Lecture 14: Capital budgeting, Net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), profitability index (PI)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is Net present value (NPV) formula?
The present value of all future cash inflows discounted at the WACC minus the initial investment
represents the expected change in firm value from taking the project
Rules:
NPV > 0 → accept project
NPV < 0 → reject project

What are independent vs. mutually exclusive projects?
Independent → firm has enough capital to finance both projects, accept all positive NPV projects
Mutually exclusive → can only accept one project or the other, choose the investment with the highest NPV
What are the strengths of NPV?
NPV uses cash flows
NPV uses all relevant project cash flows
NPV discounts cash flows correctly
tells you exactly how much value is added to firm
What is the internal rate of return (IRR)?
The discount rate that brings NPV to 0
the % return of the project
Rules:
WACC is the benchmark
IRR > WACC → accept project
IRR < WACC → reject project

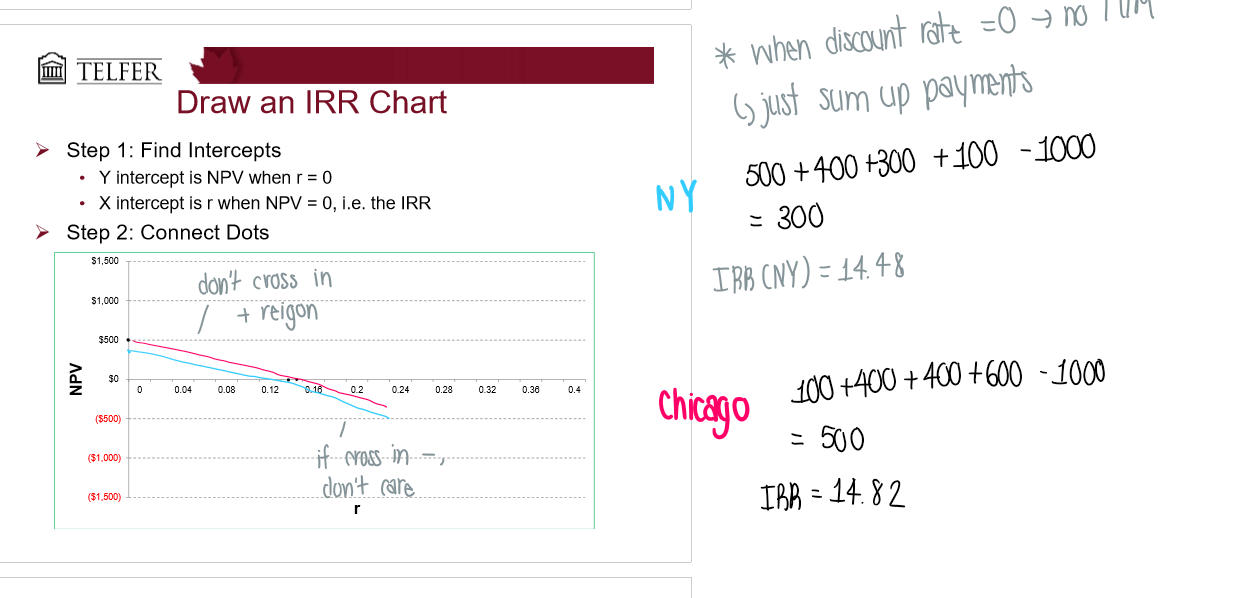
What is an internal rate of return chart?
Y is the NPV when = 0
X is the IRR
What are the 4 issues with the IRR approach?
Investing or financing?
Multiple IRRS
The scale problem
The timing problem
What is 1. Investing or financing?
When there is a positive cash flow in the beginning which turns negative later on → Means money is being borrowed!

