Archaeology final
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
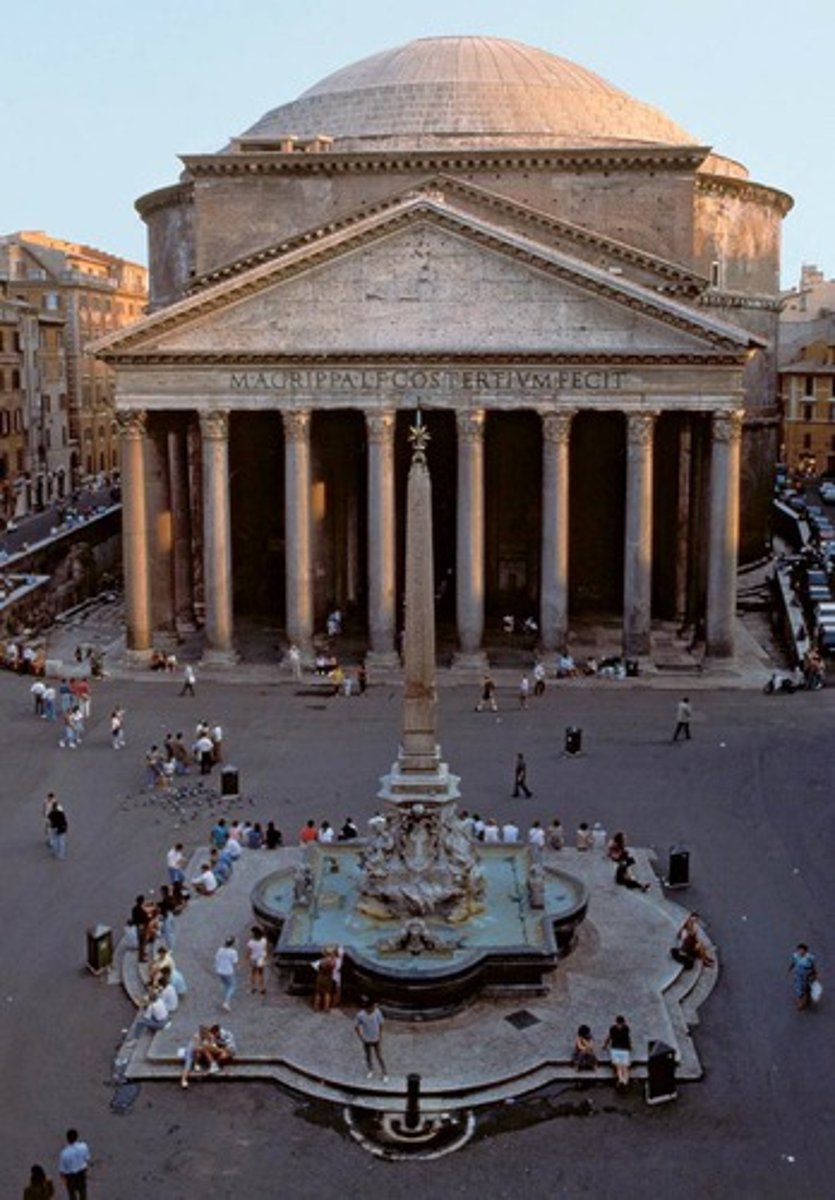
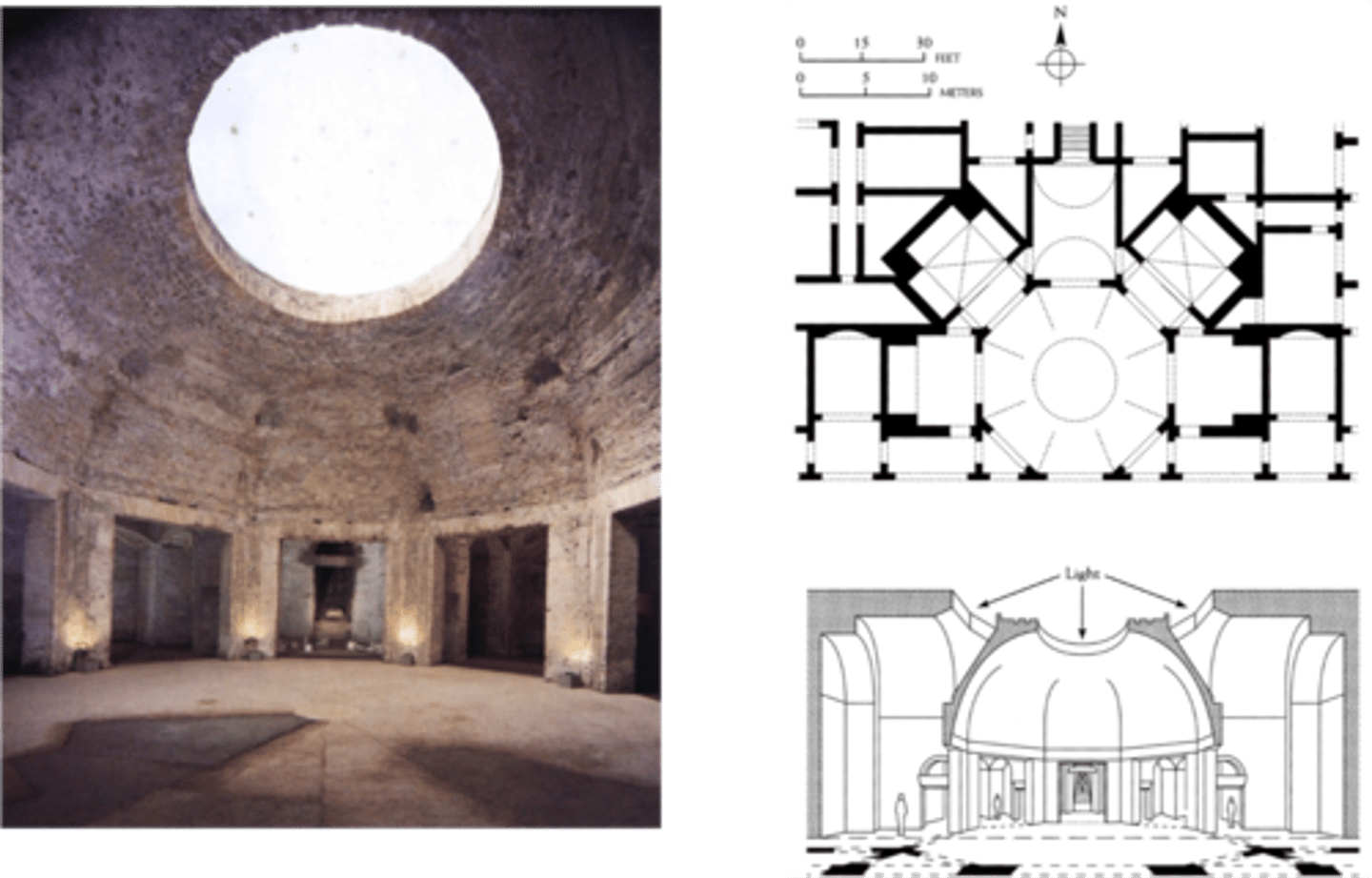
Pantheon
First commissioned by Marcus Agrippa during the reign of Augustus, completed by Hadrian in 128 AD
• Part of a complex of buildings with the Baths of Agrippa, Basilica of Neptune
• Destroyed in a fire in 80 AD, rebuilt by Domitian, burned again in 110
• Largest free dome in the premodern world: height to the oculus and diameter of interior circle are 43.3 meters

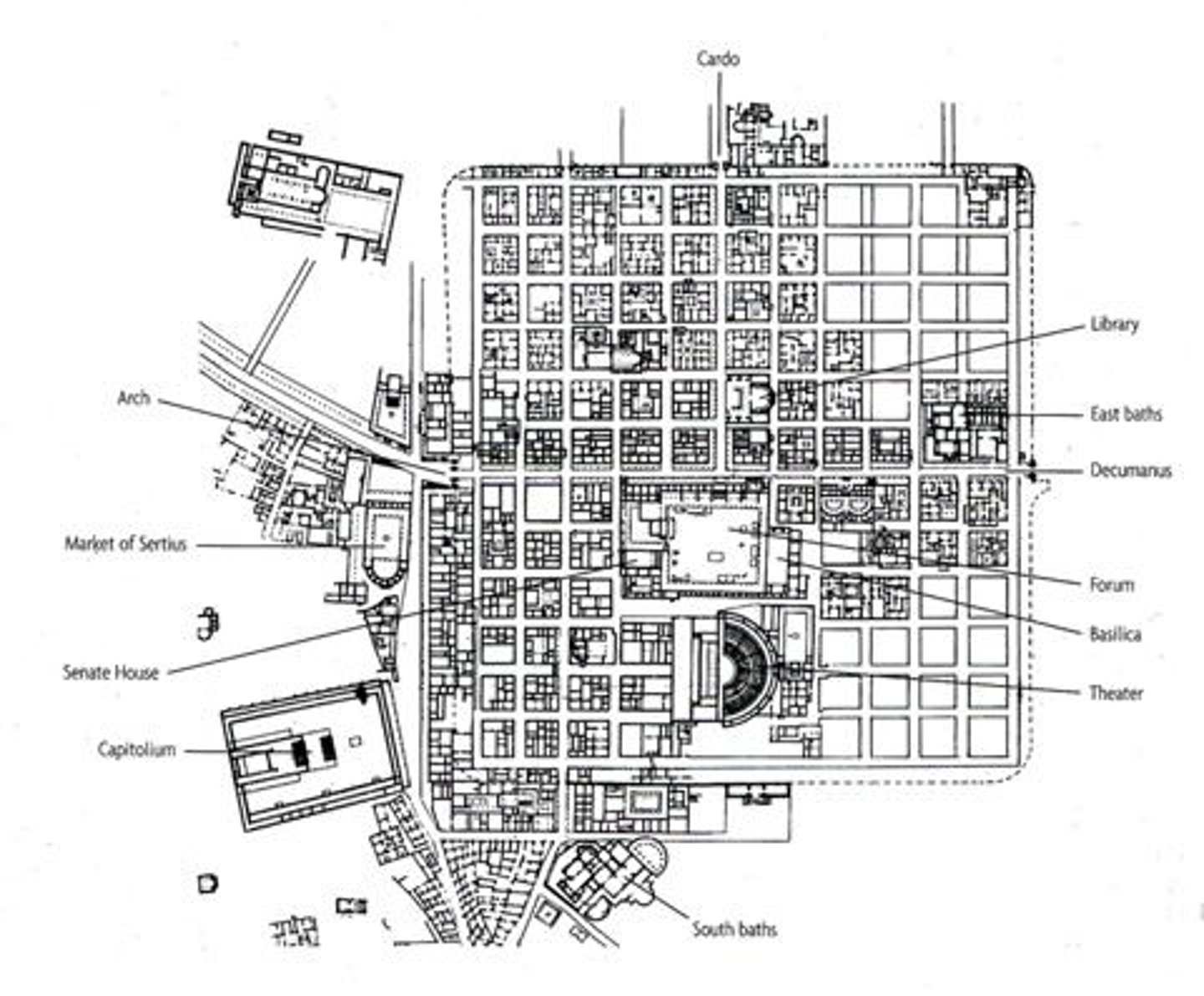
Timgad
Algeria; 100 BCE; Emperor Trajan was the patron; ruins are noteworthy for representing one of the best extant examples of the grid plan as used in Roman city planning
Trajan's Forum (and the buildings/monuments it contains)
Main monuments: equestrian statue of Trajan, Basilica Ulpia
Templum Pacis
Third of the "Imperial fora," built under Vespasian
71-75 AD
Temple of Peace

