PHYSICS PAPER 2 KEYWORDS
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Binding energy
The work required to seperate the nucleus into its constituent parts (i.e. protons and neutrons). The greater it is, the more stable the nucleus
Mass defect
The difference between the mass of the nucleus and the total mass of its individual parts
Einstein’s theory of relativity definition
States that mass and energy are related, and mass can be converted to energy and back. This is what happens in nuclear decay, when the products of a decay have lower mass than the original nuclei - the missing mass is converted to energy
Nuclear fusion
2 low-mass nuclei fuse together to create a larger nucleus. In this process the larger nucleus will, therefore, have a greater binding energy per nucleon than the low mass nuclei
Nuclear fission
A large unstable nucleus breaks apart into 2 smaller, more stable nuclei. The binding energgy per nucleon will also increase in this process
Moderator
controls the speed of the neutrons in the thermal nuclear reactor as the speed needs to be a specific value in order to induce fission. Graphite or water can be used and are chosen for their low probability of absorbing neutrons and low mass
Control rods
absorbs neutrons in the thermal nuclear reactor to ensure that there is only one thermal neutron per each fission event. They have the ability to absorb even more neutrons if the rate of release of energy needs to be reduced. The material is chosen on their ability to absorb neutrons effectively.
coolant
extracts the heat in the thermal nuclear reactor and allows it to be transferred to be used to produce electricity. It is usually water or carbon dioxide gas and is used due t the high specific heat capacity of the materials
Shielding in a nuclear reactor
The building housing the reactor is made of concrete walls in order to absorb neutrons and gamma radiation leaving the reactor. The reactor core is also constructed from steel in order to absorb beta radiation as well as some of the gamma radiation and neutrons
Emergency shutdown in a nuclear reactor
Reactors are constructed so that the control rods drop directly into the core to entirely cease fission events if the reactor gets too hot
Remote handling in a nuclear reactor
Fuel rods are operated by these devices
Storage in a nuclear reactor
Strict protocols are in place regarding how to store and transport radioactive waste
Rutherford’s scattering experiment
An ___ in 1908 which provided new evidence about the structure of the atom and resulted in the scientific community moving on from JJ Thomson’s plum pudding model of the atom and adopting Rutherford’s model
Radioactive decay
occurs when an atom is unstable and emits radiation to obtain a more stable state (it is a random process)
Activity
The number of unstabke nuclei that decay per second in a given sample
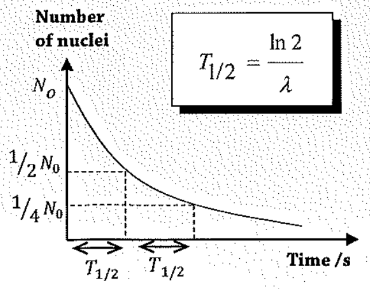
Half-life (T1/2)
the amount of time it takes for the activity of the substance to decrease to half its original value
Carbon dating
the examination of the amount of 14C left in a sample to determine its age as all living organism have a roughly equal ratio to 12C to 14C and when they die, the 14C slowly decays.
Inverse square law
When the intensity is indirectly proportional to its distance squared
Background radiation
A low level of radiation that is always around on Earth, from both natural and man-made sources of radiation
Natural - nuclear materials in ground, cosmic rays
Man-made - Buildings, nuclear power plants, medical nuclear applications
A nuclear stability graph
A plotting of isotopes by proton number (x-axis) against neutron number (y-axis), classifying them into beta - emitters, alpha emitters, beta + emitters and stable isotopes
Magnetic flux density
force per unit length per unit current on a current-carrying conductor at right-angles to a magnetic field
Fleming’s left hand rule
allows you to determine the direction of motion, field and current in relation to one another
Lenz’s law
the direction of induced current is always such that it is opposed to the change that causes the current
Faraday’s law
the induced emf in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage through the circuit
induced emf
the p.d. induced in a wire due to a moving changing magnetic flux
Cylcotrons
accelerate radioactive particles and control the direction of the particle beams in order to accurately hit the target area on a patient - used in medical machinery to provide radiotherapy treatment
magnetic flux
magnetic field strength through an area
magnetic flux linkage
magnetic field strength through a coil of wire - the flux is multiplied by the number of turns in the coil
Capacitor
an electrical device that stores charge - useful for storing energy and ‘smoothing‘ AC signals in power generation
Capacitance
charge stores per unit p.d.
