N245: Inflammation, Tissue Repair, and Wound Healing
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
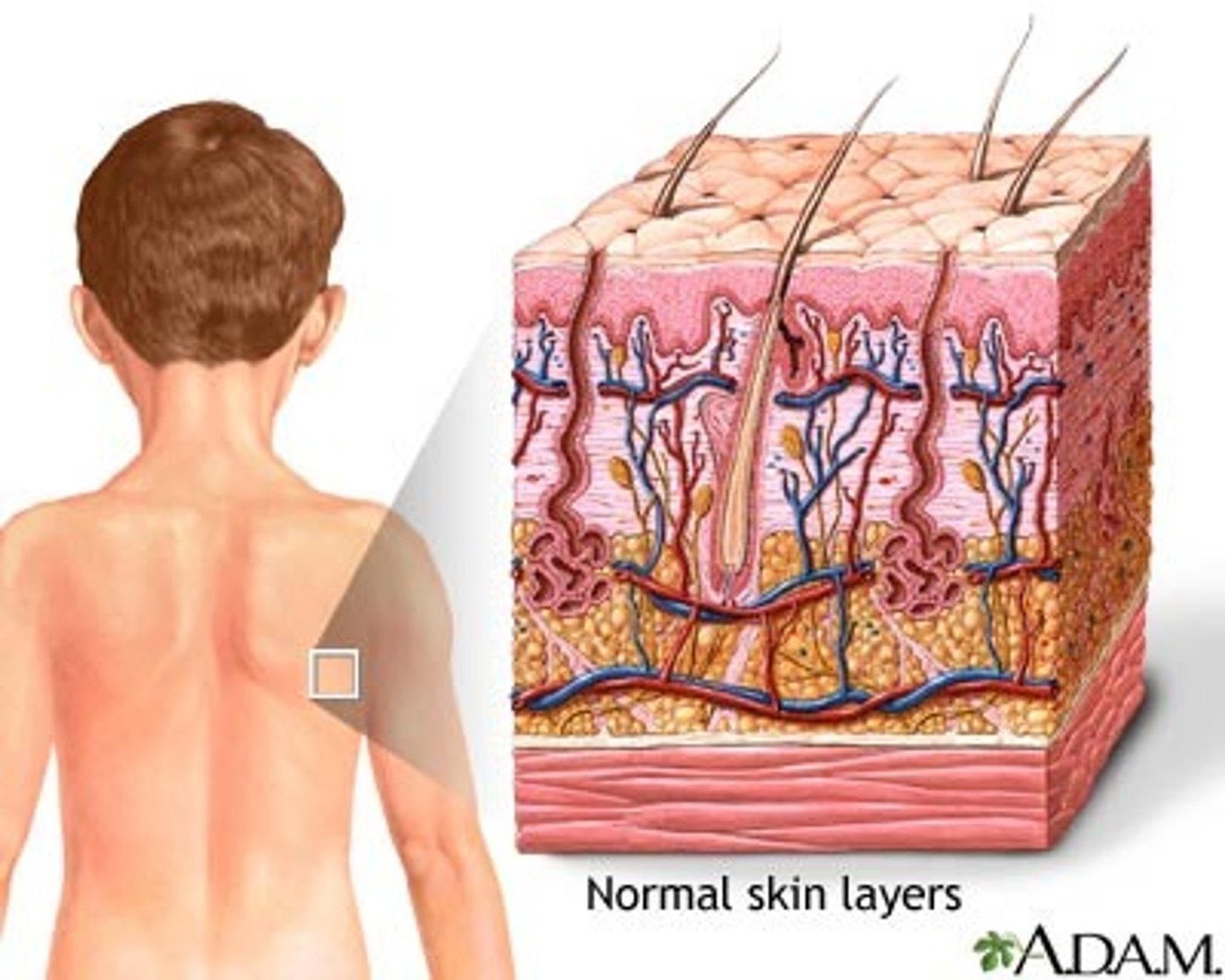
What is the first line of defense?
Skin, mucous membranes (and their secretions)
What is the second line of defense?
Includes the inflammatory process and immune system response
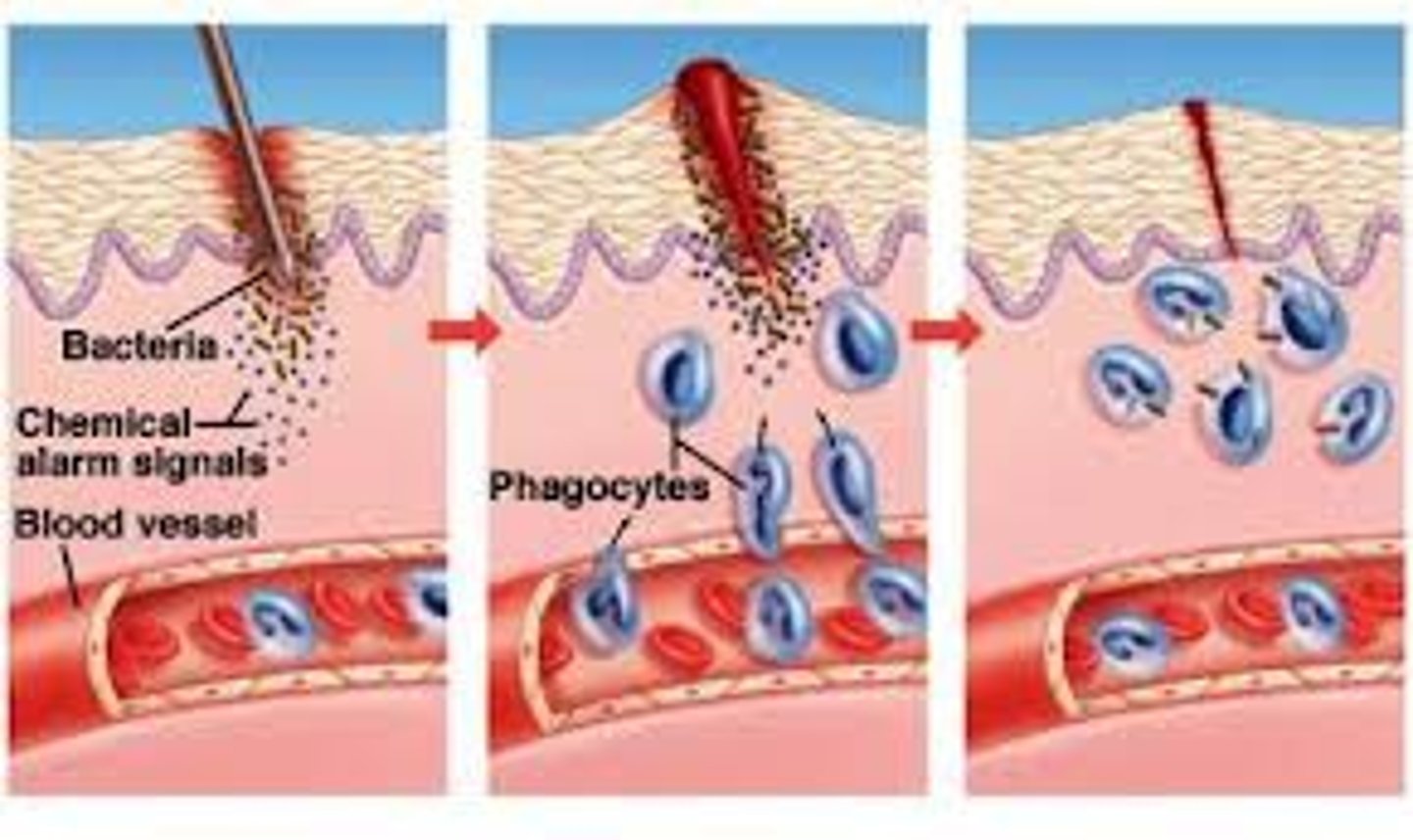
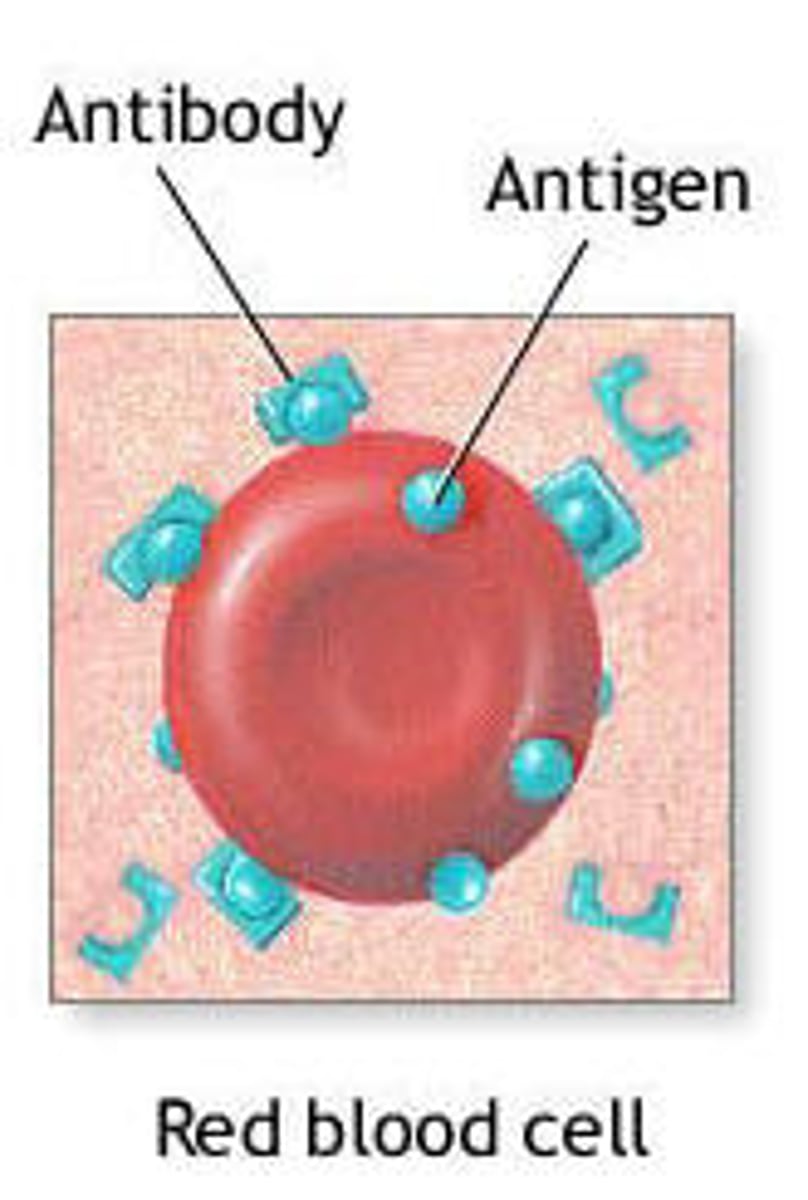
What is the third line of defense?
The production of specific antibodies
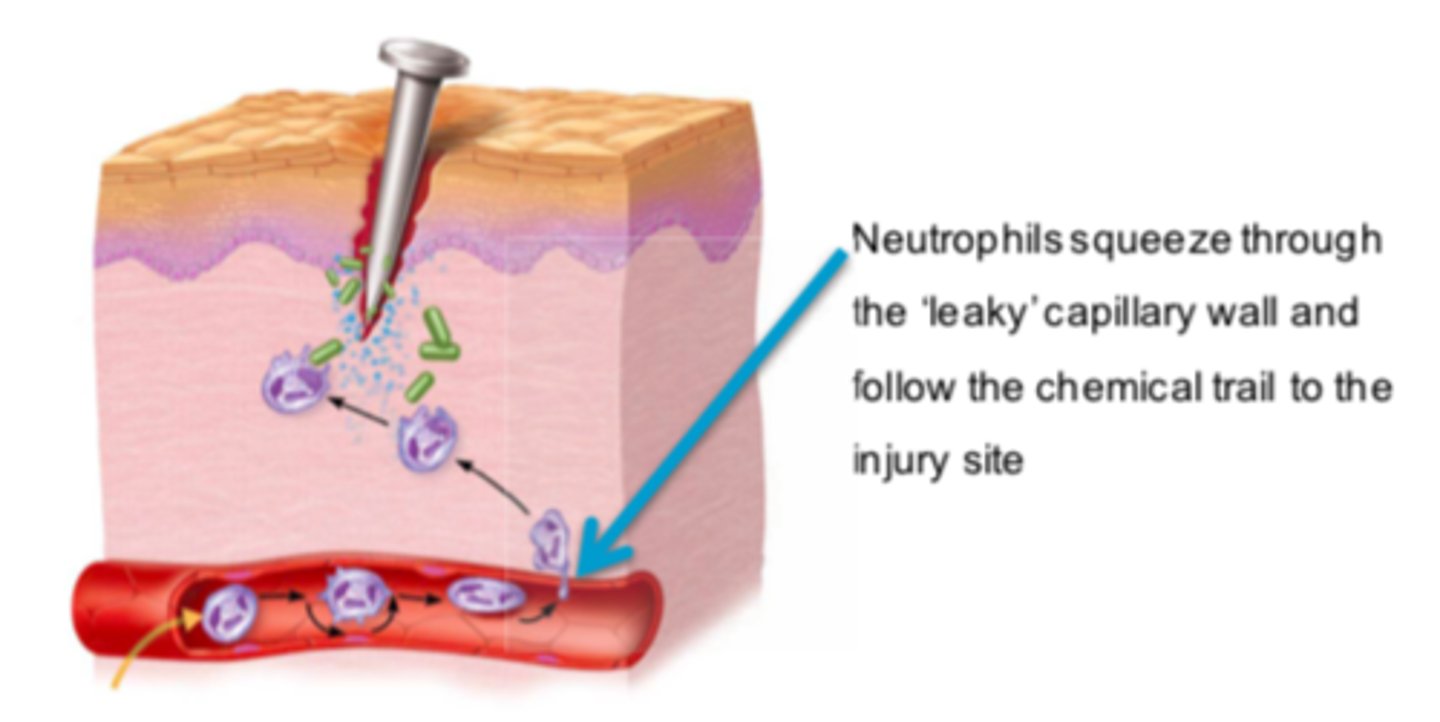
What happens to capillaries during an inflammatory response?