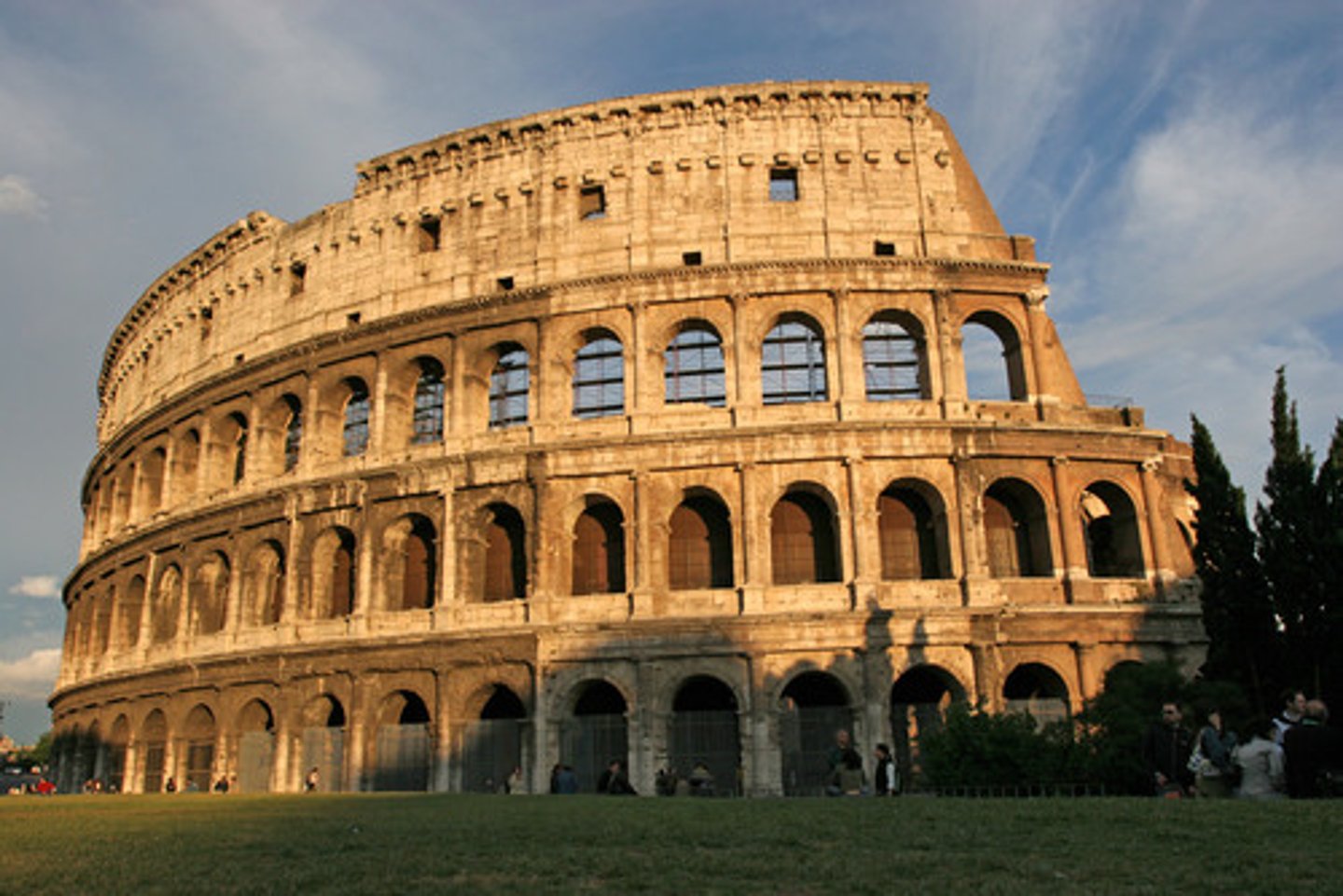
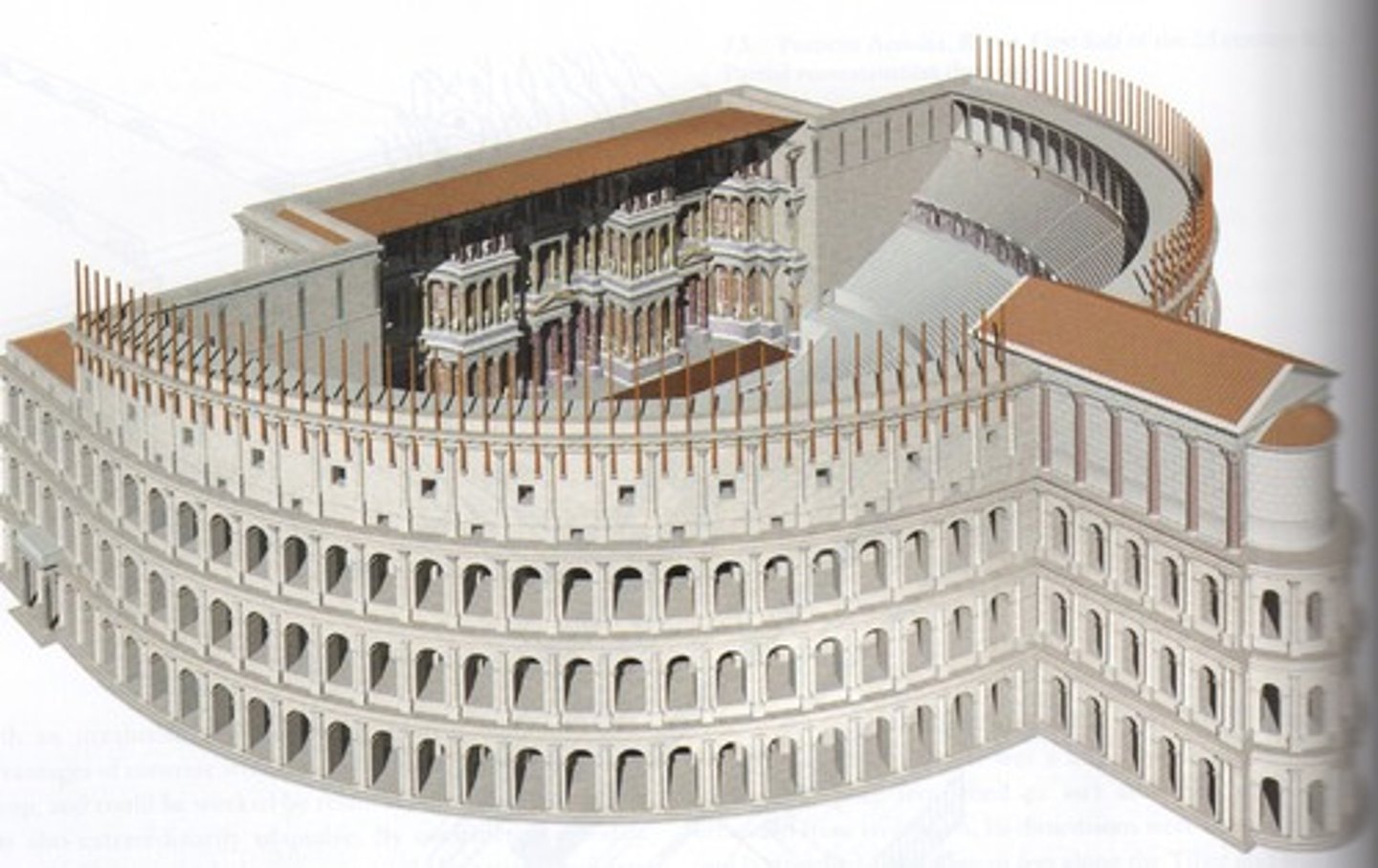
Colosseum
- The first permanent amphitheater in Rome
- Inaugurated by Titus finished by Domitian
- Elaborate social and gender segregation in the seating arrangements

Basilica of Pompeii
2nd century bce
-note the tribunal at the end used for legal matters

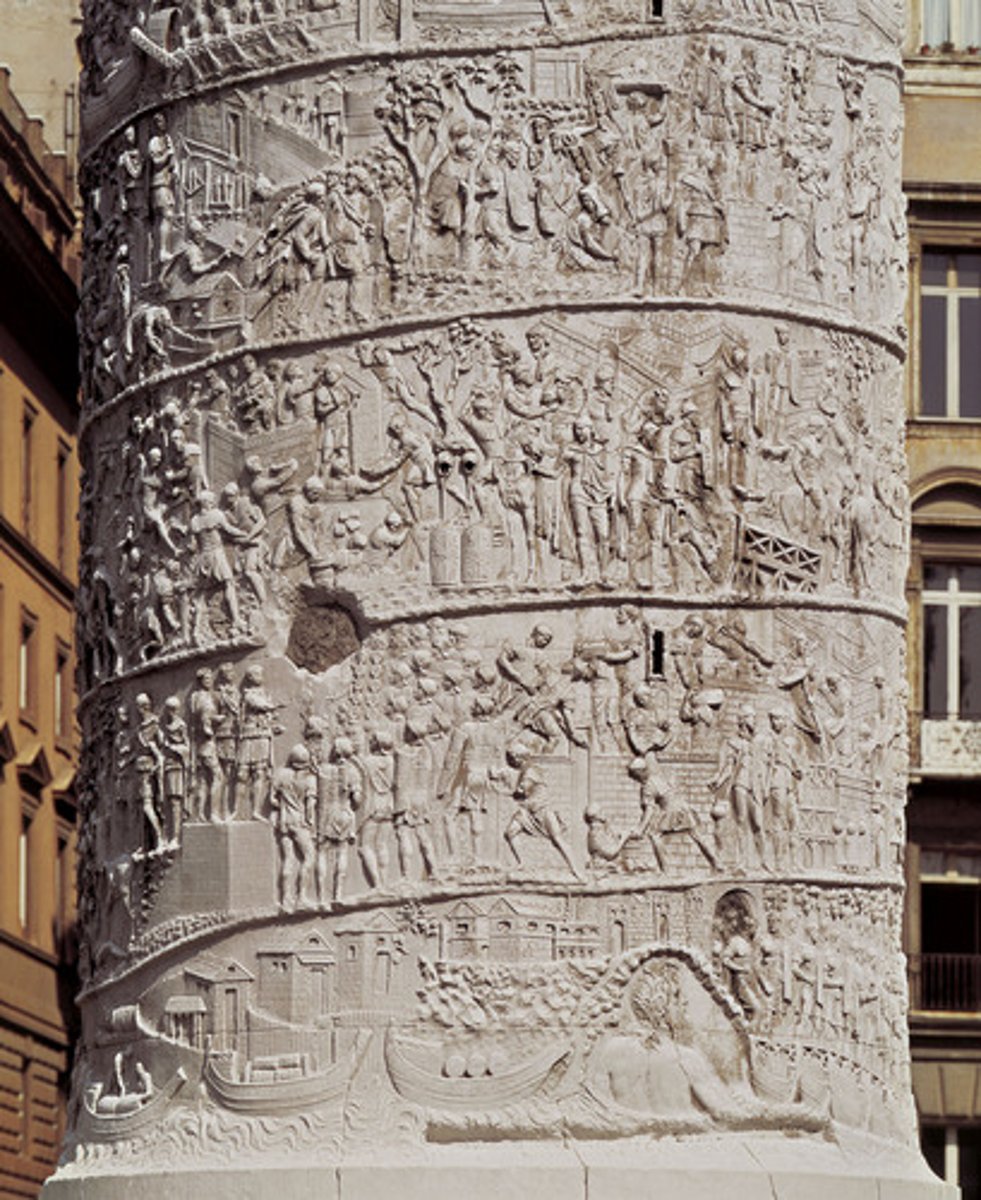
Column of Trajan
112 CE
Roman Empire

Damnatio memoriae
"condemnation of memory"
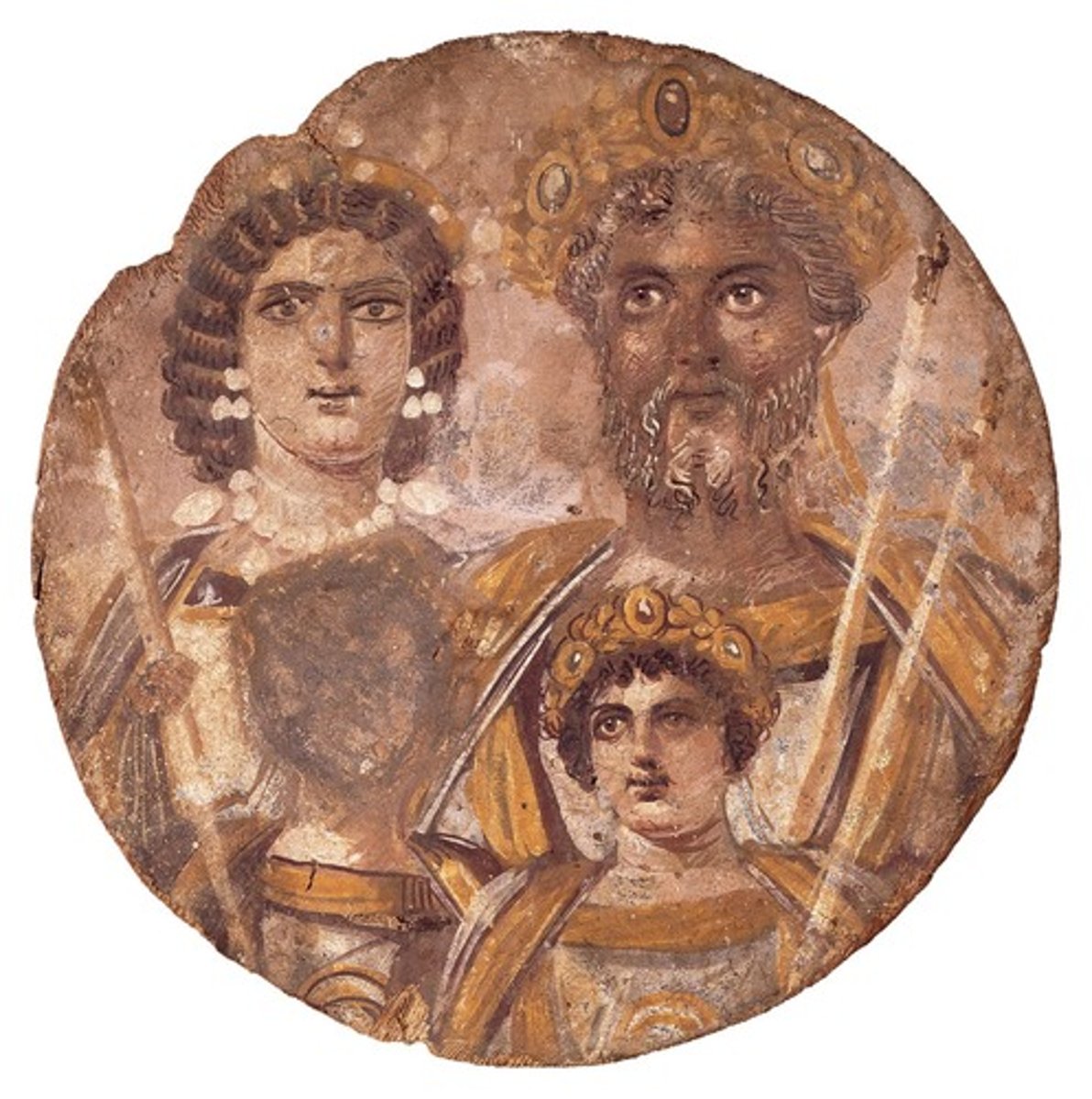