Dielectrics
any insulating materials which store a charge - tend to be good electrical insulators
Parallel plate capacitor
comprised of 2 parallel conducting plates with a dielectric in between them
relative permittivity (dielectric constant)
ratio of capacitance of the dielectric to the capacitance of the same volume of free space
Time constant (RC)
the time taken for the initial charge, current or voltage to fall to e-1 (= 0.37) of its initial value, the unit is the second
T1/2
time taken for half the charge to discharge from the capacitor
Coulomb’s law
gives the electric force between 2 charges
Electric fields
arise due to a charged object and can be represented by field lines that show the path a positive charge would take if placed in the field. It exerts an electrostatic force.
Electric field strength
defined as the force, F, per unit charge, Q, in the field
Electric potential, V
work done per unit charge on a positive charge when it is moved to a given position from infinity. it is zero at infinity
permittivity of free space
the name of a constant ε0 which = 8.85 × 10-12 Fm-1
Force field
A region in which a body experiences a non-contact foce. It can be represented by a vector
Radial field
A field that is spherical and acts towards a central point e,g, gravitational fields
Uniform field
A field that has no variation e.g. gravitational fields near the surface of planets
Gravitational field strength
th force F per unit mass m on an object in a uniform gravitational field
Gravitational potential energy Ep
The energy possessed by an object due to its place in a gravitational field. This of an object will be zero at infinity as the effects of the gravitational field will be negligible at this distance
Gravitational potential V
The gravitational potential energy per unit mass = work per unit mass to moe an object from infinity to that point. This is zero at infinity
Gravitational potential difference
The difference in gravitational potential between 2 points in space
Equipotential surface
Surfaces of constant potential e.g. orbits
Geostationary satellite
A ____ that has an orbital period around Earth’s equator of one day (24 hours), having a fixed position above the equator. The distance above Earth can be found suing Kepler’s 3rd law. Used in communications and navigation systems e.g. satnav
Synchronous orbit
A specific orbit taken by a satellite where the orbital period is the same as the rotational period and in the same direction of rotation as the object it’s orbitting
Escape velocity
Minimum velocity required for an object to escape the gravitational field of a planet
Specific latent heat of fusion
The ___ for a change from a solid to a liquid, or vice versa
Specific heat of vaporisation
The ___ for a change from a liquid to a gas, or vice versa
Gas laws
A set of experimental laws that look at the relationship between pressure, volume and temperature of a gas
Molar mass
The mass of one mole of substance in kg mol-1
Molecular mass
The mass of a molecule in u
Absolute zero
-273 oC - where the object will have minimum internal energy
Internal energy
the sum of the randomly distributed kinetic energies and potential energies of particles in a system or body
First law of thermodynamic
the change of internal energy of the object is equal to the total energy transfer due to work done and heating
Brownian motion
describes the erratic motion of a small particle when placed on the surface of a fluid. The molecules on the surface of the fluid move randomly on the surface and hit into the particle, making the particle move randomly on the surface - this produces ___, providing evidence for the molecular kinetic energy.
Pressure law
As T is increased in a contained with fixed V, the average speed of molecules increases. This causes molecules to impact the walls of a container with greater force, and p increases. p is directly proportional to T
Charles’ law
As T is increased in a flexible container, the faster moving molecules impact the walls of the container with greater force. If the walls are movable, this increase V while p remains the same. V is directly proportional to T
Boyle’s law
In a case where T is constant, but V is decreased, moleucles have less space to move in between coliisions. This increases the number of collisions, so the total force on the walls of the contained increases, increasing p. p is directly proportional to 1/V
Centripetal force
Causes an object to maintain circular motion - always acts towards the centre of rotation
Simple harmonic motion
Any oscillating motion whose acceleration is proportional to its displacement and opposing in direction to the displacement
Damped Oscillations
____ of systems that will eventually lose their amplitude and energy due to resistance from friction or air resistance
Light damping
Where the time period of an oscillation is independent of the amplitude and, therefore, each wave cycle takes the same amount of time for oscillations to decrease
Critical damping
When the minimum amount of ____ for the system’s oscillation to stop over the course of one oscillation after being released
Heavy damping
____ that is stronger than critical ___ and causes the system to return to equilibrium in a longer amount of time than with critical ___.
Free oscillation
An ____ of a body or system that moves with its natural frequency and is not acted upon by external influence
Forced oscillation
An ___ of a body or system that is initiated by an external influence
Resonance
The situation when the periodic force driving the forced oscillation is in phase with the frequency of the oscillating system
Resonance for light damping
The resonant frequency (frequency at max amplitude) will be the same as the natural frequency. The max amplitude at resonance will be greater
Resonance for heavier damping
The amplitude at resonance reduces. Frequency at which resonance occurs decreases