Electronegativity and bond polarity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is electronegativity ?
Ability of an atom to attract the bonding electrons in a covalent bond
What causes an attraction for electrons (electronegativity)?
A positive atomic core ( atom has lost outer electrons)
What is core charge ?
The resultant of the positive charge on protons and the negative charge on the outer electrons
How do you calculate core charge ?
Charge of nucleus (protons) (-) electrons on all of the inner shells (ignore outer shell electrons ).
They cancel each other out until you are left with a charge of positive or negative and a number of charge .
What 2 factors increase electronegativity ?
Higher core charge .
The group number is the core charge , but if a transition metal you have to calculate it . E.g : group 1 have a +1 core charge attracting the shared electrons.
Smaller size of atom . With less shells of electrons the core of the atom is closer to the shared electrons , giving it greater attraction to the shared electrons , therefore it pulls them forwards itself more
What are the 2 trends of electronegativity in the periodic table as a result of increasing electronegativity factors ?
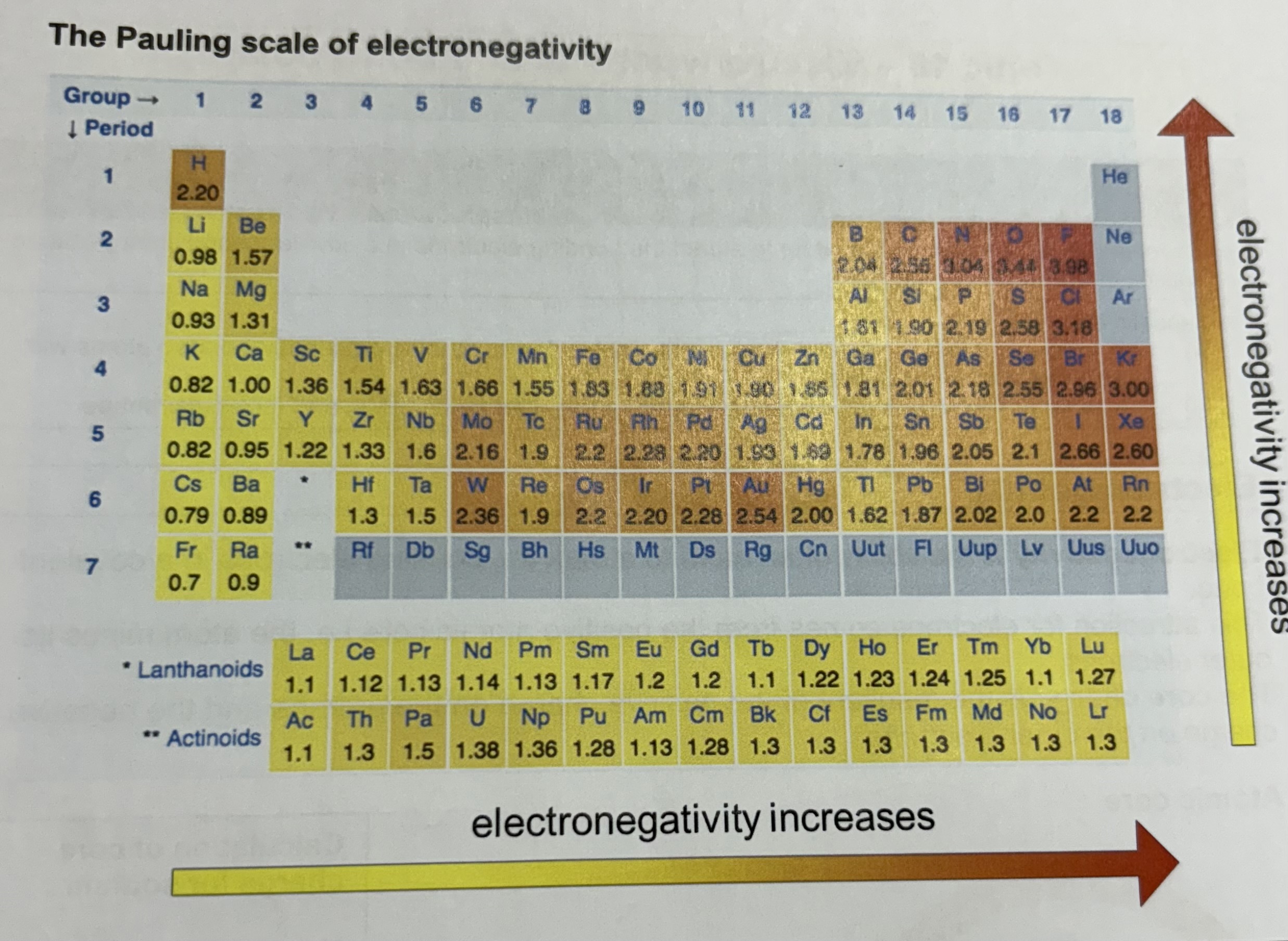
Electronegativity increases from left to right across the periodic table
Electronegativity decreases down a group
What is the Pauling scale of electronegativity ?
