood flowing into the. tissues they supply
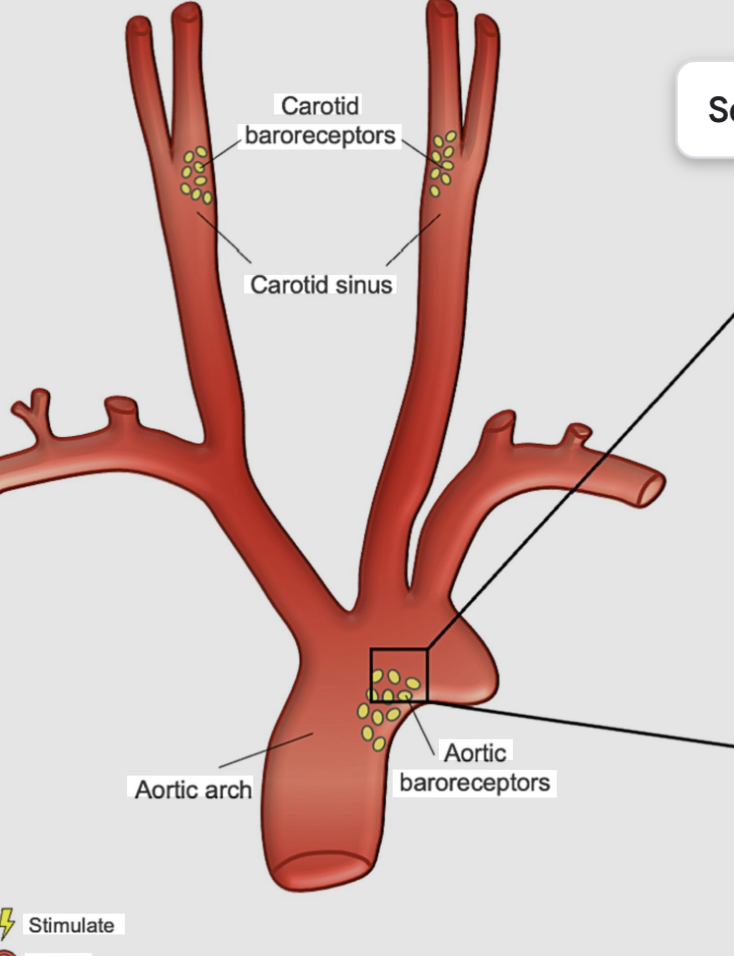
Which of the following events would be detected by baroreceptors, leading to a rapid adjustment in blood pressure?
stretching of the walls of the aorta and carotid arteries due to a rise in pressure -baroreceptors are specialized in pressure-sensitive neurons that respond directly to the mechanical stretching of arterial walls
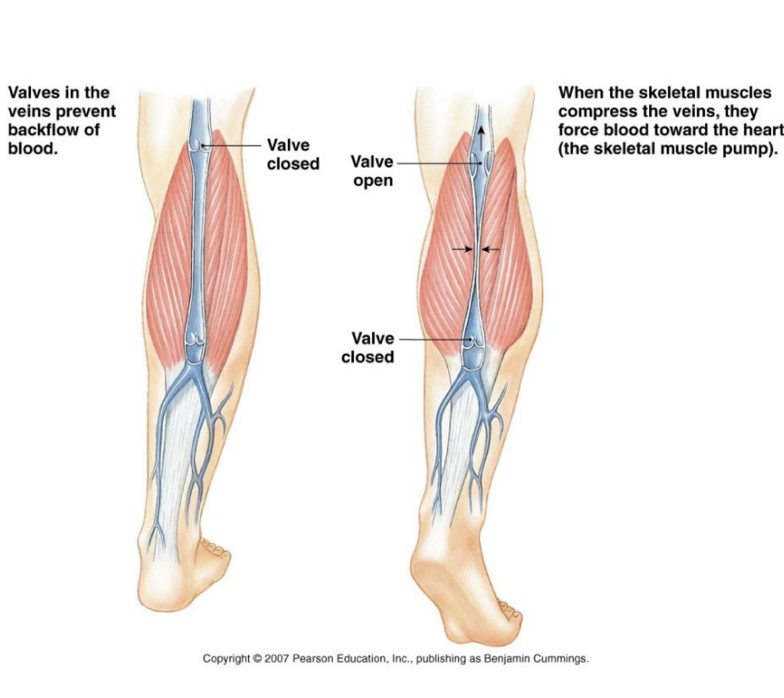
What is the function of the skeletal muscle pump in venous circulation?
