mass transport animals
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1
New cards
what is haemoglobin
quaternary protein found in red blood cells
2
New cards
what ion is found in haemoglobin
4 x Fe2+ ions
3
New cards
haemoglobin equation
haemoglobin + oxygen →
4
New cards
what is haemoglobins job
transport oxygen around the body
5
New cards
what does haemoglobin do at the lungs
loads oxygen - readily associate with oxygen
6
New cards
what does haemoglobin do at respiring tissues
unloads oxygen - readily dissociate from oxygen
7
New cards
how does haemoglobin manage to do 2 contradicting jobs
tertiary structure of polypeptides changes allowing the molecule to change shape
8
New cards
haemoglobin with a high affinity for oxygen
loads oxygen more easily but unloads it less easily
9
New cards
haemoglobin with a low affinity for oxygen
loads oxygen less easily but unloads it easily (shape makes it difficult for oxygen to bind)
10
New cards
what is the shape of haemoglobin dependant on
oxygen partial pressure
carbon dioxide partial pressure
pH
temperature
carbon dioxide partial pressure
pH
temperature
11
New cards
what does partial pressure mean
what proportion of gas is oxygen
12
New cards
as the partial pressure of oxygen increases
changes shape to make it easier for oxygen to bind
13
New cards
what does cooperative binding mean
binding of the first oxygen changes tertiary/quaternary structure of haemoglobin which uncovers/ leads to a second binding site (uncovers another Fe for O2 to bind to)
14
New cards
why do different organisms have different haemoglobin structures
dependent of structure there are different affinity’s for oxygen
15
New cards
what does % affinity mean
how well iron and oxygen binds
16
New cards
why is the haemoglobin oxygen dissociation curve ‘s’ shape
first oxygen binds causing a change in tertiary shape which allows more O2 to bind more easily (cooperative binding)
17
New cards
when CO2 partial pressure increases (Bohr shift)
haemoglobin affinity for oxygen decreases as pH decreases (becomes more acidic) and it unloads more oxygen
18
New cards
what happens to the dissociation curve when CO2 partial pressure increases
shifts to the right
19
New cards
how is the Bohr shift advantageous for exercise
increases dissociation for oxygen (low affinity) for aerobic respiration at cells/tissues (more O2 for respiration)
20
New cards
the timing of the contraction of the different chambers and the opening/closing of the valves is
controlled by changes in blood pressure
21
New cards
process of the cardiac cycle
heart is relaxed, blood passively flows into atria increasing pressure
when the pressure is greater than the ventricle, AV valve opens and blood passively flows into ventricle
atria contracts (atrial systoles)
ventricles contract (ventricular systole) increasing ventricle pressure causing AV valve shuts
when pressure in ventricles exceeds pressure in artery, semilunar valve opens
ventricles relax, when pressure falls below artery, semi-lunar valve shuts
when the pressure is greater than the ventricle, AV valve opens and blood passively flows into ventricle
atria contracts (atrial systoles)
ventricles contract (ventricular systole) increasing ventricle pressure causing AV valve shuts
when pressure in ventricles exceeds pressure in artery, semilunar valve opens
ventricles relax, when pressure falls below artery, semi-lunar valve shuts
22
New cards
what does diastole mean
relaxed
23
New cards
what does systole mean
contracted
24
New cards
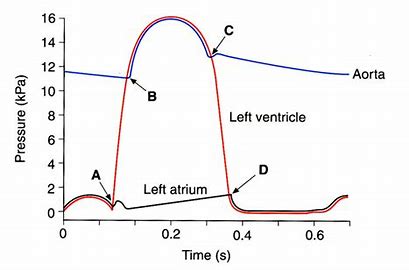
what’s happening with A B C and D
A = AV valve shuts
B= Semi Lunar valve opens
C= semi lunar valve closes
D = AV valve opens
B= Semi Lunar valve opens
C= semi lunar valve closes
D = AV valve opens
25
New cards
what is an artery
carry blood away from the heart into the atrieoles
26
New cards
what is an arterioles
smaller artery that controls blood flow from artery to capillary
27
New cards
what is a vein
carry blood from capillaries back to the heart
28
New cards
what is a capillirary
tiny blood vessels that link arterioles and veins
29
New cards
what are the different layers of veins, arteries and capilliraries
tough fibrous outer layer- resists pressure changes outside and in
muscle layer - contract and control blood flow
elastic layer - maintain blood pressure by stretching and springing back
endothelium (thin inner layer) - smooth reduces friction and thin allows for simpler diffusion
lumen - cavity that of blood vessel where blood flows
muscle layer - contract and control blood flow
elastic layer - maintain blood pressure by stretching and springing back
endothelium (thin inner layer) - smooth reduces friction and thin allows for simpler diffusion
lumen - cavity that of blood vessel where blood flows