They dilate and the spaces between cells widens
-itis
inflammation
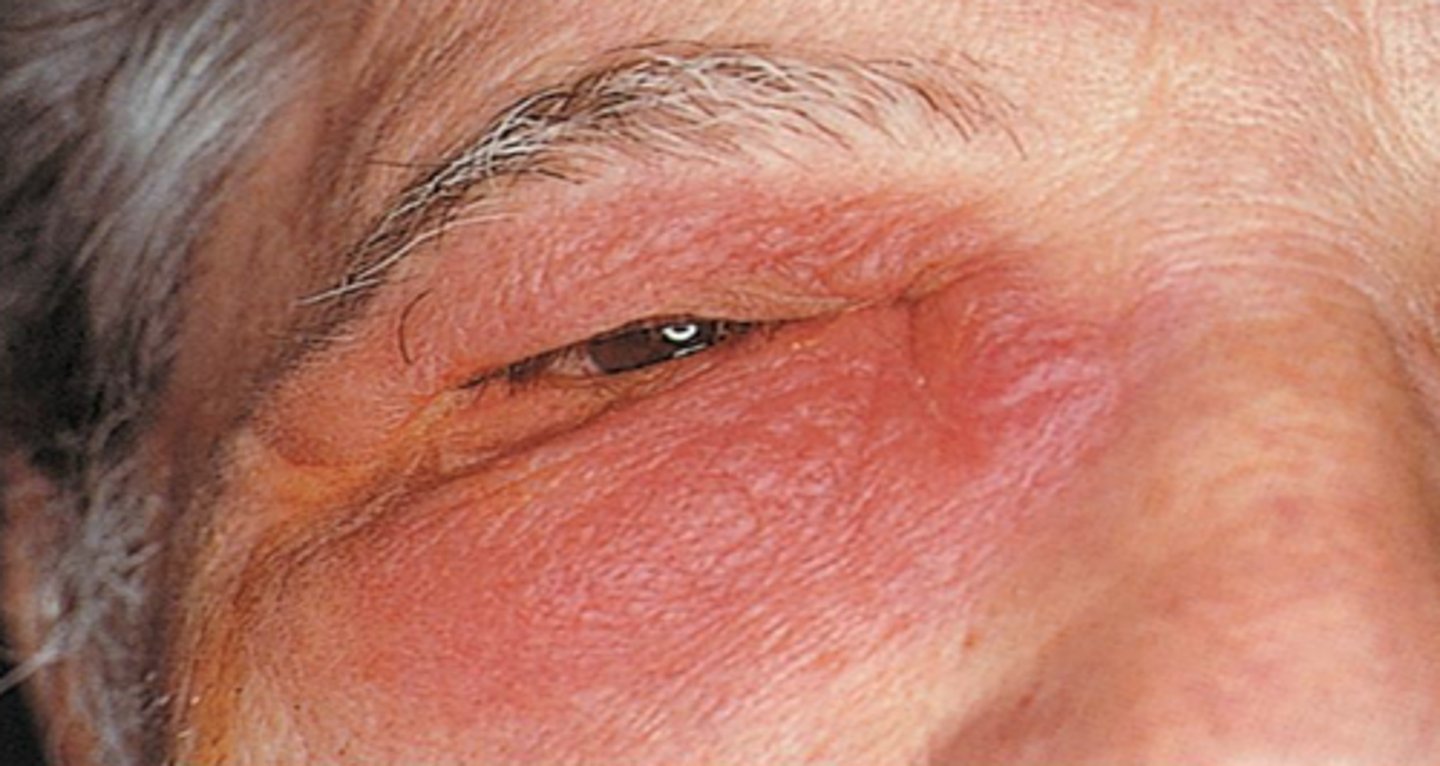
Inflammation
A normal defense response to injury, irritation, or infection
What are some causes of inflammation?
Physical damage, chemical irritation, ischemia, allergic reactions, temp changes, infection
What chemicals are released during inflammation?
1. Injured cells release bradykinin
2. Bradykinin activates pain receptors
3. Mast cells/basophils release histamine
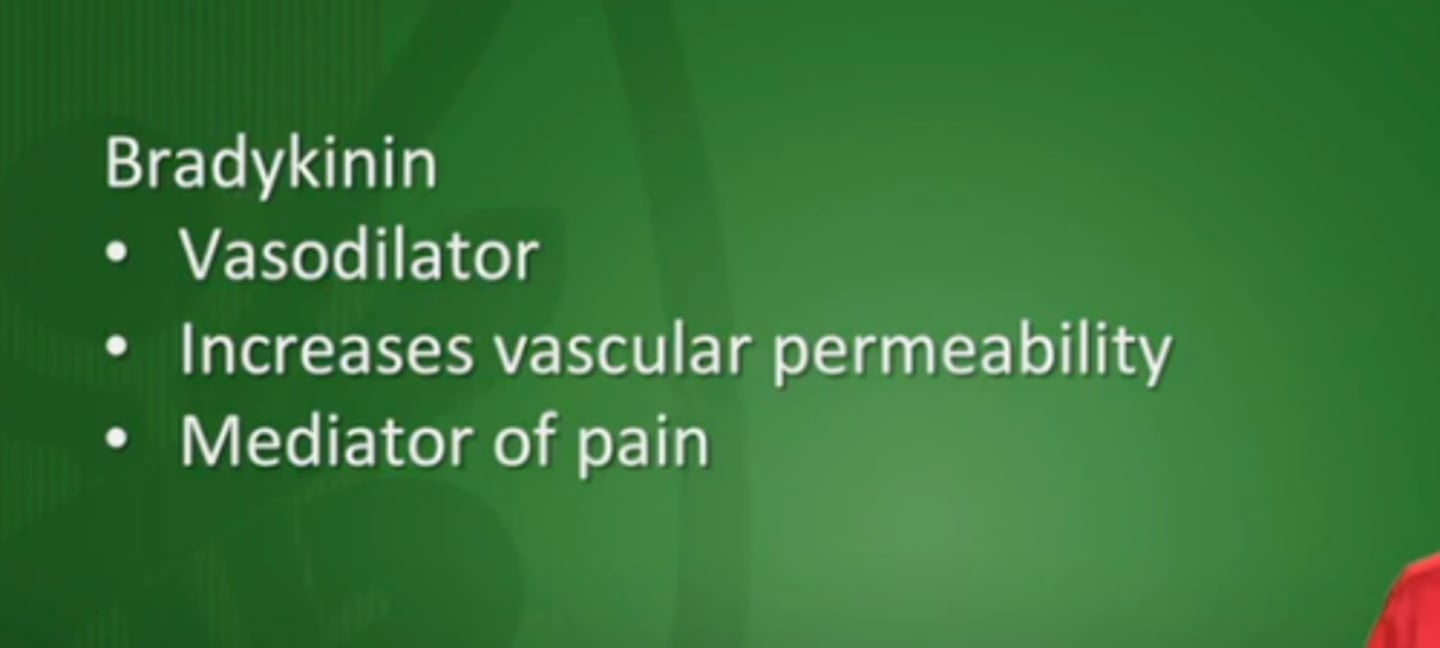
Bradykinin
A chemical mediator that is released during inflammation --> causes vasodilation
Histamine
Chemical stored in mast cells --> causes dilation and increased permeability of capillaries
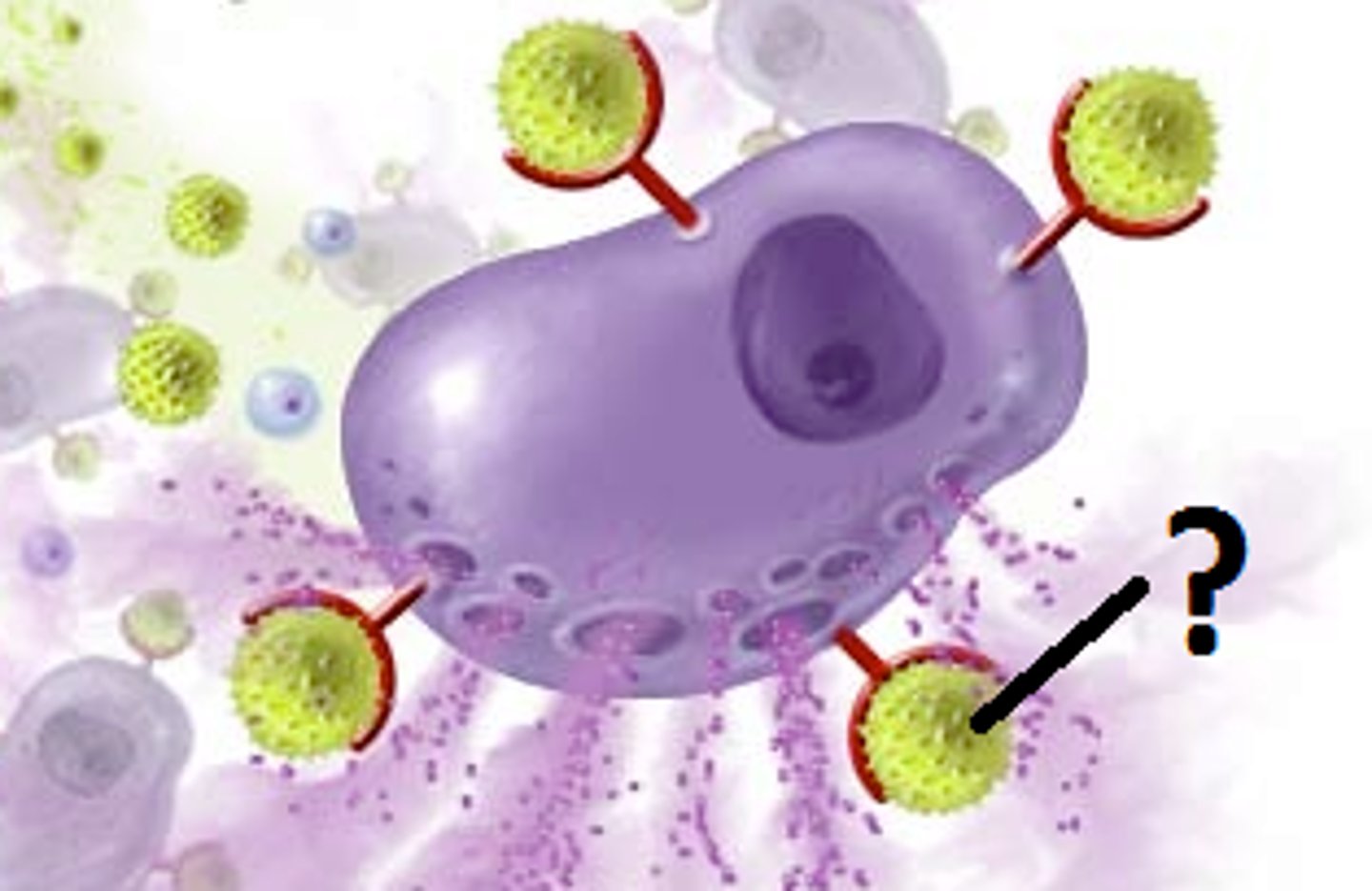
What causes capillary dilation?
Bradykinin and histamine increase blood flow and capillary permeability
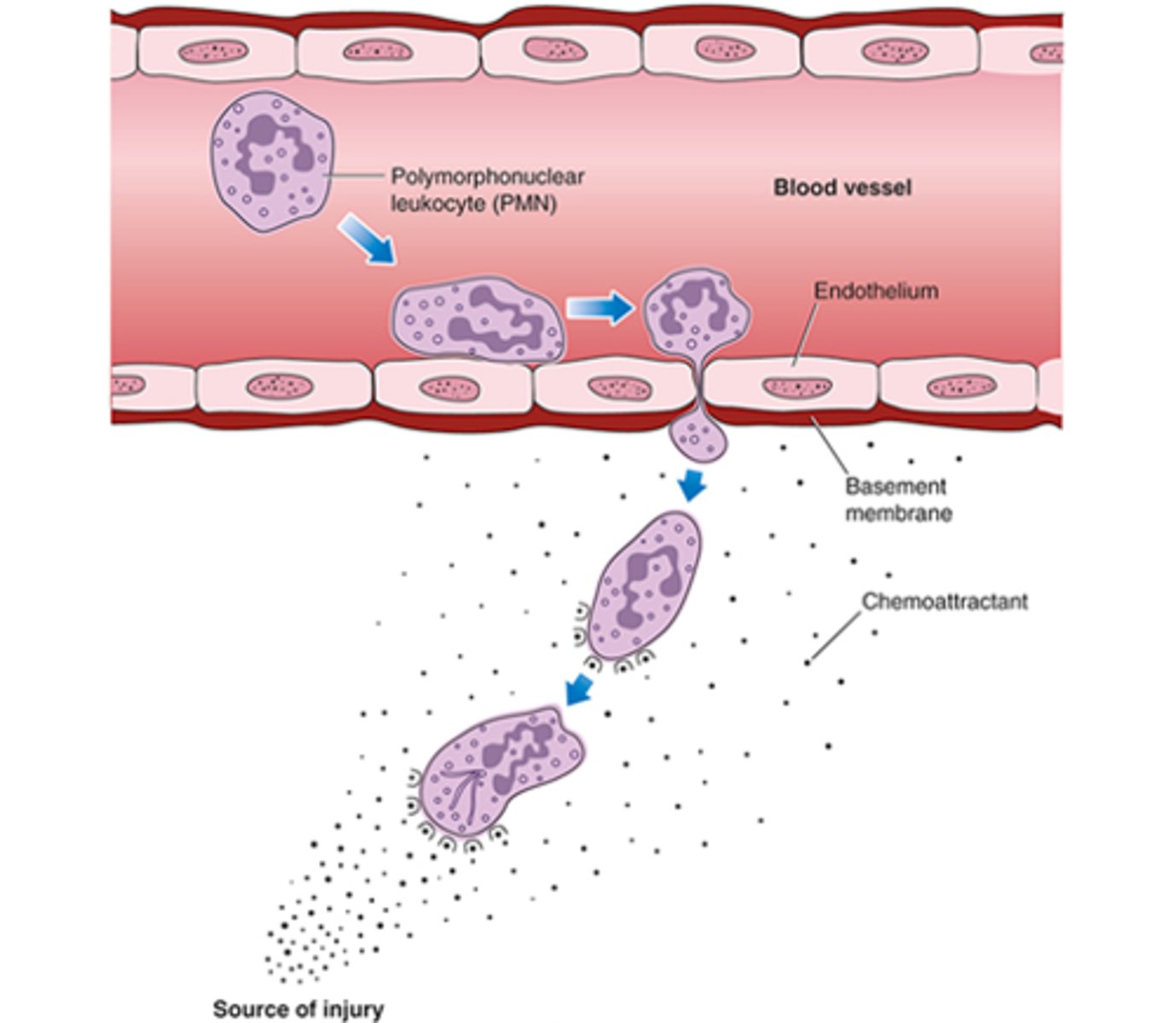
What do neutrophils do?
During the inflammatory response, neutrophils phagocytize bacteria
What do monocytes do?
