More INvestments
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Roles of Primary and Secondary Markets
Primary market: Where new securities are issued and sold for the first time (IPO, seasoned equity offering). Firms raise capital here.
Secondary market: Where existing securities are traded among investors. Provides liquidity and price discovery.
What is Risk?
The possibility that actual returns will deviate from expected returns. It reflects uncertainty in outcomes.
Concepts of Return
Income: Dividends, interest, rental payments
Capital gains/losses: Difference between purchase price and selling price.
Rate of return:
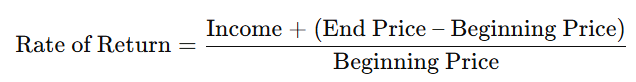
Definition of Portfolio
A collection of financial assets (stocks, bonds, cash equivalents) held by an investor.
Efficient Market Concept
Security prices reflect all available information. In an efficient market, it’s impossible to consistently achieve returns above average without taking extra risk.
Round lot vs. Odd lot
Round lot: Standard trading unit, usually 100 shares.
Odd lot: Fewer than 100 shares.
Determination of Securities Prices
Set by supply and demand in securities markets; influenced by economic conditions, company performance, and investor expectations.
Cash vs. Margin Accounts
Cash account: Investor pays full cost of securities.
Margin account: Investor borrows part of purchase price from broker (leverage).
Elements of a Short Sale
Borrowing shares, selling them in the market, and buying back later (hopefully at a lower price) to return to lender. Risk: unlimited potential loss.
Role of the SEC
Regulates securities markets, enforces securities laws, ensures fair disclosure and protects investors.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (2002)
Corporate governance reform: CEO/CFO accountability, internal control standards, limits on auditor conflicts of interest.
Role of SIPC
Protects investors against loss of cash/securities from failed brokerage firms (not market losses). Coverage up to $500,000 (with $250,000 limit for cash).
Compounding & Discounting
Compounding: Future value of present money.
Discounting: Present value of future money.
Annuity
Series of equal payments made at fixed intervals.
Ordinary annuity: Payments at end of period.
Annuity due: Payments at beginning of period.
Future Value (FV) & Present Value (PV) Concepts
FV = Value at a future date of a current cash flow.
PV = Current value of a future cash flow discounted at an appropriate rate.
Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)
Weak form: Prices reflect past market data.
Semi-strong form: Prices reflect all publicly available info.
Strong form: Prices reflect all information, public and private.
Personal Financial Statements
Balance sheet: Assets, liabilities, net worth.
Income statement (cash budget): Inflows (income) vs. outflows (expenses).
Capital Gains/Losses
Capital gain: Sell price > purchase price.
Capital loss: Sell price < purchase price.
Short-term (ST): Held ≤ 1 year, taxed as ordinary income.
Long-term (LT): Held > 1 year, usually lower tax rate.
Tax Shelters
Retirement accounts, municipal bonds, real estate depreciation.
Tax Avoidance vs. Tax Evasion
Avoidance: Legal minimizing of taxes.
Evasion: Illegal underreporting or hiding income.
Traditional vs. Roth IRA
Traditional: Contributions tax-deductible, withdrawals taxed.
Roth: Contributions not deductible, withdrawals tax-free (if qualified).
Expected, Required, Realized Returns
Expected: Forecasted return.
Required: Minimum acceptable return given risk.
Realized: Actual return earned.
Systematic vs. Unsystematic Risk
Systematic (market risk): Non-diversifiable, affects all securities (interest rates, inflation, recessions).
Unsystematic (firm-specific): Diversifiable, unique to company/industry (management decisions, strikes).
Measurement of Risk
Standard deviation: Measures total risk (variability of returns).
Beta coefficient: Measures systematic risk relative to the market.
Efficient Frontier Concept
Set of portfolios offering highest expected return for given level of risk.
Beta Values
β = 1: Security moves in line with market.
β < 1: Less volatile than market (defensive stock).
β > 1: More volatile than market (aggressive stock).