UNIT 1 - biological neuron
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
why are psychologists concerned with human biology?
psychologists from the biological perspective study the links between our biology and our behavior & mental processes.
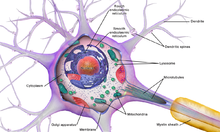
what is the cell body (soma)?
the part of the neuron that contains the nucleus
the life-support center
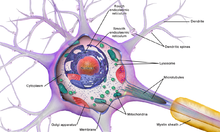
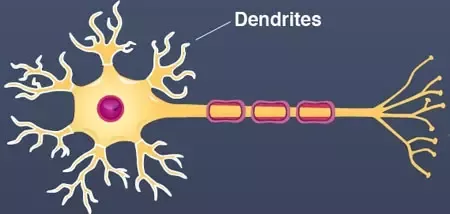
what are the dendrites?
bushy, branched extensions that receives & combines messages from other neurons
transmits those impulses towards the cell body (soma)
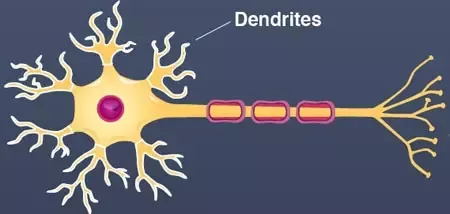
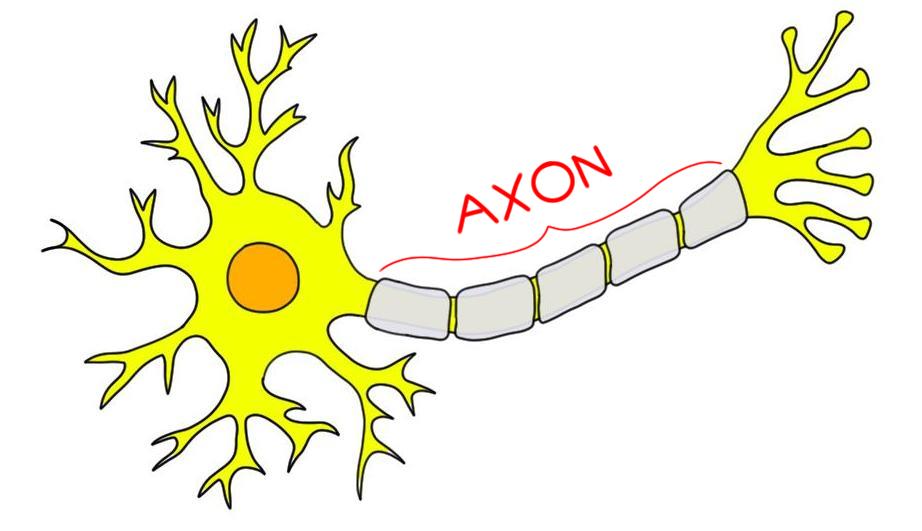
what is the axon?
