Restorative Art I - MSFS 245
1/389
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Go from the known to the unknown
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
390 Terms
Restorative Art
Care of the deceased to create natural form, color, and texture; limited to visible parts of remains (start w/ underneath base structures); form refers to shape of surface structure, recognizable by its outline and surface
Restorative Art (cont.)
Scientific thinking (understanding anatomy and color), community engagement (technique learning and conversations w/ fellow embalmers), be willing to try new things
Incentives for achieving proficiency
Psychological effect on family and friends, professional responsibility (our goal), develop a following (reputation, pushing the envelope w/ materials, problem solve and apply other fields to ours)
Laboratory procedures
Analyze situation, excise and clear damage area, clean off bone fragments and foundation, start from known and work toward unknown, top or bottom (if crushed inside out), put puzzle together, dry/suture/wax lacerations and avulsions, restore any missing features
Case considerations and types of RA
Major vs Minor restorations, pathology, aging, postmortem changes, effects of embalming, trauma
Building a base
Anatomical planes and directions, Latin vocab, bones/muscles/skin (facial features - ear, nose, mouth, eye)
Everybody is different
Alignment of facial features, profiles, facial shapes, division of face into zones
Two sides of same coin
Embalming and RA closely intermingled, RA part of EVERY embalming, washing body (gives better picture of what they looked like), setting features, vessel selection (fluid distribution, incision visibility), fluids and solutions (disinfection + preservation = restoration), monitoring injection process, appropriate incision closure (set up for waxing and cosmetics), wash body again, post-embalming restorative techniques, cosmetics, dressing body, placement in casket
Preservative art
Proteins and formaldehyde, pH, bacterial activity, temp, balancing moisture
Embalming chemicals
Buffers, humectants, surfactants, anticoagulants, other preservatives
Prep room detective
Case analysis, long term care, decomp, pathology
Pleasantry
Closing the mouth and eyes, grooming/positioning of the hands
Keeping an eye on things
Identify and respond to dehydration, swelling, other problems
Autopsy preparation
Disruptive process to head and torso, can affect the way people appear in casket
Organ and tissue donation
Disruptive process, tissue to be preserved, limbs to be restored
What comes after
Tissue building, compresses, waxes, tissue damage
Tissue building
Equipment necessary (syringe and tissue fluid), how to do it (hidden points of entry)
Waxes and their application
Types of waxes and uses, heating and cooling, hardening and softening
Tissue damage
Addressing trauma, pathology, skin disorders, communication w/ family; case studies
Final piece of the puzzle
Photography, color theory, lighting, cosmetics, dressing and casketing, preparation of unembalmed body
Can you make them look like this again?
Photographic viewpoints and lighting, types of photos
Lighting
Types of light fixtures, color theory application, lighting in FH, outcomes of colored lighting
Color theory
Basics, how we see color, application to RA
Cosmetics
Color theory application, types, natural skin tone recreation, brushes, contouring
Hair care and replacement
Caring for hair, wigs, replacement of hair, types of artificial/natural hair, coloring hair
Dressing and casketing
Difference between men’s and women’s clothing, cutting/not cutting clothes, placement in casket, finishing touches
Preparation of an unembalmed body
Safe handling, dressing, cosmetizing, following family’s wishes
Permission for restoration
