BIO120 CH3
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
what is cell theory
All organisms are made up of cells
The cell is the fundamental unit of life
Cells come from preexisting cells
do organisms have many or one cell?
Unicellular and multicellular
what is the smallest independent unit of life
the cell is the smallest independent unit of life
what characteristics do cells demonstrate
Cells demonstrate characteristics such as evolution, reproduction, use energy, response to environment, and homeostasis.
how do cells reproduce
divide from parent cells to produce daughter cells through processes like mitosis and meiosis.
structure is closely related to what in a cell?
function
what allows a cell to perform its function?
shape
what are the two different types of cells
prokaryotes and eukaryotes
where do prokaryotic cells store genetic info
nucleoid
what maintains the structure of prokaryotes?
cell walls
which is bigger, prokaryotes or eukaryotes
Eukaryotes
which type of cell has internal membranes?
eukaryotes
membranes define compartments containing
cell organelles
where do eukaryotes store DNA
Nucleus
what is the shape of chromosomes in prokaryotes
circular
what is the shape of chromosomes in eukaryotes
antiparallel strands (straight)
process of transcription and translation in eukaryotes speed:
transcription and processing of RNA happens in nucleus, then in cytoplasm translation occurs LATER
features of both eukaryotes and prokaryotes
have dna
are cells
transcription and translation
has cell wall
independent unit of life
cells are defined by:
membranes
what do membranes do
membranes act as physical barriers to distinguish exterior and interior of cells and their components
what is the main component of cell membranes
lipids
what components (3) can be found in cell membrane
lipids (main) carbs proteins
how many layers of lipids in cell membranes
2
what is made of glycerol backbone
phospholipids
what are phosopholipids
made of glycerol backbone attached to a phosphate group and 2 fatty acids
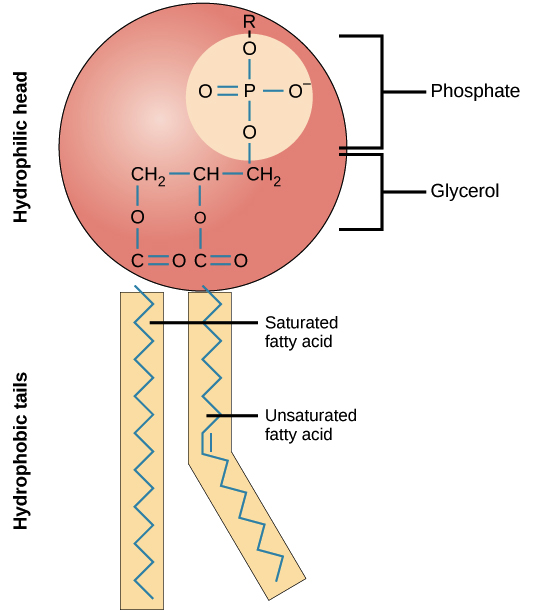
what part of lipid bilayer contains glycerol and phosphate group
hydrophilic head
what part of lipid bilayer contains fatty acids
hydrophobic tail
what is amphipathic
molecules that are both hydrophobic and hydrophilic
what part of bilayer interacts more with environment
head
are fatty acid tails polar or nonpolar
nonpolar
is water polar or nonpolar
polar
how do phospholipids arrange their polar heads in aqueous environments
to the outside to interact with water
how do phospholipids arrange their nonpolar tails in aqueous environments
on inside away from water
phospholipids are all arranged the same way(T or F)
False, phospholipids form different structures based on shape
what do phospholipids form when placed in water at neutral pH
liposomes
what is a liposome
spherical bilayer formed when phospholipids are placed in water at neutral pH
what shape are liposomes
sphere
what does the water pH need to be for liposomes to form
neutral pH
what structure can capture other molecules inside (spherical)
liposomes
what do liposomes do
break and filter (with semi-permeable membrane) some molecules
what type of membrane do liposomes have
semipermeable
liposomes can ______ and _______ in some environments
break, reform
what types of molecules do liposomes capture
nucleic acids and other molecules
early membranes were semi-permeable (T or F)
false, they were likely not semipermeable
why do lipids interact so often
due to extensive Van Der Waals forces
what are van Der Waals forces
temporary polarization because of electron presence around atoms
Van Der Waals forces are easily _______ and ________
broken, reform
what allows lipids to move more rapidly thru a cell
van der waals forces
what part of the cell is dynamic and constantly changing and moving thru the cells life
cell membrane
membranes are _______
fluid
what particle is able to move freely within cell membranes
liipids
what features affect membrane fluidity
number of C=C double bonds
length of fatty acid tails
how does # of C=C double bonds impact membrane fluidity
Less double bonds = less movement in membrane
how does length of fatty acid tails impact membrane fluidity
Longer tails = more surface area for Van der Waals forces = less lateral movement in membrane