attached to the soma
the long cable of a neuron that helps passes messages from the soma down to other neurons, muscles, or glands
(acts like a highway)
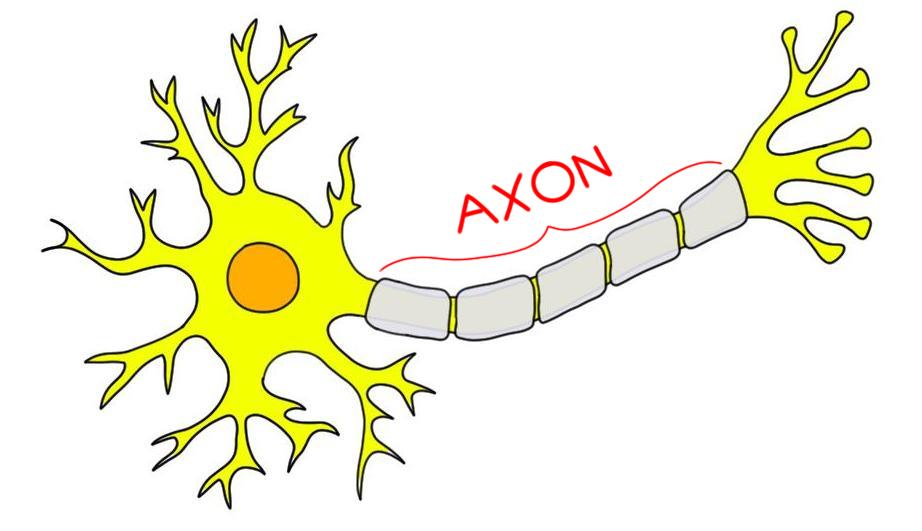
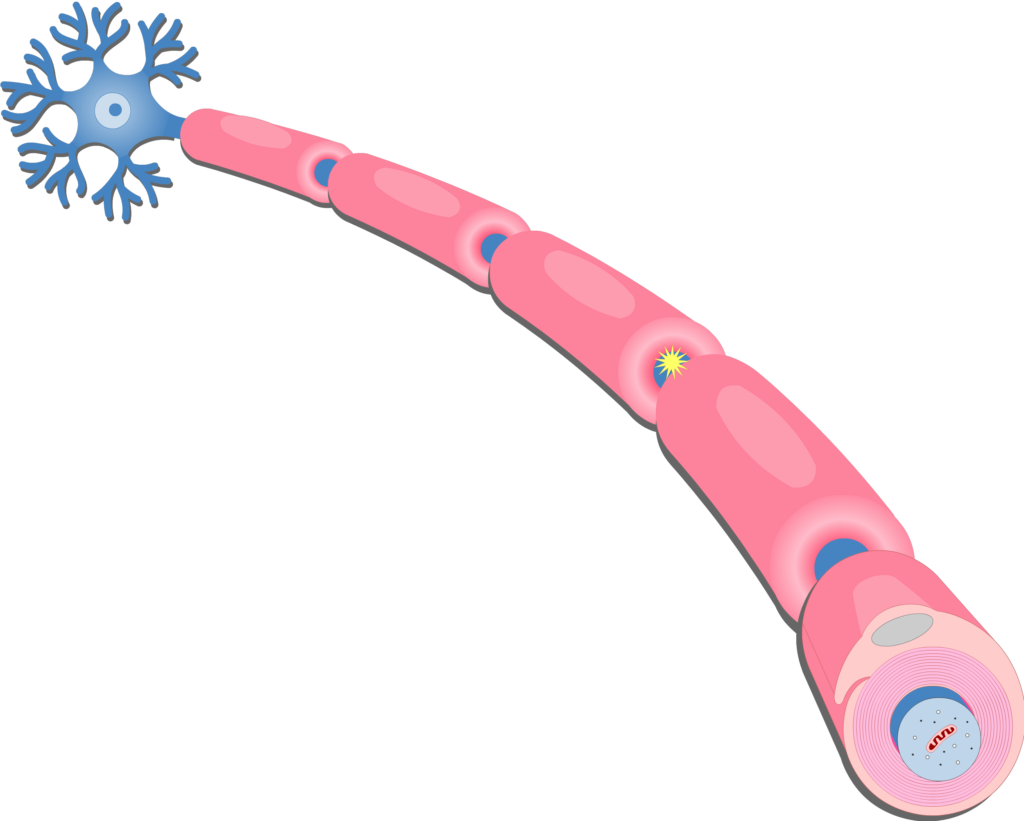
what is the myelin sheath?
