Fungi and Plant Structure: Key Concepts and Features
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Comestibilidad
Toxic mushroom causing severe poisoning symptoms.
Amanita phalloides
Deadly mushroom known for phallotoxins.
Eukaryotes
Organisms with complex cells containing nuclei.
Heterotrophs
Organisms obtaining nutrients by absorption.
Mycelium
Interwoven hyphae forming the vegetative body.
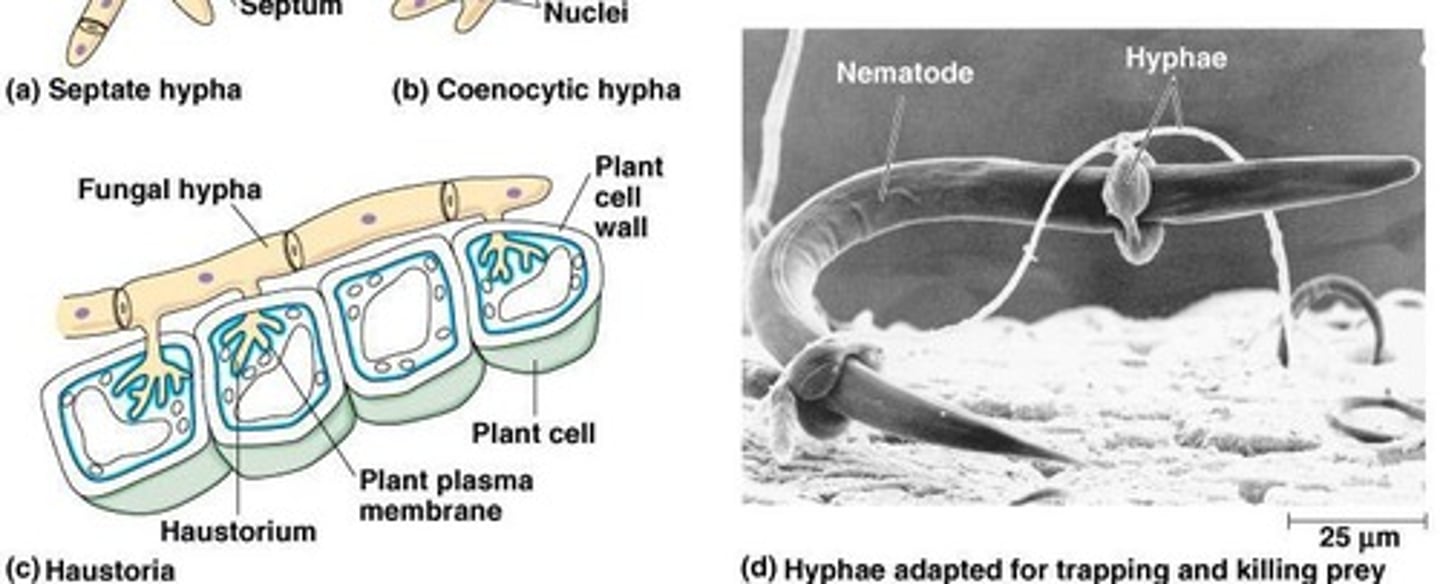
Hyphae
Filamentous structures making up fungal bodies.
Chitin
Nitrogen-based polysaccharide in fungal cell walls.
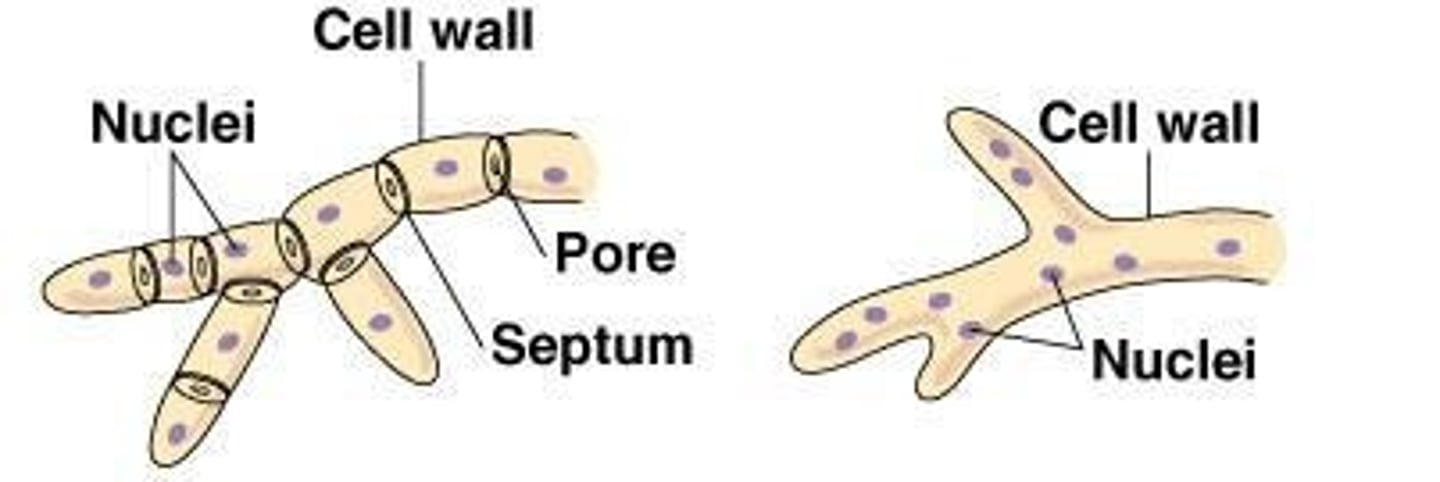
Septate
Hyphae divided by septa into compartments.
