Plants and photosynthesis
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the word equation for photosynthesis
Water + carbon dioxide —sunlight—> glucose + oxygen
What absorbs light energy in the leaf
Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts
Which is the by product of photosynthesis- oxygen or glucose
Oxygen
What are the uses of glucose in a plant
Transformed into cellulose, proteins and oils / stored as starch / Used in respiration to release energy
What 3 factors affect photosynthesis
Temperature / Light intensity / Carbon dioxide
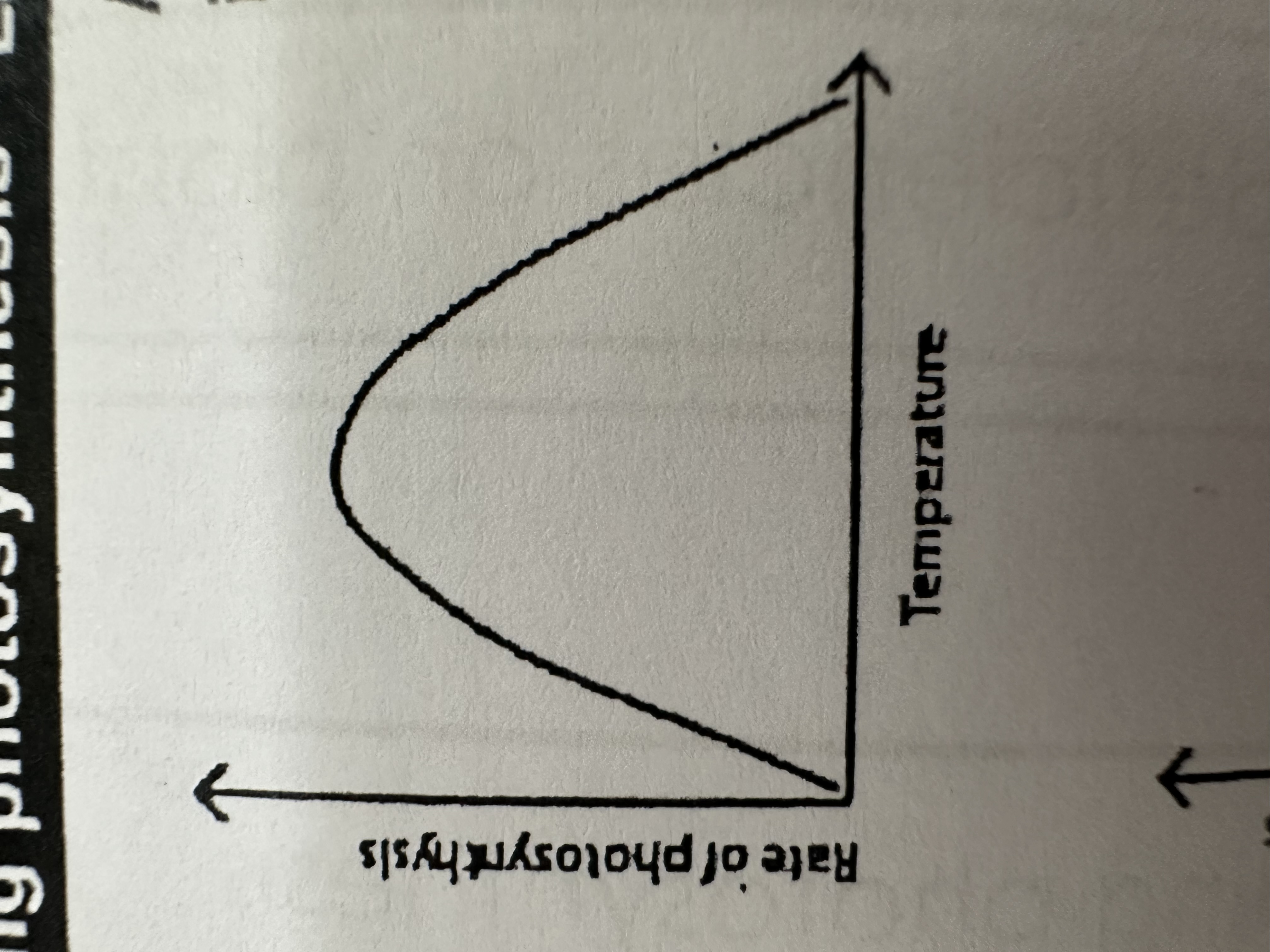
When temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis…. ,because…
Increases to an optimum then decreases because photosynthesis is controlled by enzymes and their activity increases until they denature.