Christian catacombs
caves beneath the city for secret burial and private services, later as a place of worship, mass with the dead
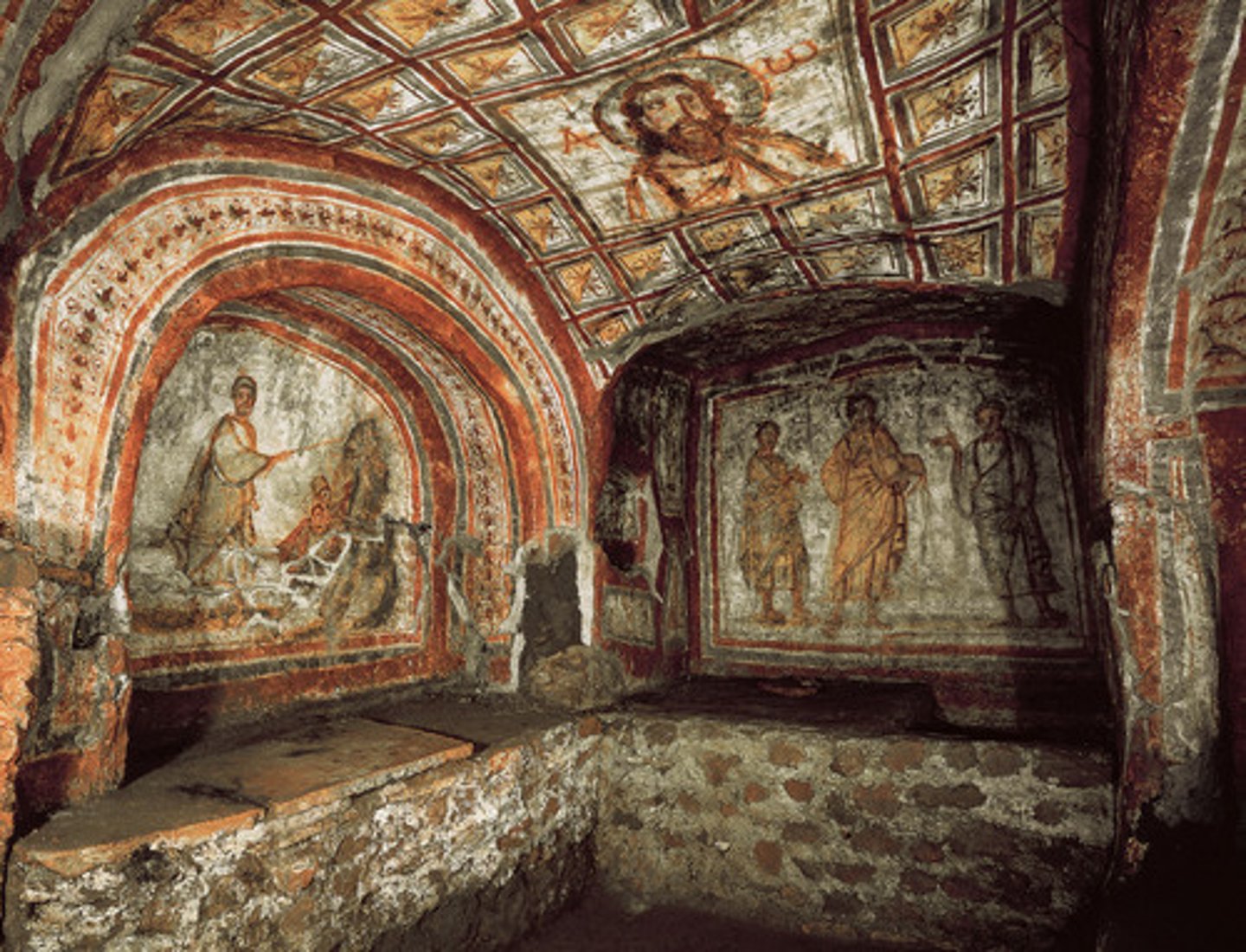

Domus Aurea
Latin for "House of Gold." It refers to the palace that was built at the center of Rome after the fire during Nero's reign.
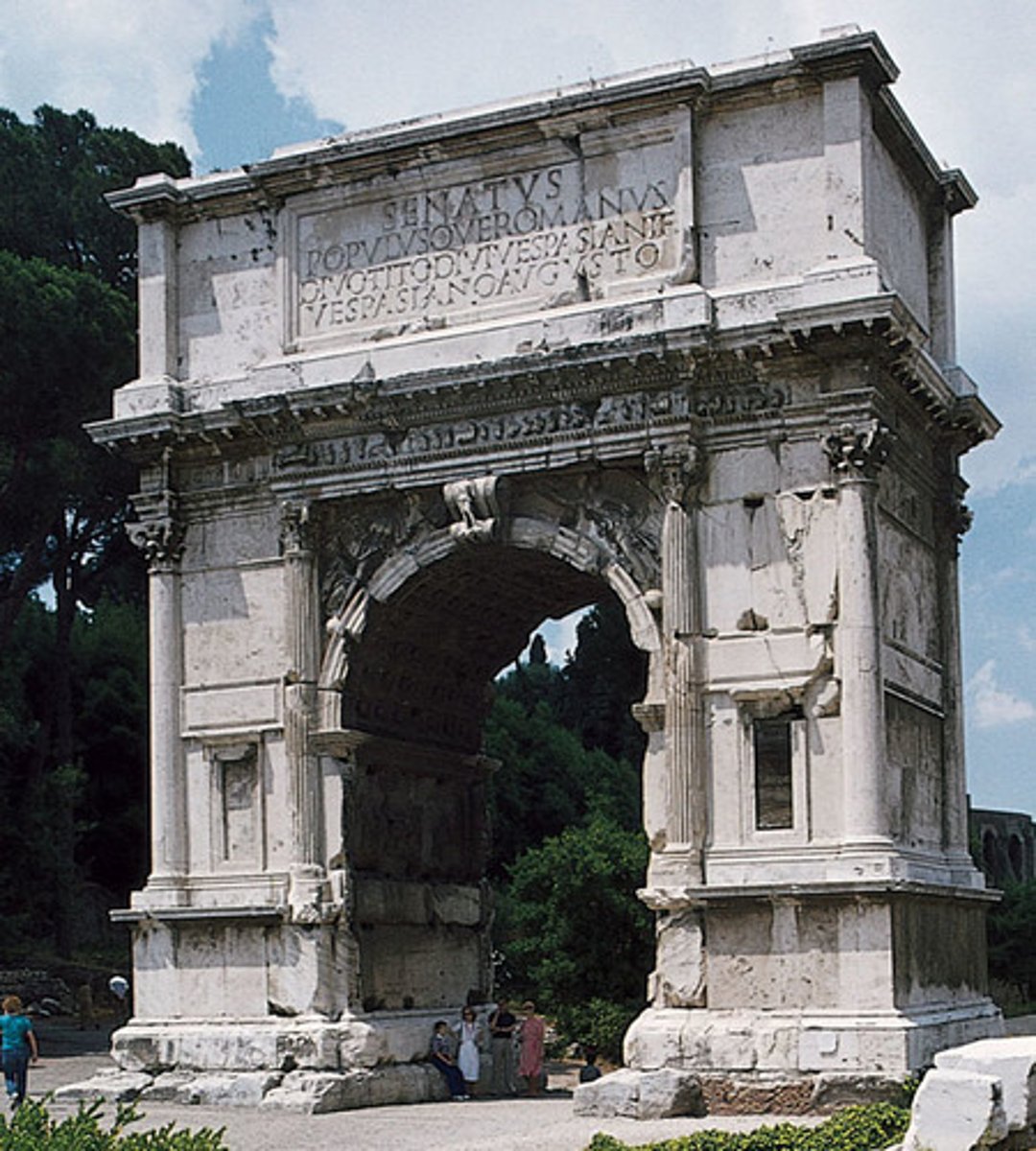
Arch of Titus
81 CE

Forum of Pompeii
regular elongated rectangle, 38 times 142 meters and was built with surrounding colonnades
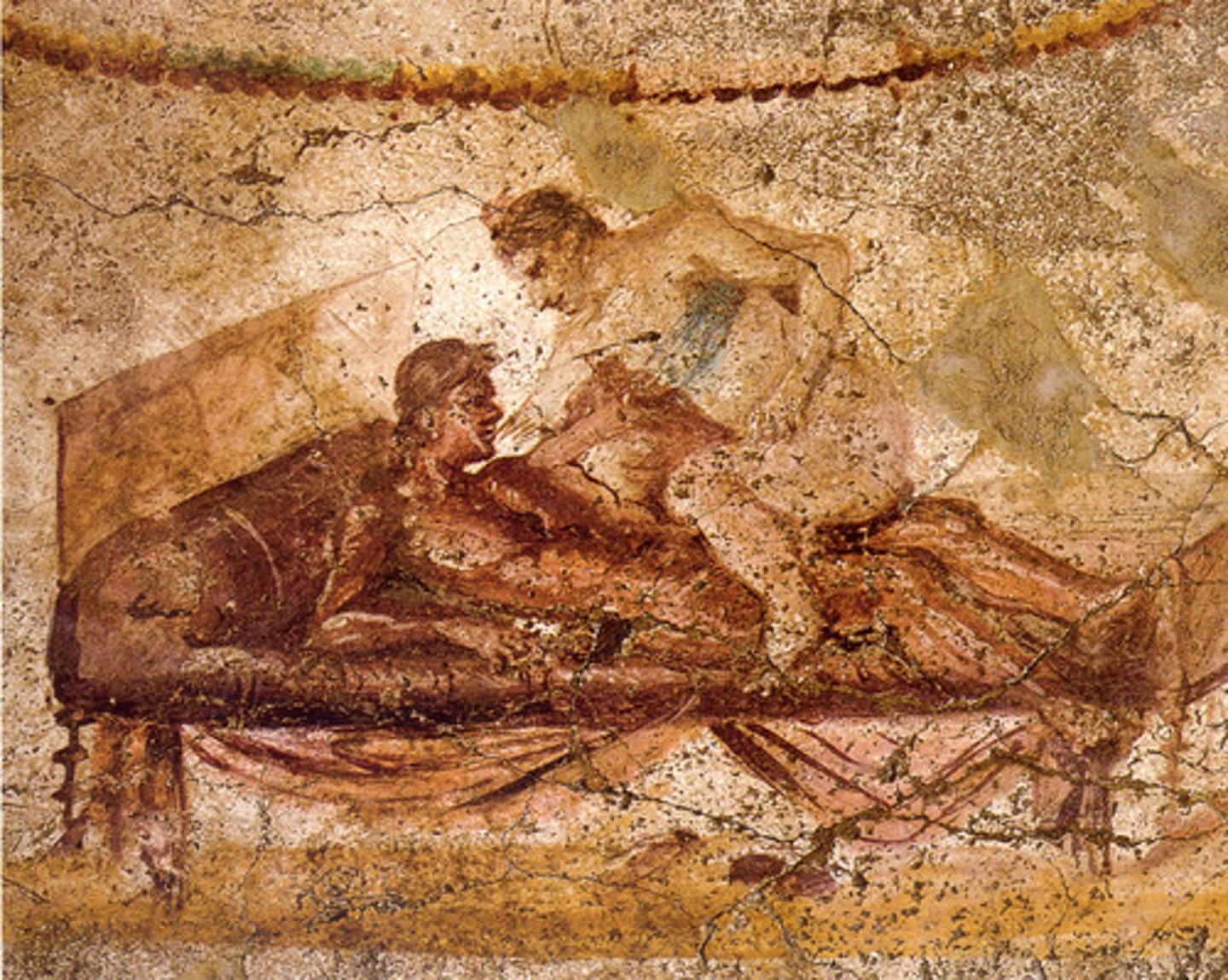
The lupanar at Pompeii
official brothel

The house of the Faun at Pompeii
-Represents extreme decoration of roman homes
-threshold mosaics spell welcome, depict a dog
-narrative scenes on the walls
-friezes showing figures and landscapes

Ephesus (especially the Library of Celsus and the Terrace Houses)
-Represents extreme decoration of roman homes
-threshold mosaics spell welcome, depict a dog
-narrative scenes on the walls
-friezes showing figures and landscapes