To compress veins during muscle contraction forcing blood toward the heart-when skeletal muscles contract they squeeze the embedded veins and with the help of one way valves this action propels blood against gravity
The renin-angiotensin system is a medium-term regulator of blood pressure. What is the direct role of Angiotensin II in this process?
It is a potent vasoconstrictor and stimulates the secretion of aldosterone - Angiotensin II raises blood pressure by cinstricting blood vessels and by signaling the adrenal glands to release aldosterone which promotes salt and water retention
At the arterial end of a capillary, what is the relationship between capillary hydrostatic pressure and blood colloid osmotic pressure that results in net filtration?
Capillary hydrostatic pressure is higher than blood colloid osmotic pressure -The higher blood pressure at the arterial end acts as pushing force that overcomes the pulling force of osmotic pressure driving fluid out into the interstitial space
How does the respiratory pump facilitate venous return during inspiration?
arteries are faster than veins
true
veins carry blood
from the tissue to the heart (low pressure)
arteries carry
blood under high pressure to tissues
Carotid sinus reflex initiated by bacoreceptors in the wall of the carotid sinus
helps regulate blood pressure in the brain
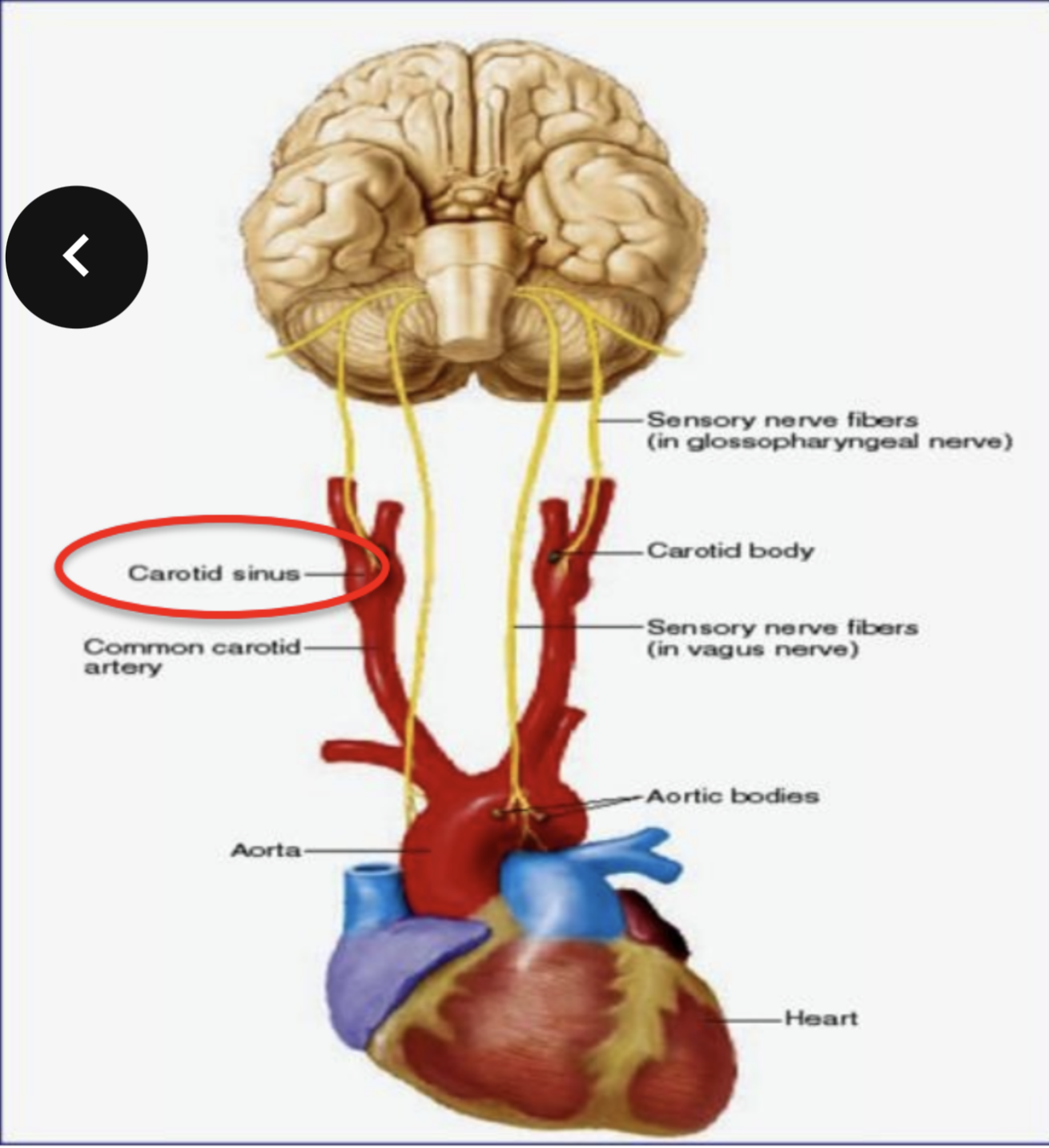
what are baroreceptors and where are they located
pressure sensitive sensory receptors - they are located in the aorta, international; carotid arteries and other large arteries in the neck and chest
what do baroreceptors do
send impulses to the cardiovascular center to help regulate blood pressure- their activity stimulates the cardiac parasympathetic intervention
why is our heart rate and blood pressure higher when you stand up
what does the aortic relflex do ?
it is initiated by the baroreceptors in the wall of the ascending aorta and arch of the aorta which regulates systemic blood pressure
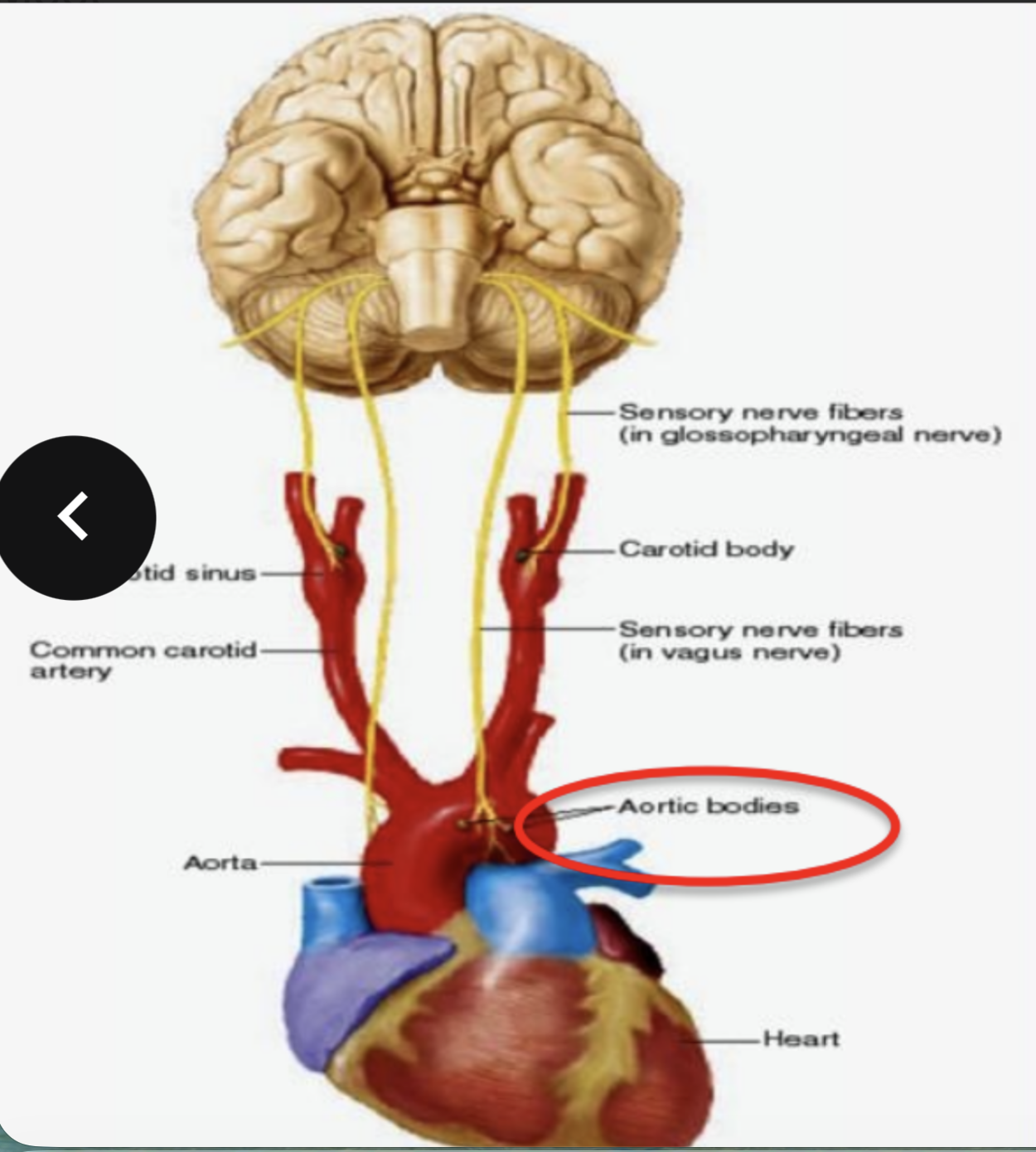
what do chemoreceptors do and where are they
