Amine Preparation via Nucleophilic Substitution
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What is the name of the reaction mechanism used to prepare amines from halogenoalkanes?
Nucleophilic Substitution.
What type of amine is produced when a halogenoalkane reacts with ammonia?
A primary amine (1° amine).
Write the overall equation for the reaction of bromoethane with excess ammonia.
CH₃CH₂Br + 2NH₃ → CH₃CH₂NH₂ + NH₄⁺Br⁻
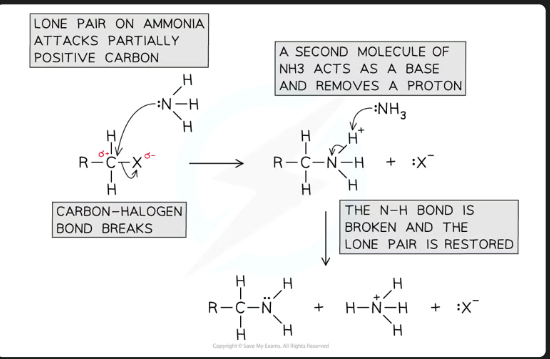
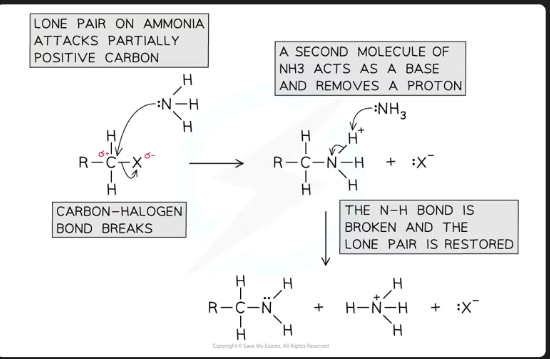
What is the initial product formed when ammonia attacks a halogenoalkane, before deprotonation?
An alkylammonium salt (e.g., R-NH₃⁺ X⁻).
Why is it essential to use excess concentrated ammonia in this reaction?
To suppress further substitution and prevent the primary amine from reacting with another halogenoalkane to form secondary and tertiary amines. This ensures the primary amine is the major product.
What type of amine is produced when a halogenoalkane reacts with a primary amine?
A secondary amine (2° amine).
What solvent is typically used for this reaction?
Ethanol
Explain why a mixture of amines is formed with limited ammonia.
The primary amine (RNH₂) is formed first.
If ammonia is limited, there will be significant amounts of the primary amine present.
This primary amine can itself act as a nucleophile and attack another molecule of the halogenoalkane, leading to the formation of a secondary amine (R₂NH). This process can continue to form tertiary amines (R₃N) and quaternary salts.
What is the role of ammonia in the second step?
It acts as a base to deprotonate the alkylammonium salt.