chemistry organic compounds
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
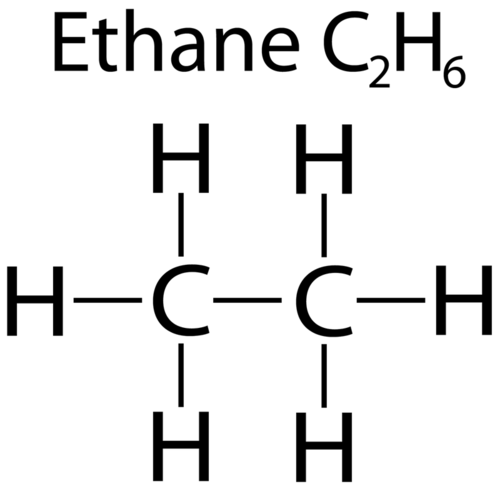
What defines a Saturated Hydrocarbon?
A hydrocarbon containing only single bonds between carbon atoms. It follows the general formula CnH2n+2.
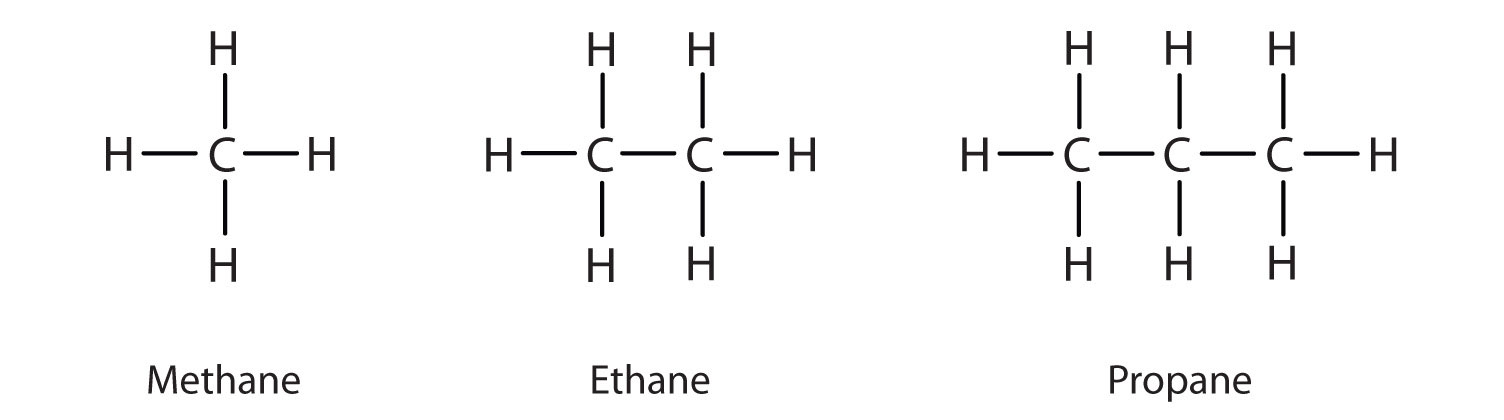
What are the general formula and typical suffix for Alkanes?
