Terms for analyzing visual texts
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For Paper 1 and graphic novels on Paper 2
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
1
New cards
Types of visual (elements in) texts
* Photograph
* Drawing/illustration
* Image
* Portrait
* Graphic
* Abstract/figurative landscape
* Brochure
* Pamphlet
* Painting
* Graffiti
* Flyer
* Drawing/illustration
* Image
* Portrait
* Graphic
* Abstract/figurative landscape
* Brochure
* Pamphlet
* Painting
* Graffiti
* Flyer
2
New cards
Medium
Definition: The material or form used by an artist
Examples: pen and ink, water color, digital, photography
Effect: Different mediums impacts readers differently based on connotations and level of realism
Examples: pen and ink, water color, digital, photography
Effect: Different mediums impacts readers differently based on connotations and level of realism
3
New cards
Motif
The literal content (without analyzing the meaning)
4
New cards
Setting
The context in which a story takes place, including time, place, and social environment. It can affect the plot and characters' behavior.
5
New cards
Narrative
Type of writing that tells a story with characters, plot, and setting. Often includes a conflict and resolution. Can be fiction or non-fiction.
6
New cards
Action
The art of storytelling, either in written or spoken form, which includes the description of events, characters, and settings in a logical sequence.
7
New cards
Focus
* Background
* Foreground
* Dimension
* Depth
* Symmetry
* Intersection and direction of lines
* The one-point perspective construction with convergence of the receding horizontals at the horizon
* Foreground
* Dimension
* Depth
* Symmetry
* Intersection and direction of lines
* The one-point perspective construction with convergence of the receding horizontals at the horizon
8
New cards
Perspective/vantage point/angle
* Birds-eye view: High angle which can show dominance
* Frog’s perspective: Low angle which can show submission
* Eye level
* Frog’s perspective: Low angle which can show submission
* Eye level
9
New cards
Framing
* Close up shot (heads and shoulders)
* Mid/medium shot (upper part of a person’s body)
* Long distance shot (full person showing long distance or depth)
* Mid/medium shot (upper part of a person’s body)
* Long distance shot (full person showing long distance or depth)
10
New cards
Shades
* Contours (outline)
* Light
* Shadow
* Contrast
* Tones
* Colors
* Monochrome
* Blurred
* Light
* Shadow
* Contrast
* Tones
* Colors
* Monochrome
* Blurred
11
New cards
Clustering, repetition and patterns
Techniques used to analyze visual texts. Clusters of elements may tie them together and create an effect. Repetition emphasizes key elements. Patterns show relationships between elements.
12
New cards
Body language, facial expressions and eye contact
If characters are present in the visual text, their body language, facial expressions and potential eye contact can impact the tone/atmosphere of the text. E.g. direct eye contact and a strong build may make the reader feel threatened.
13
New cards
Symbolic values
Of objects, colors in the text
14
New cards
Denotation vs connotation
Denotation = literal meaning
Connotations = socio-cultural and personal associations
Connotations = socio-cultural and personal associations
15
New cards
Cultural codes
Cultural codes are visual cues, symbols, and references that are used in visual texts, such as advertisements, films, and art, to convey cultural meaning and create a connection with the audience. These codes can include colors, images, clothing, and gestures that are associated with specific cultural values, beliefs, and stereotypes. Understanding cultural codes is important for analyzing and interpreting visual texts and their intended messages.
16
New cards
Tone, atmosphere, attitude
The tone, atmosphere, and attitude in visual texts refer to the emotions and feelings that the image conveys to the viewer. It can be created through the use of color, lighting, composition, and other visual elements. The tone can be serious, playful, somber, or any other emotion that the artist wants to evoke in the viewer. The atmosphere is the overall feeling of the image, while the attitude is the artist's perspective or opinion about the subject matter.
17
New cards
Design
The design (layout, look, color, overall artistic impact) of a visual text can create certain connotations that affect how the reader views the text.
E.g. a traditionally professional design can build ethos.
E.g. a traditionally professional design can build ethos.
18
New cards
Interplay of words and images in composite texts
* Text anchorage: the text steers the interpretation of the image
* The primacy of the text
* Relay: text/image relationship which is complimentary
* Text and image oppose each other
* The primacy of the text
* Relay: text/image relationship which is complimentary
* Text and image oppose each other
19
New cards
Layout
* Size and positioning of objects
* Construction
* Left to right and top to down
* Normal reading and scanning pattern for English-speaking countries
* Lines
* Often used to provide directions and paths for the eye to follow
* Construction
* Left to right and top to down
* Normal reading and scanning pattern for English-speaking countries
* Lines
* Often used to provide directions and paths for the eye to follow
20
New cards
Font
What we use
21
New cards
Typeface
Definition: What words look like visually
Effect: Creates mood and atmosphere depending on style and associations
Effect: Creates mood and atmosphere depending on style and associations
22
New cards
Typography
Definition: Size and style of typeface
Examples: Modern, strong, crisp, sharp, classical, professional, rounded, soft, humorous, bold types, etc.
Effect: Depends from person to person, as it is subjective. Sparks a certain emotion in the reader which supports the writer’s purpose.
Examples: Modern, strong, crisp, sharp, classical, professional, rounded, soft, humorous, bold types, etc.
Effect: Depends from person to person, as it is subjective. Sparks a certain emotion in the reader which supports the writer’s purpose.
23
New cards
Posed/staged
When the element being photographed is directed by the photographer to sit, stand, move, etc. in a specific way.
Affects how the photograph is received. Overly posed might have a negative effect on the viewer.
Affects how the photograph is received. Overly posed might have a negative effect on the viewer.
24
New cards
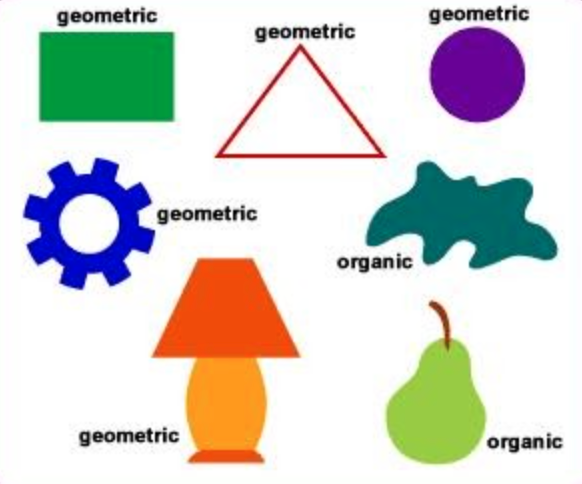
Geometric vs. organic shapes
Geometric: Closed figures created using points, line segments, circles and curves. Based on math principles.
Organic: Curvilinear in appearance, similar to those found in nature such as plants, animals and rocks. Not as constrictive.
Organic: Curvilinear in appearance, similar to those found in nature such as plants, animals and rocks. Not as constrictive.
25
New cards
Caricature
Definition: A picture, description or imitation of a person or group in which certain striking characteristics are exaggerated.
Effect: Either humor or grotesque, depending on the creator’s purpose (entertain or criticize)
Effect: Either humor or grotesque, depending on the creator’s purpose (entertain or criticize)

26
New cards
Serif-font
Have lines (or feet) at the end of strokes

27
New cards
Sans-serif/non-serif fonts
The lines and strokes of the typeface end cleanly without any additional flare.

28
New cards
Script, novelty, ornamental or decorative fonts
Artistic fonts with unique shapes and personalities.
Tend to have stronger character than traditional serif or sans-serif fonts.
Tend to have stronger character than traditional serif or sans-serif fonts.