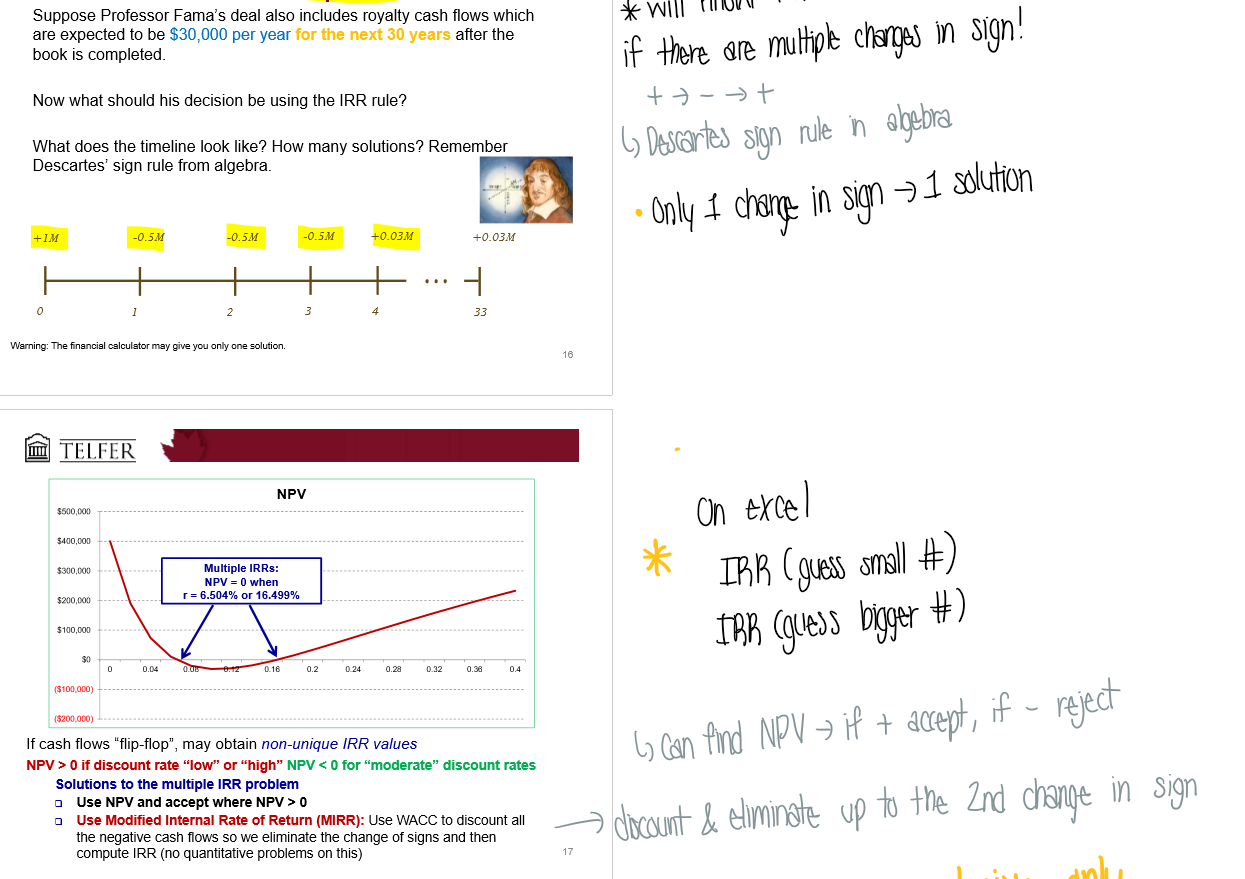
What is 2. Multiple IRRs?
Multiple IRR’s → means there are multiple changes in sign
goes from + → - → +
If there’s only 1 change in sign, there’s 1 solution
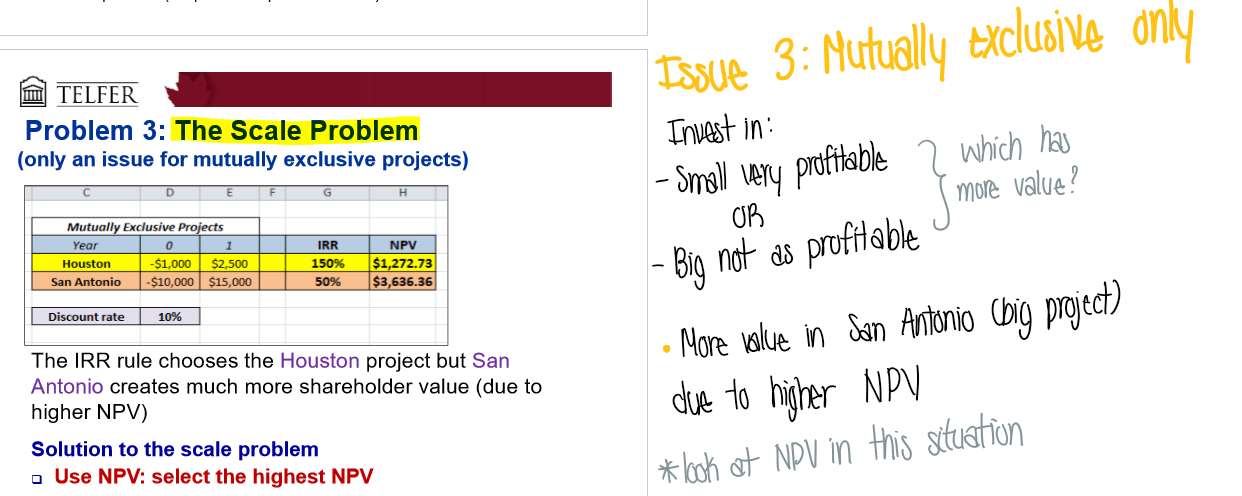
What is 3. The scale problem?
Mutually exclusive projects only
Invest in small very profitable vs. Big but not as profitable → which has more value?
more value is the big project due to higher NPV!