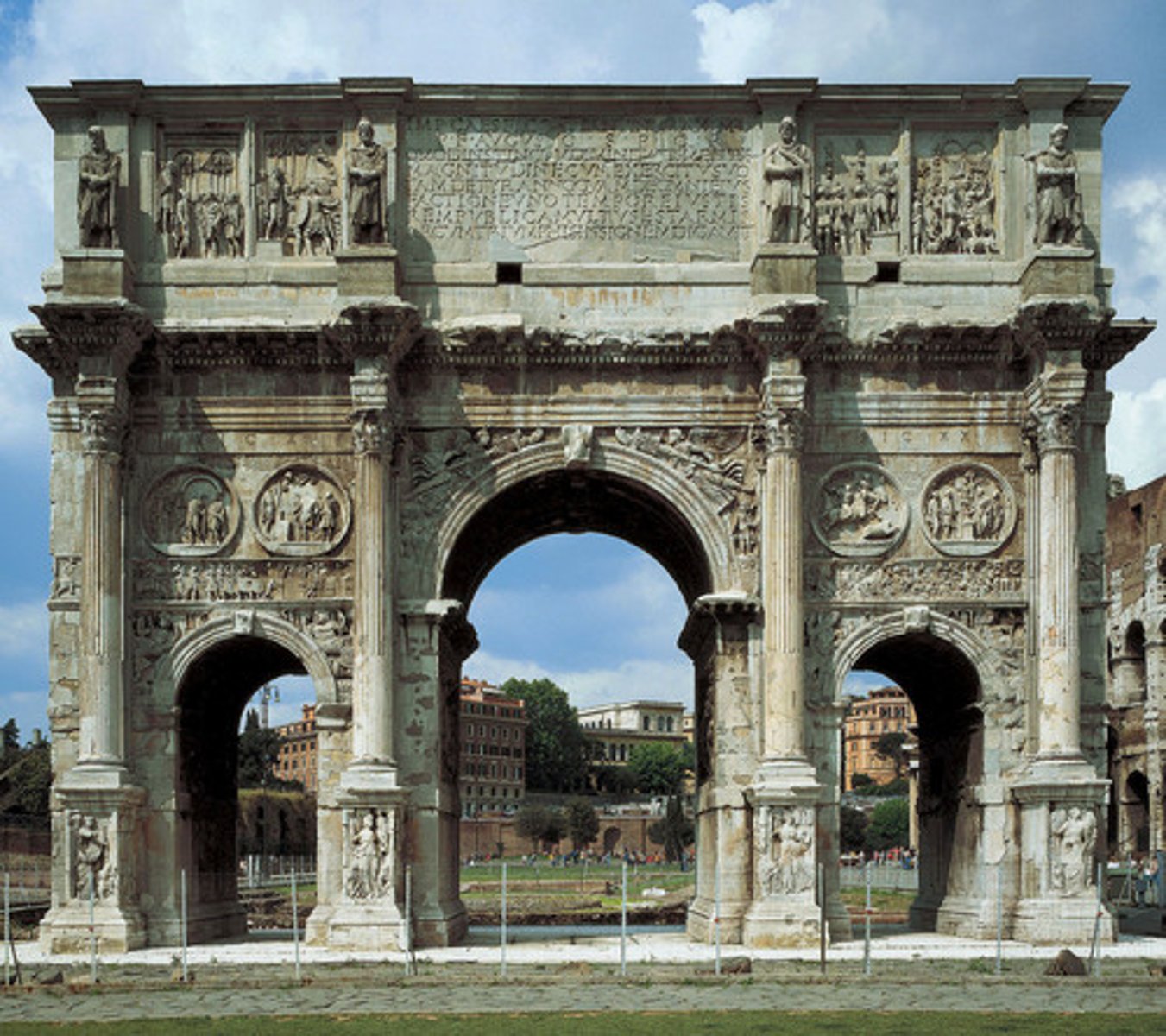
Arch of Constantine
- dedicated in 315 A.D. in honor of his defeat of Maxentius
- Located near the Colosseum, three archways
- Decorated with sculpture taken from earlier monuments (Trajan, Marcus Aurelius, Hadrian)
- Friezes from the time of Constantine - stylistic change, non-naturalistic approach, lacks spatial depth, Constantine is disproportionately large, other figures stumpy, doll-like

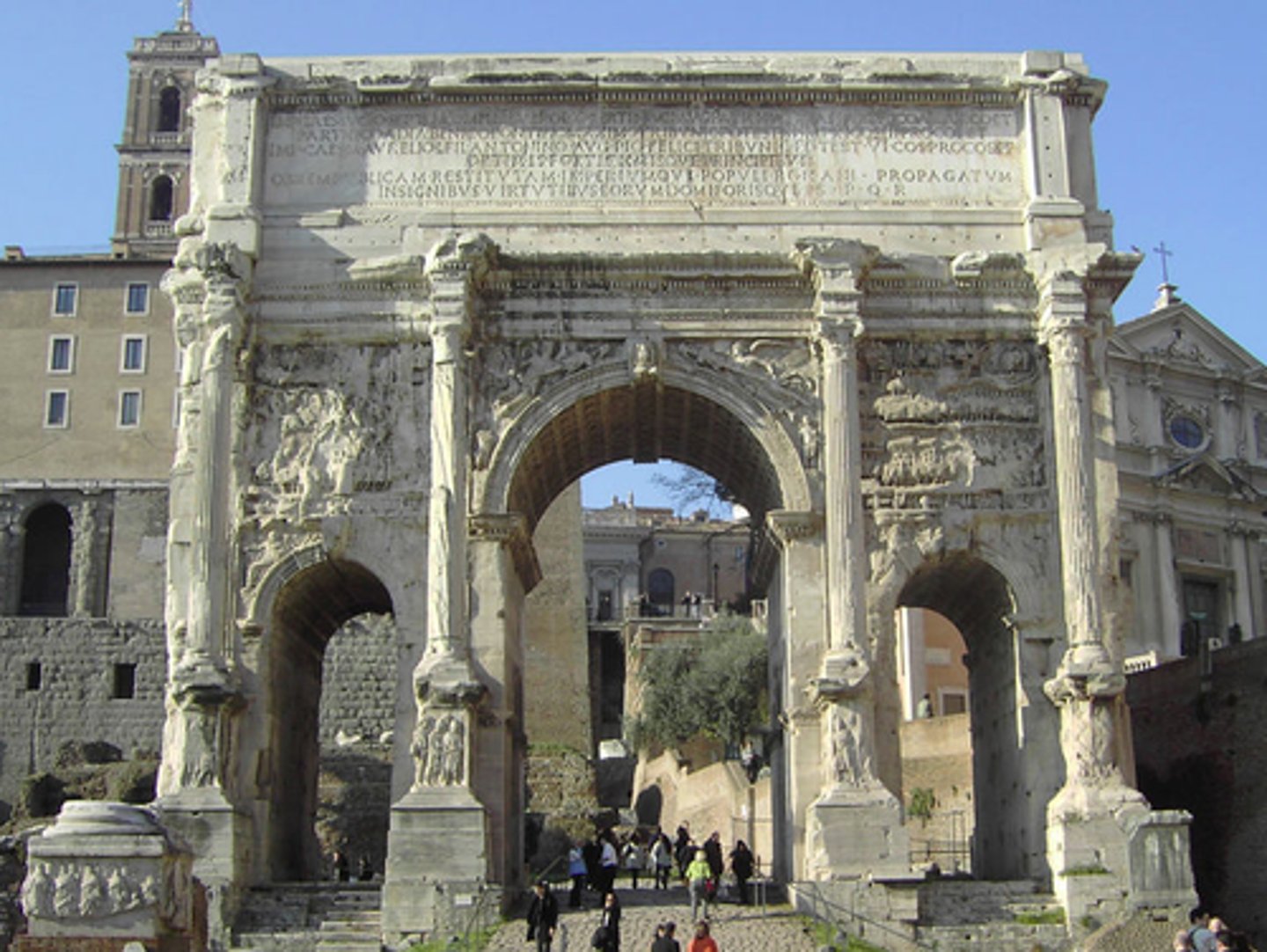
Arch of Septimius Severus
• Dedicated in 203 AD to commemorate Septimius Severus' victory over the Parthians at Ctesiphon in 197 AD
• Geta removed from the dedicatory inscription as part of his damnatio memoriae
• New style of representation-panels depict multiple aspects of historiated events in one space without clear registers

Column of Marcus Aurelius
was carved in the late 2nd century, more stylized and less strictly accurate physical and historical representation became popular, exaggerated gestures and distorted features that were obviously intended to evoke a sense of emotion or horror as might be expected in engaging in a conduct of war
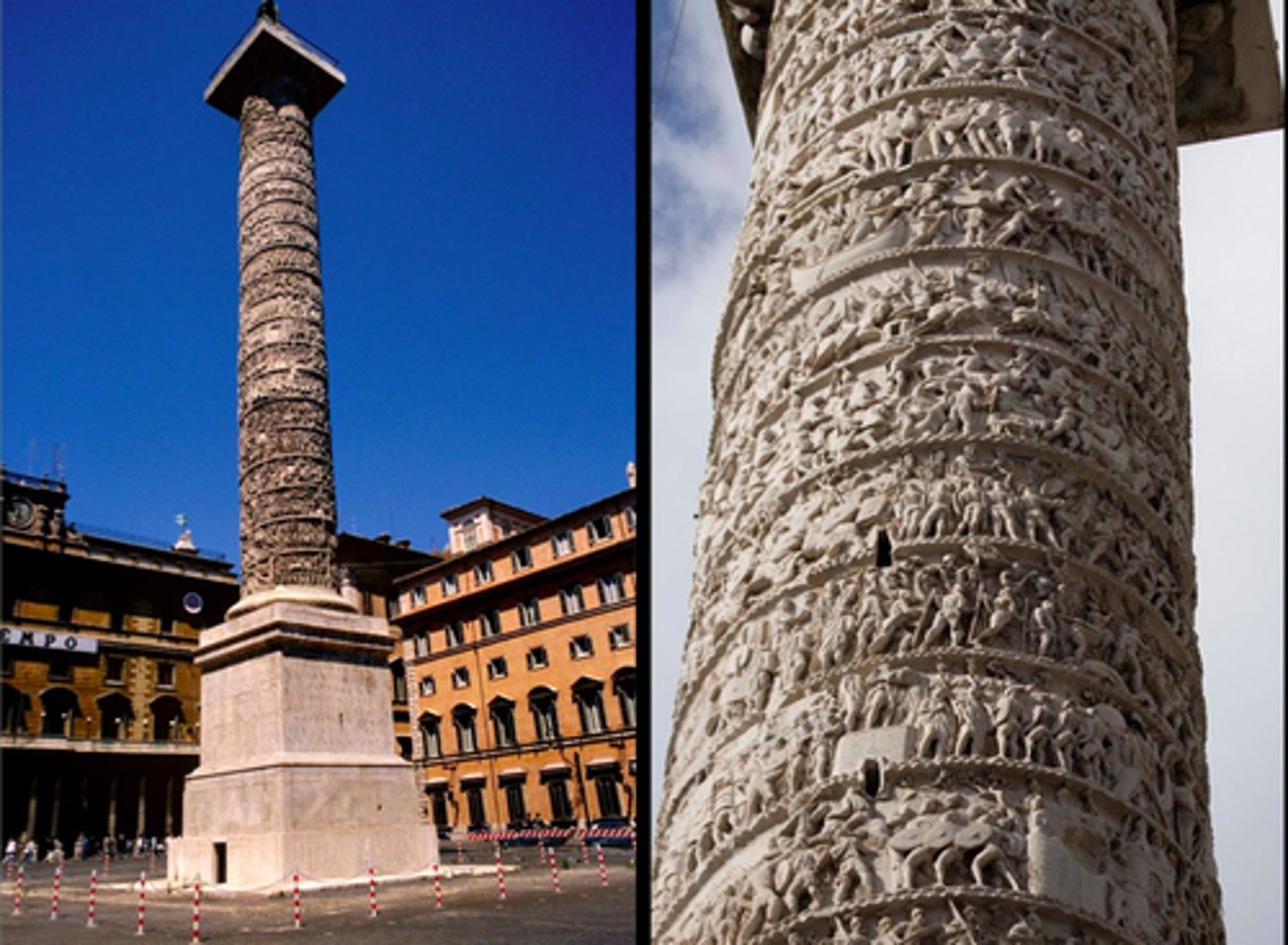