they are sensory receptors that monitor the chemical composition of blood - they are located close to baroreceptors of the carotid sinus and arch of aorta - in carotid bodies and aortic bodies respectively
what happen when body goes into hypoxia
the sympathetic nervous system is activated by chemoreceptors
the sympathetic nervous system is activated by chemoreceptors
vagus (x) nerves
sympathetic
fight or flight- raises heart rate and blood pressure
parasympathetic
slows heart rate -rest and digest
why are HR and BP higher when standing (baroreceptors)
BP drops and baroreceptors detect reduced stretch from this BP drop and fires less frequently -Your brainstem (specifically the medulla) interprets this as low BP and activates the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) while reducing parasympathetic (vagal) activity.
what are CNS schema receptors
neurons in certain area of the CNS
what is ischemia
lack of oxygen and nutrients in the brain
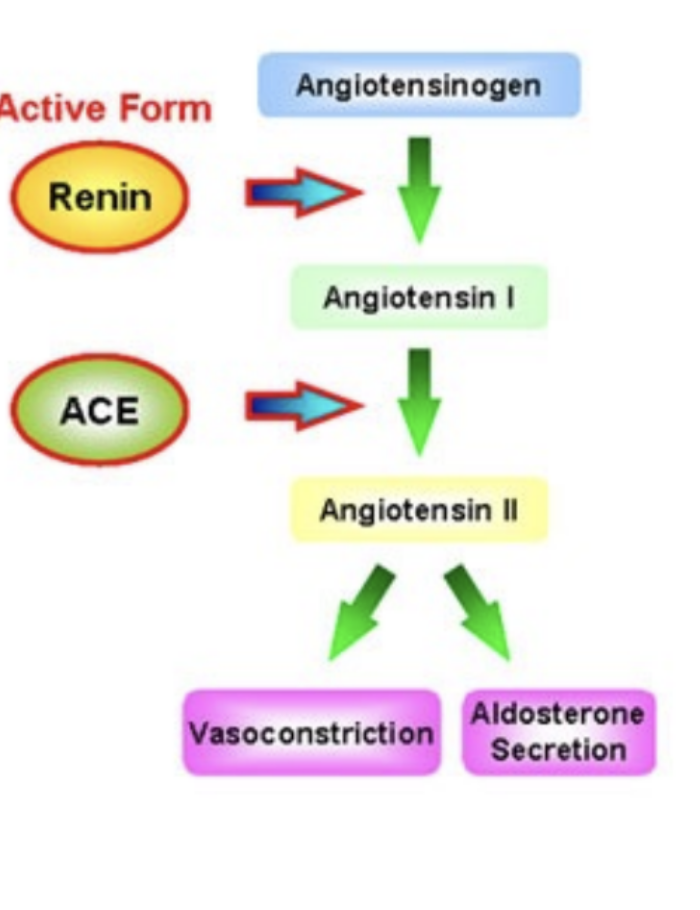
What is the first step in vascoconstrctor system renin-angiotensin