General Formula: CnH2n+2. Suffix: -ane. (e.g., methane, ethane, propane, butane)
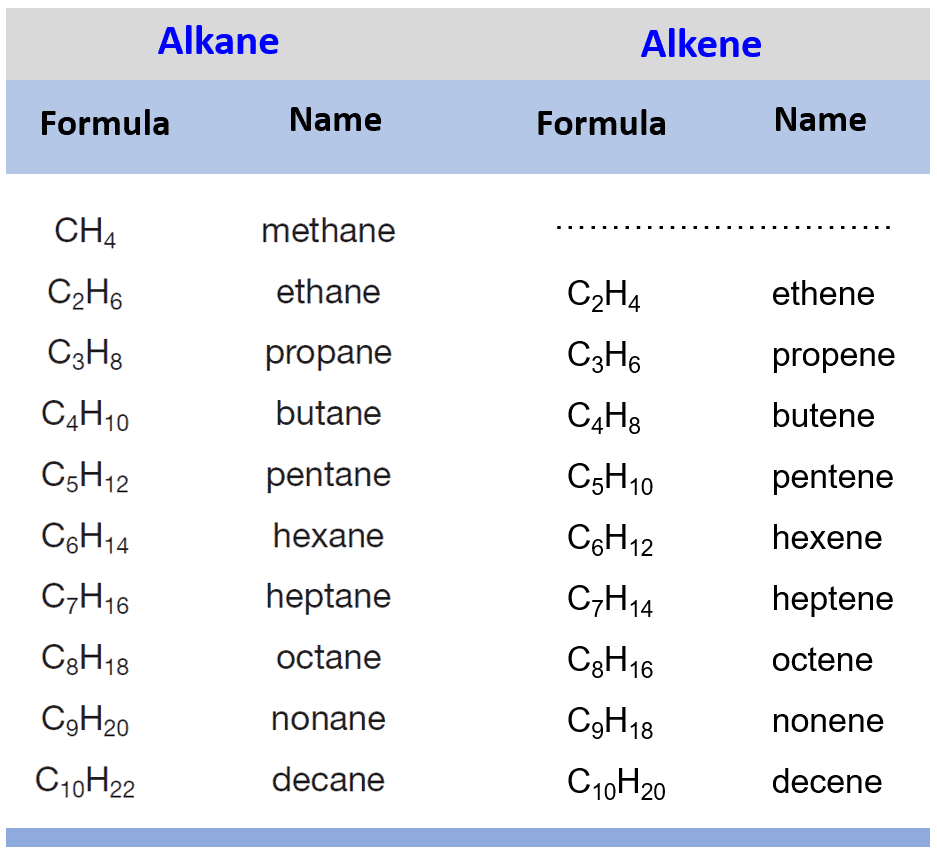
What are the general formula and typical suffix for Alkenes?
CnH2n. Suffix: -ene. (Contains at least one carbon-carbon double bond)
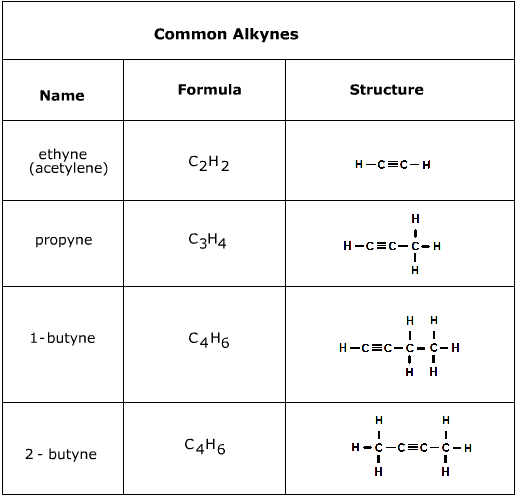
What are the general formula and typical suffix for Alkynes?
General Formula: CnH2n-2. Suffix: -yne. (Contains at least one carbon-carbon triple bond)
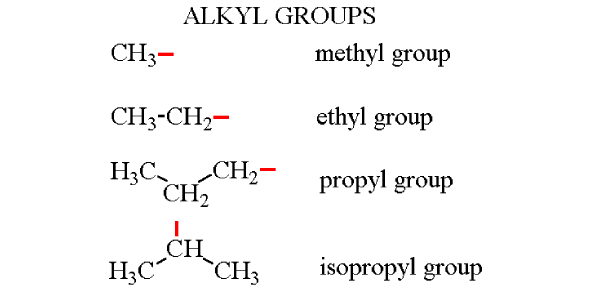
Define Alkyl Group and give common examples.
A functional group consisting of an alkane chain missing one hydrogen atom. Examples: methyl (-CH3), ethyl (-CH2CH3), propyl (-CH2CH2CH3), butyl (-CH2CH2CH2CH3).