cell membranes only contain one type of lipid (T or F)
false, cell membranes have multiple types of lipids
what substance has one region that is hydrophobic and one hydrophilic
cholesterol
what is a major component of animal cell membranes
amphipathic
at makes up 30% of membrane lipids
Cholesterol
cholesterol makes of ______% of cell membranes
30%
hydrophilic head is what type of molecule
hydroxyl group (-OH)
how does temp affect membrane fluidity
High temperatures = low membrane fluidity
Low temperature = high membrane fluidity
how does cholesterol at high temps impact membrane fluidity? (what does it do to phospholipids)
Ring structure interacts with fatty acid tails, reducing phospholipid mobility
Increases rigidity in high temps
how does cholesterol at low temps impact membrane fluidity? (what does it do to phospholipids)
The cholesterol keeps phospholipid molecules from packing too close together in cold temps
Cholesterol regulates fluidity
what is the function of transporter proteins
move ions or molecules across the membrane (like a tunnel)
what is the function of receptor proteins
allow the cell to receive signals from the environment, creating a response inside the cell
what is the function of anchor proteins
attach to other proteins and help maintain cell structure and shape
what is the fluid mosaic model
lipids proteins and carbs coexist in the cell membrane and are able to move within it
what is a structure that allows molecules to move laterally
lipid bilayer (membrane fluidity)
what is a crucial component of all cells
cell membranesd
are cell environments stagnant or always changing
always changing
how do cell membranes control molecules coming in and out
mitigate molecular traffic and sustain the intracellular conditions
how do cells maintain homeostasis
thru selectively permeable membrane
how does movement of molecules across cell membrane occur
when there is a concentration gradient
how does diffusion work
high concentration → low concentration
what is passive transport
movement across cell membrane via diffusion
how do oxygen and carbon move thru the cell
thru passive transport
what is facilitated diffusion
passive transport occurring with the help of protein transporters
what are the two types of membrane transporters
channel proteins and carrier proteins
what are channel proteins
create an opening between inside and outside of membrane to allow movement of molecules
what are carrier proteins
bind to molecules in order to transport them across the membrane
how does water move across cell membrane
passive transport
how are water molecules able to travel thru phospholipid bilayer
The size of water molecules enables some transport through the phospholipid bilayer, despite hydrophobic tails
what is the main way water comes thru membrane
via channel proteins called aquaporins
what is osmosis
net movement of a solvent (dissolve other substances) across semipermeable membrane
how does water move via osmosis?
high concentration of solute to lower concentration
water concentration ________ as solute concentration _________
decreases, increases
what is osmotic pressure
the tendency of a solution to draw water in by osmosis
_______ solute concentration = __________ osmotic pressure of the solution
higher, higher
what is active transport
movement of substances against a concentration gradient (uphill)
what type of transport requires energy
active transport
how is active transport possible? (what performs function)
transport proteins in the membrane that act as pumps
what needs to be moved against a concentration gradient
sodium and potassium
what is primary active transport
movement of ions thru membrane (needs ATP)
what is electrochemical gradient
gradient with both electrical and chemical componenets
how do you calculate electrochemical gradient
Sum of the chemical gradient (solute concentration difference) and electrical gradient (charge difference)
what drives the movement of other molecules in active transport
movement of protons
how do cells maintain their size (what type of transport)
Active transport
what is hypertonic
when cell rejects water bc concentration greater outside cell
what is hypotonic
when cell takes in water bc concentration great inside cellw
what is isotonic
water is coming in and out of cell evenly