Base of the Column of Antoninus Pius
restored in 1706-08 and erected in the centre of Piazza di Montecitorio
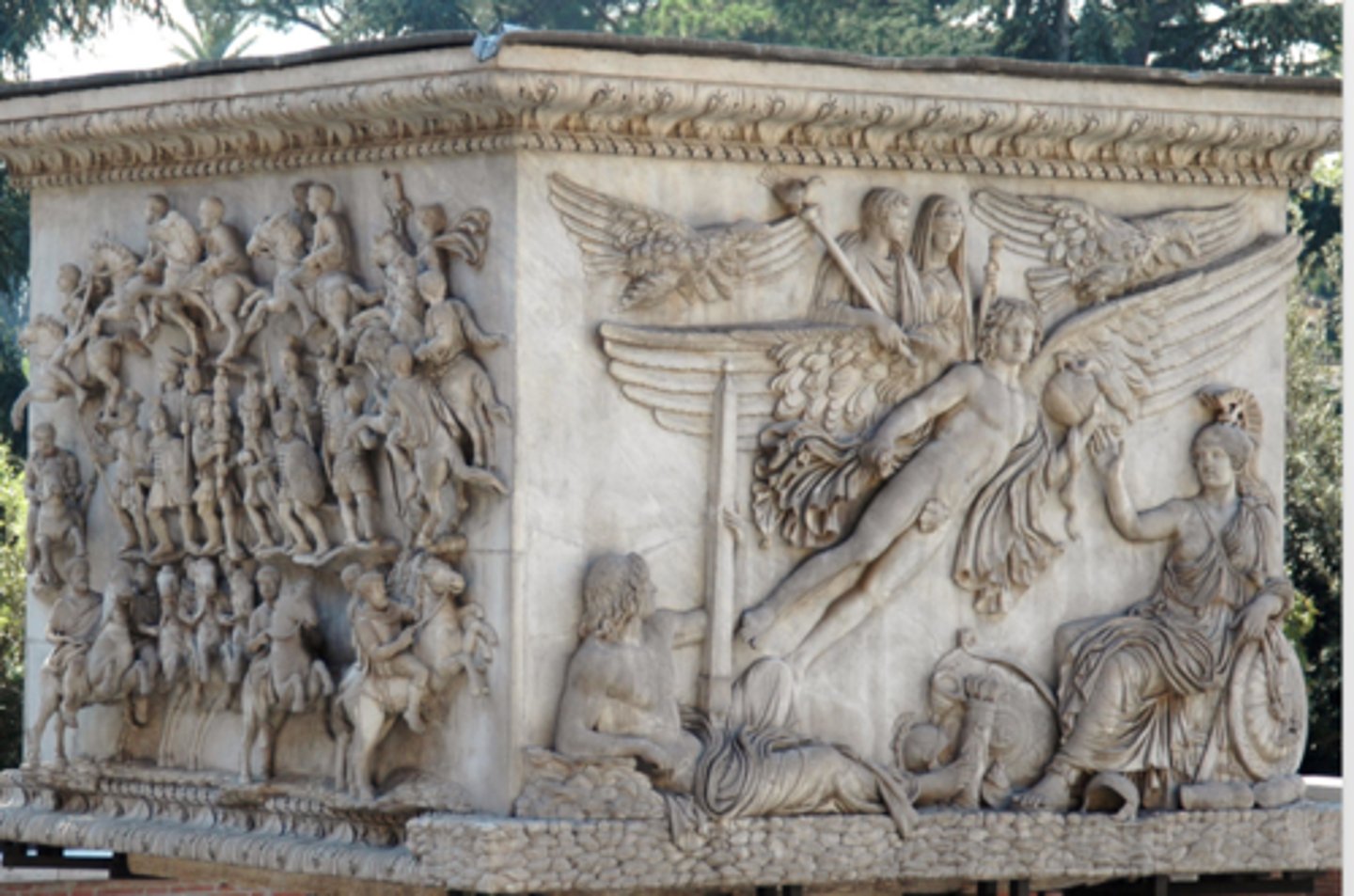

Mythological sarcophagus
heir to a long Roman tradition that celebrated the past by preserving images of the dead

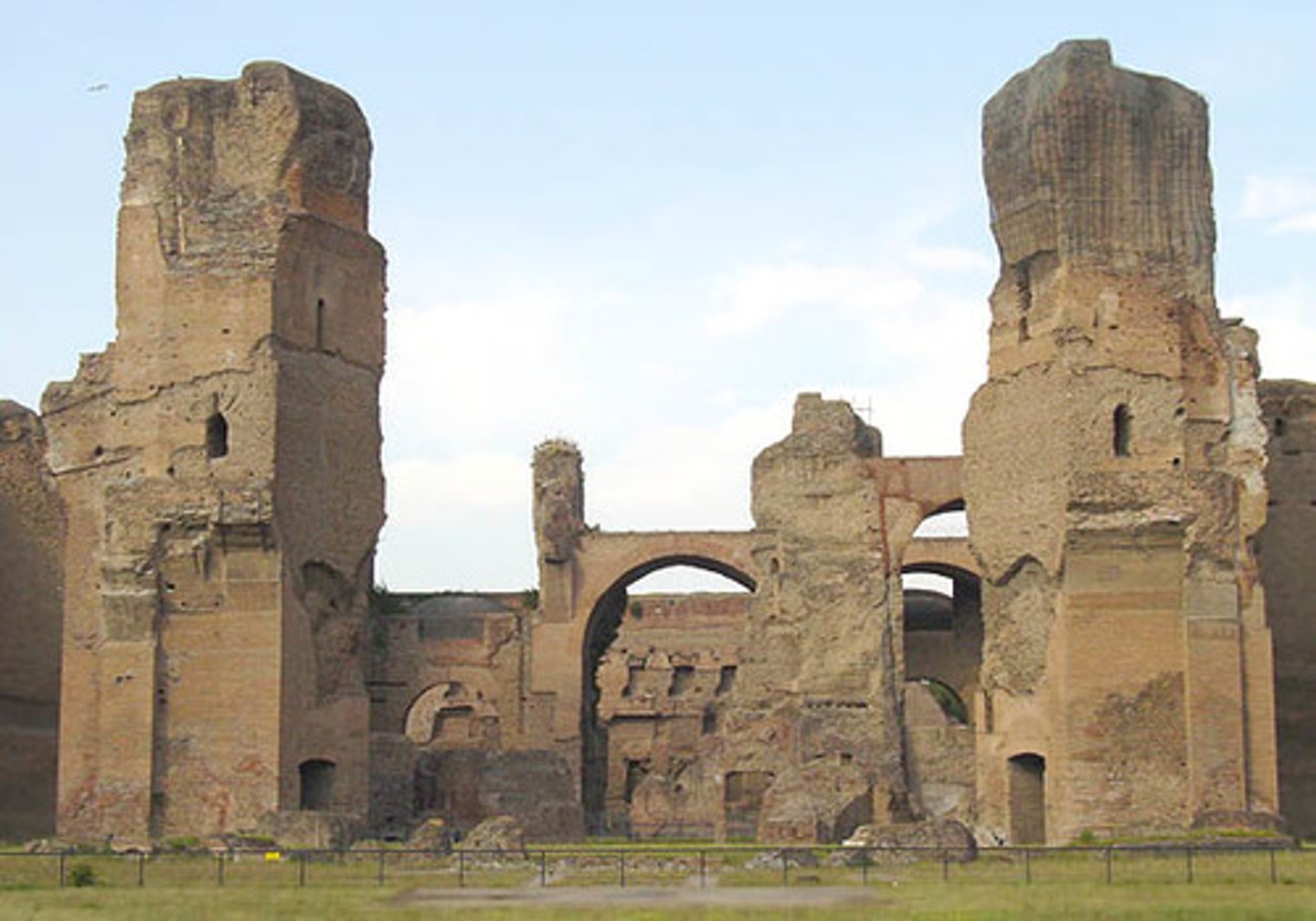
Baths of Caracalla
Built by Emp. Caracalla to please his citizens (vicious ruler) large pools, spas, gym, gardens...basically ancient country clubs for citizens to relax in luxury

Portrait mummies
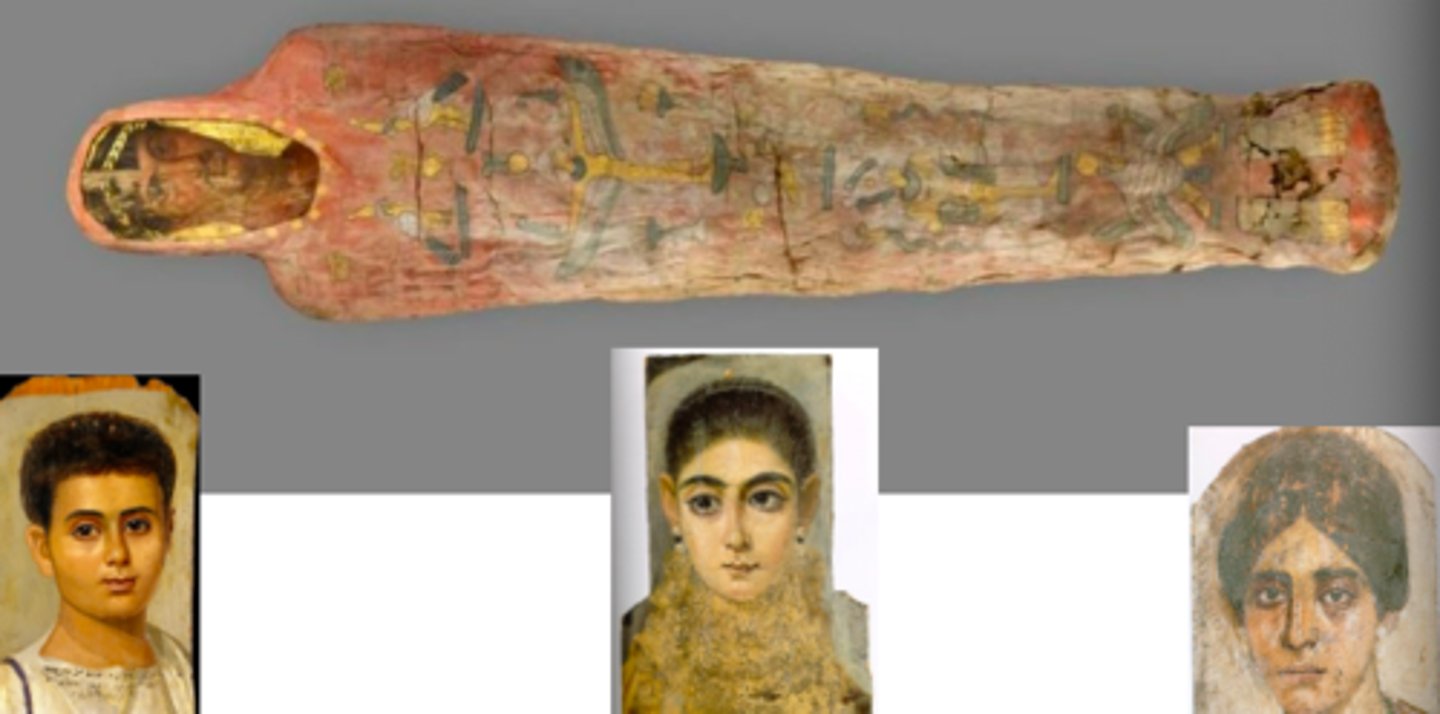

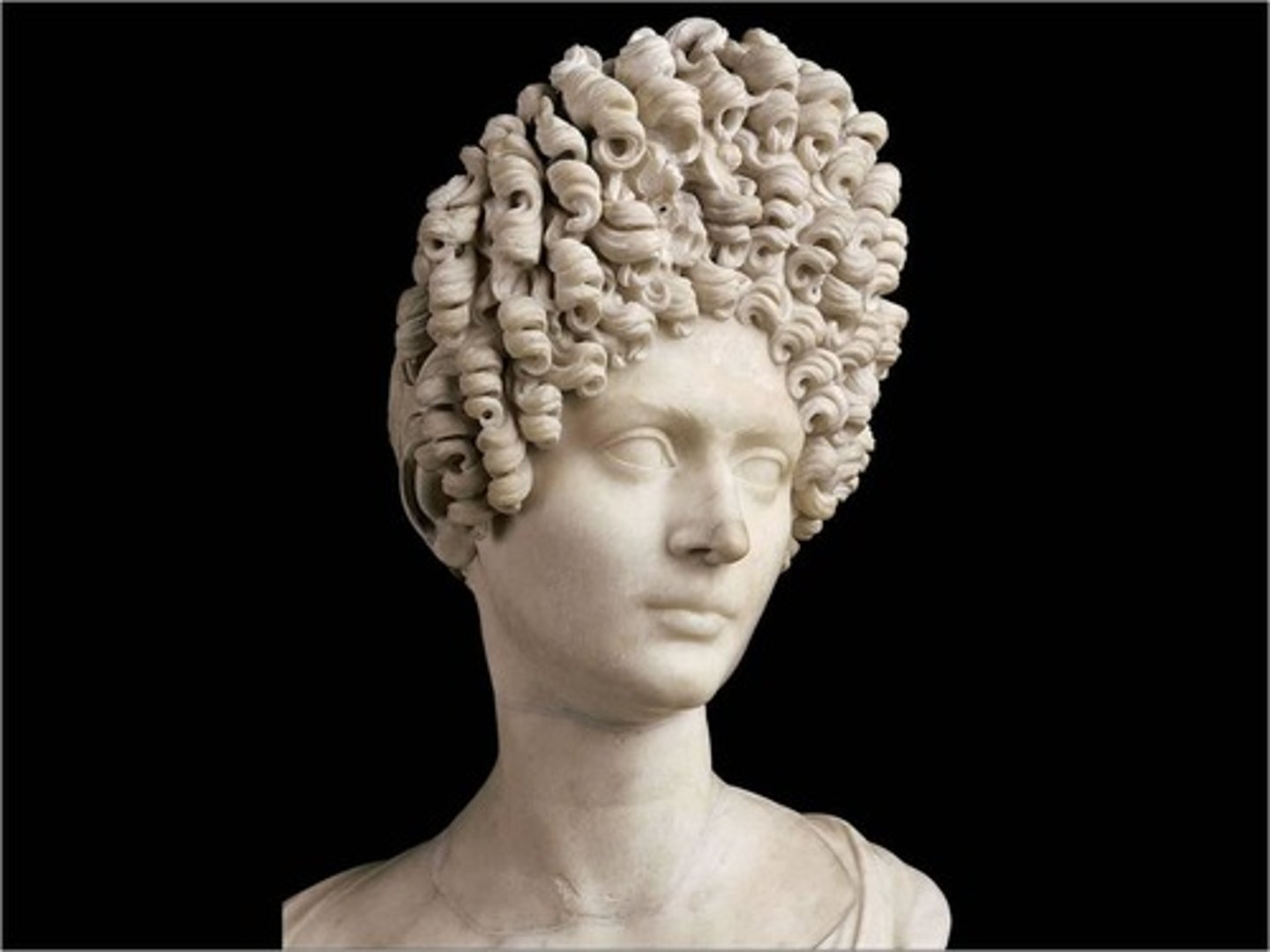
The Flavian Lady
90 C.E., Imperial, idealized beauty with graceful long neck and tilted head, cutting-edge fashionable coiffure, hair creates a dramatic interplay of light and shadow, hair created with a drill