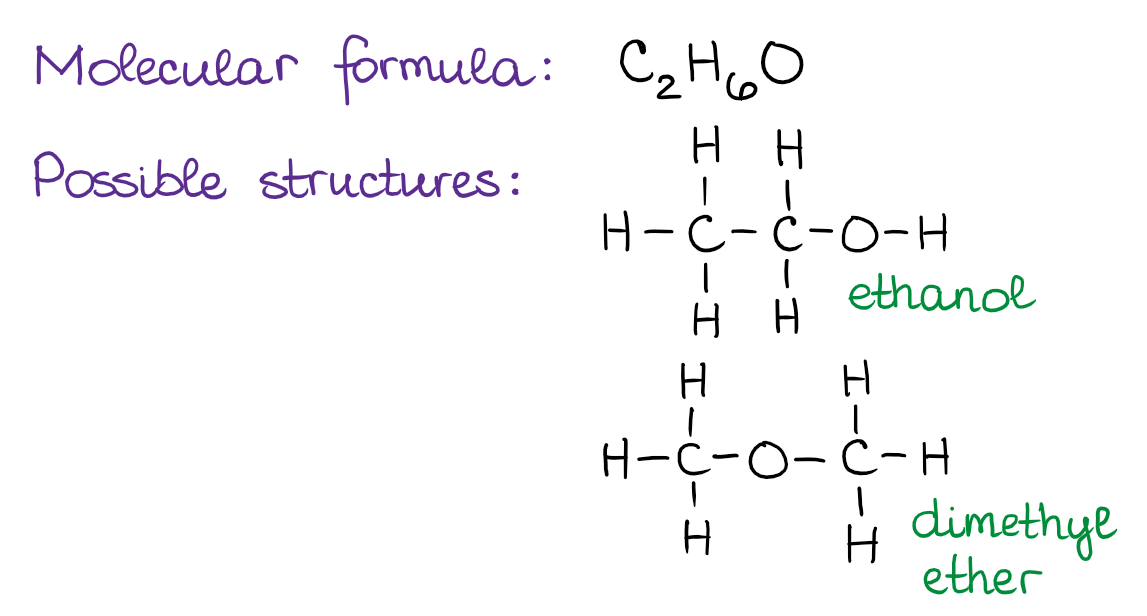
Define Isomers in organic chemistry.
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas (different arrangement of atoms).
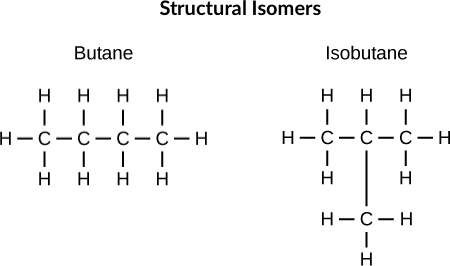
What are Structural Isomers?
Isomers that differ in the connectivity of their atoms (e.g., n-butane vs. isobutane).

What are Functional Group Isomers?
Isomers that have the same molecular formula but different functional groups (e.g., ethanol (an alcohol) vs. dimethyl ether (an ether), both C2H6O).
List typical characteristics of most Organic Compounds.
Low boiling/melting points, generally poor conductors of electricity, often insoluble in water (nonpolar).
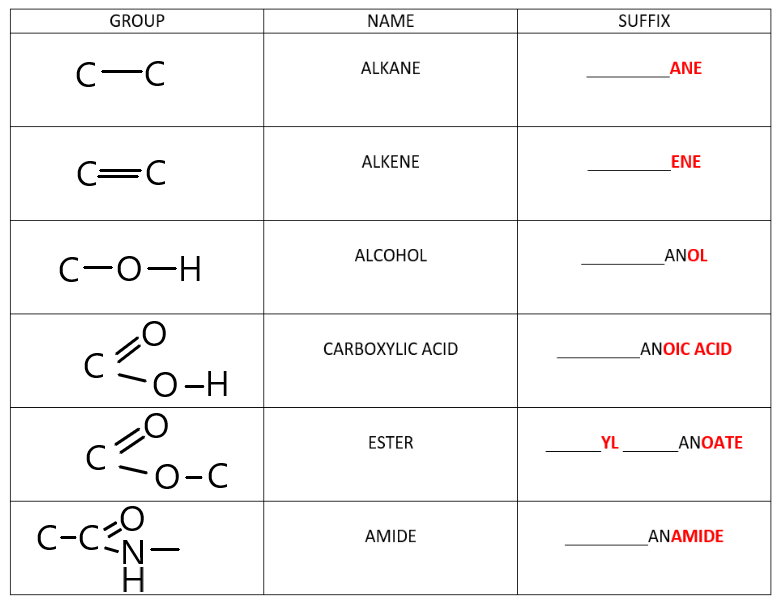
What is the functional group and suffix for Alcohols?
Functional Group: Hydroxyl group (-OH). Suffix: -ol.