During the inflammatory response, monocytes become macrophages and eat the microbes
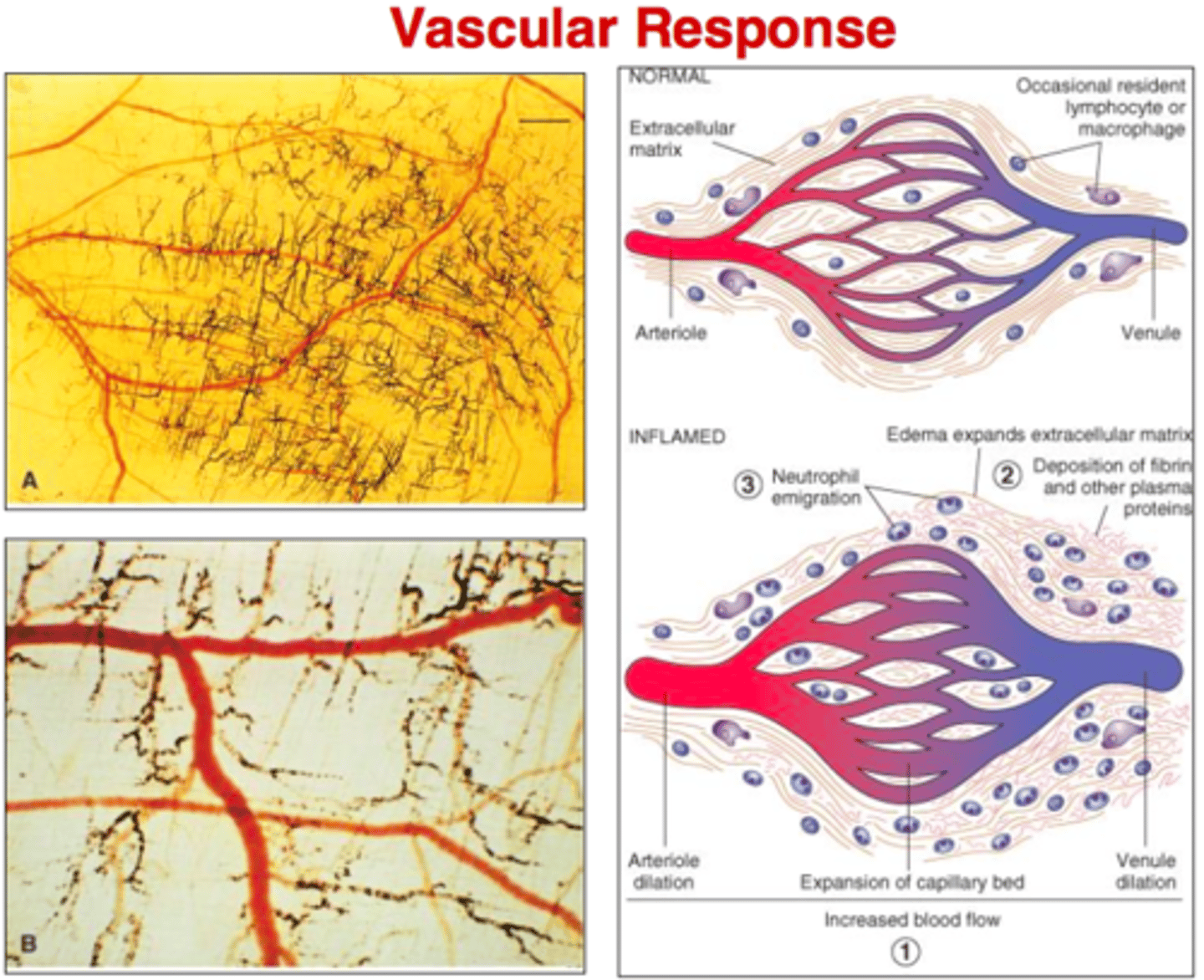
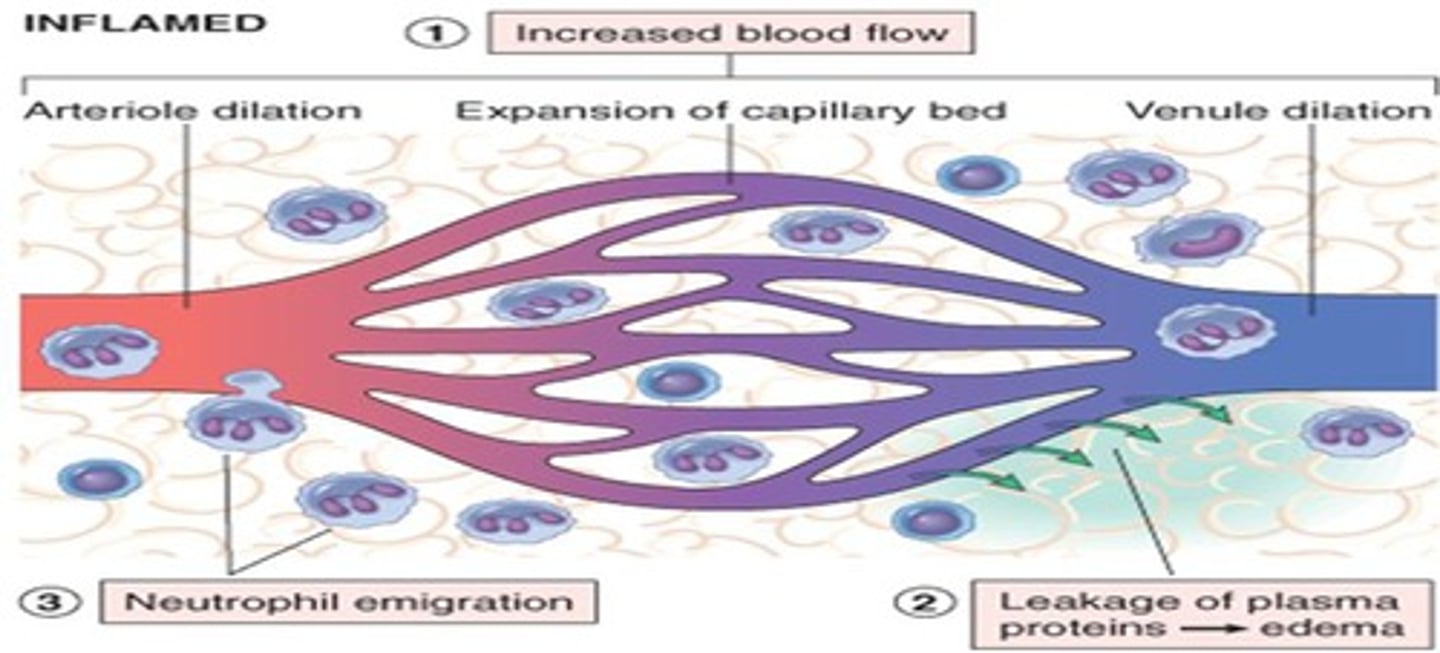
Vascular phase of inflammation
Overall vasodilation and increased capillary permeability
Cellular phase of inflammation
Involves white blood cells leaving the circulatory system, moving to the site of injury, and becoming activated
What are the outcomes of inflammation?
RASP:
Resolution
Abscess
Scar
Persistent inflammation
Does inflammation change depending on the cause?
No, the steps of inflammation are the same regardless of the cause
Steps of inflammation
1. Vasodilation
2. Hyperemia
3. Increase in capillary permeability
4. Chemotaxis to attract cells of the immune system
Arachidonic acid
A pro-inflammatory chemical messenger released by injured cell membranes
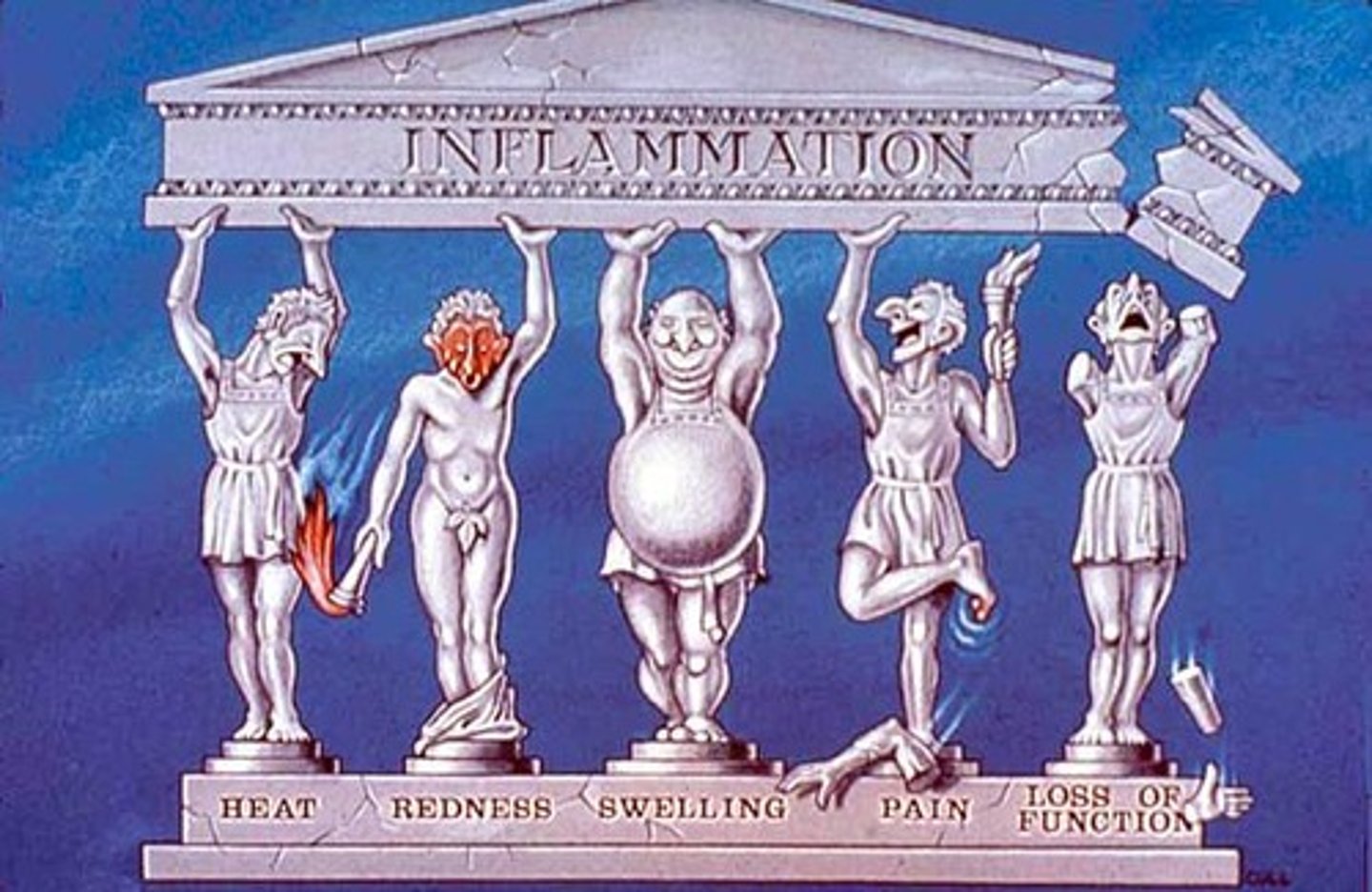
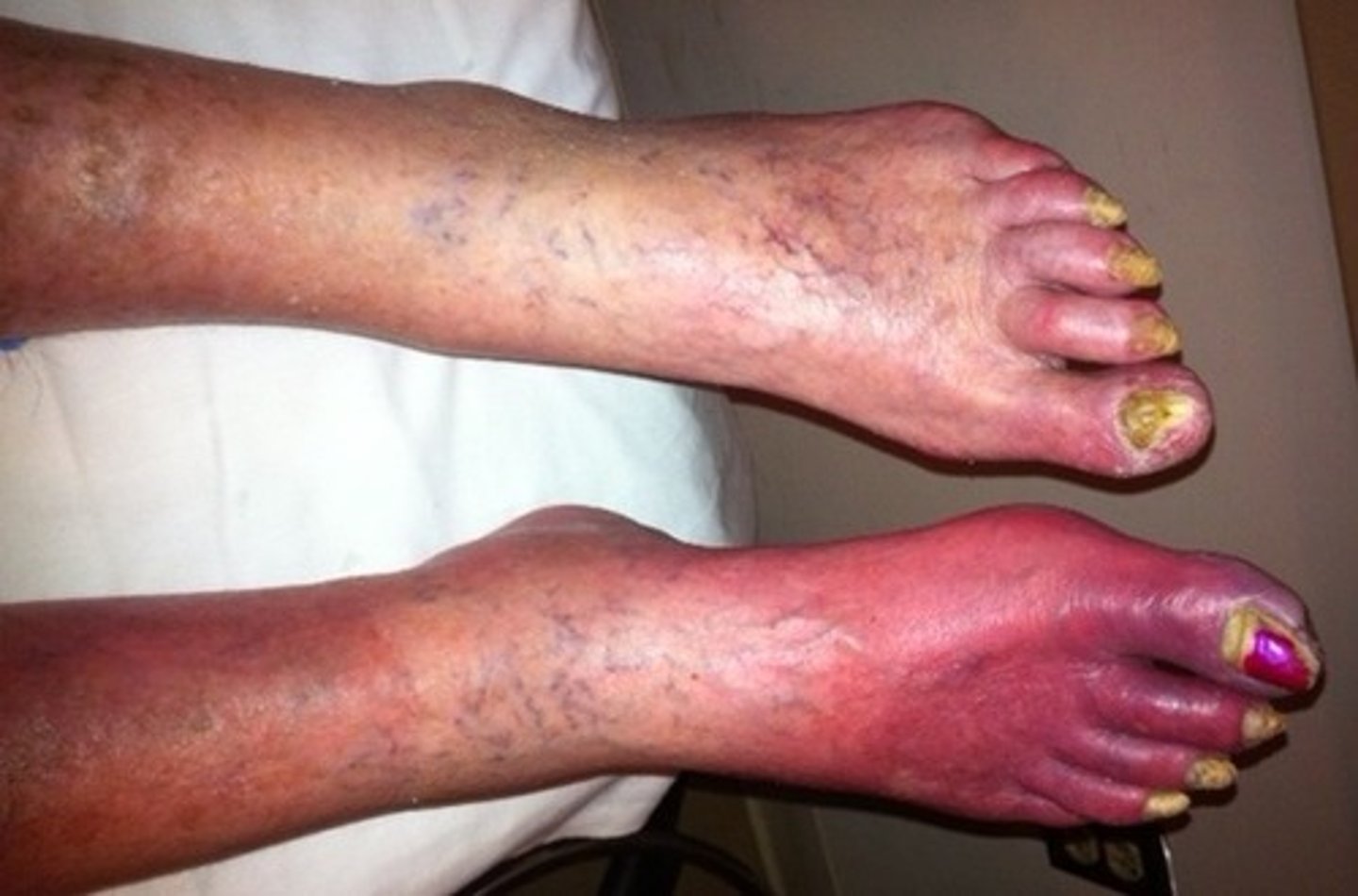
5 signs of inflammation
Heat, redness, swelling, pain, loss of function
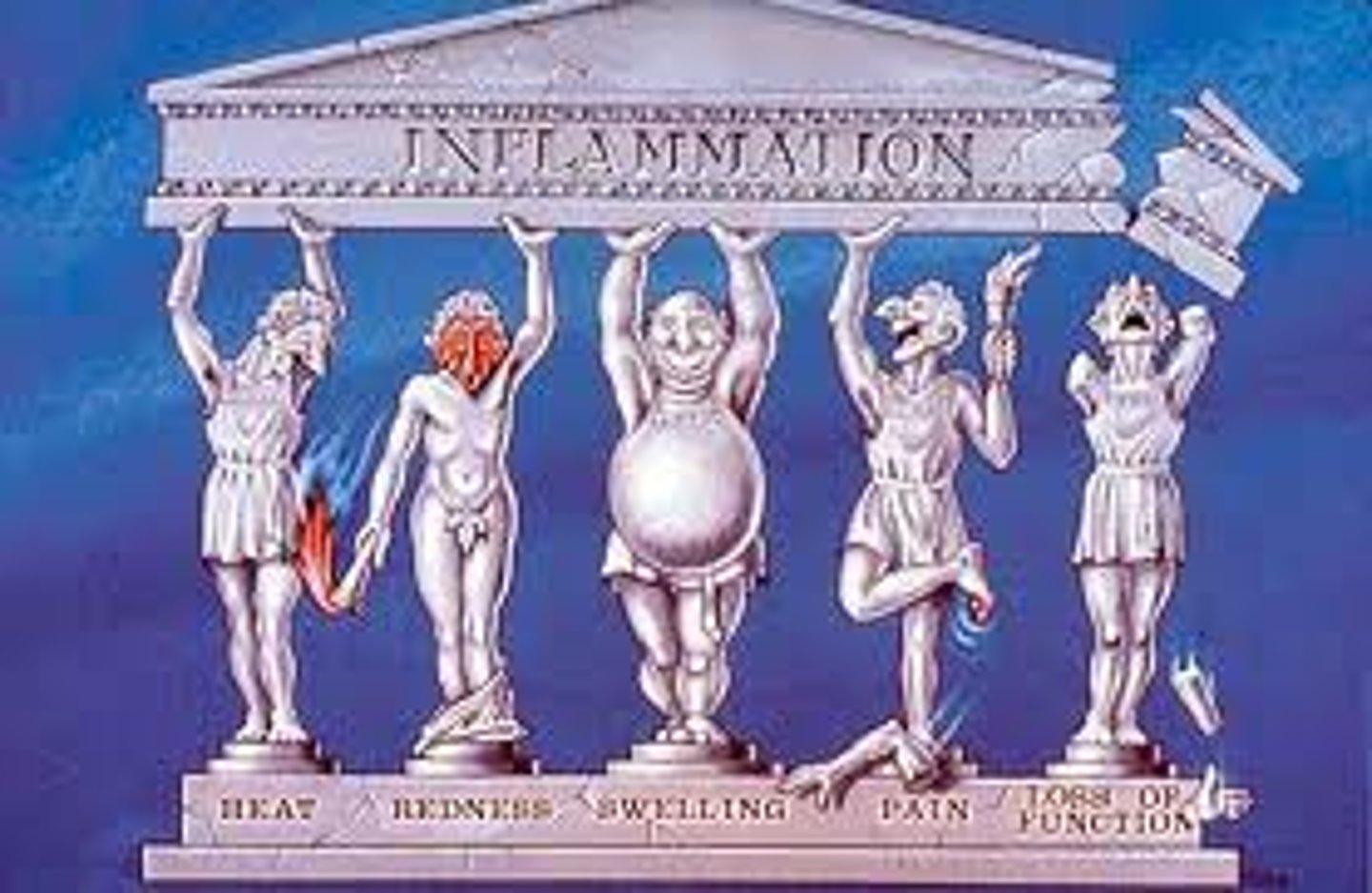
Rubor
Redness
Tumor
Swelling
Calor
Heat

Dolor
Pain

Functio laesa
Loss of function
What causes redness?