30
New cards
why do arteries have thicker muscle walls then veins
smaller arteries can be constricted and dilatated in order to control volume of blood passing through them
31
New cards
why is the artery elastic layer relatively thicker than the veins
important blood pressure in artery is kept high. Elastic wall is stretched during diastole and relaxed during systole
32
New cards
why is the overall thickness of the artery great
resists blood vessel bursting under pressure
33
New cards
why are their no valves in arteries
blood is under constant high pressure, tend to not flow backwards
34
New cards
why is the muscle wall of arterioles thicker than arteries
contraction of the muscle allows constriction of lumen, restricting blood flow therefore controlling blood flow in capillaries
35
New cards
why is the elastic layer in arterioles thinner than artery
blood pressure is lower
36
New cards
why is the muscle wall of the vein relatively thin
veins carry bloodflow away from tissue and therefore constriction and dilation doesn’t control blood flow to tissues
37
New cards
why is the elastic layer relatively thin in the veins
low pressure of blood in the veins
38
New cards
why are vein wall overall thin
overall pressure in veins is too low to cause any bursting, allows them to flatten easily
39
New cards
why do veins have valves
ensure valves don’t flow backwards which it might do as pressure is low
when body muscles contracts, veins flatten compressing blood, valves ensure this pressure is in one direction only
when body muscles contracts, veins flatten compressing blood, valves ensure this pressure is in one direction only
40
New cards
what are the functions of the capillaries
exchange metabolic materials (O2, CO2 and glucose) between blood and cells in the body (blood flow is slow)
41
New cards
why are capillary walls mainly lining layer
extremely thin = diffusion distance is short = quicker diffusion
42
New cards
why are there lots of branched capillaries
large surface area for exchange
43
New cards
why do capillaries narrowly diameter
no cell is far from a capillary for exchange so short diffusion pathway
44
New cards
why do capillaries have a very narrow lumen
red blood cells are squeezed flat against side of capillary, closer to oxygen cells (reduces diffusion distance)
45
New cards
why are their spaces between epithelial cells in capillaries
spaces for wbc to escape to fight infections
46
New cards
capillaries are ‘leaky’
allows molecules such as water glucose and oxygen to move in and out but doesn’t NOT allow whole cells + plasma proteins to leave
47
New cards
what is tissue fluid
substance that moves in and out of blood capillaries (blood plasma)
48
New cards
what are the 2 factors that affect tissue fluid
hydrostatic pressure (heart creates high hydrostatic pressure when ventricles contracts)
water potential
water potential
49
New cards
what are the 2 ends of the capillarys called
arteriole end
venous end
venous end
50
New cards
process of tissue fluid
blood enters the capillary with relatively high pressure
high pressure causes some tissue fluid to move out
as blood travels along capillary, pressure decreases. when pressure in = pressure out fluid stops leaving
water potential of capillary decreases because the blood is more conc. as plasma proteins are stuck in (creates a water potential gradient)
water moves back into capillary via osmosis
some tissue fluid returns to the blood via the lymphatic system
high pressure causes some tissue fluid to move out
as blood travels along capillary, pressure decreases. when pressure in = pressure out fluid stops leaving
water potential of capillary decreases because the blood is more conc. as plasma proteins are stuck in (creates a water potential gradient)
water moves back into capillary via osmosis
some tissue fluid returns to the blood via the lymphatic system
51
New cards
an effective transport system
reduces diffusion distance
52
New cards
what does double circulatory system mean
blood passes through the heart twice in a complete circuit of the human body - this maintains blood vessel
53
New cards
blood vessel that brings oxygenated blood into the heart
pulmonary vein
54
New cards
blood vessel that brings oxygenated blood out of the heart
aorta
55
New cards
blood vessel that brings deoxygenated blood into the heart
vena cava
56
New cards
blood vessel that brings deoxygenated blood out of the heart
pulmonary artery
57
New cards
valve between atrium and ventricle
atrioventricular valve
58
New cards
valve between ventricle and blood vessel
semilunar valve
59
New cards
what type of muscle is the heart made of
cardiac
60
New cards
why does the left side of the heart have thicker muscle
creates more pressure