the insulating fatty tissue layer that covers the axon of some neurons
helps speed the transmission of neural impulses
(protective covering - the pink parts in the pic )
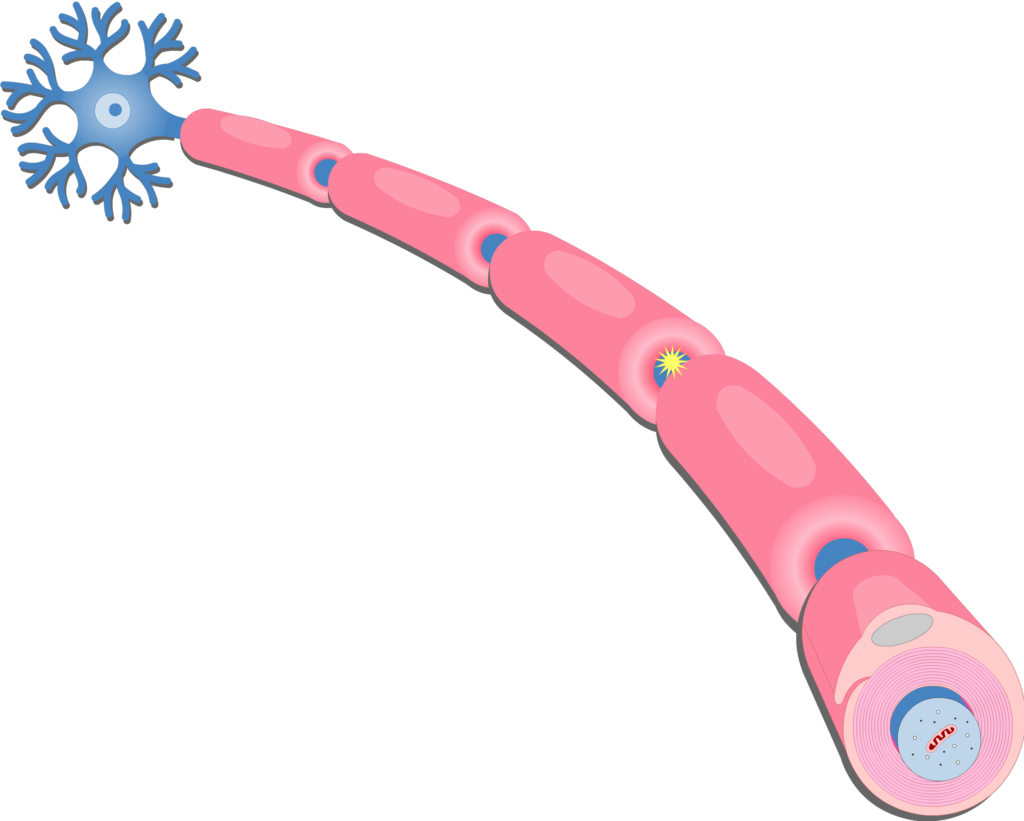

what is myelin and why is it so important?
myelin is a protective covering that wraps around the axon of neurons. it’s so important because deterioration of the myelin sheath can lead to motor impairments, like multiple sclerosis.
at birth, babies haven’t myelinated the axons of their neurons. the development of the myelin sheath (not complete until around age 25) is crucial to Behavior, Movement, and Thought.

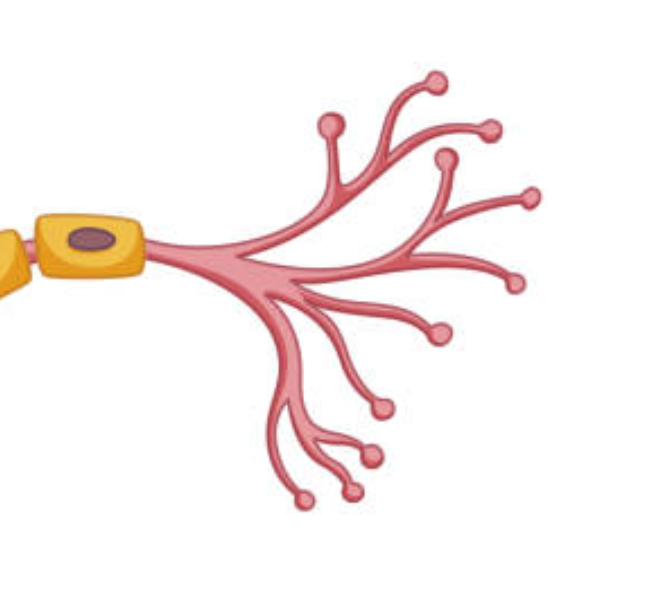
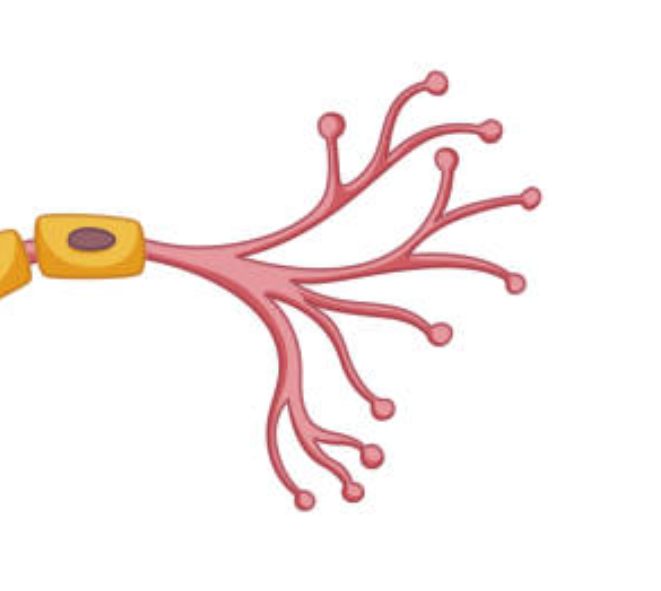
what are the terminal branches?