increased blood flow and vasodilation
What causes swelling?
Increased capillary permeability --> causes a shift of protein and fluid into the interstitial space
What causes pain?
Swelling puts pressure on nerves, release of chemical mediators (e.g., bradykinins)
What causes loss of function?
Pain and swelling impair function
Exudate
Inflammatory fluid that leaks out of cells (high in protein, blood, and immune cells)
Serous exudate
Watery: contains fluid, some proteins, and white blood cells
Hemorrhagic exudate
Exudate that contains blood
hemorrhage = bleeding
Fibrinous exudates
Exudate that contains a large amounts of fibrinogen --> forms a thick and sticky clot
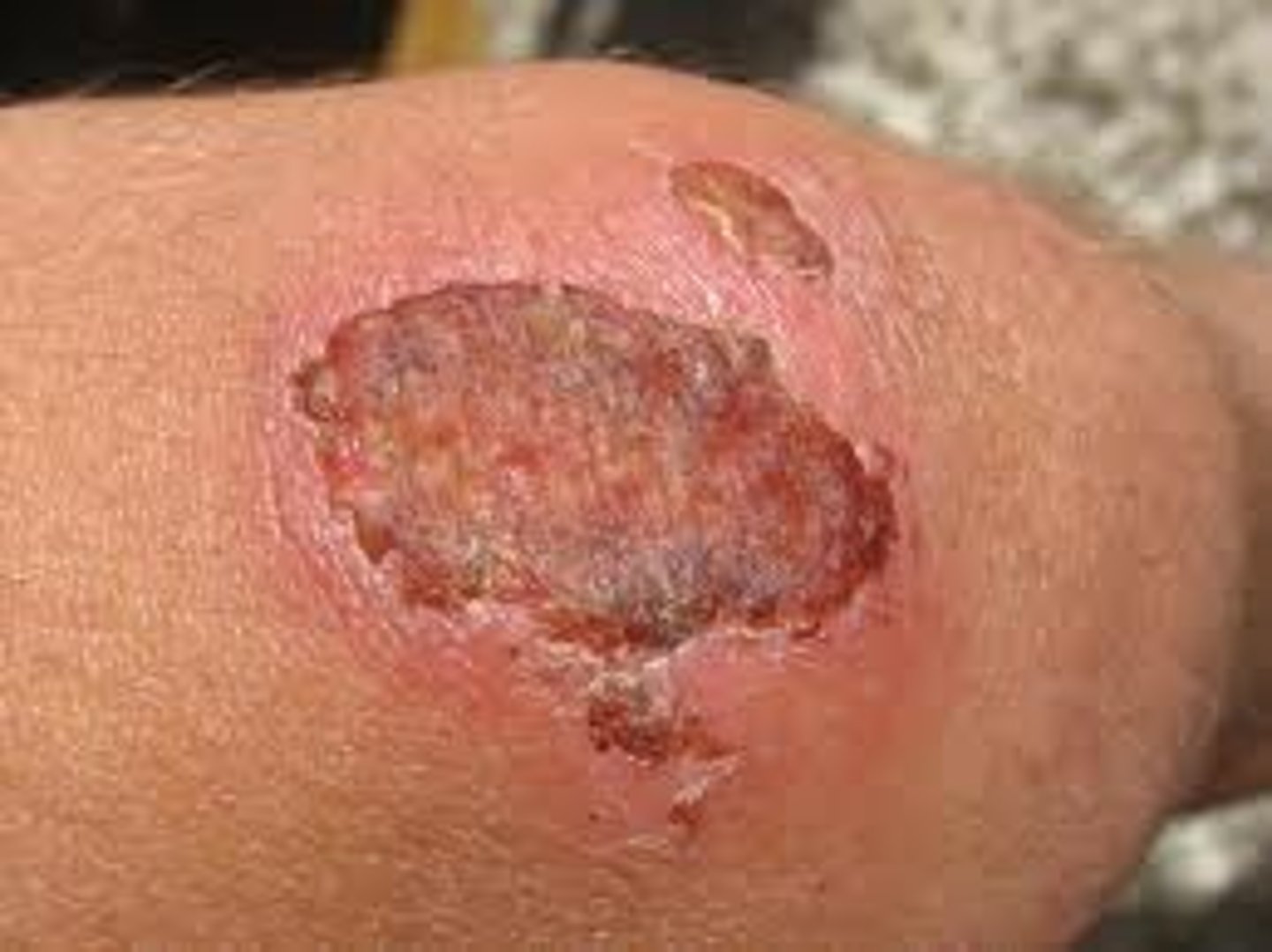
Membranous/Pseudomembranous Exudates
Exudate that develops on mucous membrane surfaces and are composed of necrotic cells
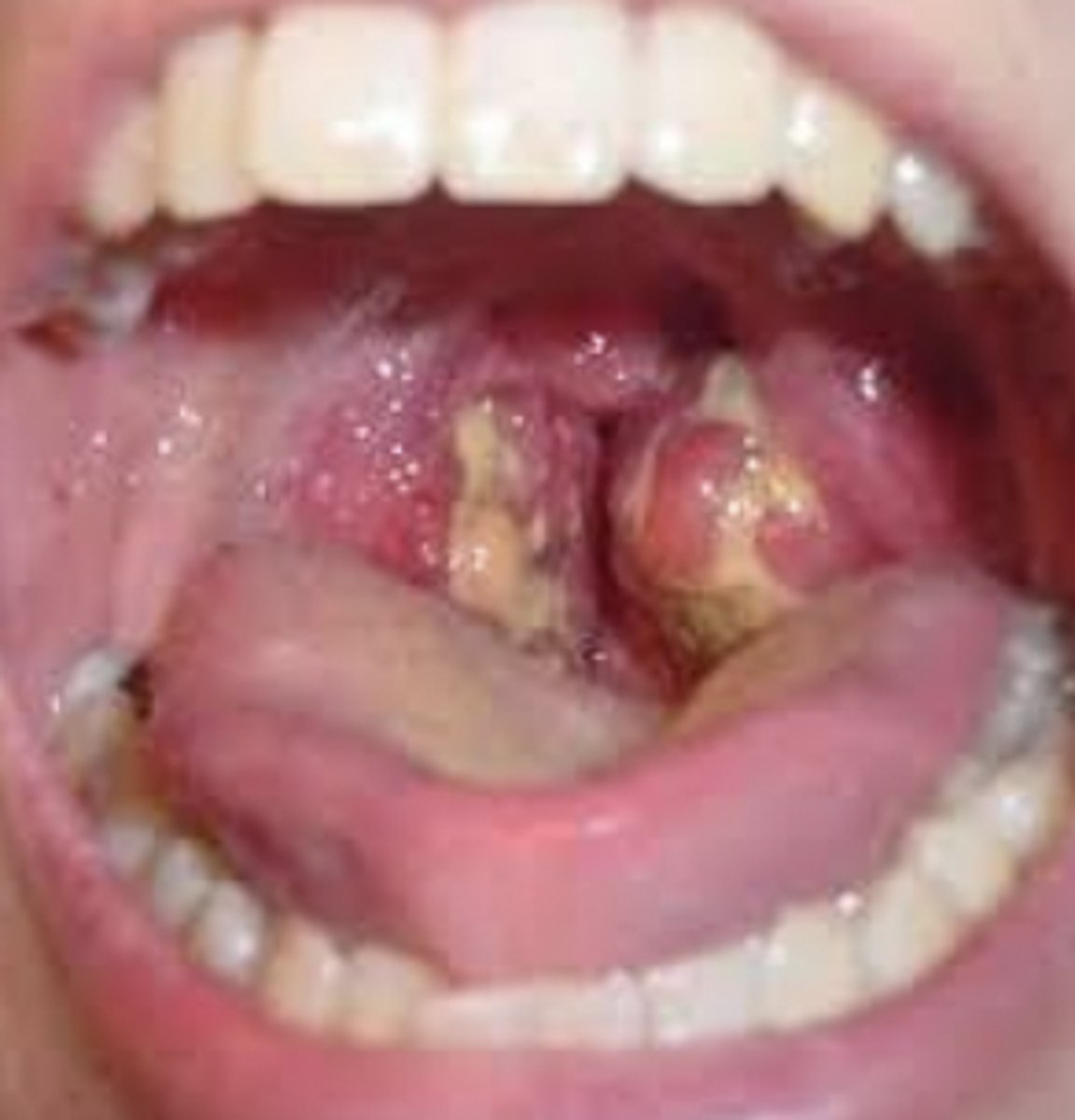
Purulent/Suppurative Exudates
Exudate that contains pus; composed of white blood cells, proteins, and tissue
I'm so sorry this picture is literally vile... but i guess it will help with the desensitization
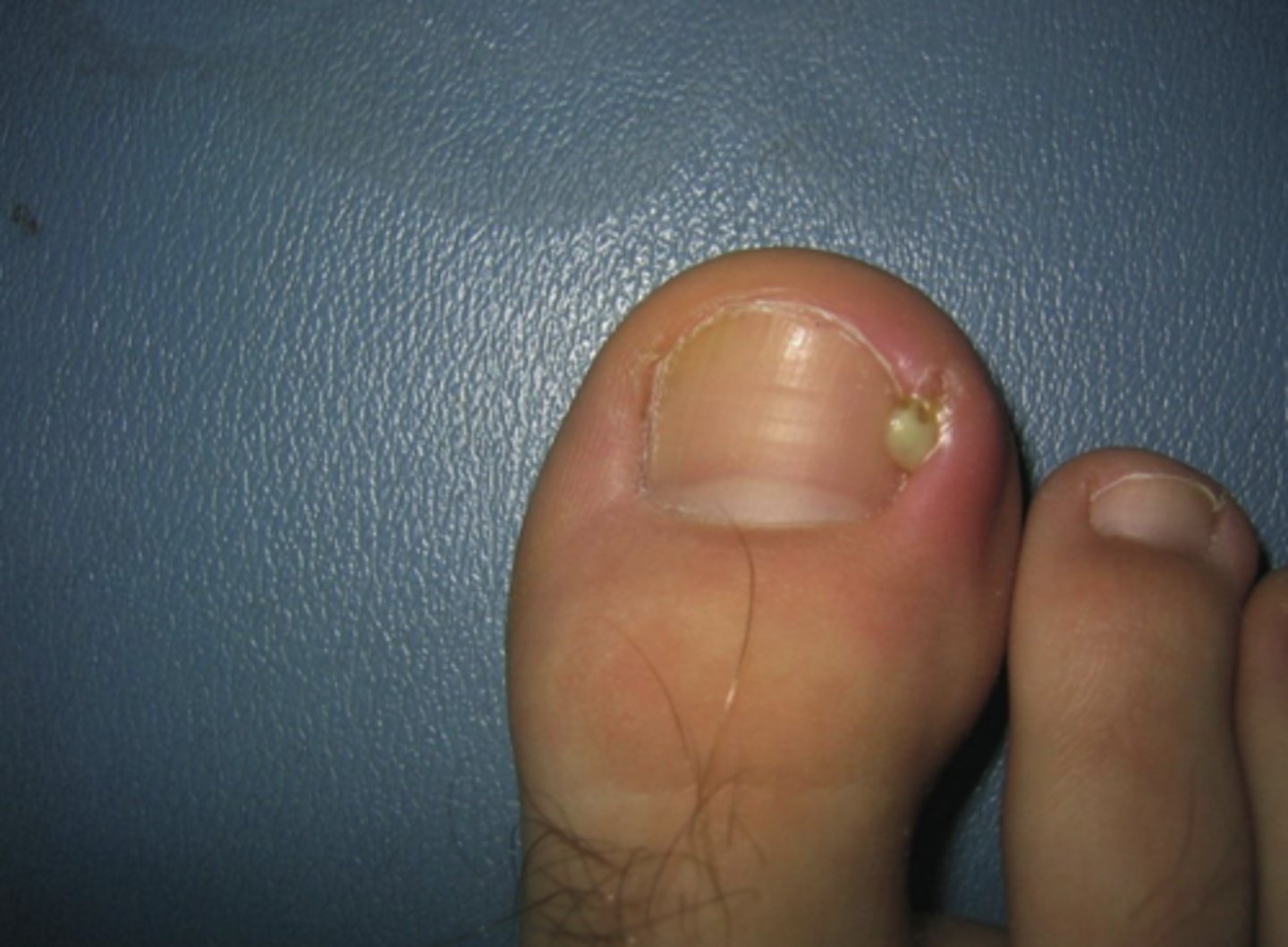
Abscess
A localized collection of pus underneath the skin
Pyrogens
Substances that cause fever
Interleukins
Proteins (cytokines) that stimulate the growth of B and T lymphocytes
Tumor necrosis factor
A chemical that causes inflammation and triggers apoptosis
Systemic affects of inflammation
1. Fever (pyrexia)
2. Headache/fatigue
3. Anorexia

What time of the day is fever highest?