Coenocytic
Hyphae lacking septa, forming a continuous structure.
Dispersal
Process of releasing spores for reproduction.
Chytrids
Primitive fungi with flagellated zoospores.
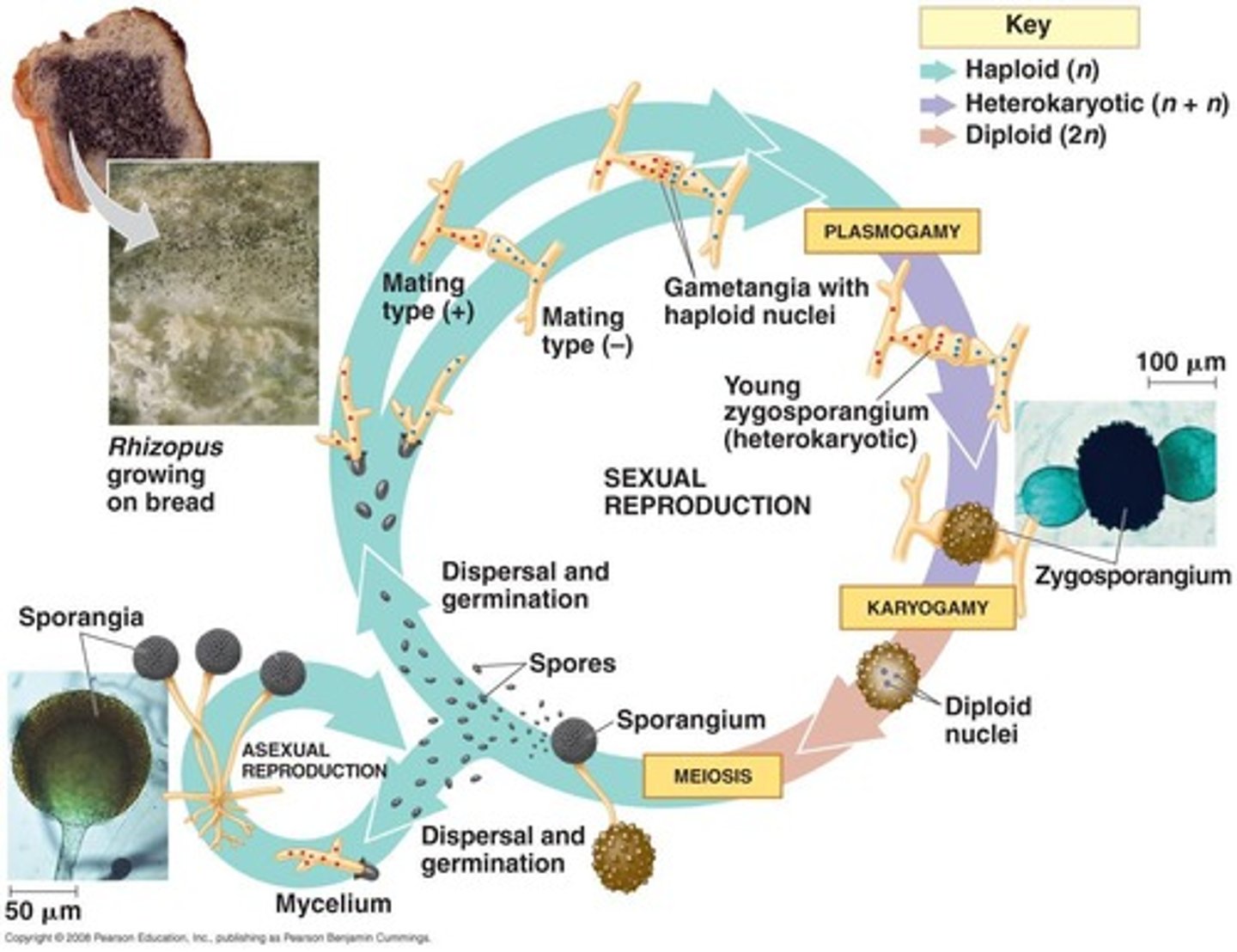
Zygomycota
Fungi with coenocytic hyphae, includes black bread mold.
Glomeromycota
Fungi forming endomycorrhizae with plant roots.