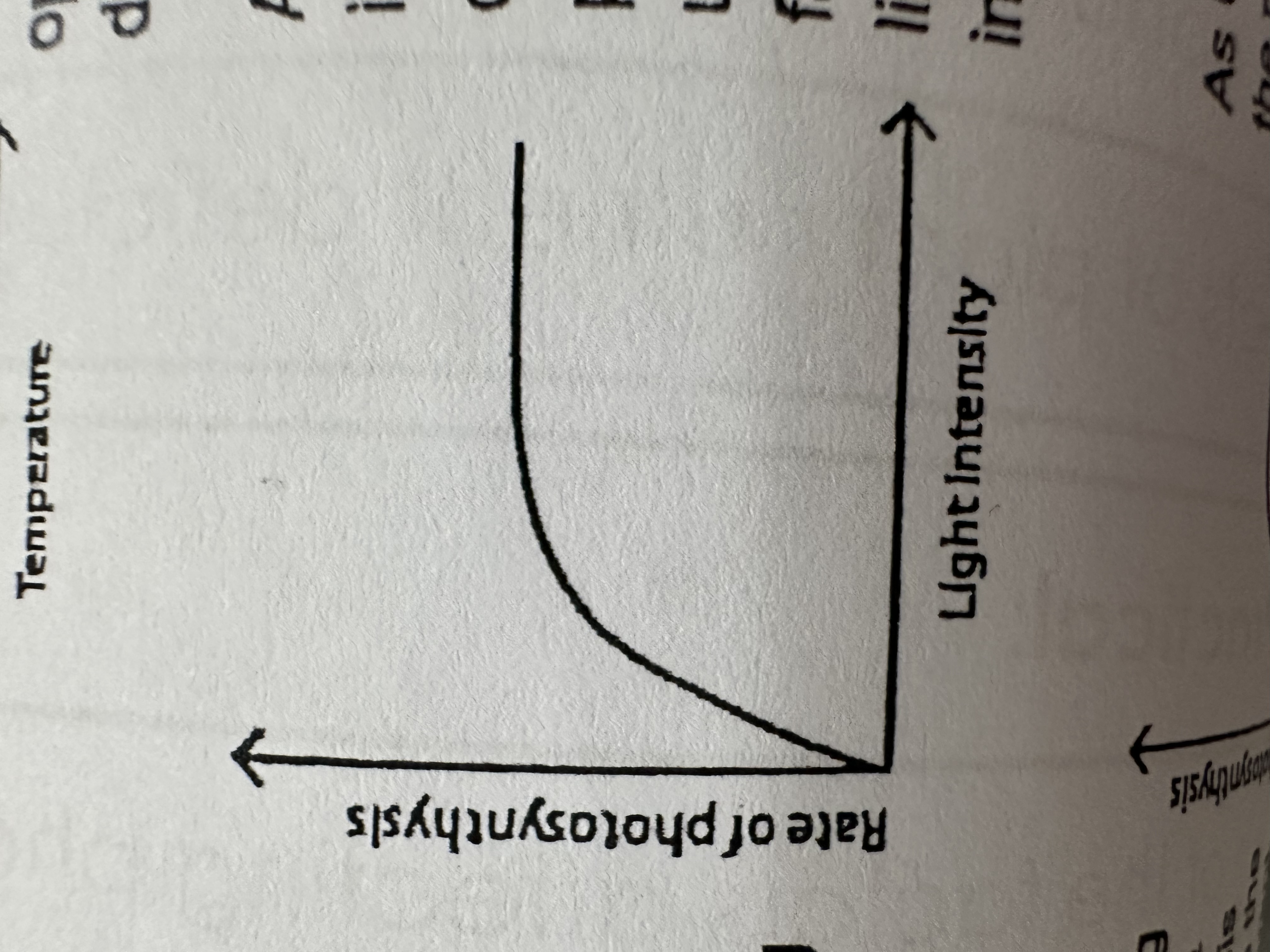
When light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis… until…
Increases until lack of another factor e.g. Carbon Dioxide limits any further increase.