At night

Leukocytosis
An increase in the number of white blood cells
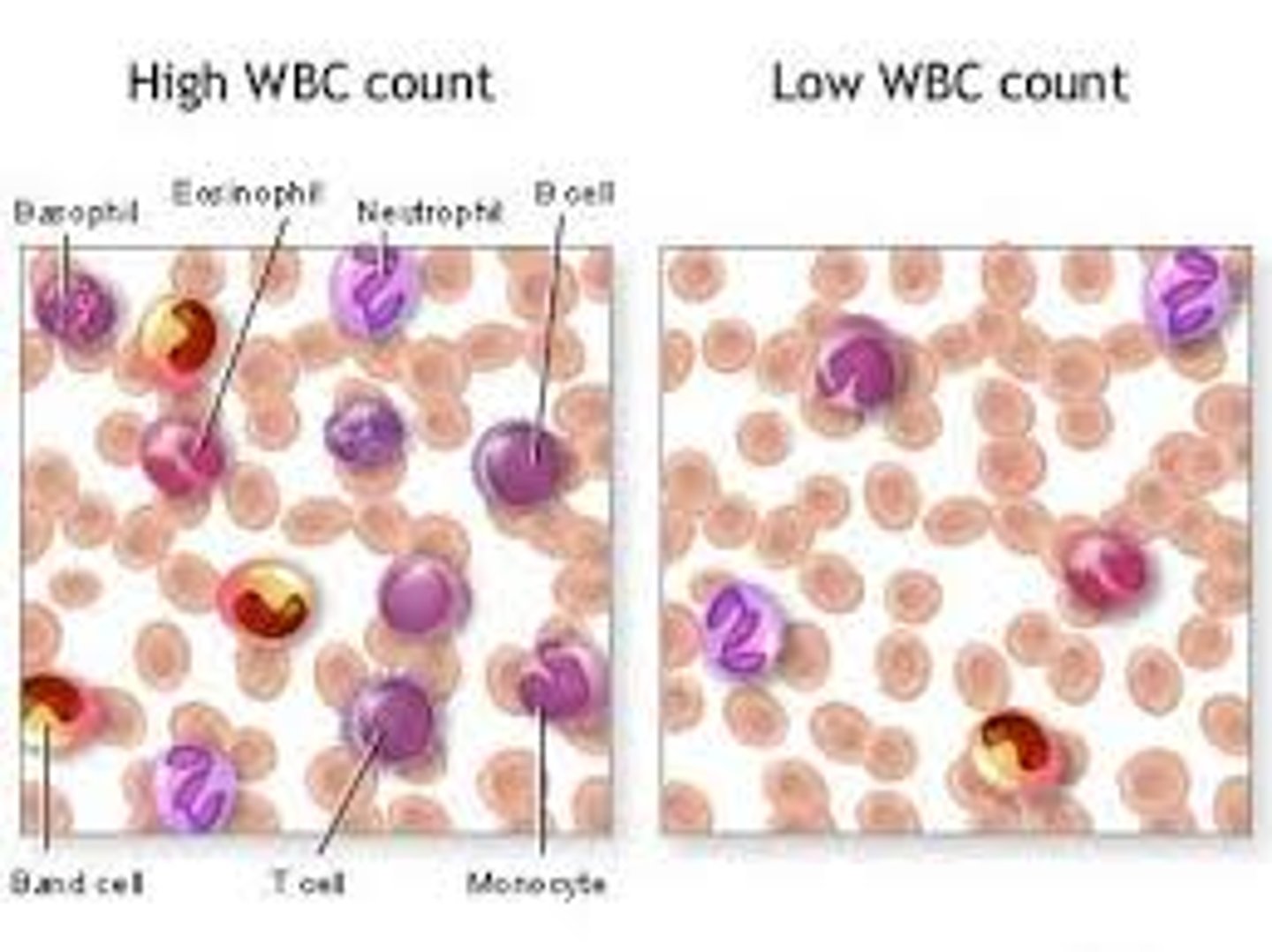
How does leukocytosis change with inflammation?
The amount of WBCs increases during periods of inflammation
What is the expected erythrocyte sedimentation rate during inflammation?
This test measures how quickly red blood cells settle in a test tube
Inflammation causes RBCs to clump together --> the more inflammation, the higher/faster your ESR
How could a differential count determine the cause of inflammation?
A differential count determines the amount of each type of white blood cell in the blood --> helps determine whether infection is bacterial or viral
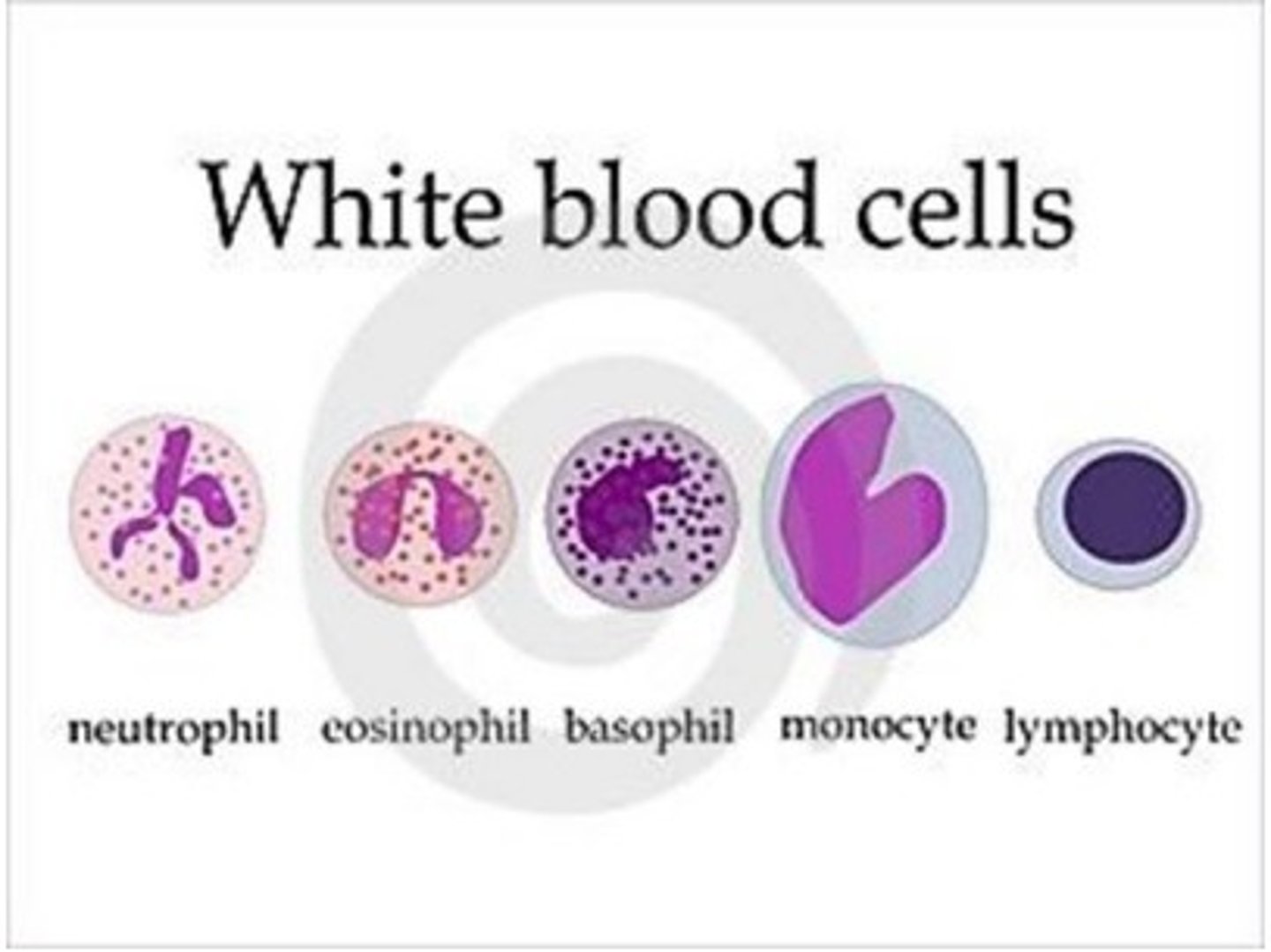
How can circulating plasma proteins determine the presence of infection?
Normally, C-reactive protein (CRP) is not found in blood
When there is an infection, CRP will attach to bacteria to prepare them for phagocytosis
Chronic inflammation
Long-lasting, out-of-control inflammatory response that continues for more than a few weeks
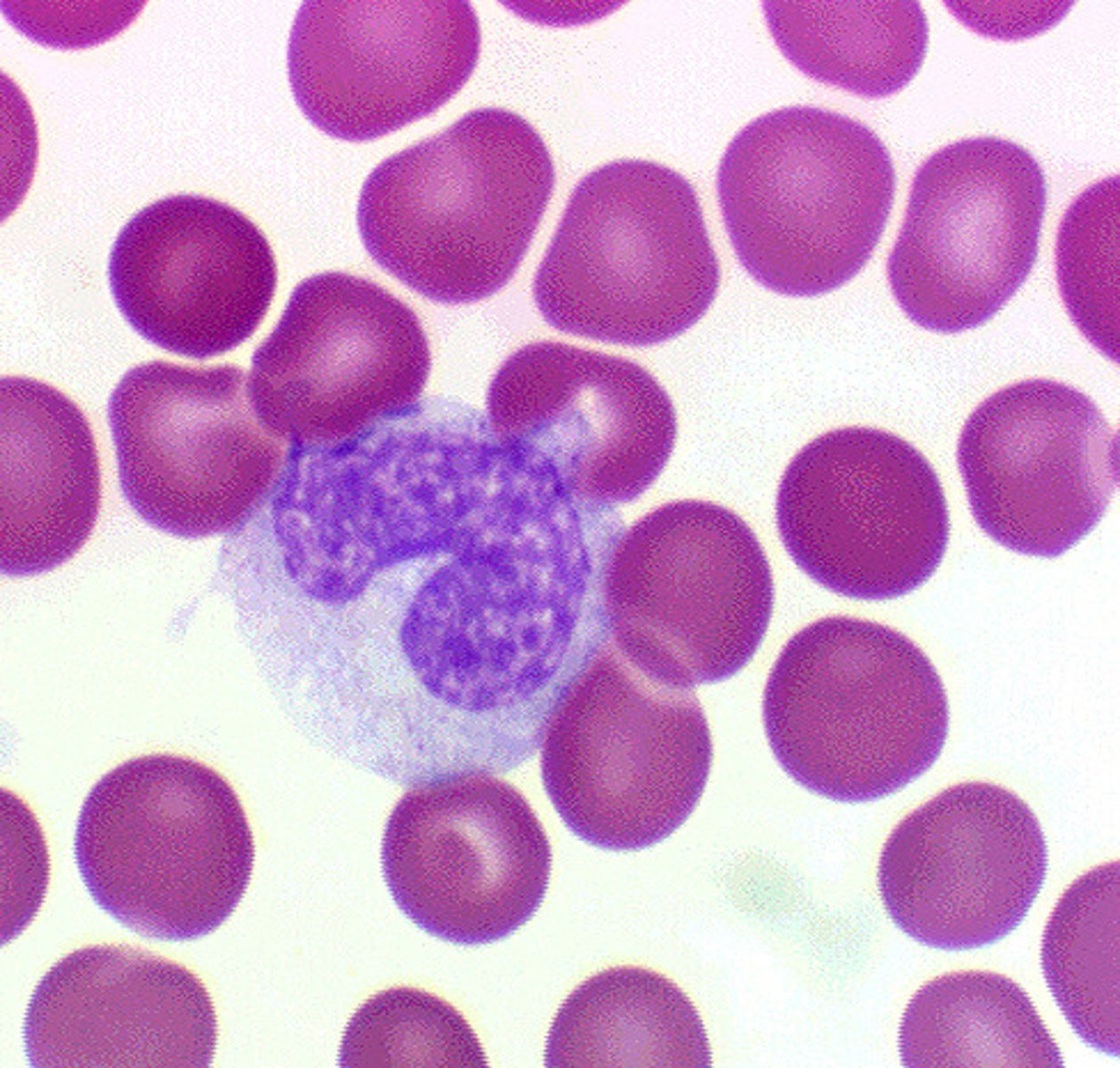
Which WBCs are present during chronic inflammation
Presence of more lymphocytes and macrophages
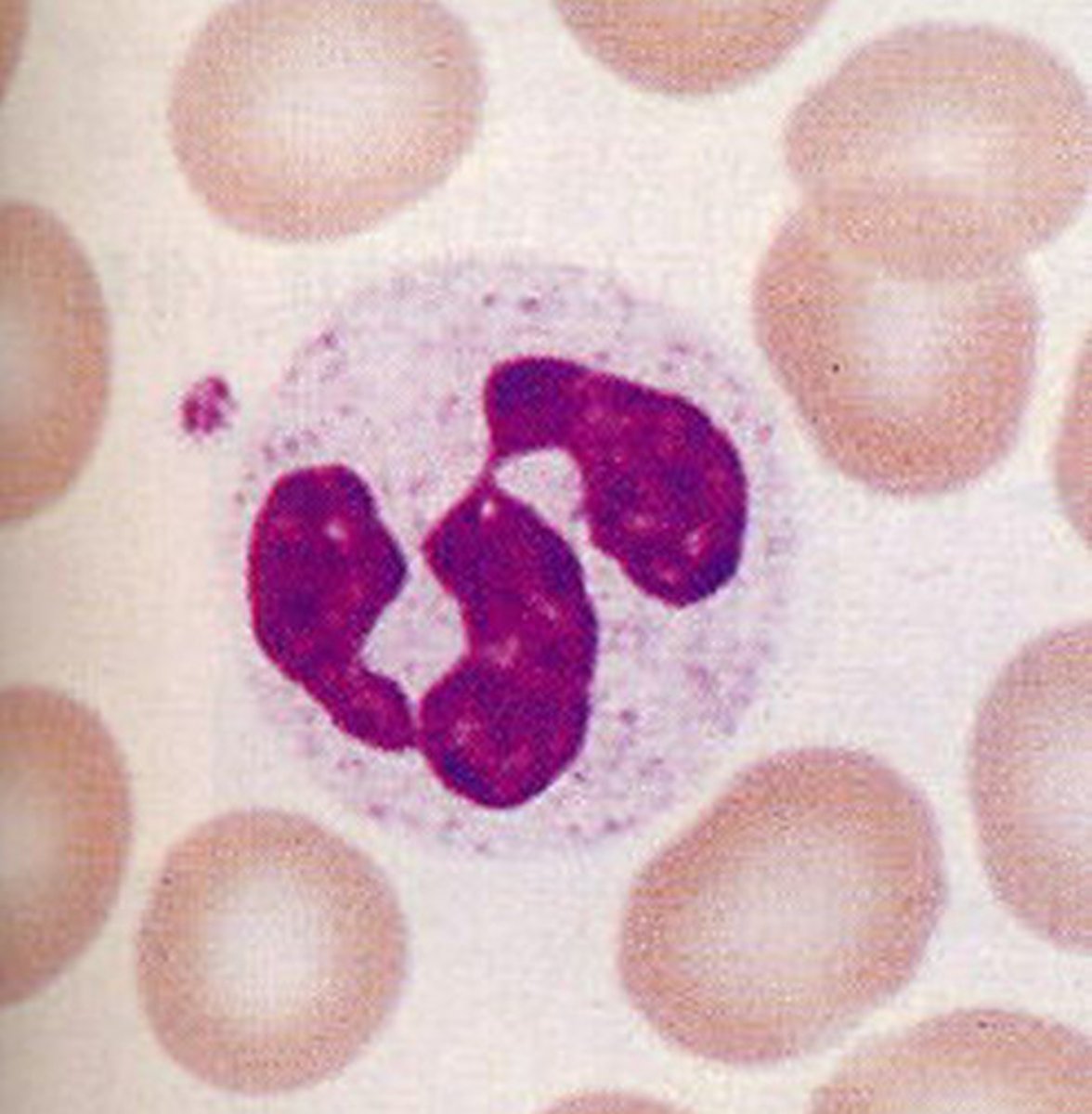
Which WBCs are present during acute inflammation?