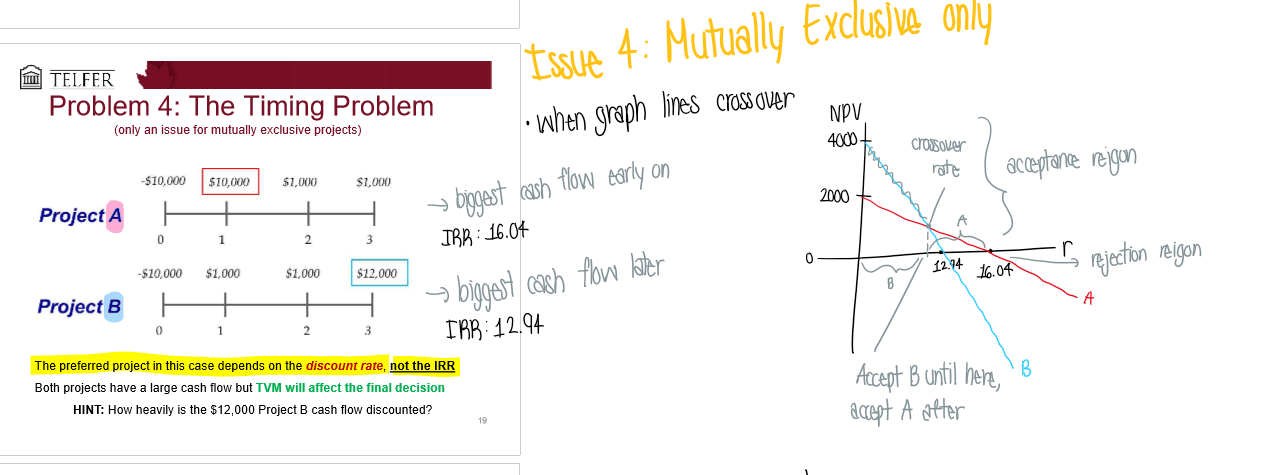
What is 4. The timing problem?
For mutually exclusive projects only
when the graph lines crossover
Project A has biggest cash flow early on vs. project B has biggest cash flow later
You accept B until the intersection rate, then accept A after → once it hits the negatives, reject
How do you find the crossover rate?
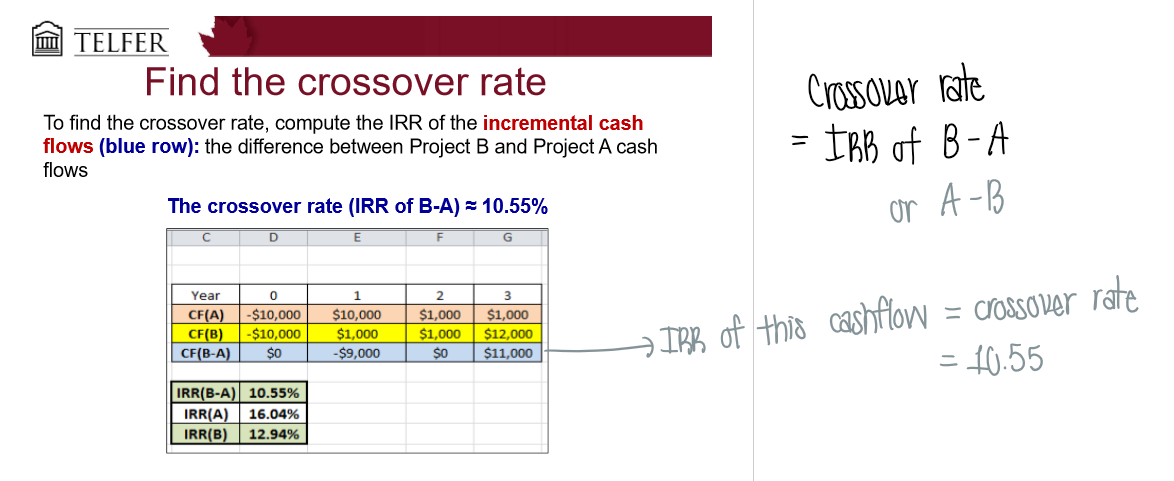
What is the payback period rule?
Payback period: amount of time required for an investment to generate cash flow to recover its initial cost
Payback period rule: a project is accepted if its payback period is less than a cutoff period

What are the strengths & weaknesses of the payback period rule?
Strengths:
simple & easy to calculate & understand
useful for firms with limited access to capital
not very limited in practice
Weaknesses:
timing of cash flows is ignored
cash flows after are ignored → may lose out on big cash flow after cutoff period
arbitrary benchmark
What is the profitability index formula??
Tells us how much each dollar invested in the project generates in present value
similar to NPV → divide by initial investment
how many $ you get relative to initial investment
PI > 1 → accept project
PI < 1 → reject project
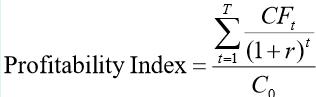
What is the strength & weakness of the profitability index?
Weakness: Mutually exclusive projects
PI is a ratio & doesn’t account for $ scale of the project
more value in bigger project
Strength: Capital rationing
ratio used to rank projects → useful if a big list of projects