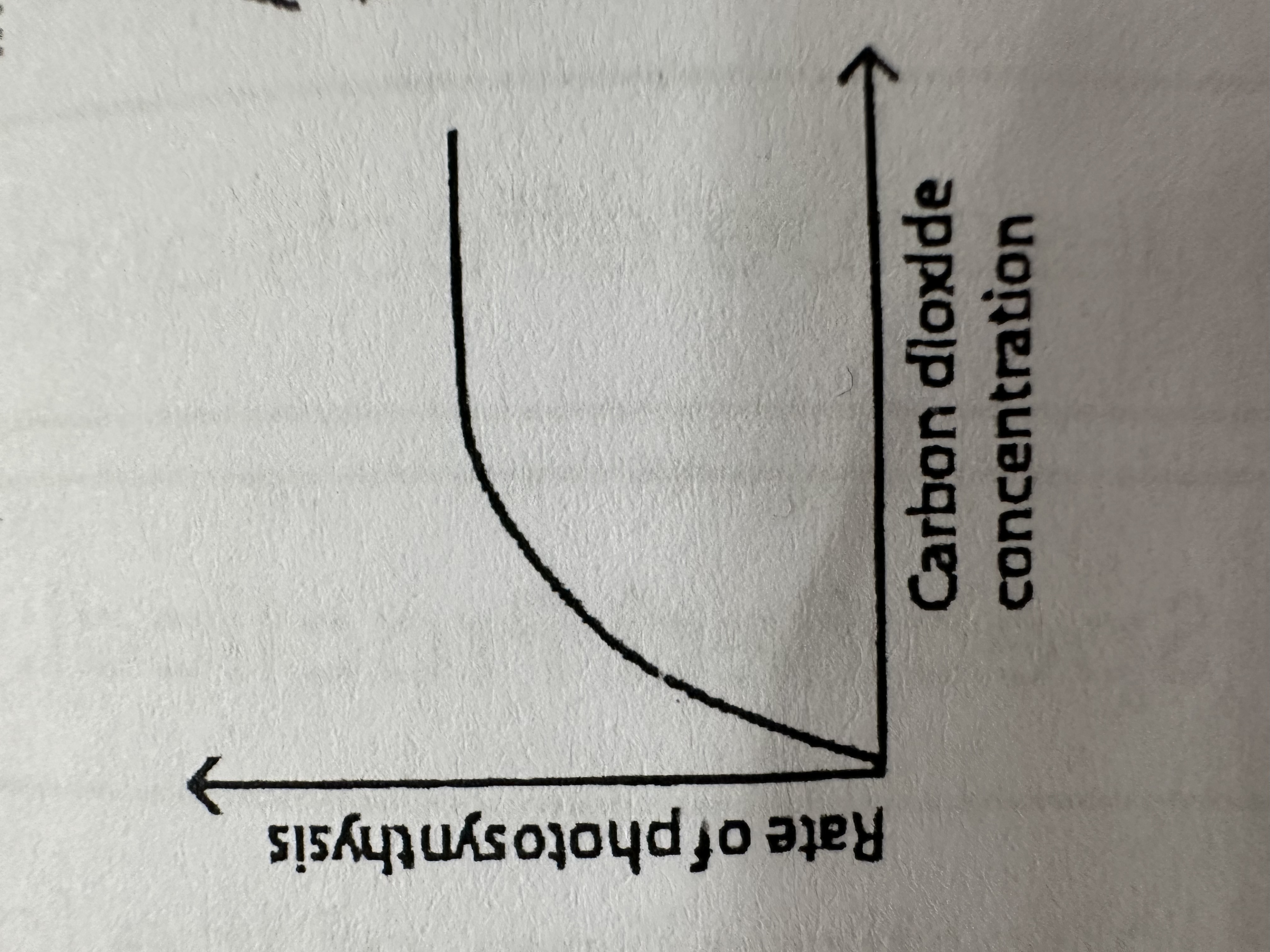
When Carbon Dioxide increases, the rate of photosynthesis… until…
Increases until lack of another factor e.g. light intensity limits any further increase.