There is an increased presence of neutrophils
Epithelioid cells
Macrophages that have differentiated so that they specialize in taking up debris and other small particles
Granuloma
A small area of inflammation (contains epithelioid cells)
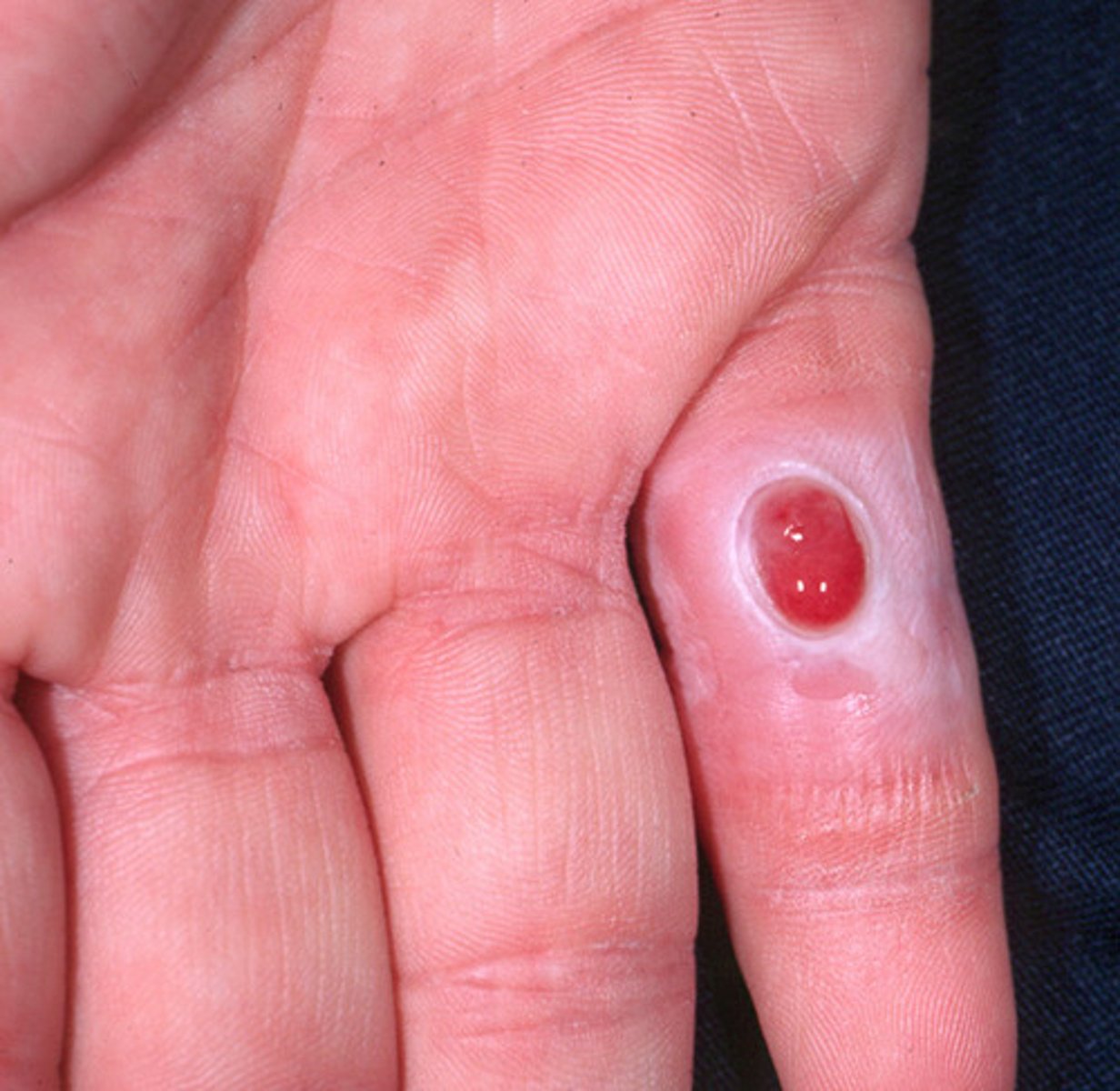
How can foreign bodies cause granulomas?
Splinters, sutures, asbestos can cause granulomas
Granulomas associated with microorganisms include...
Tuberculosis, syphilis, fungal infections, brucellosis
How can inflammation lead to infection?
1. Microbes can penetrate tissues more easily when they are swollen
2. The exudate creates a hospitable environment for microbes
How does inflammation lead to skeletal muscle spasm?
Inflammation --> pain --> muscle spasm

How can inflammation lead to ulcers?
Prolonged inflammation can cause cell death and necrosis --> leading to ulcer formation
Labile cells
Cells that undergo mitosis regularly and quickly
Stable cells
Cells that stop dividing when growth is complete (they can divide if they are injured)
Permanent Cells
Cells that cannot undergo mitosis
Resolution
Healing that leaves the body with limited damage
Regeneration
The damaged cells are replaced with functional cells
Replacement/Fibrosis
The damaged tissue is replaced by scar tissue (non functional)
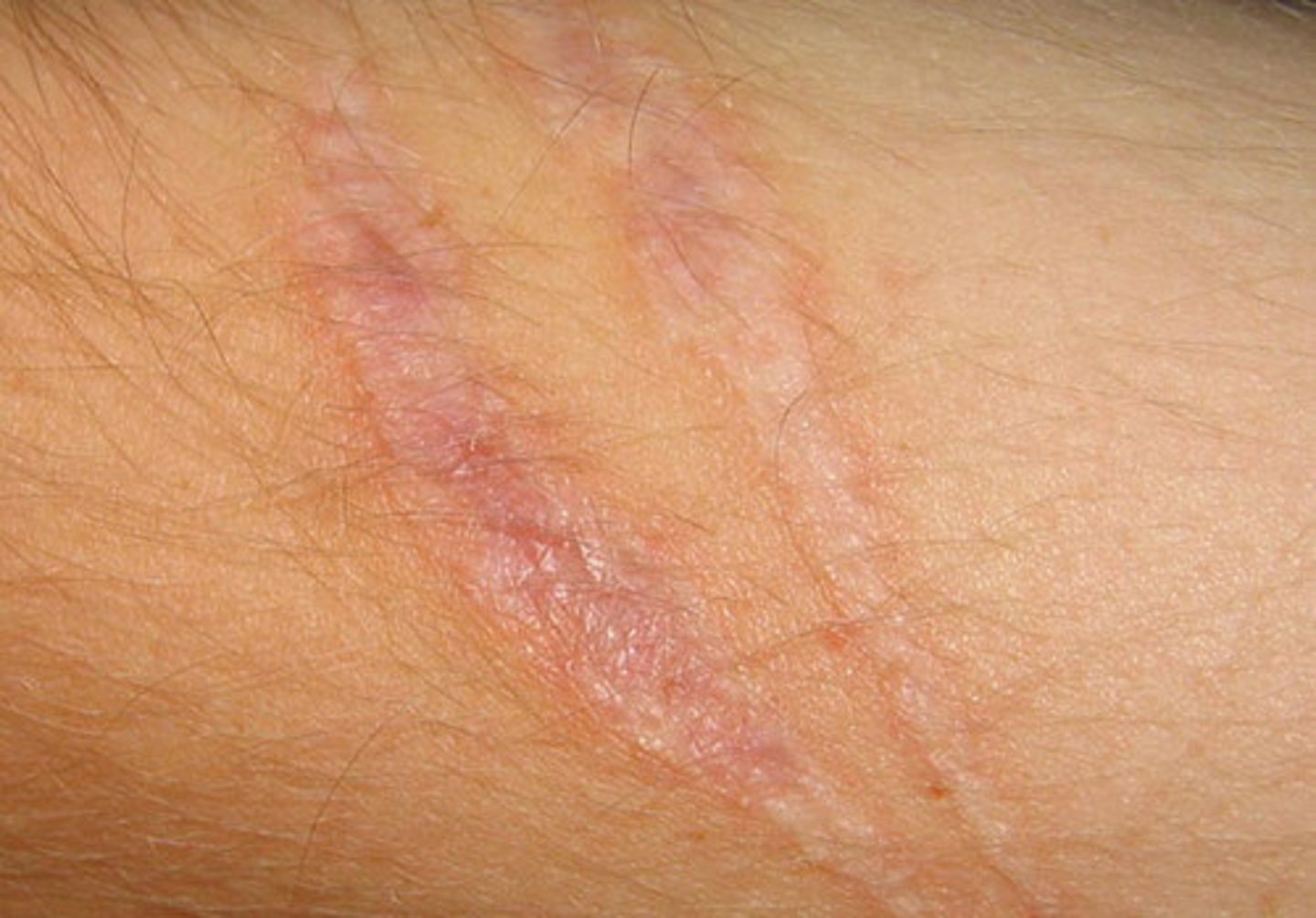
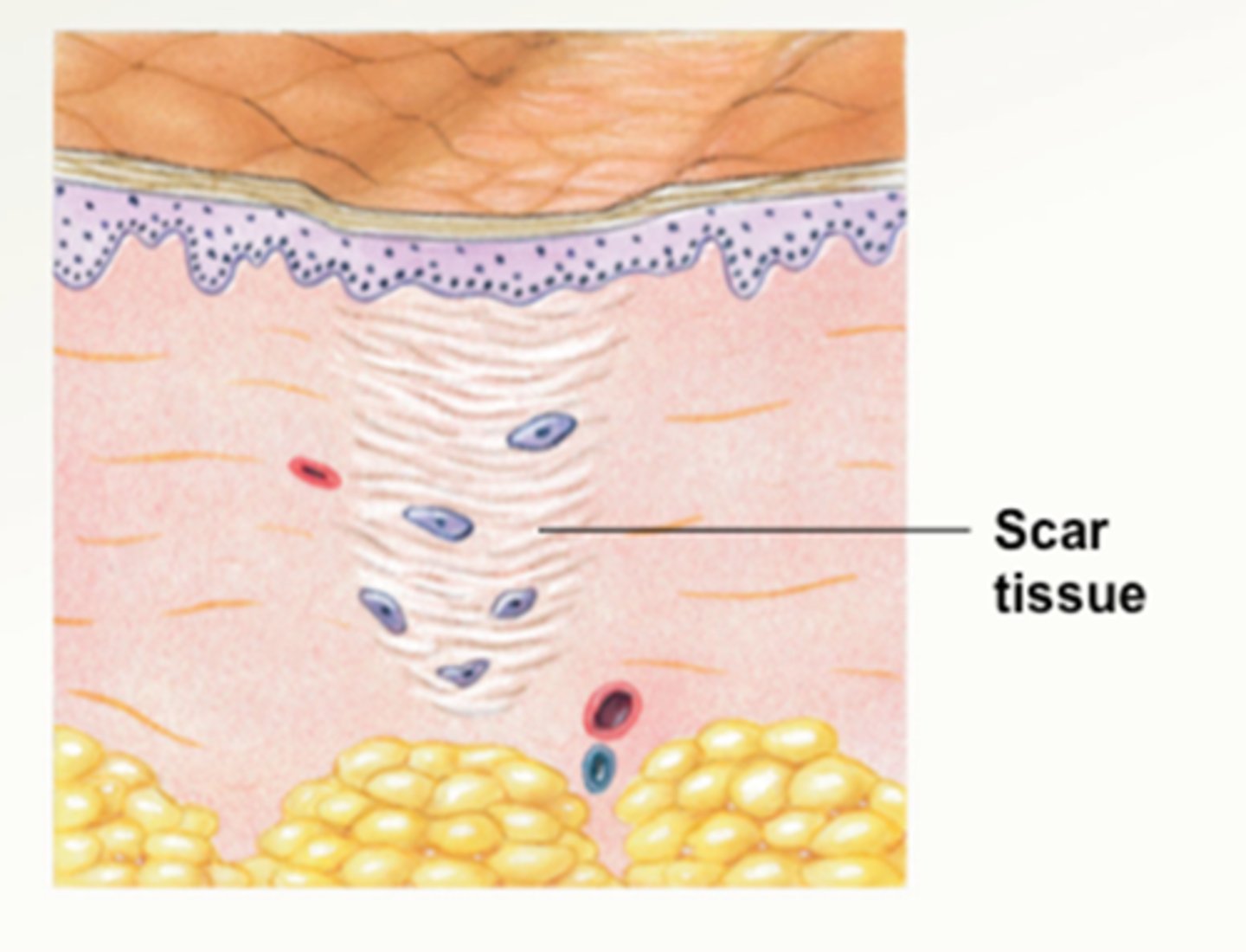
Scar tissue
Tissue that forms at the site of healing wounds; made mostly of collagen
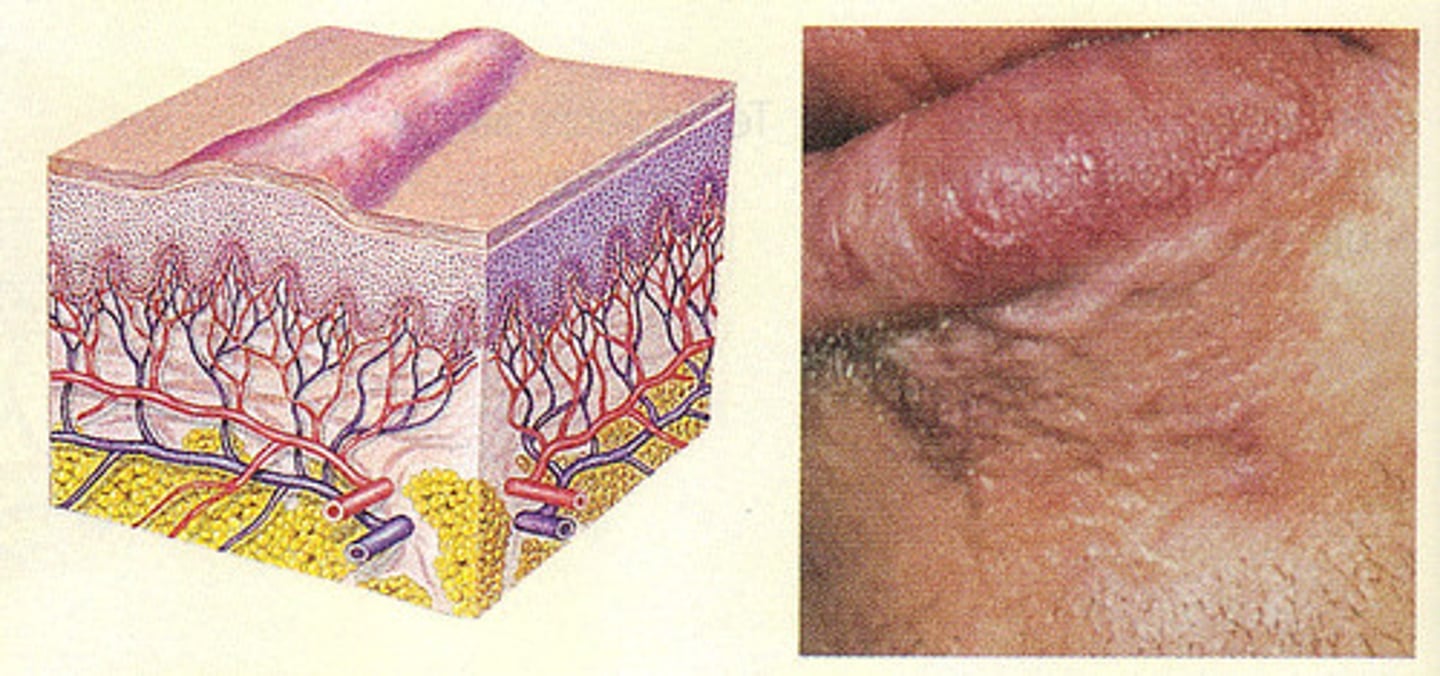
What happens if scar tissue forms in an area with permanent cells?