blood flow to kidneys decrease, juxtaglomerular cells in the kidney secrete renin into the blood stream- meanwhile liver releases angiotensinpgen
what does angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) do in the second step of the Vasoconstrictor system
act on their substates to produce the active hormone angiotensin II
what does angiotensin ii do
raises blood pressure in two ways
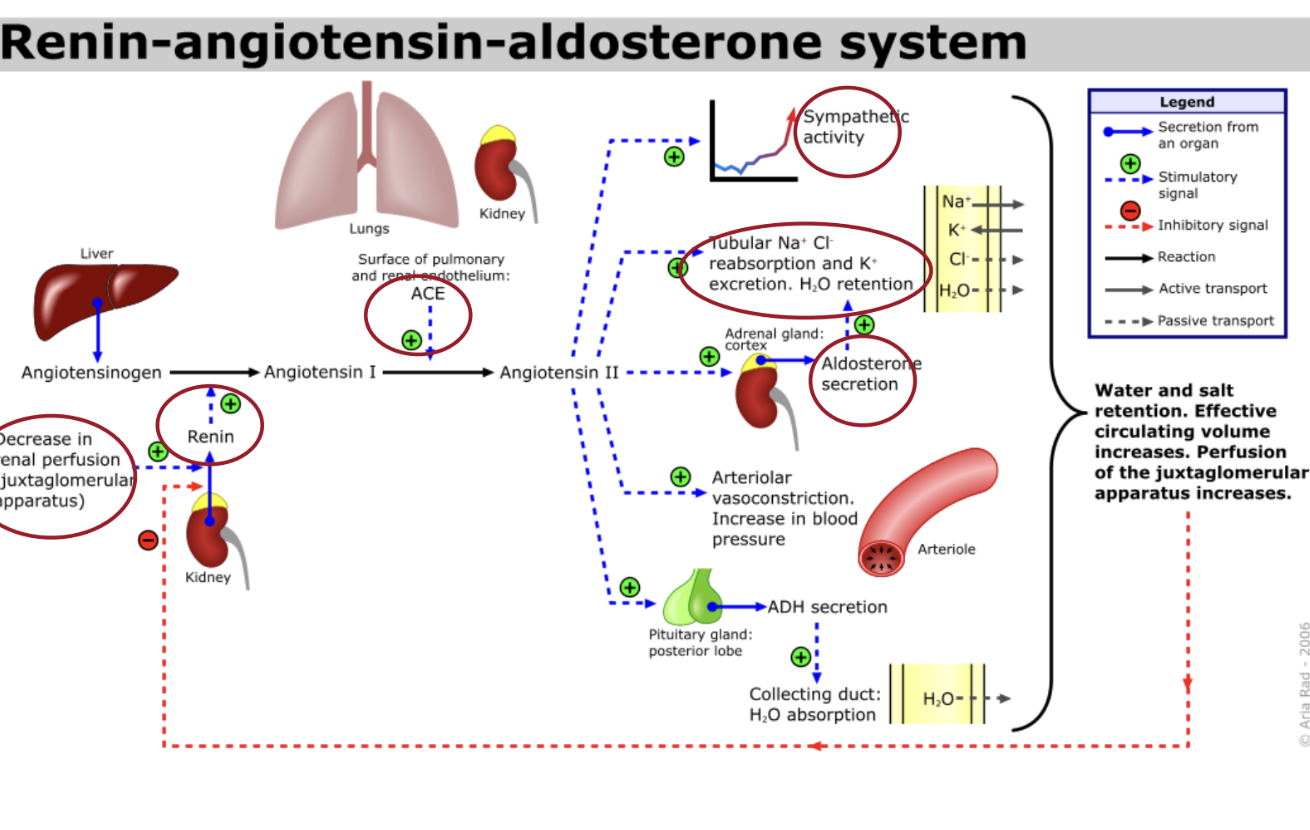
how does angiotensin ii raise blood pressure
-it is a potent vasoconstrictor and raises blood pressure by increasing systemic vascular resistance
-it stimulates the secretion of aldosterone which increases reabsorption of sodium ions and water by the kidneys -this reabsorption increases total blood volume which increases blood pressure
how is the kidney involved in the regulation of blood pressure
regulates blood volume which influences cardiac output. Acts to retain or eliminate Na + and water — resulting in increases or decreased blood volume
how are variation of salt and water determining of blood pressure?