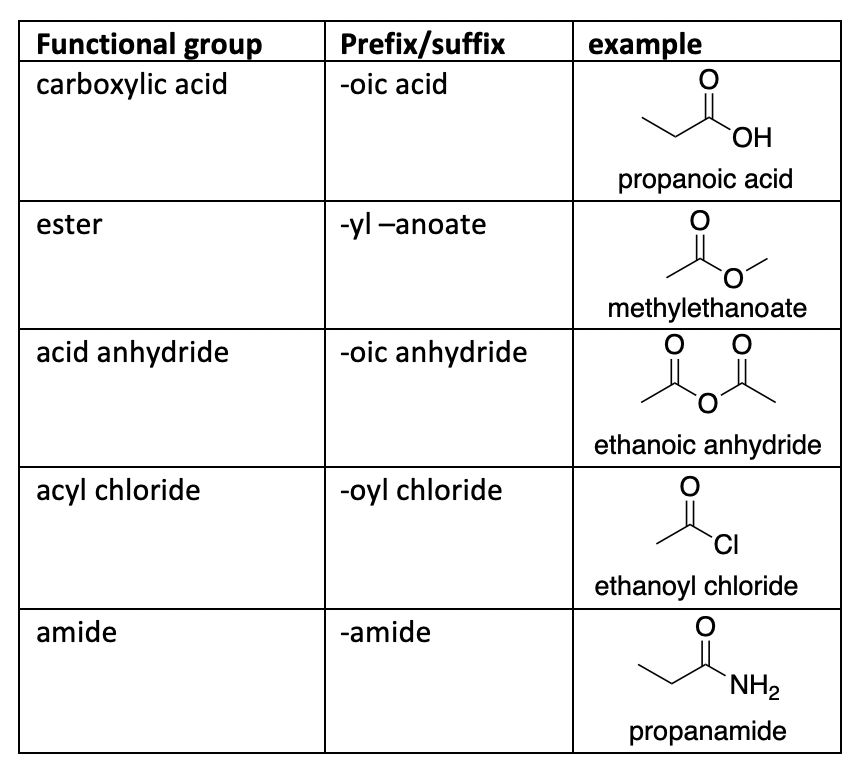
What is the functional group and suffix for Carboxylic Acids?
Functional Group: Carboxyl group (-COOH or -C(=O)OH). Suffix: -oic acid.
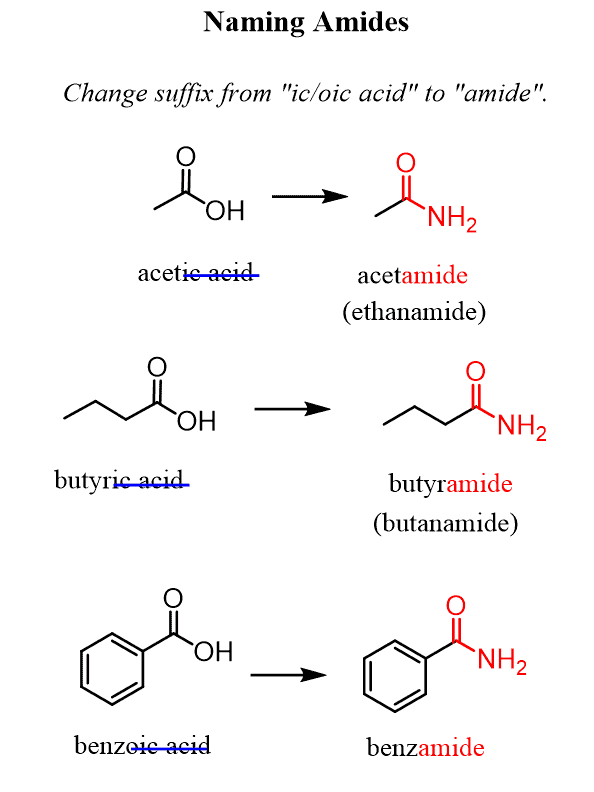
What is the functional group and suffix for Amides?
Functional Group: Amide group (-CONH2 or -C(=O)NH2). Suffix: -amide.