What is a permanent dipole and where are they found ?
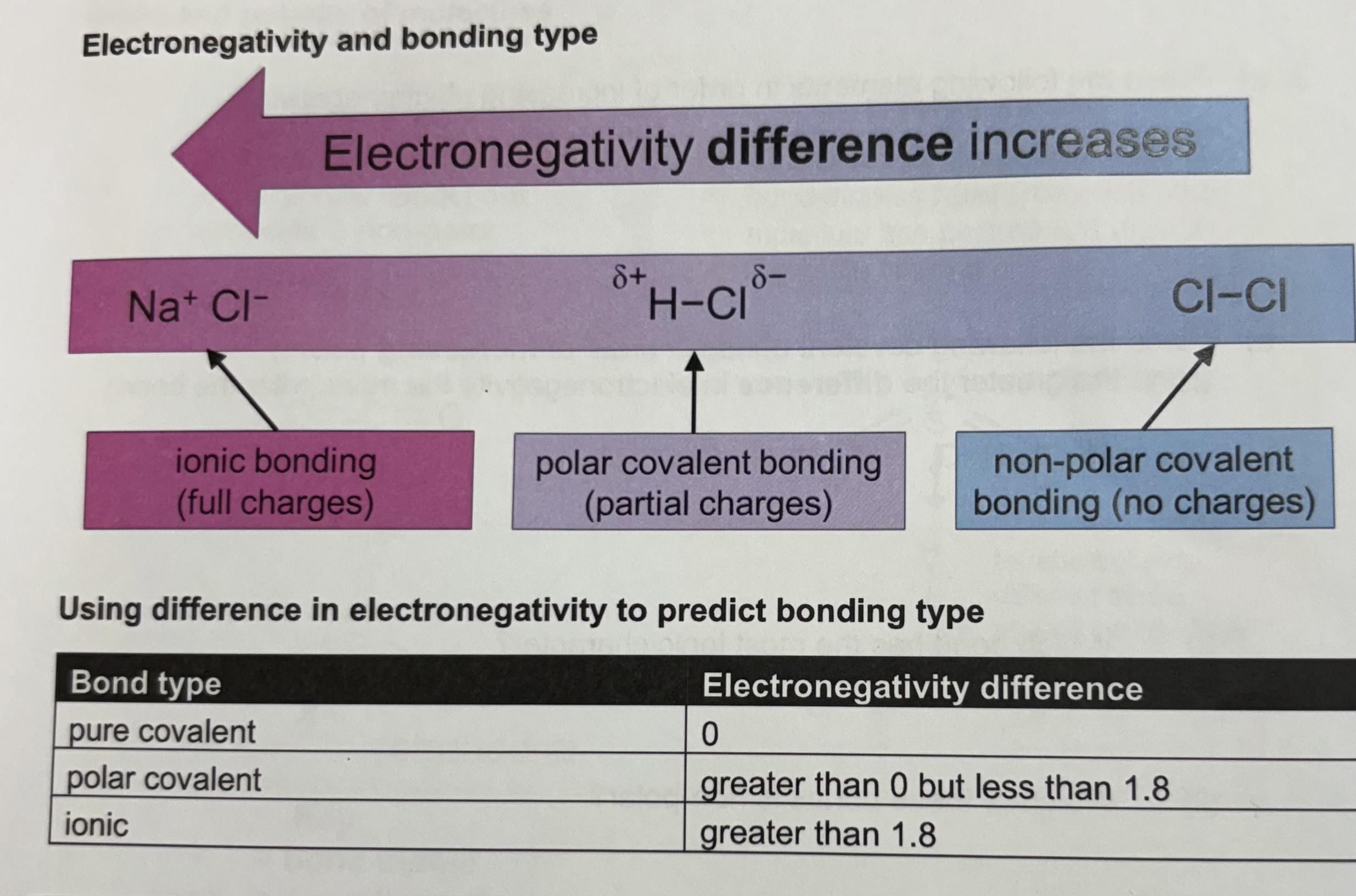
A small charge difference across a bond that results from a difference in the electronegatives of the bonded atoms .
They are in polar covalent bonds .