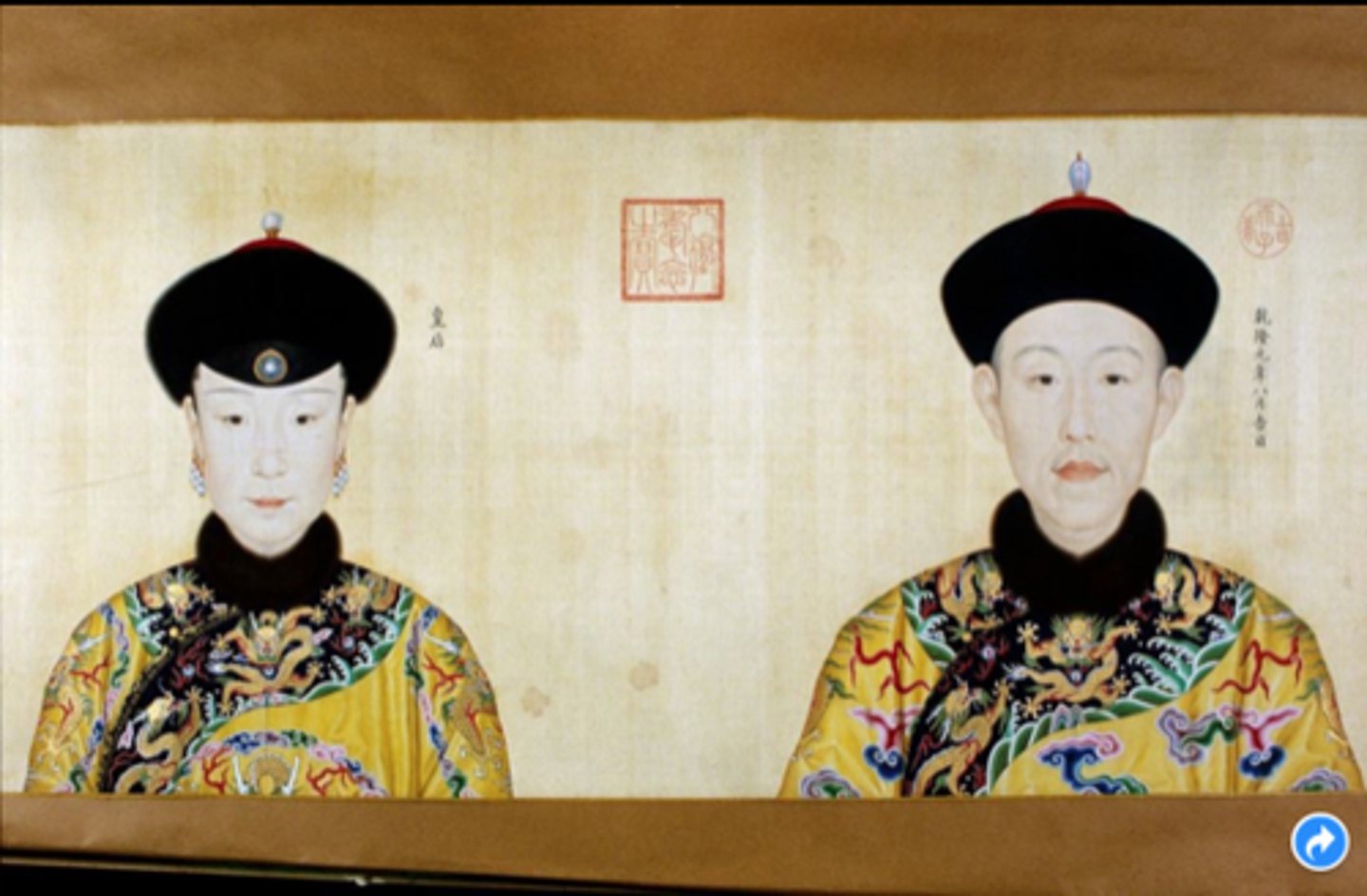
Imperial portraits
Displayed by rulers to assert legitimacy, like in the Ching Dynasty

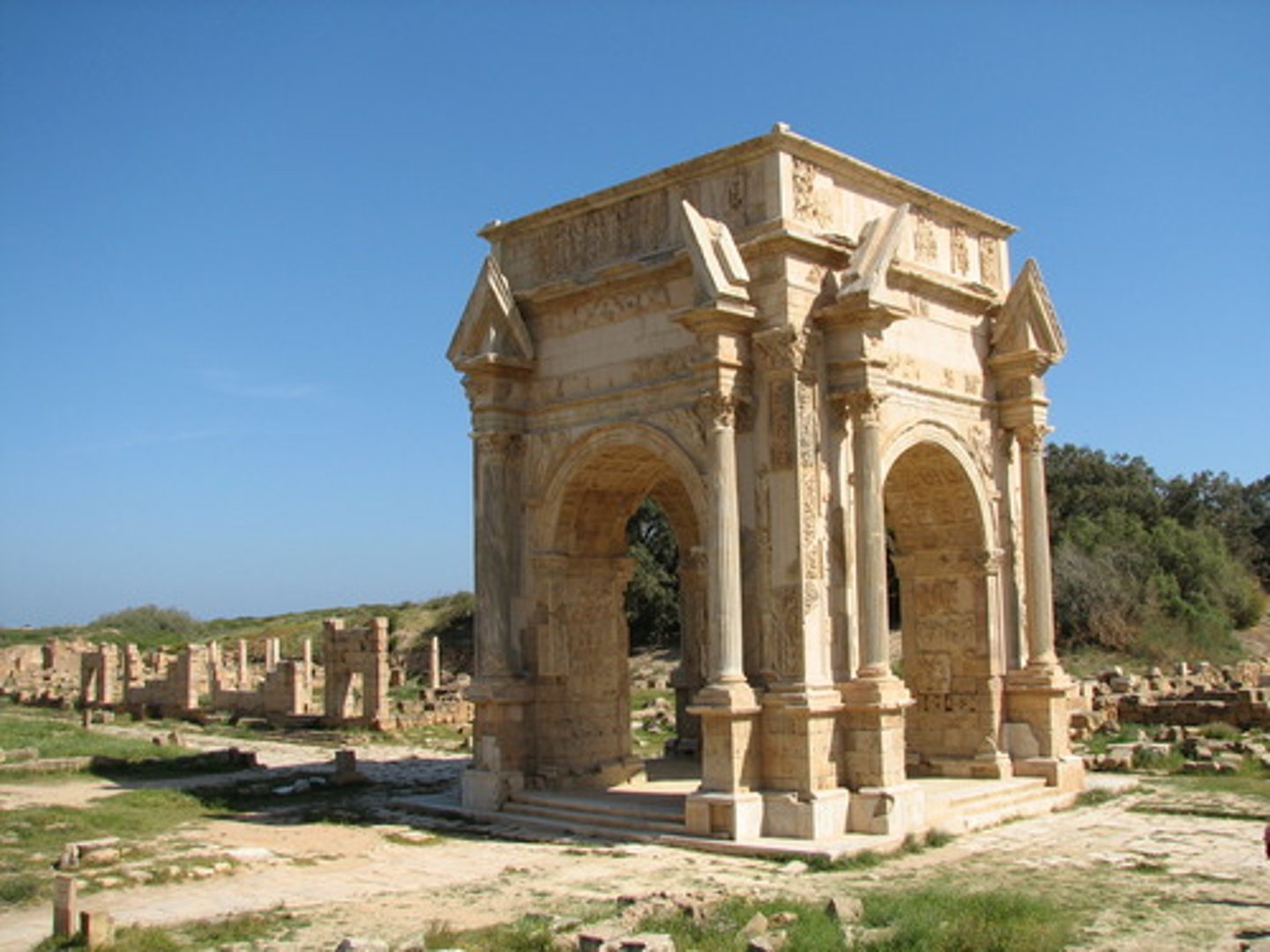
Leptis Magna
birthplace of Septimius Severus, gets a lot of funding and becomes the most important city in Roman North Africa (modern day Libya)

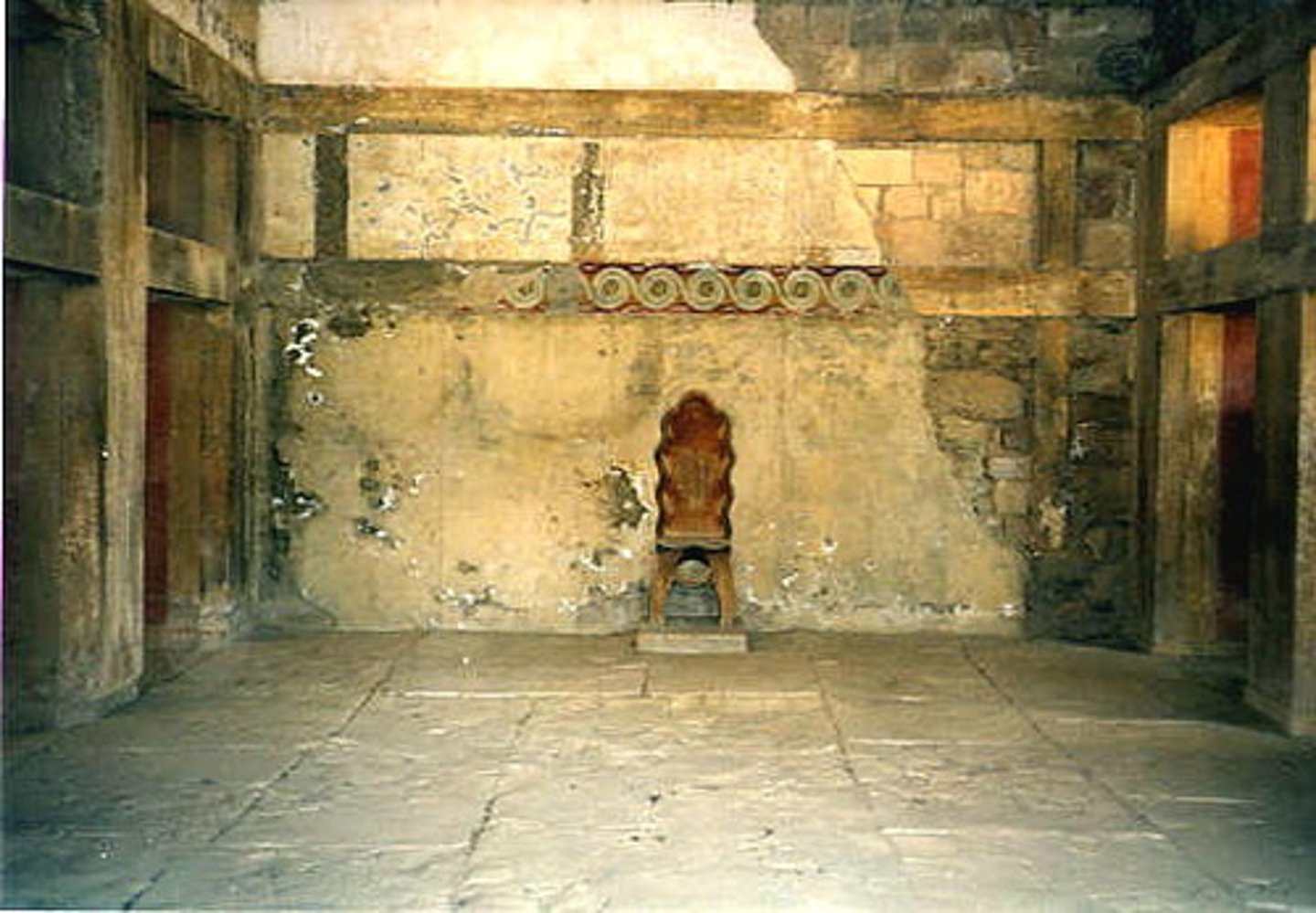
Bronze Age Greece
3000 - 1000 BCE
•Feldman's international style and social stratification
•Palaces: Minoan (Knossos) and Mycenaean (Mycenae, Pylos)
•Wall paintings: interest in nature, representation of religious themes
•Pottery: from imitation metallic to the beginnings of iconographic representation

