bruh
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
Concentration
The amount of solute in a given volume of solution.
Dissolving
The process where solute particles become surrounded by solvent molecules.
Hydrogen Bond
A strong dipole-dipole interaction between hydrogen and a highly electronegative atom (N, O, F).
Induced Dipole
Temporary polarization of a neutral atom or molecule caused by nearby charges.
Dipole
A molecule with positive and negative ends due to uneven electron sharing.
Insoluble
Unable to dissolve in a given solvent.
Soluble
Capable of dissolving in a solvent.
Solvent
The substance that does the dissolving (usually in greater amount).
Solute
The substance being dissolved.
Saturated Solution
Contains the maximum amount of solute at a given temperature.
Unsaturated Solution
Can dissolve more solute at a given temperature.
Mole
6.022 x 10^23 particles of a substance.
Molarity (M)
Moles of solute per liter of solution.
Precipitate
A solid formed in a solution during a chemical reaction.
Physical Model
A tangible representation (e.g., a model of a molecule).
Conceptual Model
An abstract explanation (e.g., the quantum model of the atom).
Atom
The smallest unit of an element.
Proton
Positively charged subatomic particle in the nucleus.
Neutron
Neutrally charged subatomic particle in the nucleus.
Nucleon
A proton or neutron.
Atomic Number
Number of protons.
Mass Number
Protons + Neutrons.
Atomic Mass
Weighted average of all isotopes.
Atomic Spectrum
Set of wavelengths emitted by electrons moving between energy levels.
Photon
A packet of electromagnetic energy.
Quantum
A discrete quantity of energy.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Range of all types of EM radiation.
Wavelength
Distance between peaks of a wave.
Hertz (Hz)
Unit of frequency, 1 cycle per second.
Isotope
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons.
Ion
An atom with a charge due to lost or gained electrons.
Electron
Negatively charged subatomic particle.
Inner Shell Shielding
Inner electrons block the attraction of valence electrons to the nucleus.
Effective Nuclear Charge
Net positive charge felt by valence electrons.
Valence Shell
Outermost shell of electrons.
Valence Electron
Electron in the outermost shell involved in bonding.
Nonbonding Pair
Electron pairs not shared in bonding.
physical models
when a tangible structure helps understand form/scale (e.g., a DNA model).
conceptual models
for abstract systems (e.g., atomic orbitals, electron clouds).
Thomson (Cathode Ray):
Discovery of electrons
Rutherford (Gold Foil
Discovered nucleus; atom is mostly empty space.
Bohr (Spectral Lines
Electrons exist in specific energy levels.
Properties of Light
Has both wave and particle nature
Orbitals
Regions of high electron probability.
Capacity:
s: 2
p: 6
d: 10
f: 14
Ion Charge
Protons - Electrons.
Metals
lose e⁻ → cations
Nonmetals
gain e⁻ → anions
Metallic Bonding
Electrons delocalized over lattice of metal atoms.
Explains conductivity, ductility, malleability.
Electron Geometry
Total regions of electron density.
Molecular Shape
Based on atoms only e.g., Linear, Bent, Trigonal Planar, Tetrahedral.
Solution
Homogeneous mixture of solute in solvent
Electronegativity
Atom's ability to attract e⁻.
Polar Bond
Electrons shared unequally
Nonpolar Bond
Electrons shared equally
Molecule Polarity
Depends on bond polarity & shape
Dipole-Dipole
Between polar molecules
Dispersion (London)
Weakest, in all molecules
Ion-Dipole
Between ion and polar molecule
Inducing Dipoles
I₂ becomes polarizable due to large electron cloud
Fluorine induced dipole
Hard to polarize due to high electronegativity
Methane (gas) vs. Octane (liquid)
Stronger dispersion forces in octane due to larger size.
Saran Wrap Sticking
Due to dispersion forces
Molarity Calculation
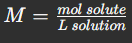
Activation Energy
The minimum energy needed to start a chem reaction
Avogadros Number
6.022 x 10^23: number of atoms or molecules in 1 mole of substance
catalyst
substance that speeds up a chem reaction whichout being consumed
chemical equation
symbolic represnetation of chem reaction
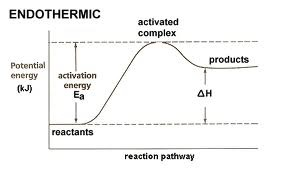
Endothermic
reaction that absorbs heat from surroundings
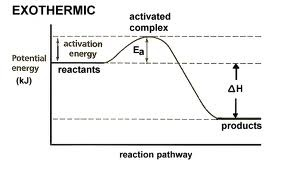
Exothermic
reaction that releases heat to the surroundings
Formula Mass
sum of atomic masses in a chem formula
Molar Mass
Mass of one mole of a substance in g/mol
Reaction Rate
speed at which reactancts are converted to products in a reaction
Acid
Substance that donates a proton (HYDROGEN+/in front)
Base
substance that accpets a proton or donate OH-
Amphoteric
substancce that can act as both acid AND base
hydronium ion (H3O+)
formed when an acid donates a proton to water
Hydroxide ion (OH-)
made when a base dissolves in water
basic solution
contains more OH- than H3O+
acidic solution
has more H3O+ than OH-
neutral solution
equal amt of H3O+ & OH-
pH
scale that measures acidity or basicity

Salt
ionic compound formed from acid base neutralization
reduction
GAIN of electrons
Oxidation
LOSS of electrons
half reactions
seperate equations showing both oxidation & reduction
oxidizing agent
this is what causes oxidation: gets reduced
reducing agent
causes reduction: gets oxidized
Solubility Determinates
Factors are polarity, temperature, and pressure
Temperature effects on Solubility (S)
solid in liquids: solubility INCREASES with temperature
Temperature effects on Solubility (G)
Gases in liquids: solubility DEACRESES with temperature
Increase Gas solubility in liquid
The LOWER the temp & INCREASE pressure
Nonpolar Gas (CO2 & O2)
a lil soluble in water
soap molecules
Soap has polar heads & nonpolar tails
Hard Water
hella high concentration of dissolved minerals Ca2+ & Mg2+
Hard Water + Soap (problem)
The Ca & Mg forms scum with the soap cuz hella insoluble
Hard Water + Soap (solution)
(Water softners) ion exchangers like Na+ ions to replace the Ca & Mg
Chemical Reaction
process where reactancts turn into products
Reactants
starting substnaces the OG
Products
The result NEWGEN
balancing equations
use coefficients to balance the atoms on both sides