the ends of the axon containing terminal buttons. it converts electrical signals into chemical ones
the “roads” that allow a neuron to communicate with other neurons
what are glial cells?
cells that support, nourish, & protect neurons to help them function properly
they play a role in learning, thinking, & memory
the most abundant cells in the Central Nervous System (CNS)
how is a neural impulse generated?
a neural impulse is generated when a neuron reaches its minimum threshold. once the threshold is hit, the neuron triggers an action potential, the electrical impulse that travels down its axon
chemical → electrical signals process
neurotransmitters that are involved in learning & memory?
acetylcholine (ACh)
glutamate
neurotransmitters involved in movement?
acetylcholine (ACh)
dopamine
neurotransmitters involved in mood?
seratonin
endorphins
feel-good neurotransmitter, influences motivation & goal-directed behavior, cognition
dopamine
neurotransmitter that regulates your appetite & digestion
seratonin
neurotransmitters involved in pain perception?
endorphins
substance P
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter, reduces your brain activity making it less likely for a neuron to fire
GABA (gamma amino butyricacid)
major excitatory neurotransmitter, increases brain activity making it more likely for a neuron to fire
glutamate
neurotransmitter that gives you feelings of euphoria & pleasure, can reduce the body’s stress response
endorphins
neurotransmitter that is released in fight or flight response, wakefulness & alert neurotransmitter (adrenaline), also a hormone!
norepinephrine
neurotransmitter that promotes inflammation in response to injury, regulates emotion & social behavior
substance P
schizophrenia = too much of…
dopamine
too little acetylcholine (ACh) =
alzheimers (memory loss)
myasthenia gravis (muscle weakness)
too little dopamine =
parkinsons disease (problems with moving your body)
ADHD
too much dopamine =
schizophrenia
euphoria, difficulty sleeping, overly-energized
too much norepinephrine =
stress
anxiety
bipolar disorder
too much GABA =
drowsiness
impaired cognition (reduced brain activity)
too much glutamate =
seizures
migraines
too little GABA?
insomnia, seizures, chronic pain
MRI
best for structural imaging
use it when: you want detailed images of brain anatomy, like looking for tumors, brain injuries, or structural abnormalities
fMRI
best for brain activity
use it when you wanna see which parts of the brain are active during specific tasks, like thinking or moving. great for research on brain functions!
EEG
best for electrical activity
use it when you need to measure brain waves & electrical activity. super useful for diagnosing conditions like epilepsy or sleep disorders.
PET
best for metabolic processes
use it when: you wanna see how the brain uses glucose & other substances. often used in cancer diagnosis & to study brain disorders.
CT
best for quick structural imaging
use it when: you need a fast way to look for bleeding, fractures, or tumors, especially in emergency situations
MEG
best for magnetic fields
use it when: you want to measure the magnetic fields produced by brain activity. great for recording brain functions w/ high precision & high temporal resolution
selective permeable
a membrane allows certain substances to pass through while blocking others (like a concert bouncer)
- helps maintain right balance of ions inside & out the cell