Since permanent cells cannot regenerate, the area containing scar tissue will be non-functional
Example: myocardial infarction
What is the goal of wound healing?
To restore the structural and functional integrity of injured tissue
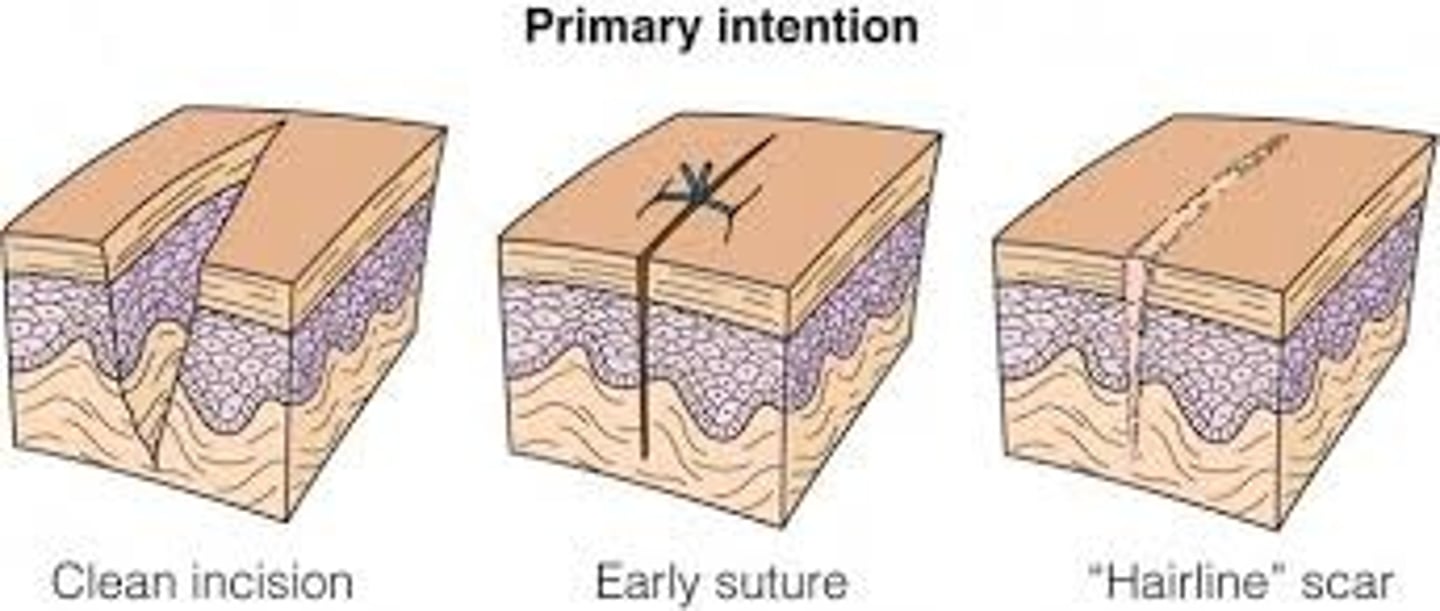
Primary intention healing
Small, clean wounds that heal with little tissue loss
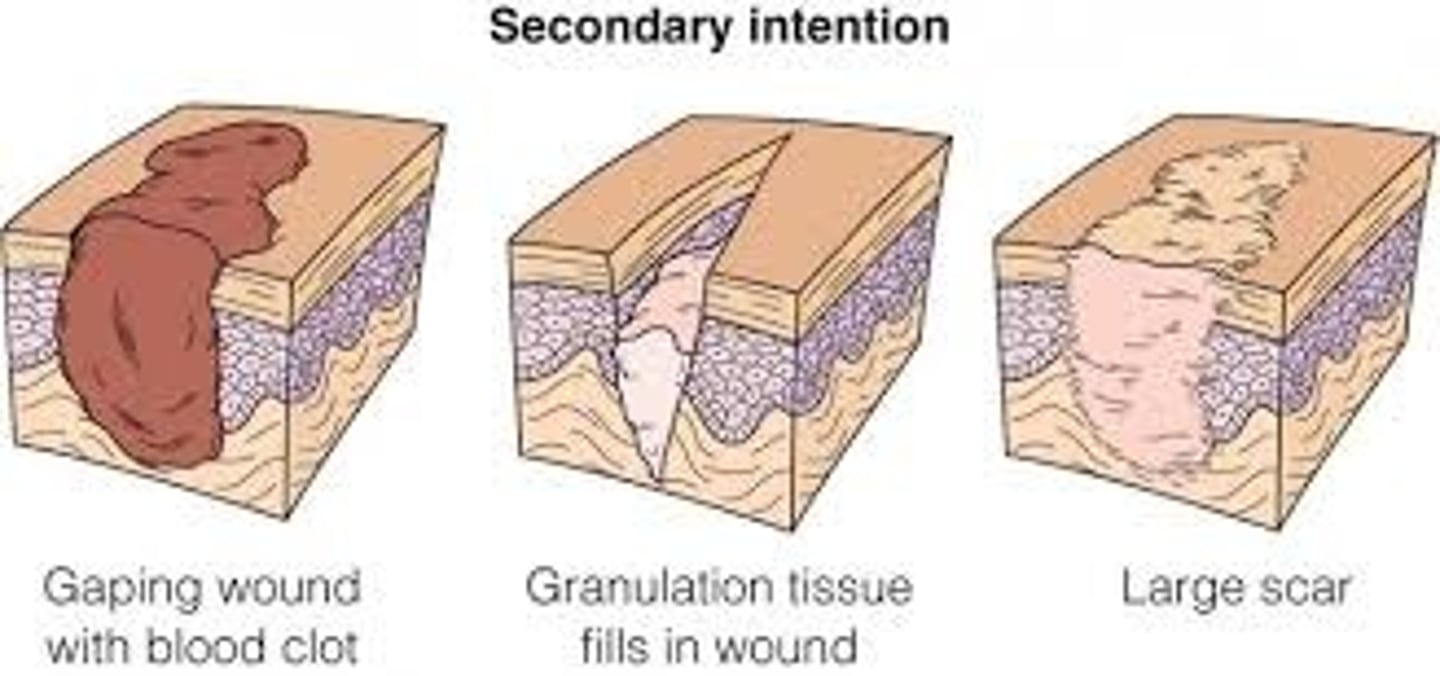
Secondary intention healing
Large, contaminated wounds that heal with major tissue loss
What are the stages of wound healing?
1. Inflammatory
2. Proliferation
3. Maturation
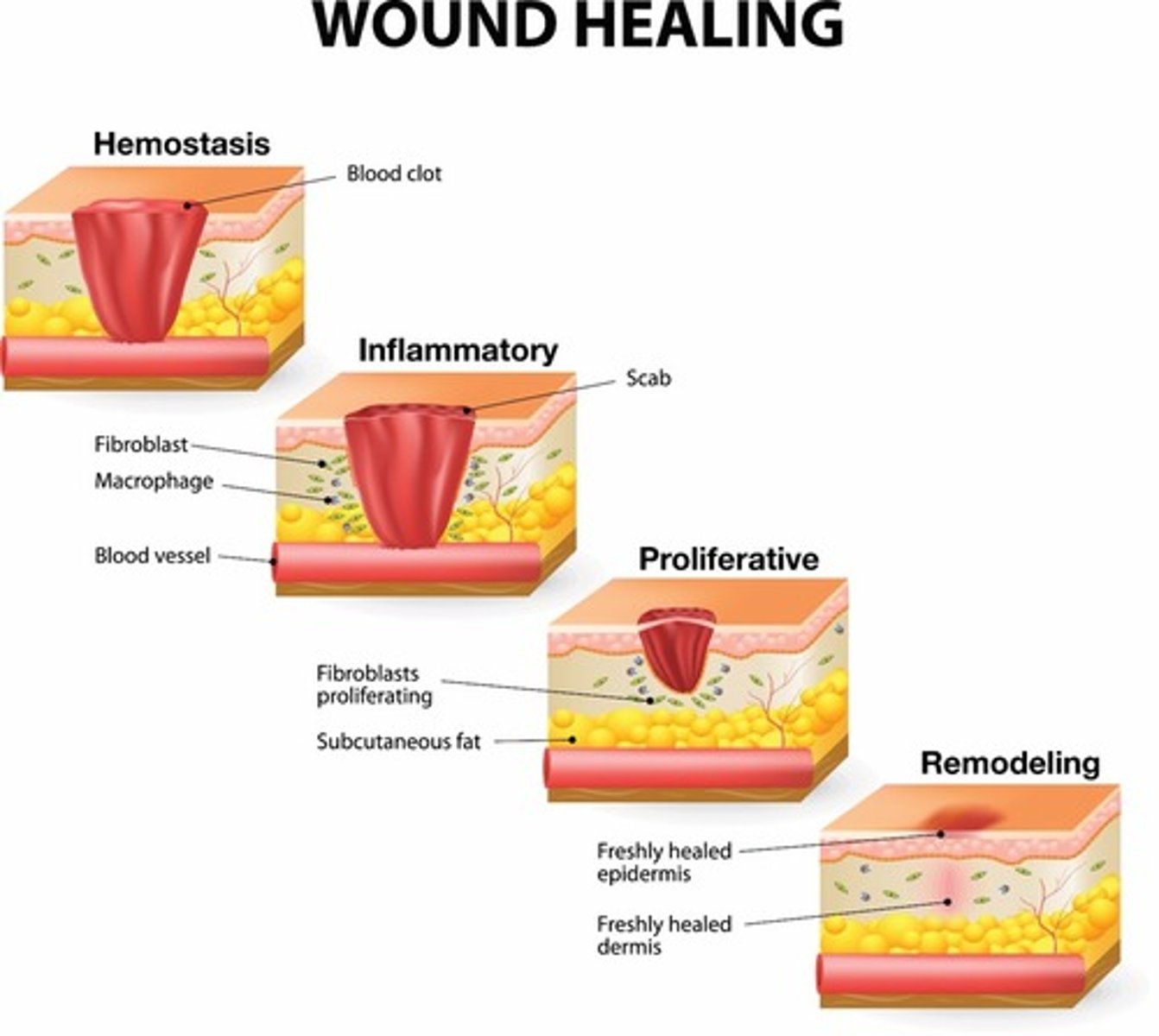
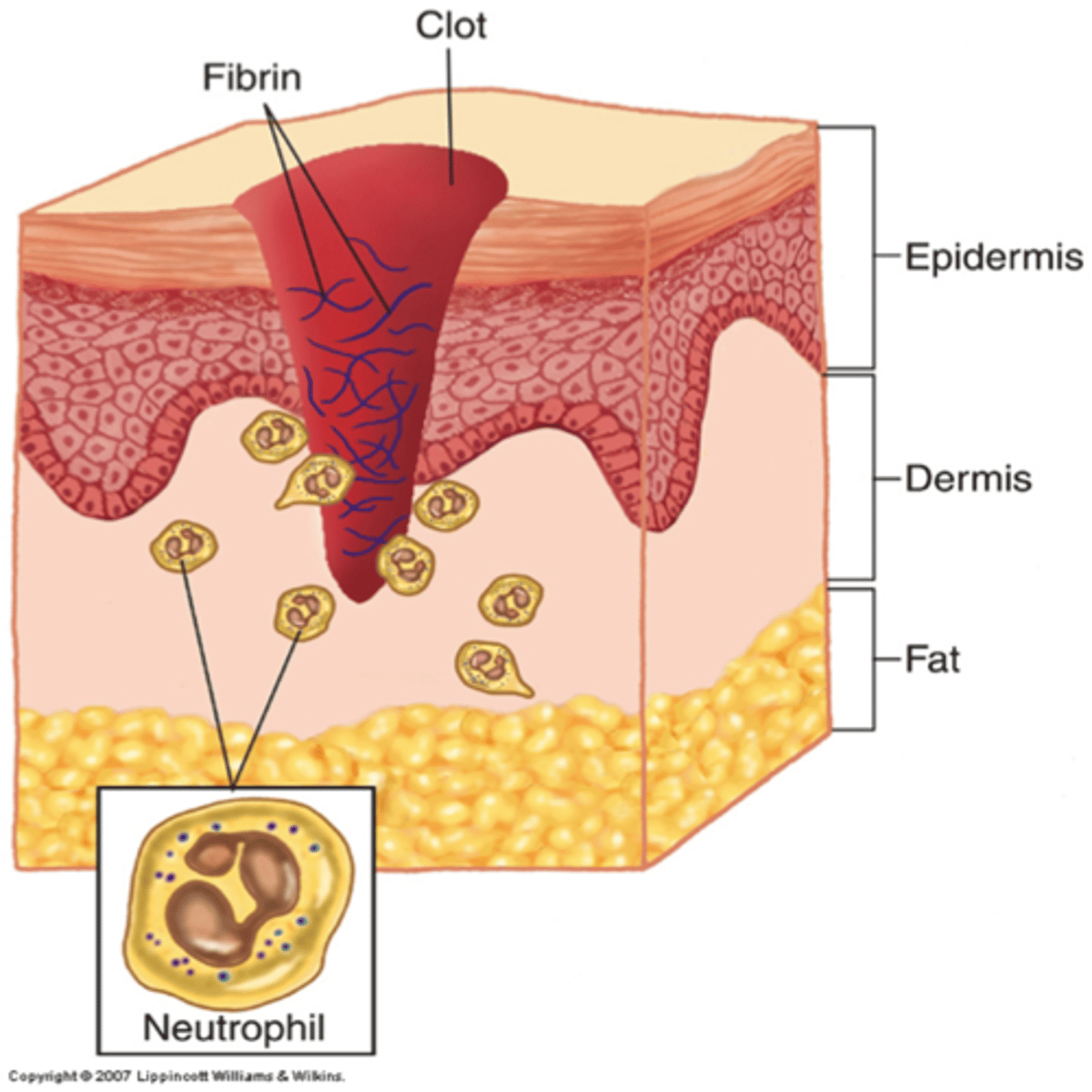
Inflammatory phase
The initial phase of wound healing; includes blood clotting and invasion of WBCs
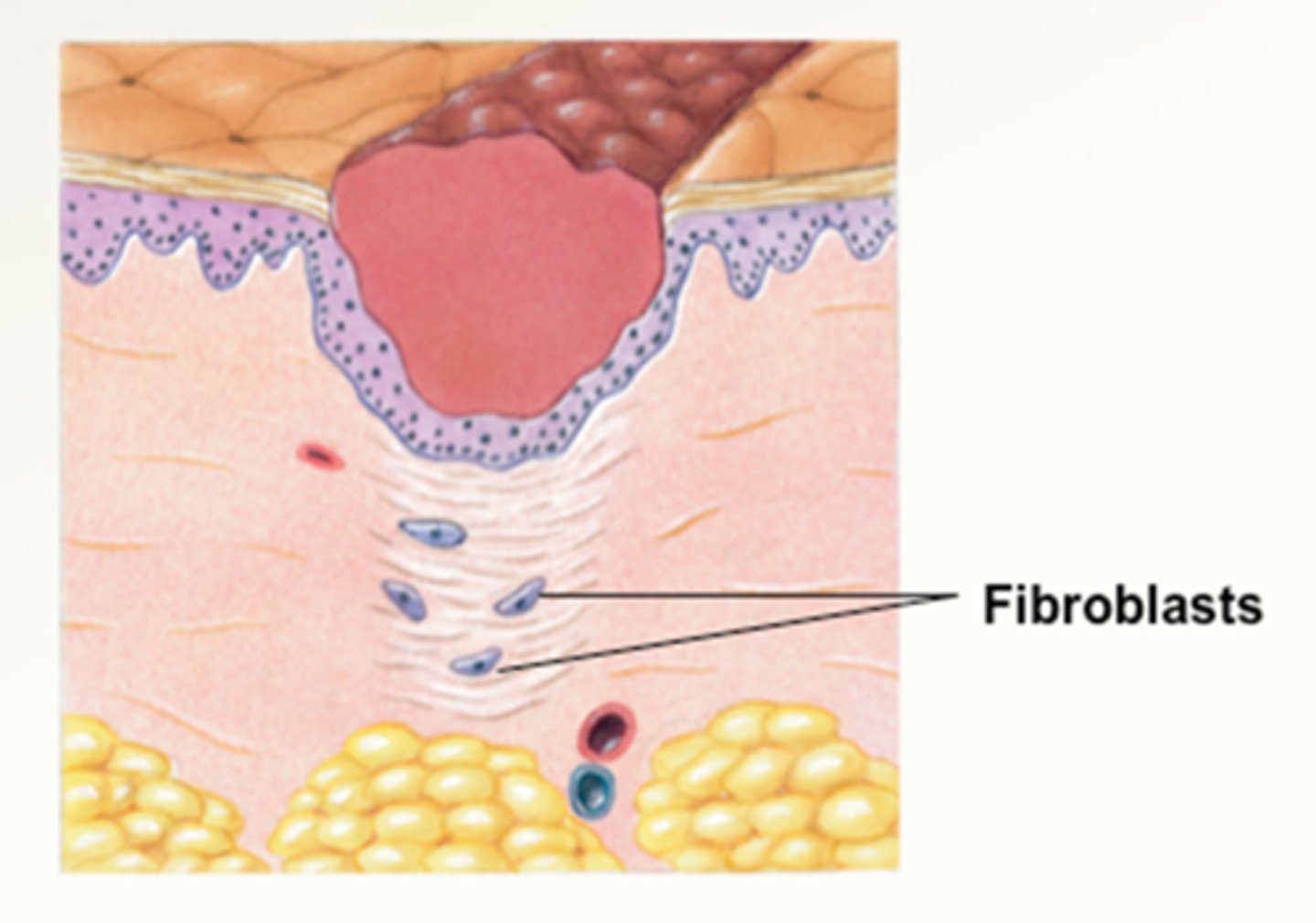