Ascomycota
Sac fungi with diverse species and habitats.
Basidiomycota
Fungi including mushrooms and important decomposers.
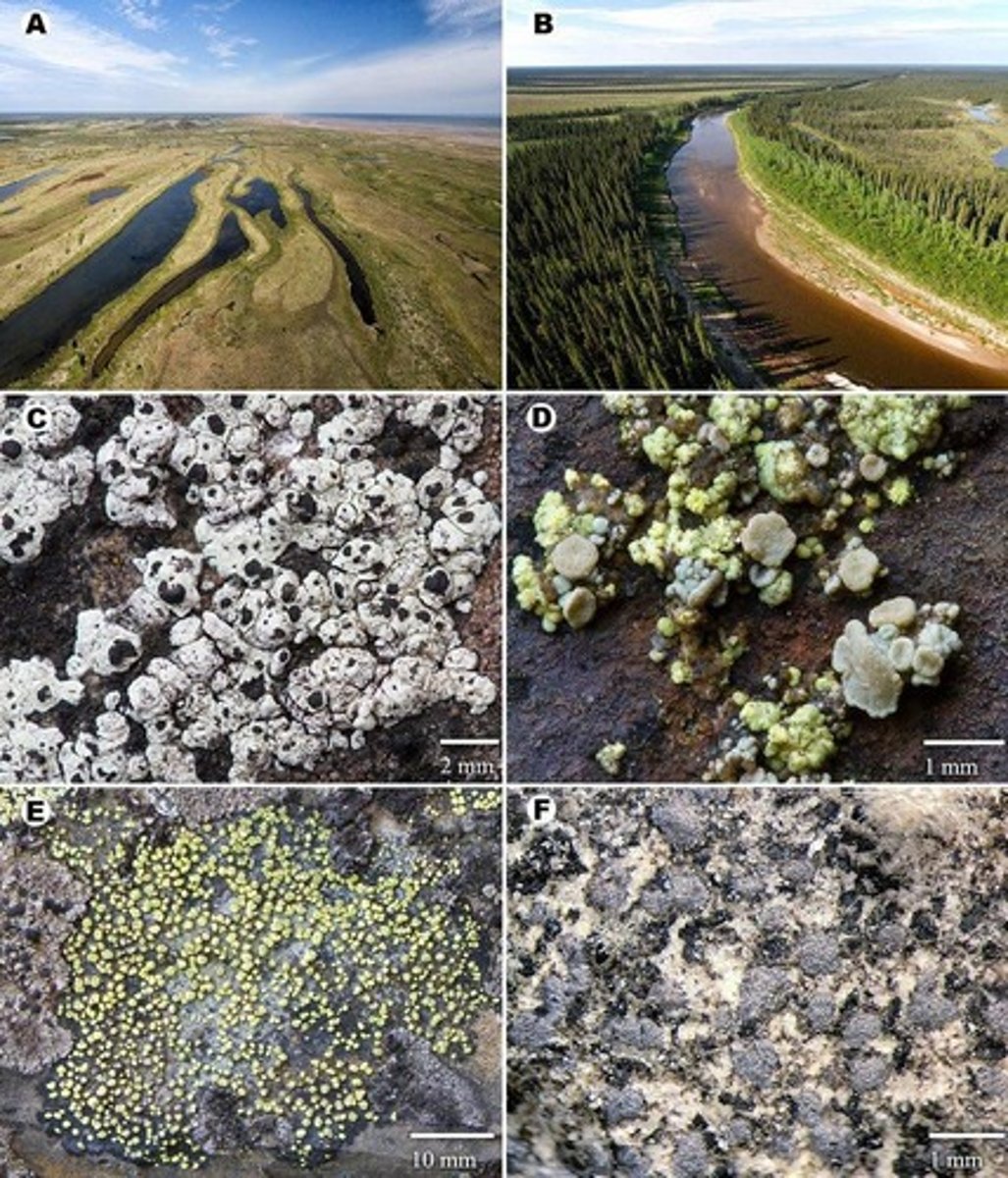
Lichens
Symbiotic association of fungi and photosynthetic organisms.

Mycorrhizae
Fungal associations enhancing plant nutrient absorption.
Penicillium
Fungus used to produce antibiotics.
Rhizopus
Common black bread mold in Zygomycota.
Ectomycorrhizae
Fungi forming external associations with plant roots.
Endomycorrhizae
Fungi penetrating plant root cells for symbiosis.
Apical meristems
Regions of active growth at root and shoot tips.
Lateral meristems
Growth regions adding girth to woody plants.
Dermal tissue
Protective outer layer of plant organs.
Vascular tissue
Transport system for water and nutrients in plants.
Ground tissue
Filling tissue in plants, involved in storage.
Parenchyma cells
Flexible cells involved in storage and photosynthesis.
Collenchyma cells
Supportive cells with thicker walls in young shoots.
Sclerenchyma cells
Rigid cells providing structural support in mature plants.