How is the rate of photosynthesis measured when investigating the affect of temperature?
Recording the volume of oxygen produced in different temperatures
How is the rate of photosynthesis measured when investigating the effect light intensity?
By moving a plant closer to a light source and recording the O2 produced
How is the rate of photosynthesis measured when investigating the effect of carbon dioxide?
Enclose the leaf in a transparent bag/jar with sodium hydroxide this chemical absorbs CO2.
What are the stomata
Made of guard cells and can open and close to allow gas exchange in the day and prevent water loss at night
How do we test a leaf for starch?
Leaves kept in the dark for 24 hrs are destarched. They can the be used to investigate photosynthesis in different conditions. If a plant has been photosynthesising its leaf will contain starch.
The test:
1. Boil the leaf to kill it
2. Decolorise using ethanol
3. Wash to soften
4. Test with iodine- a blue/black colour shows the presence of starch.

A nitrate deficiency causes plants to have
Poor growth
A potassium deficiency causes plants to have
Yellowing of leaves
A phosphate deficiency causes plants to have
Poor root growth
Water is used in…
Photosynthesis, transport of minerals and provides support by filling the cell vacuoles.
Cell vacuoles keep cells… and prevents…
turgid and prevents cells becoming flaccid and wilting
Water from the xylem evaporates into…/ Some water vapour is lost from the… in …
Air spaces / stomata in transpiration
Water can also be used for…
Photosynthesis
What is transpiration
The loss of water vapour by evaporation from the leaves of plants
What 4 factors affect the rate of transpiration
Temperature / humidity / wind speed / light intensity
What does the phloem do
Transport of sucrose in all directions - translocation
What happens to sucrose when it leaves the phloem
It can be converted to starch or glucose
How does sucrose get into the phloem
Neighbouring cells, companion cells, contain many mitochondria to actively transport it into the phloem
Where does sucrose come from
Glucose produced in photosynthesis
Xylem vessels are vessels are adapted to allow water to move easily from the… to…
Roots to the leaves
Does the xylem carry water up or down the plant
Up the plant only
What is transpirational pull
Water diffuses out of the leaves via the stomata then more water is pulled up to fill the space
Minerals are actively transported into root hair cells which allows water to be drawn by…
Osmosis into the root cells then to the xylem
The active transport needed to transport minerals into root hair cells means that the cells are actively ___ requiring lots of ___
Respiring / oxygen
What is glucose used for
Respiration -release energy / cellulose- cell walls / starch- storage / amino acids - build plant proteins / lipids- store energy inside seeds.
Excess glucose made by a leaf is stored as..
Starch (one use)
What colour does iodine turn in the presence of starch
Blue/black
What is a control variable
Something you keep the same
What is the function of the waxy cuticle
The waxy layer reduces evaporation from leaf surfaces.
What is the upper epidermis
A thin layer of cells that are transparent to allow light to reach photosynthesising cells.
What is the function of the palisade mesophyll
Top of the leaf, contains many chloroplasts (maximise light absorption)-tightly uniform packed
What is the function of the spongy mesophyll layer
Contains air spaces between cells to allow the movement of gases
What is the function of air spaces
To allow carbon dioxide and oxygen through the leaf
What do guard cells do
They can close to prevent excessive water loss by evaporation in dry conditions.
What does the stomata do
It allows gases to move in and out of the leaf and allows water vapour to diffuse out of the leaves, maintaining the forward movement of water in the xylem.
What is the Formula for transpiration rate
Distance moved/Time taken
How do we estimate transpiration rate using a potometer?