intake must equal excretion to maintain balance
what does Atrial Natriuretic Peptide do (ANP)
Decreases blood pressure in emergency
Increases Na+ excretion and water elimination
how does ANP lower blood pressure
promotes salt and water excretion, relaxing blood vessels (vasodilation) and blocking blood pressure-raising hormones -helping to reduce blood volume and pressure when the atria stretched by excess fluid or high pressure
what does ADH do (antidiuretic hormone)
regulates water balance, blood pressure and sodium levels by telling your kidneys to reabsorb more water making urine more concentrated and reducing water loss-
mediates insertion of aquaporins into nephron connecting duct cells. As a result more water is reabsorbed into the blood
causes arteries to constrict
what’s happening in capillaries -
tiny blood vessels -exchange happens between the blood and the tissues.
what is blood (hydrostatic) pressure in capillaries
pushes fluid out— at the beginning of the capillary blood pressure is around 40 mm Hg- this pressure is created by heart pumping blood -ushes plasma (water + dissolved substances) out of the capillary and into the extracellular (interstitial) fluid.
what is oncotic (osmotic) pressure in capillaries?
The extracellular medium contains proteins.
Proteins attract water.
This creates oncotic pressure, which pulls water toward the area with more protein
what is capillary flux (net movement of fluid)
At the start of the capillary:
Hydrostatic pressure (push out) is strong
Oncotic pressure is weaker
Result: Plasma leaves the capillary and enters the extracellular space
This movement of fluid is called——
when plasma leaves the capillary
oxygen diffuses from blood to tissues, nutrients (glucose, ions amino acids) moves to cells and cells get what they need
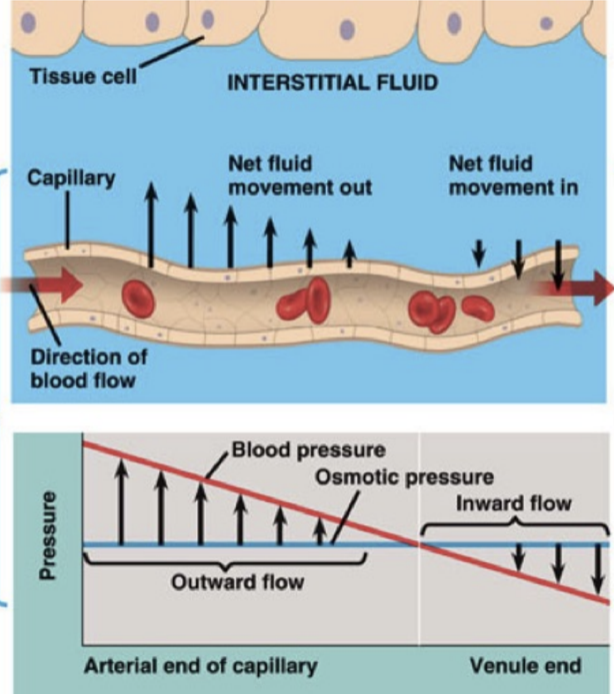
at the arterial end of there capillary
blood p
ressure is greater than osmotic pressure and fluid flows out of the capillary into the interstitial fluid
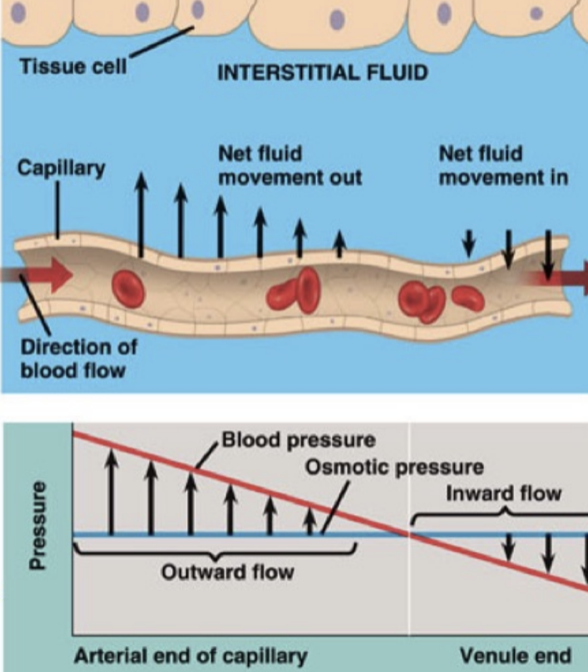
at the venule end of a capillary blood pressure
is less than osmotic pressure and fluid flows from interstitial fluid in the capillary
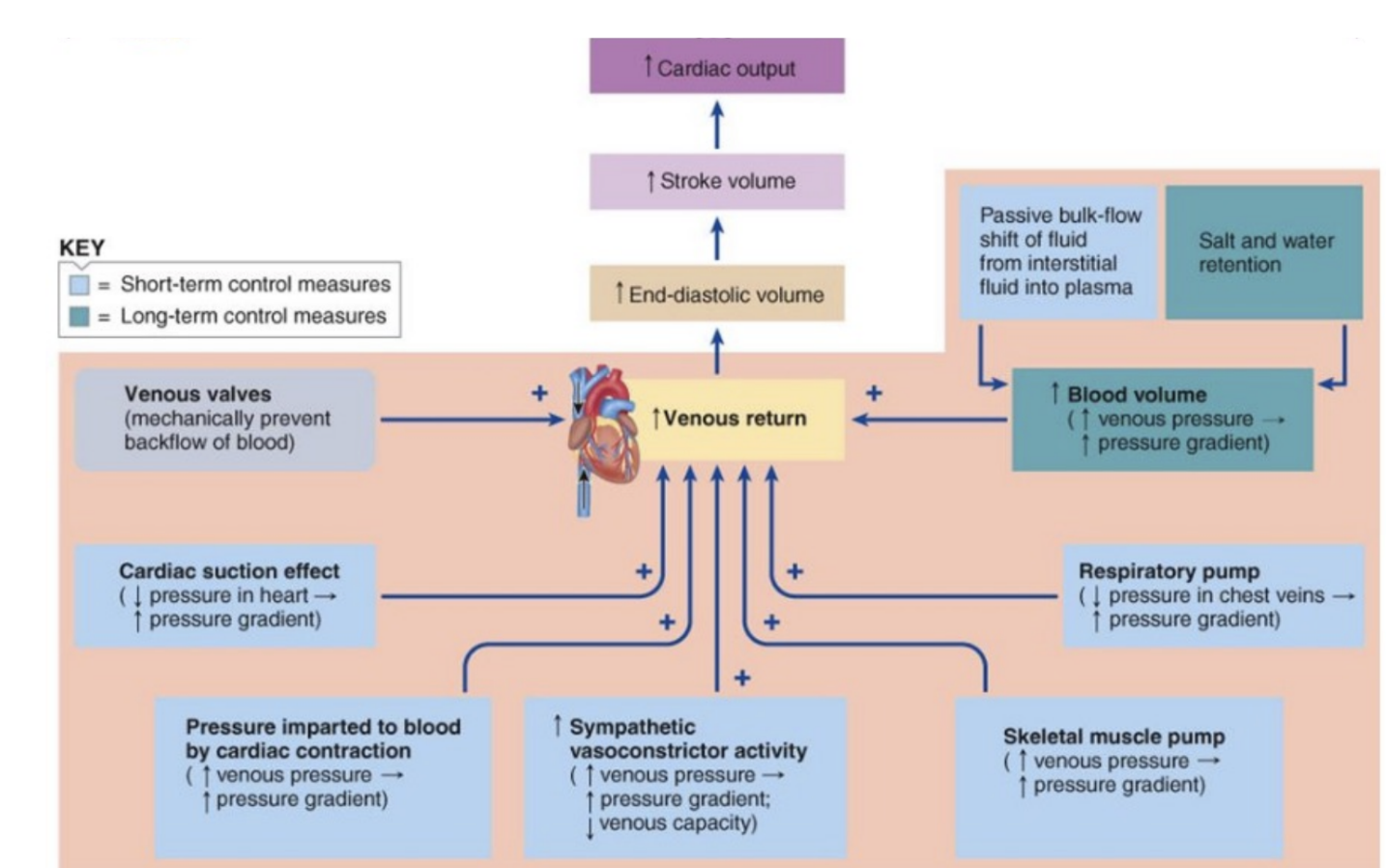
venues return
blood returns to heart through veins - the volumes of blood that circulates from the capillaries to the right atrium per unit of time - should be same as cardiac output
why does venous return happen