How does electronegativity relate to bonding type ?
What is a polar molecule?
A molecule that has an overall dipole taking into account any dipoles across the bonds .
What 2 things must a molecule have to have a permanent dipole ?
Difference in electronegativity between atoms in its bonds
Must not be totally symmetrical
What are bond dipoles ?
Dipoles across individual bonds within a molecule
What is an overall dipole ?
The dipole that can result from the addition of all the bind dipoles in a molecule
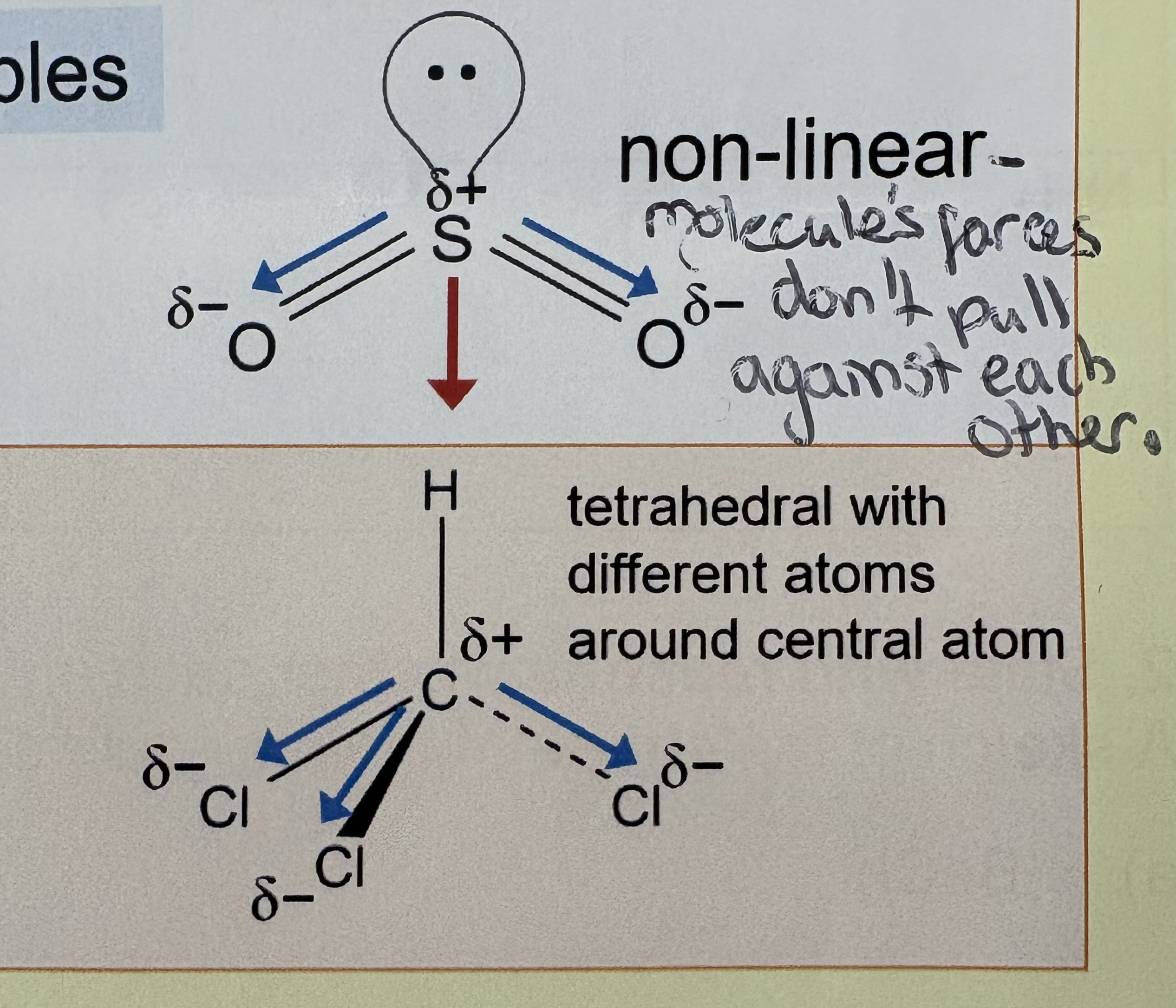
How can a molecule have no overall dipole ?
