AP Statistics - Chapter 4
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
“Bad” Sampling Methods
Convenience Sample
Voluntary Response Sample
Have bias - the design of a statistical study shows bias if it would consistently underestimate or consistently overestimate the value you want to know
Convenience Sample
Sample selected by taking from the population individuals that are easy to reach
30 students from the school library. Won’t accurately represent the homework habits of all students at the high school because students who hang out in the library tend to be more studious
Voluntary Response Sample
People decide whether to join a sample by responding to a general invitation
Call-in, text-in, write-in, and many Internet polls. Attract people who feel strongly about an issue, and who often share the same opinion
Overestimate bias
“Good” Sampling Methods
Simple Random Sample (SRS)
Stratified Random Sample and Strata
Cluster Sample and Clusters
Systematic Random Sample
Response Error - not everyone answers honestly
Nonresponse Error - not everyone replied
Simple Random Sample (SRS)
Sample chosen in such a way that every group of n individuals in the population has an equal chance to be selected as the sample
Ex - From a town with 100,000 residents, randomly select 1,000 people
Stratified Random Sample and Strata
Sample obtained by classifying the population into groups of similar individuals, called strata, then choosing a separate SRS in each stratum and combining these SRSs to form the sample
Ex - A researcher randomly selects and interviews fify male and fifty female teachers from a staff of 500 teachers
Ex - A market researcher randomly selects 200 drivers under 35 years of age and 100 driver over 35 years of age
Cluster Sample and Clusters
Sample obtained by classifying the population into groups of individuals that are located near each other, called clusters, and then choosing an SRS of the clusters. All individuals in the chosen clusters are included in the sample
Ex - All of the teachers from 85 randomly selected nation’s middle schools were interviewed
Ex - A researcher for an airline interviews all of the passengers on five randomly selected flights
Systematic Random Sample
Selects a random starting point from the population, then a sample is taken from regular fixed intervals of the population depending on its size
Every fifth person boarding a plane is search thoroughly - random starting point
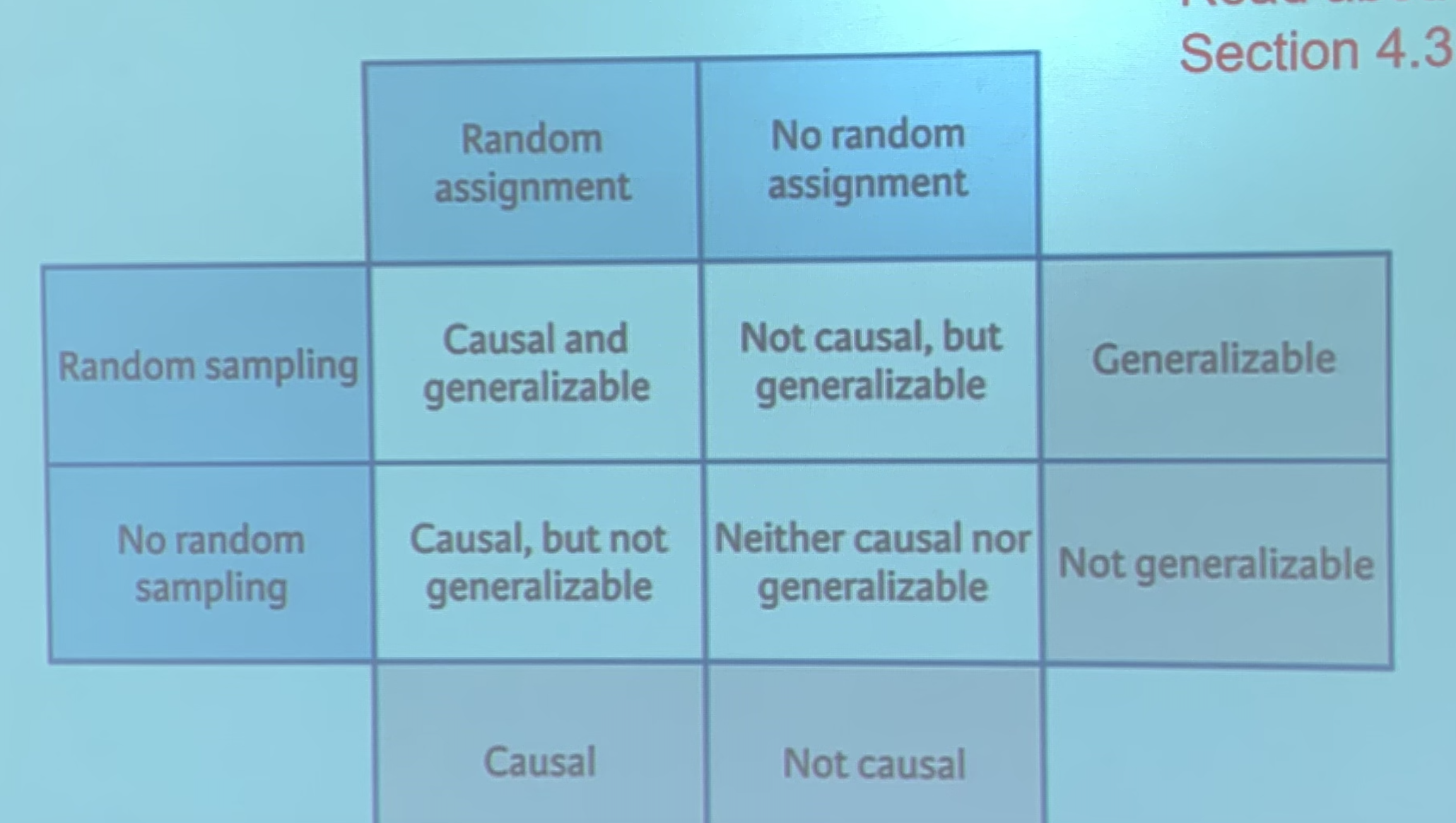
Observational Study
volunteers, no randomization, no set thing or treatment people are made to do, watching for patterns
Experiment
Deliberately imposes some treatment to observe response to see if treatment causes change in response
Evidence on average (group)
Causation
Experimenter has control
Confounding variables
2 variables are associated in a way that their effect cannot be distinguished
Difference between both groups
Not controlled variables
Effect entire group
In observational study
Good experiment
Comparison - 2 groups are compared
Randomize who gets what treatment - spinner, flip a coin, names in a hat
Control all factors only - difference between groups should be treatment
Repeat - use enough subjects to make conclusion
Placebo
Fake Treatment
Placebo Effect
People respond to anything - response to dummy treatment
Statistically significant
Observed responses so large not by chance
Blocking
NOT stratified
Block
Group of experimental units that are known before the experient to be similar in some way that is expected to affect response to treatment
by gender
Randomized block design
Random assignment of experimental units to treatments is carried out separately within each block
Double Blind
Neither subject or those who interact + measure response know which treatment a subject has
A third party did the randomization
Single Blind
Either subjects will know treatment and those measuring response variable don’t (or vice versa)
Matched Pairs Design
Type of randomizes block design for comparing two treatments
Create blocks by matching pairs of similar experimental units
Chance is used to determine which unit in each pair gets each treatment
Sometimes, a “pair” in a matched pair deisgn consists of a single unit that receives both treatment. Since the order of the treatments can influence the response, chance is used to determine with treatments is applied first for each unit
Scope of Inference