The Iron Age
1200 - 500 BCE
Decentralization of wealth and power
•Weakening of ties with overseas groups
•But some persistence: Lefkandi burials
•Beginnings of the polis
•Monumentalization: hero cults, early temples
•Writing
•Early narrative art
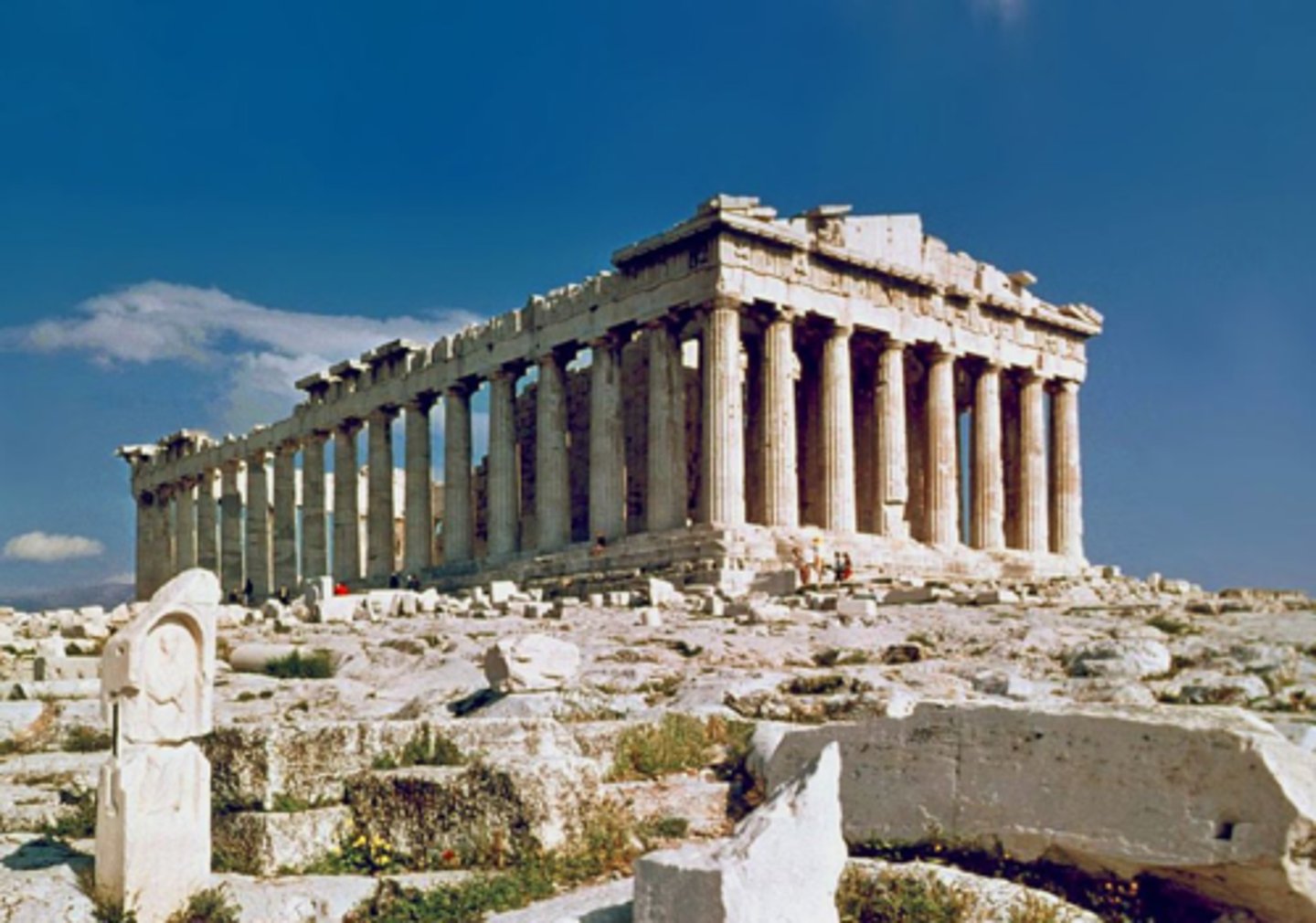
Classical Period
480 - 323 BCE
Birth of naturalism in Greek sculpture as a result of the Greco-Persian Wars
•New forms of sculpture, red-figure vase painting
•First portraits (the Tyrannicides)
•Experiments with combining Ionic and Doric architecture
•Concentration of wealth in Athens à Buildings of the Acropolis

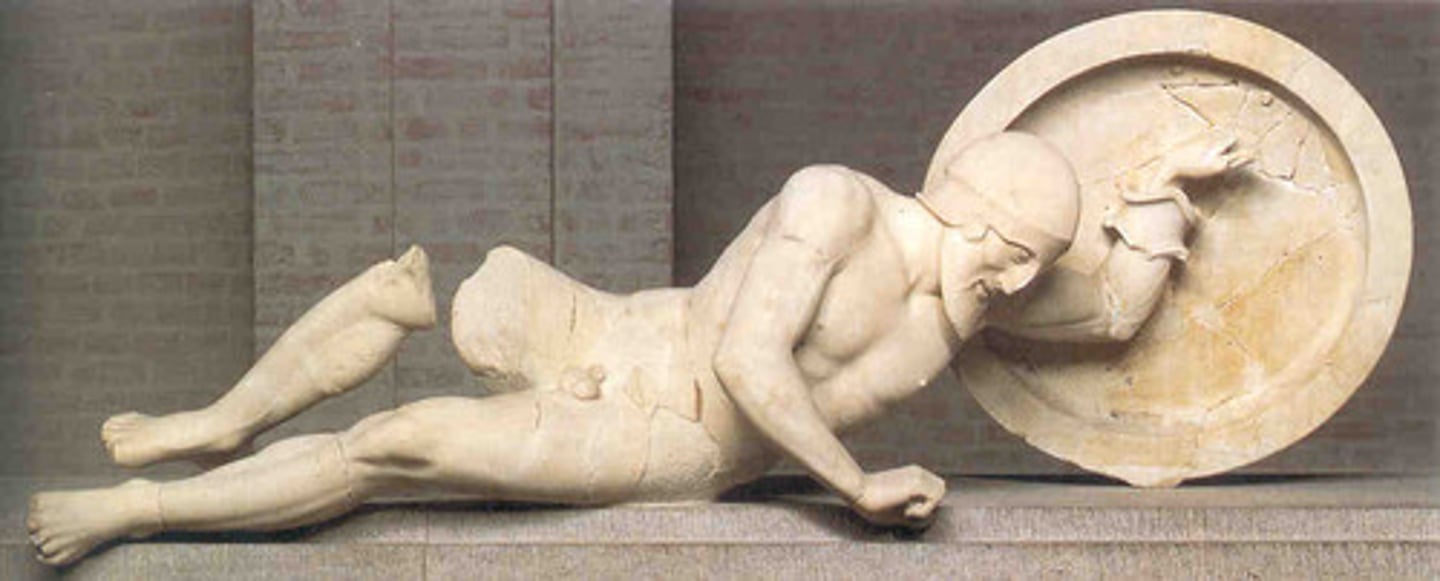
Later Archaic
3000 - 1000 B.C
•Popularization of korai and kouroi
•Development and growth of classical architectural forms: Doric and Ionic styles
•Growing room for narrative in art: architectural sculpture, black figure pottery
•Individuation: relief stelai

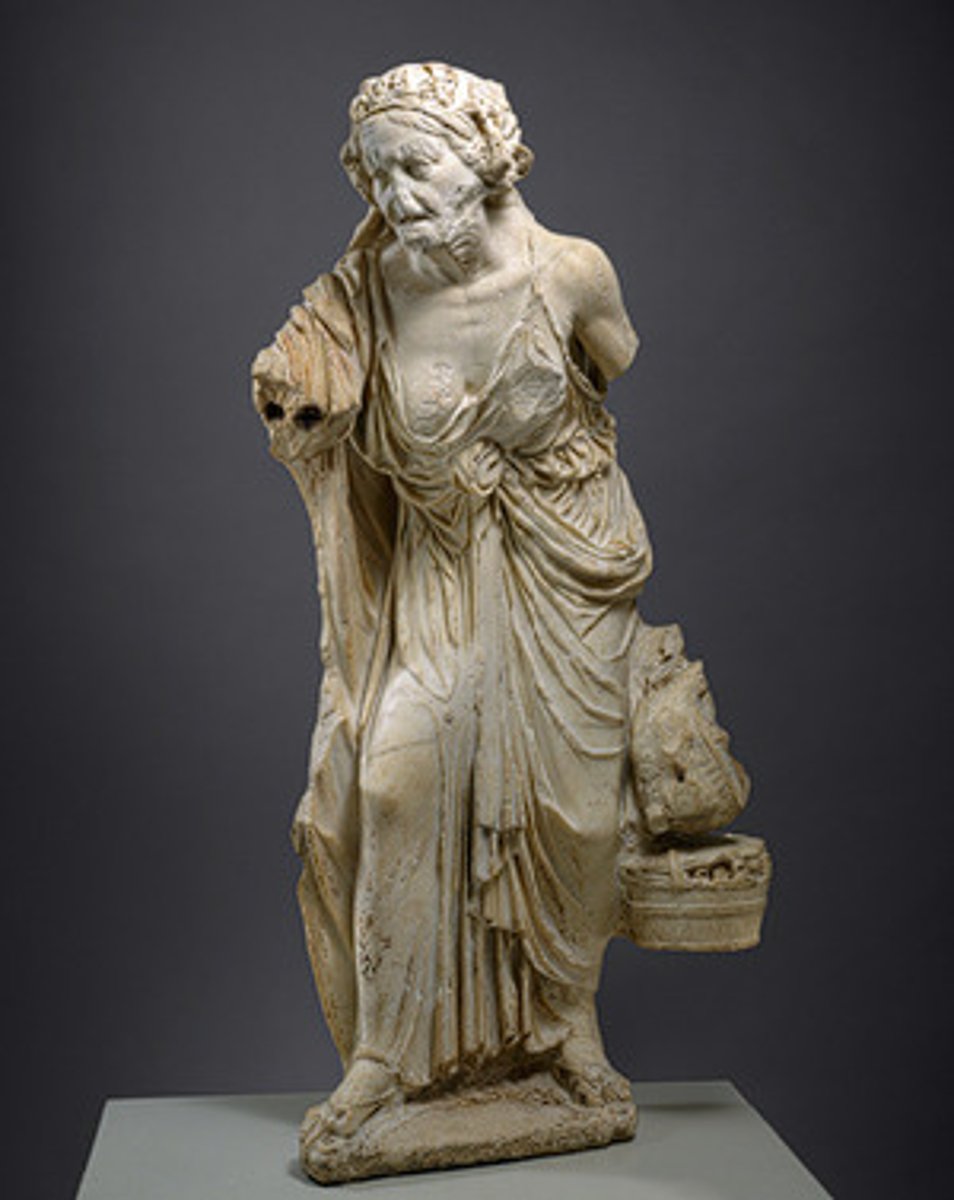
The Hellenistic World
•Alexander's conquests à shifting cultural boundaries, more mixture
•Oikoumene, cosmopolitanism
•More theatrical and emotion in sculpture
•Euergetism by royalty and elites à growth of portraiture, monumentalization of cities
•Art as decoration