Symmetrical molecule
Bond dipoles cancel out
Non-polar
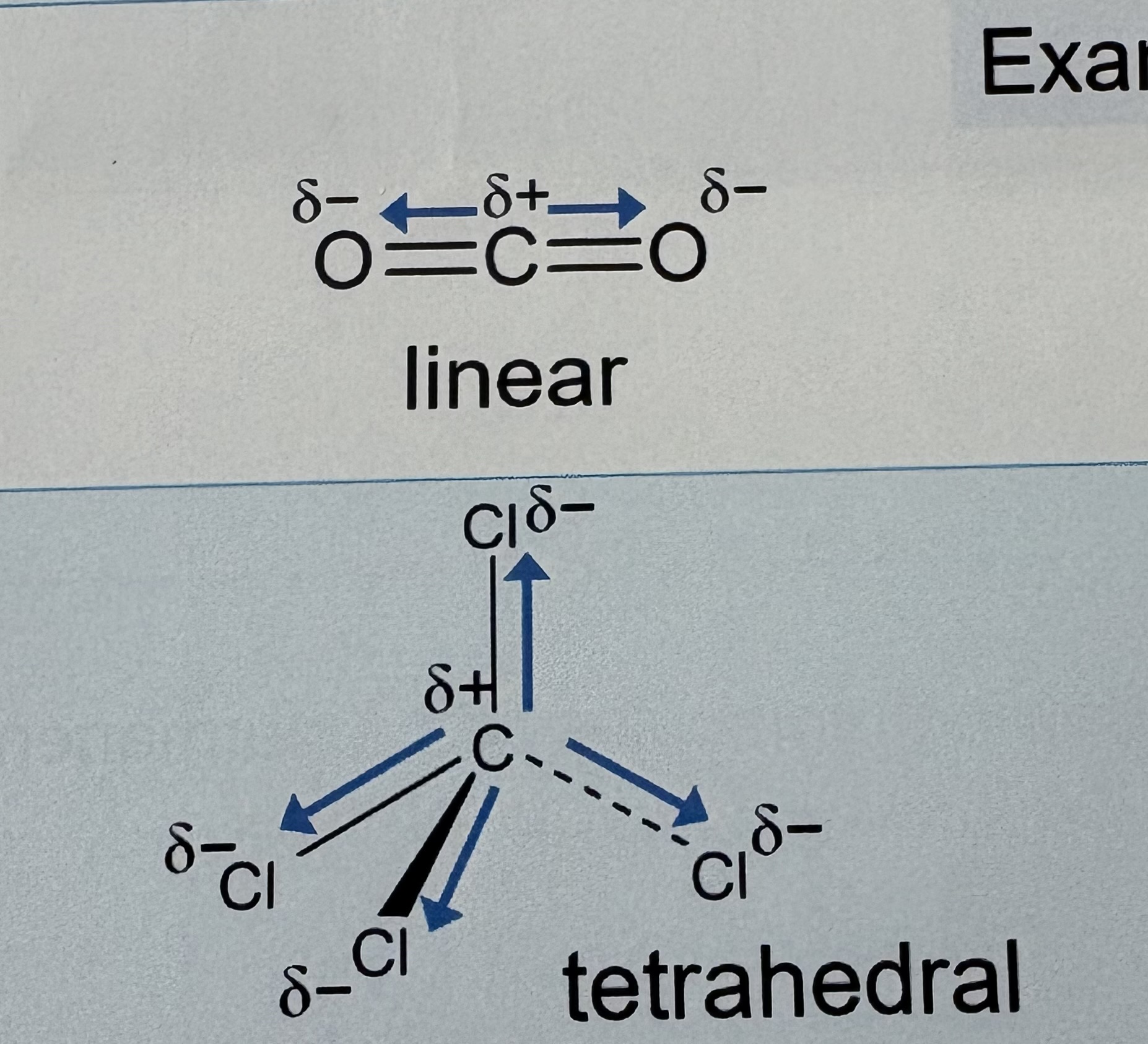
How can a molecule have an overall dipole ?
Not totally symmetrical
Bond dipoles reinforce each other
Molecule has a permanent dipole
Molecule is polar
What are induced dipoles ( London forces ) and how do they happen ?
Happen in most non-ionic substances
Electrons are evenly distributed but always moving in a compound with little to no electronegativity
Random movement means a dipole will form
This will induce a dipole in neighbouring molecules
What 2 factors effect the strength of induced dipoles ?
Number of electrons- the more electrons, the stronger the forces are
Shape- The larger the surface area is, the more contact there is to transfer the dipole forces
When does hydrogen bonding occur ?
When there is a large difference in electronegativity
Hydrogen bonds to nitrogen , oxygen or fluorine
What does hydrogen bonding cause and why ?
Causes unusually high boiling points
Causes water to be less dense than ice
As it is the strongest type of bonding out of all of the intermolecular forces