Secured from someone in authority before making incisions/excisions, necessary for major restorations (can legally be described as mutilation), not needed for those incurred in prep of remains (setting features, distention, leakage, tissue discoloration)
Excision
The act/procedure of removing by/as if by cutting out
Incision
Surgical cut made in skin/flesh
Minor restorations
Day-to-day procedures such as setting features, tissue building, swelling reduction, discolorations, realignment of fracture, cosmetics, dressing and casketing
Major restorations
Time consuming/skill (ask permission) such as soft tissue repair, deep wound prep, bone reconstruction, hair restoration, sub-tissue surgery, modeling of facial features, dental fixes, recoloring discolored face
Causes of RA - Injuries
Fractures, contusions, swelling, torn tissue, abrasions, discolorations, loss of hair, damage to facial features
Causes of RA - Pathology
Swelling, torn tissues, discolorations, hair, tumors, medical devices, lesions, addiction
Causes of RA - Age
Discoloration, changes in mouth, weight loss, hair loss, hygiene
Causes of RA - Postmortem time period
Movement of body fluids, decomp (desquamation, discoloration, gases, odor, purge), subcutaneous emphysema, contact pressure, autopsy, tissue donation, dehydration
Desquamation
The sloughing off of epidermis that occurs as skin cells decompose
Effects of embalming
Dehydration, discolorations, swelling, poor preservation
Adhesives (glue)
Adhere tissues together, secure incisions, create ‘tacky” surface for cosmetics; cyanoacrylates (Super glue/Kragle) are in applicator, spray, adhesive strips, or brush; polyethylene glycol polymers are in brushes
Aneurysm hook
Blunt dissection, raising vessels, setting features, face measurement, securing calvarium clamps, facial markings, can have regular/cradle handle
Aneurysm needle
Blunt dissection, raising vessels, setting features, face measurement, securing calvarium clamps, facial markings, has “eye” in hook portion which could be used for passing ligatures around vessel (similar to hook, but has sharp pointed tip)
Armatures
Used as a base for wax/cosmetic (wire, styrofoam, plastic)
Calvarium clamps
Secure calvarium after autopsy
Compresses
Soaked cotton/gauze (bleaching, pressure, preservation, moisture retention), cranial cap absorbent pads are perforated 8”x15” lint free cotton sheet that absorbs 10x its weight in liquid
Cotton
Soft, white, fibrous substance; absorb chemicals for compresses, absorbs moisture, support
Electric spatula
Tissue dryer, heating element, reduce swelling, dehydrates and cauterizes; keep it lubed and keep it moving w/ massage cream
Massage cream
Retains moisture/prevents dehydration, cosmetic removal, don’t use sparingly (glob it on), useful at end of embalming before cosmetics
Needle injector
Used to insert a “barb” into mandible and maxilla to hold lower jaw in closed position, several types of handles available which can make device easier to use, electric version also available; stay parallel to gums
Eye caps
Creates form, secures eye, plastic (most common - flesh/clear colored) metal, cloth
Mouth formers
Restore contour to mouth, curved/flat, serrated side for security, holes for threading ligature
Feature builder
Regular (cellulose and alcohol, react w/ moisture to gel), firming (same reaction as regular, contains formaldehyde); feature builder solvent (solution of alcohol and some water, used to dissolve feature builder of both types)
Hypodermic needle
Hollow tube w/ a pointed opening at end, tissue building, hypodermic injection for preservation, thickness measured in gauge, length selection based on delicacy of operation
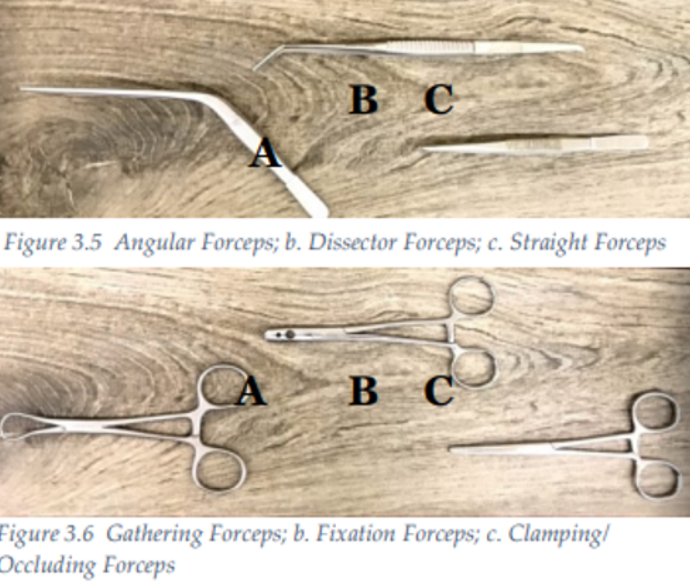
Forceps
Spring forceps (angular/drainage, straight, dissector), clamping and occluding, gathering, fixation
Incision spreader
Holds open incision
Scissors