Pre-Roman Italy
500 - 1 BC
•7th-3rd centuries BCE (overlaps with Republic in Rome)
•Culture groups: Etruscans, Samnites, Villanovans and MORE
•Key Themes: connections with Archaic/Classical Greece (red-figure pottery, Archaic styles in sculpture), persistence of Italic culture/forms (terracotta sculpture, tufa architecture)
Key evidence: tombs and other funerary remains
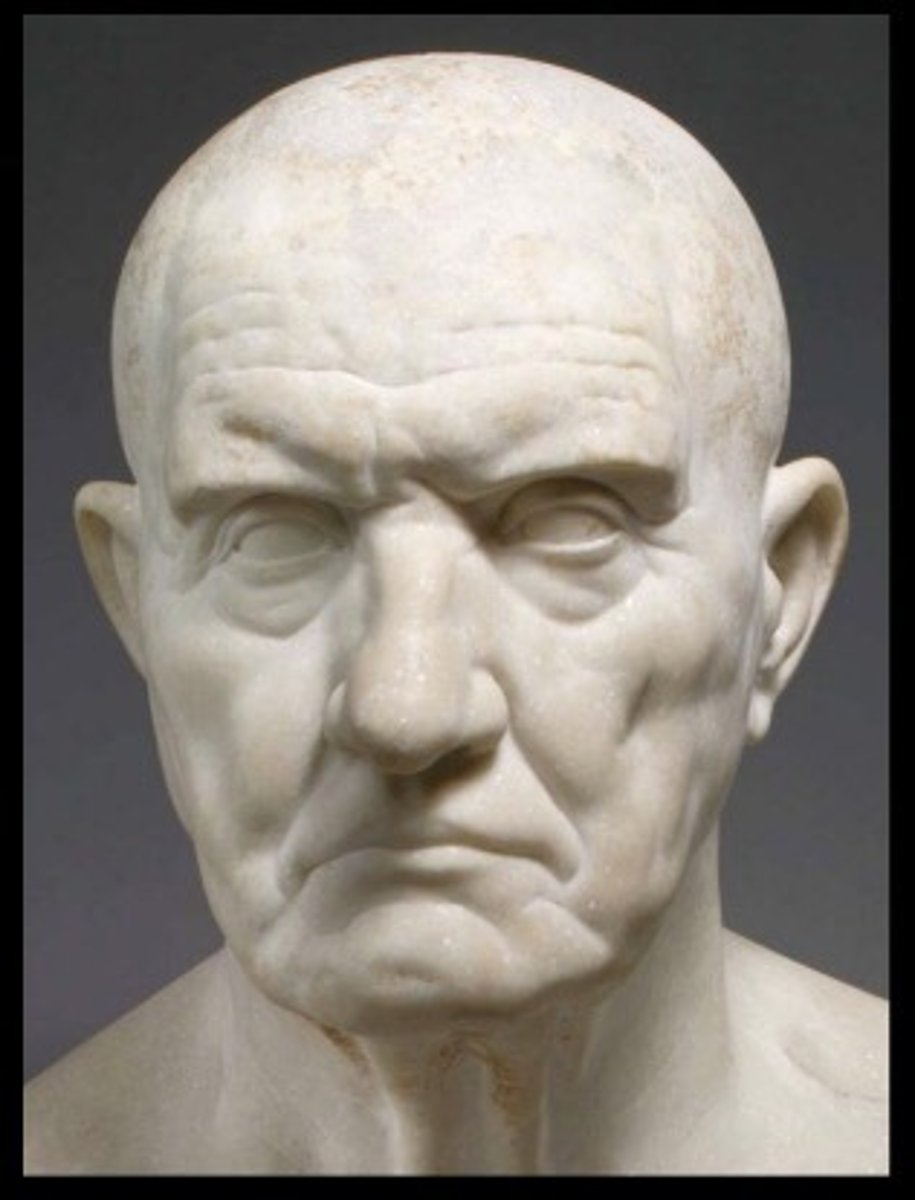
Early-Mid Roman Republic
509 - 133 BCE
•Early development of Rome and Roman architecture (Sant'Omobono)
•Growing strength and competition among Rome's Senatorial elite à development of Roman Forum and its political buildings
•Key infrastructure: Cloaca Maxima, Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus
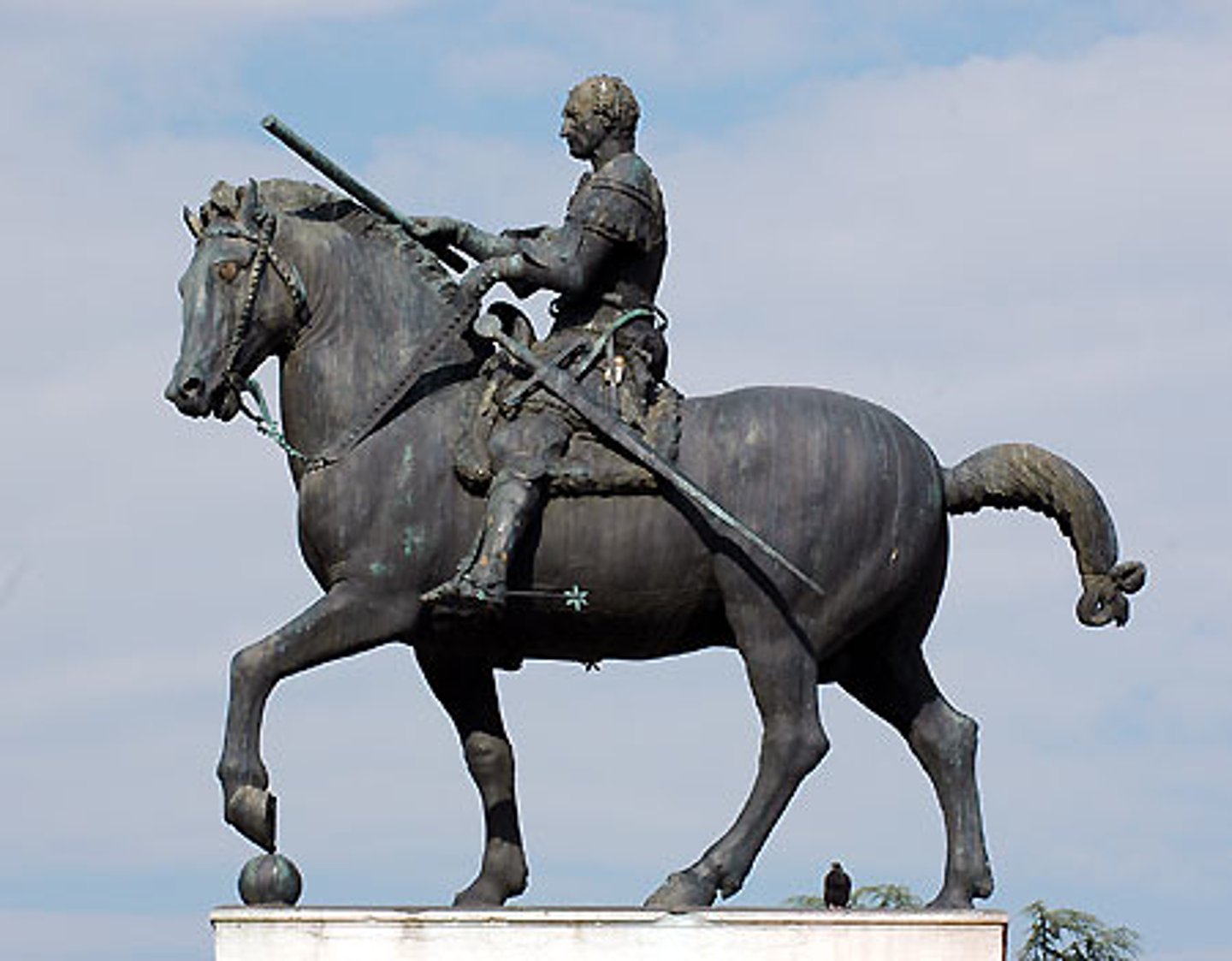

Late Republic Roman
133 - 27 BCE
•Increasing competition and centralization of power among a few elite clans: manubial temples
•Shift in portraiture style away from naturalistic towards more veristic styles
•Freedmen's reliefs
•First permanent entertainment structures at Rome (Theater of Pompey)
•First imperial forum (Forum of Julius Caesar)

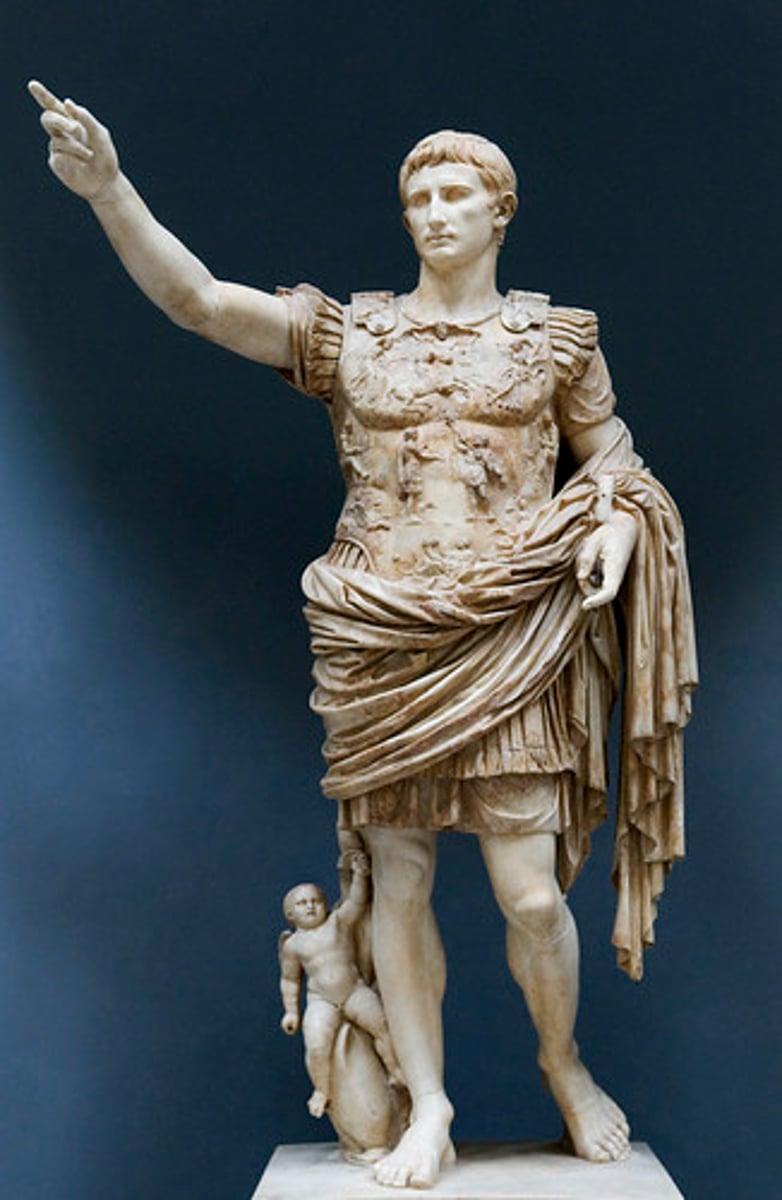
Age of Augustus
63 BCE - 14 CE
•Key themes: allusion to Classical Athens, Augustan building program, values-oriented iconography (pietas, family relationships)
•Building on Caesar's legacy: Fora of Caesar and Augustus
•Myth-making about Rome: the Ara Pacis
•Developing the persona of the emperor: the Prima Porta Augustus

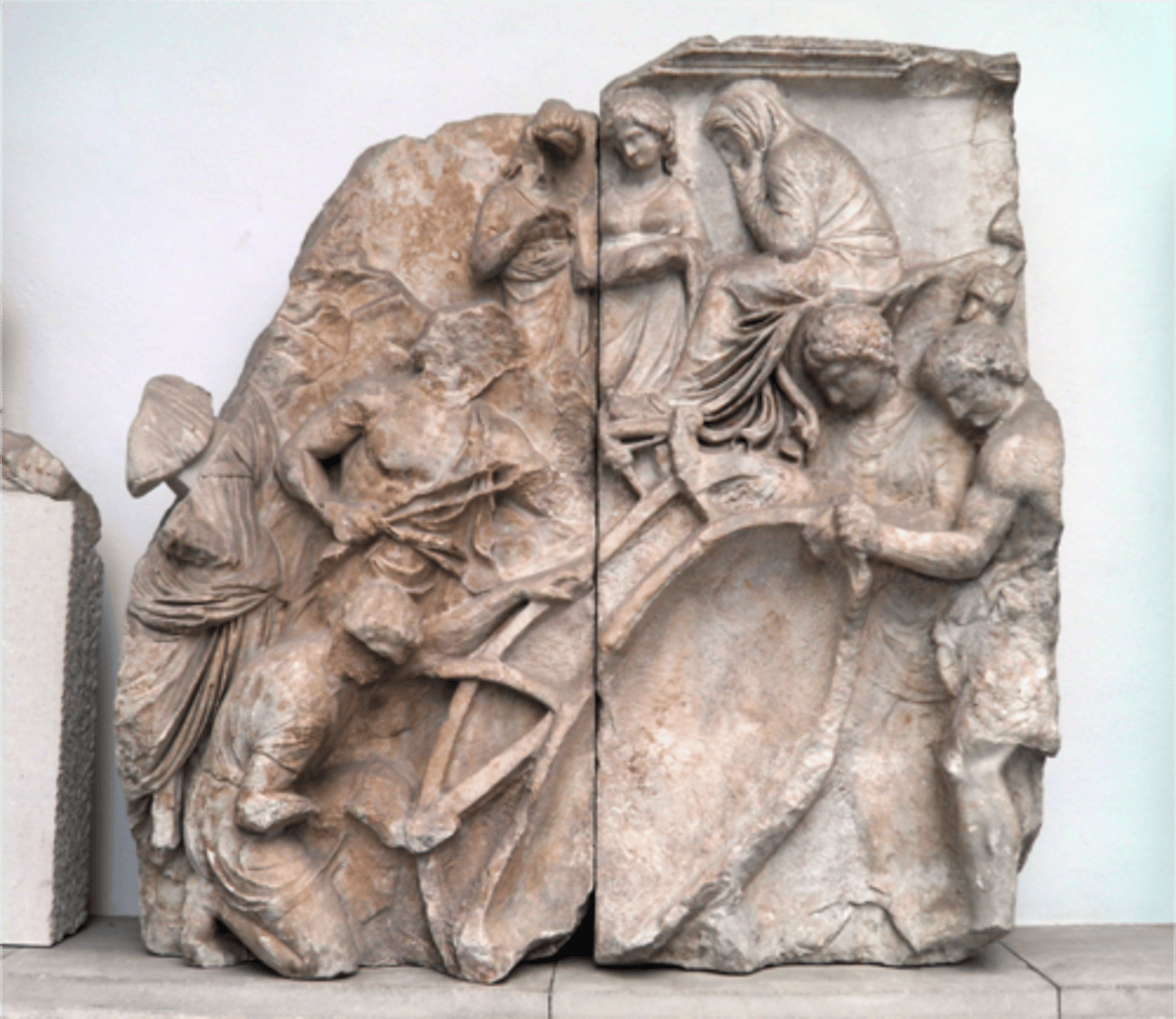
Pergamon Altar: Case Study
- Built on the acropolis of Pergamon, thought to have been designed by sculptors from Rhodes
- ca. 180-160 BCE
- Depicts a Gigantomachy on the exterior, local hero myth on the interior
- Key example of baroque style typical of Hellenistic sculpture (very expressive faces and bodies, dynamic postures, lots of drilling to create light and shadow)

Kerameikos Cemetery
Athens' main cemetery during Archaic and Classical periods
Ai-Khanoum (case study)
- One of the Alexandrias, founded by Hephaestion
- Colony of veterans
- Several aspects follow Greek norms: gymnasium, roughly Hippodamian plan, theater
- Key stop on overland trade routes, market for luxury goods (e.g. "The Silk Road")
Slipper Slapper
- Ca. 100 BCE
- Eclectic mythological group of Aphrodite, Pan, Eros
- Rebecca Martin: Phoenician mythology
Forum of Augustus at Rome
-A place where elections, public speeches and gladiator matches took place
-Built by Augustus adjacent to the Forum of Caesar
You are the queen at the Bronze Age palace of Thebes. Recently, your husband has died and it is time for you to plan his funeral. How will you bury the king? What kinds of grave goods will you put in his tomb, and why? How do you want him to be remembered?
laid in a tholos tomb, stone cut beyond the citadel
inner chamber wrapped in linen, dressed in garments fit for a king
weapons like sword and shield to represent the honor as a king and for Thebes
pottery and ceramic: vases, jars, cups, etc
jewelry: identiy and so the gods will approach him
offerings for the gods