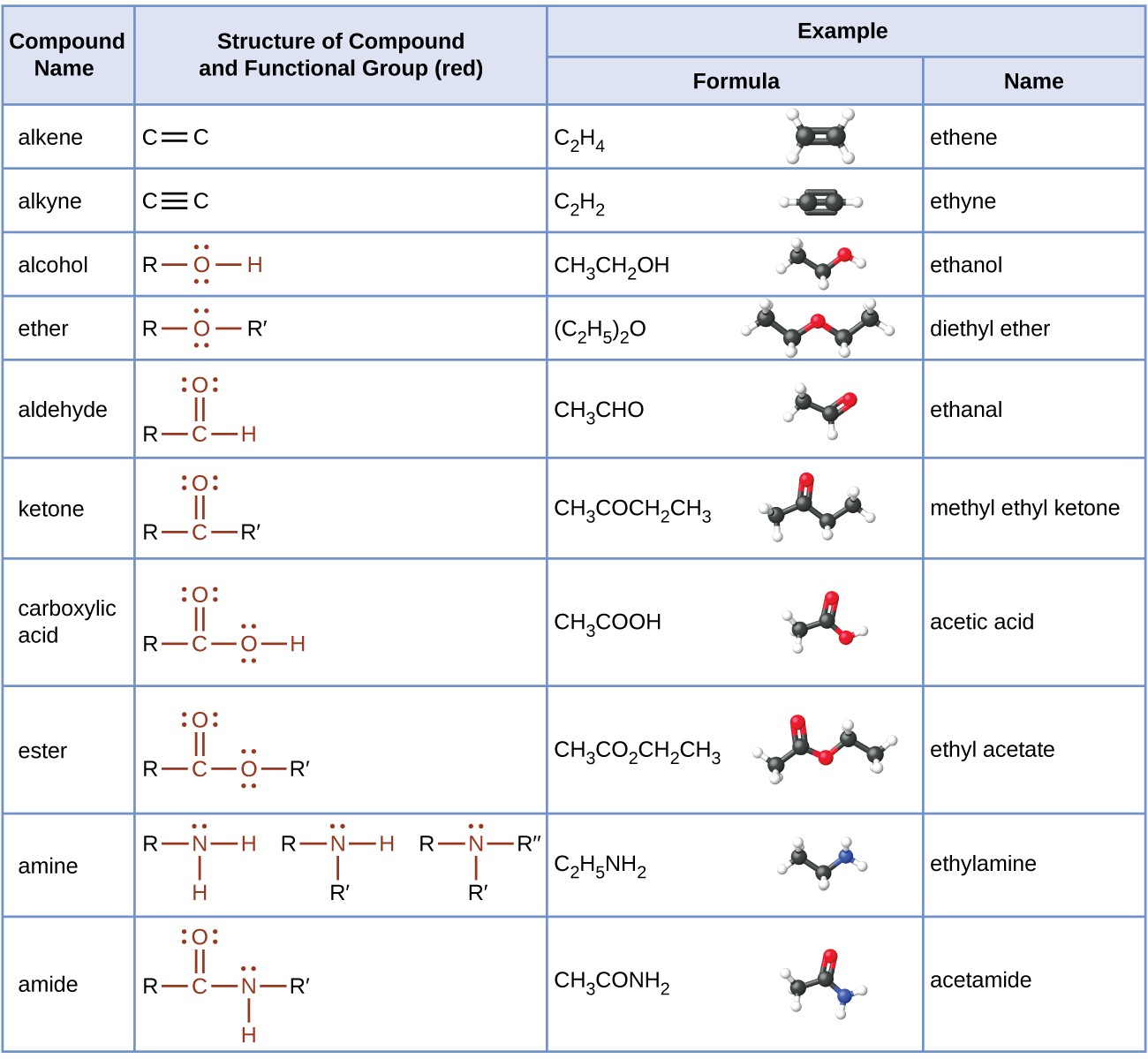
What is the functional group and typical suffix for Amines?
Functional Group: Amine group (-NH2, -NHR, -NR2). Suffix: -amine (or treated as a substituent using amino-).
How are Halogenated Hydrocarbons typically named?
By using prefixes for the halogen atoms (e.g., chloro- for chlorine, bromo- for bromine, fluoro- for fluorine, iodo- for iodine) before the parent alkane name, with numbers indicating position.