Proliferation phase
The second phase of wound healing; new tissue forms, fibroblasts produce fibrin
Maturation phase
The third phase of wound healing; scar tissue forms, cells differentiate
How can scar tissue cause loss of function?
Scar tissue may replace nerves, muscles, and glands
How can scar tissue limit range of motion?
Scar tissue is not elastic --> ROM may be decreased
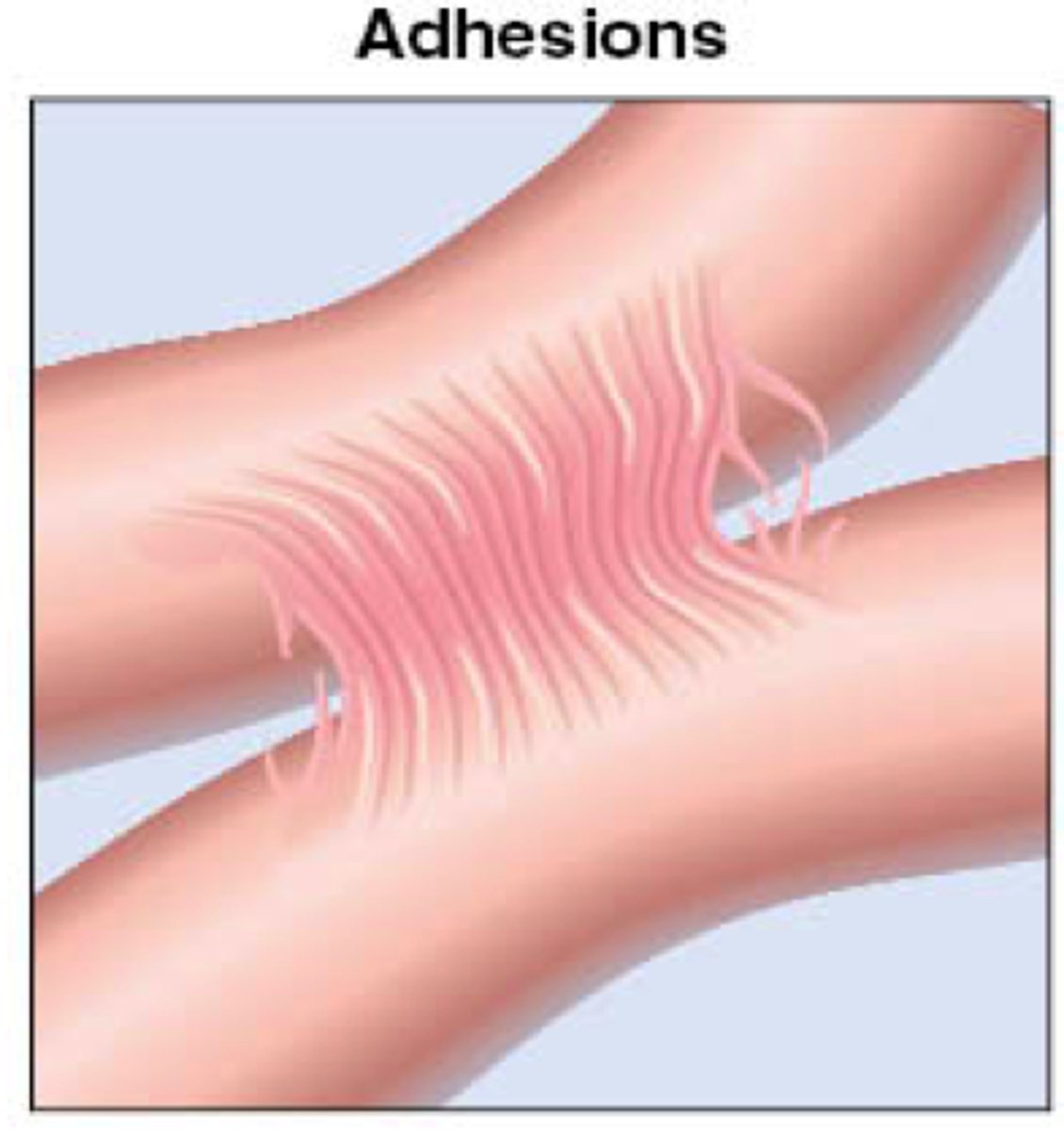
Adhesions
Bands of scar tissue that link two surfaces that are normally separated
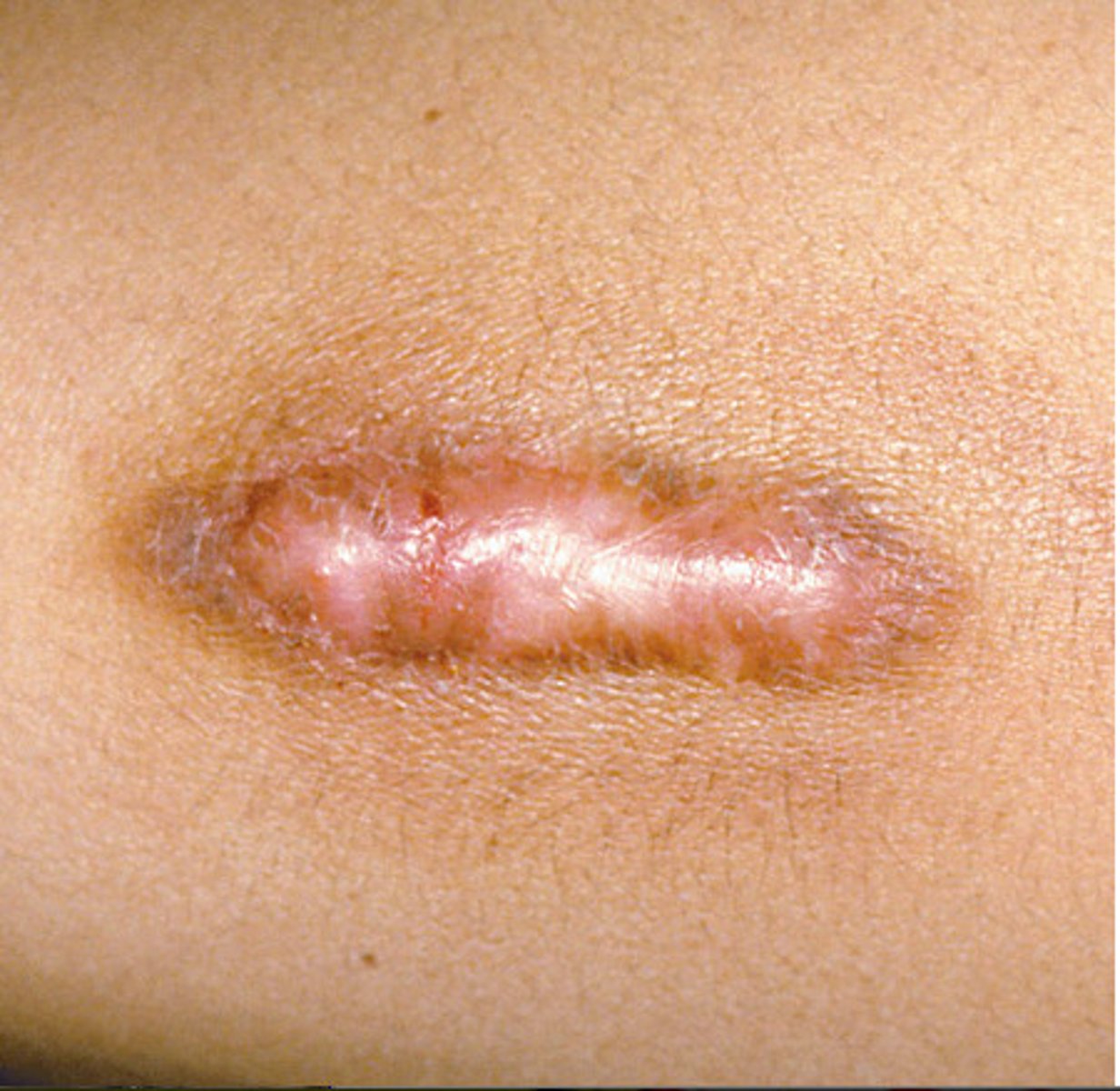
Hypertrophic scar tissue
Overgrowth of fibrous tissue during scare formation --> leads to keloid formation
How can scar tissue cause ulceration?
Scar tissue can limit bloodflow --> leading to tissue death