blood flows back to the heart because of pressure difference (pressure gradient) - blood always flows from higher to lower pressure
what is the pressure difference involved in venous return
-venules - about 16 mmHg
right ventricle / right atrium about 0 mmHg — small but enough to push blood back to the heart
what is the role of the left ventricle in venous trturn
the left ventricle contracts and pumps blood into the arteries - indirectly keeps the blood moving -arteries → capillaries → veins -pressure created the left ventricle ultimately helps drive venous return
respiratory pump & venous return
inspiration facilitates return- Breath in → lower pressure blood enters heart, Breathe out → higher pressure, blood leaves heart
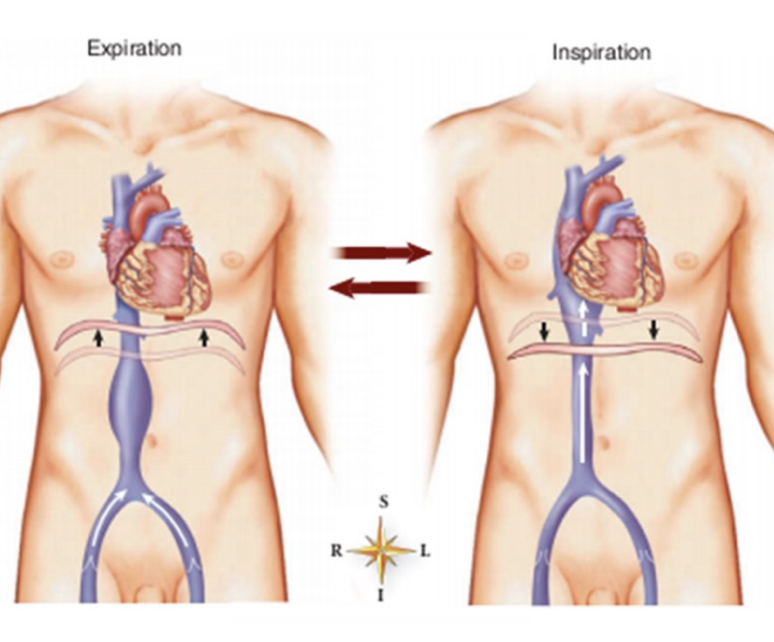
how does the respiratory pump affect venous return
the respiratory pump operates by alternative ately increasing pressure in the thorax during expiration (thus pushing central venous blood into he heart) and decreasing thoracic pressure during inspiration (pulling venous blood into central veins)—- during inspiration pressure becomes negative which helps establishment of pressure gradient

Muscle pump
Skeletal muscles contracts and squeezes veins and opens valves, pumping blood toward the heart