Used for cutting and opening arteries/veins; vary in length but may be straight, curved, pointed, blunt
Grooved director
Expands to help guide drain tube/device into vein for drainage; Mickey Mouse tool
Hair dryer
Drying hair and nail polish, heating hair for coloring purposes, melting wax, extension cord
Hypovalve trocar
Injects tissue hypodermically, small gauge trocar, one-way handle activated by button, attached to embalming machine; push button going in, release button pulling out
Trocar button
Threaded plastic screw used for closing trocar punctures, may also be used to close small punctures/surgical drain openings/intravenous line punctures; available in several sizes, use liquid sealer after
Trocar button applicator
Used to insert trocar button
Ligature
Filament used to bind tissue, linen/cotton/polyester, waxed/unwaxed, different thicknesses available, selection based on operation
Mortuary mastic/putty
Used to restore contour to features (mouth, eyes, autopsy, incisions), applicator/spatula
Nasal aspirator
Attached to aspirator hose, nasal passages and throat, tracheostomies
Autopsy aspirator
Attaches to aspirator hose, removes fluid from cavity and viscera bag; listen for changes in suction
Hydro aspirator
Creates vacuum when water is run through mechanism; friend and enemy
Plastic garments
Worn on deceased to protect clothing and contain moisture, different sizes, secure; unionalls, coveralls, capri pants, pants, stockings, sleeves, shirt
Plastic wrap
Rolled plastic on dispenser, place under autopsied heads over pillow on casket, secure long incisions, prevent leakage
Stay Cream
Seal-N-Form (fills and seals wet tissue, helps hold dentures in place and fills out emaciated cheeks), Kalip Stay Cream (fully workable and easily applied, can be used on delicate tissues of eyes/lips/nostrils, smooths unsightly wrinkles and folds in place, useful for filling tiny separation which can occur between lips as well as small fissures on lip)
Positioning devices
Adjustable/styrofoam head blocks, head rest, body rests, extremities positioners, arm and hand rests consist of 2 curved metal arm holders attached by adjustable strap
Scalpel
Small knife, detachable/permanent blade, incisions and excisions
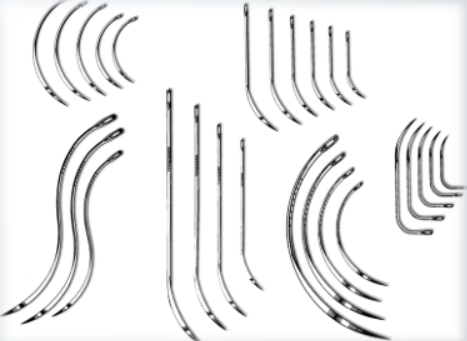
Suture needles
Half curved, double curved (“S” curve), circle curved, loopuyt double curve/back curve, L shaped; all come in multiple gauges and lengths
Waxes
Beeswax/paraffin/petroleum, types (lip wax, surface restorer/soft wax, modeling wax, wound filler/firm wax - large holes), multiple tones
Anatomical position
Standing upright, facing forward, feet flat, palms out
Anterior
Before/towards front; opposite is posterior
Deep
Away from surface; opposite is superficial
Distal
Away from center of body/point of attachment; opposite is proximal
Intermediate
Between 2 structures
Lateral
To side of/away from middle; opposite is medial
Medial
Towards middle; opposite is lateral
Superior
Top of head/above, opposite is inferior
Inferior
Feet/below; opposite is superior
Posterior
Back/towards rear; opposite is anterior
Oblique
Deviation from parallel/perpendicular angles
Proximal
Nearer the center of body/point of attachment; opposite is distal
Superficial
Closer to surface; opposite is deep
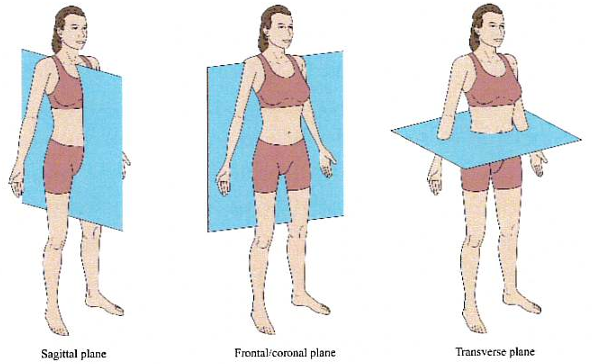
Coronal body plane
Division of body from Anterior → Posterior
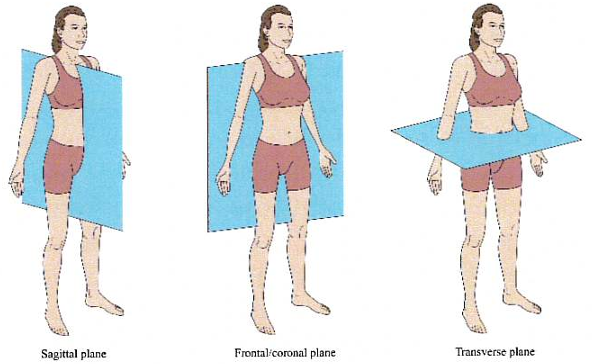
Transverse body plane
Division of body from Superior → Inferior
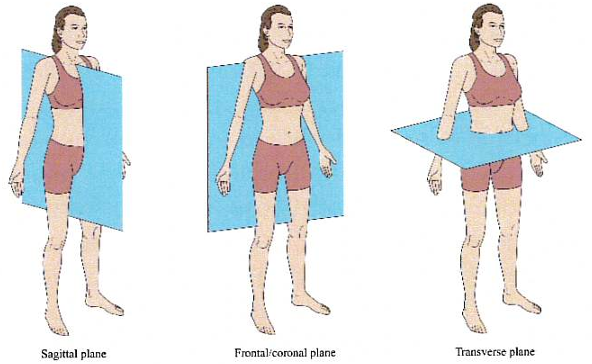
Sagittal body plane
Division of body from Left → Right; can be done anywhere on body, called midsagittal if divided directly in middle
Anguli
Corner/bend
Labii
Lip
Lacrimal
Weeping/tears
Maxilla
Jaw
Nuchal
Nape of neck
Occipital (location)
Back of head
Oculi
Eye
Oris
Mouth/speech/expression
Palatine
Roof of mouth
Palpebrae
Eyelid
Parietal (location)
Wall of hollow cavity/organ
Ciliary
Lashes/eyebrow