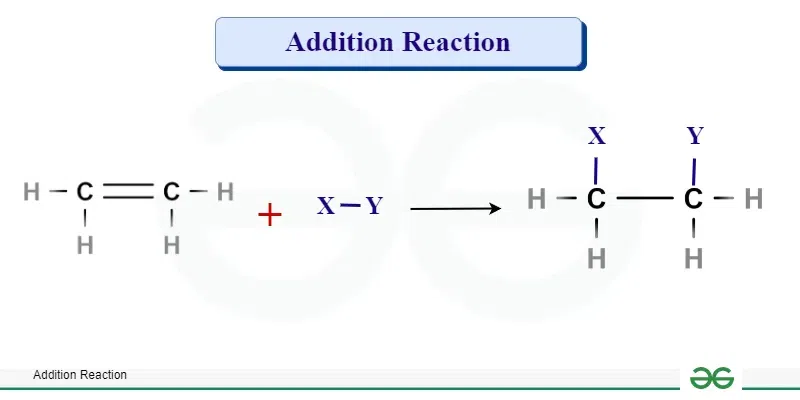
Describe an Addition Reaction in organic chemistry.
A reaction where atoms are added to an unsaturated molecule (containing double or triple bonds), breaking the multiple bond and forming new single bonds. (e.g., alkene + halogen)
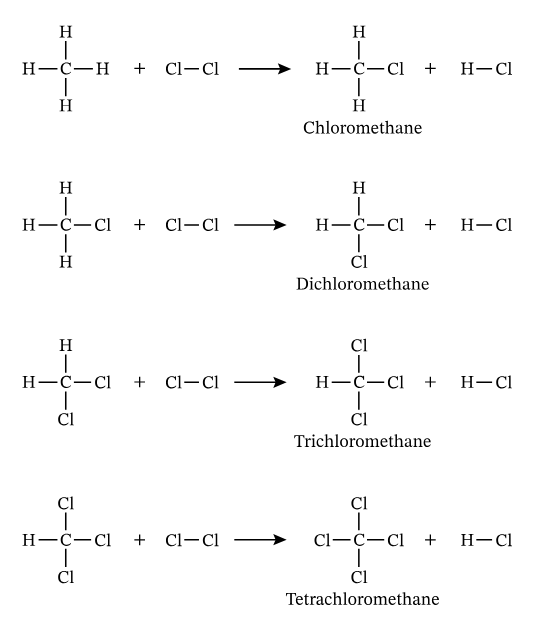
Describe a Substitution Reaction in organic chemistry.
A reaction where an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms. (e.g., alkane + halogen)
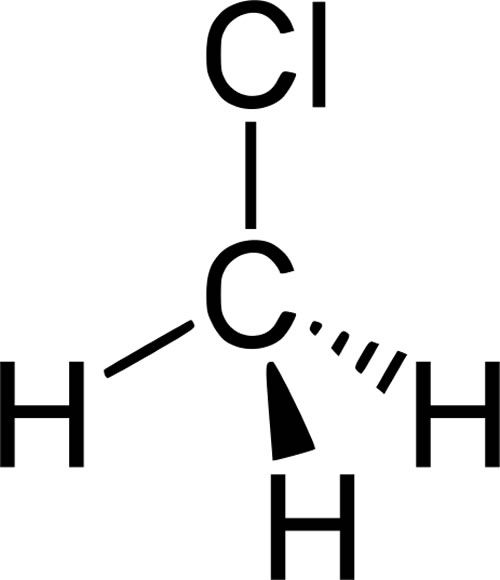
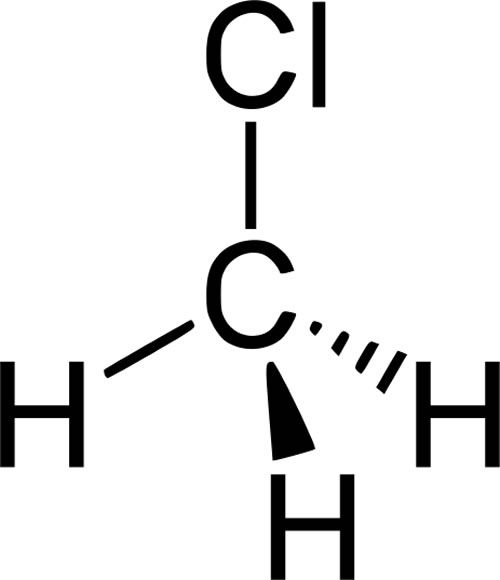
What is a Halogenated Hydrocarbon?
An organic compound where one or more hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon have been replaced by one or more halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I).
Example: Chloromethane (CH3Cl), 1,2-Dichloroethane (CH2Cl-CH2Cl)