reg test fuck ass procedures
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
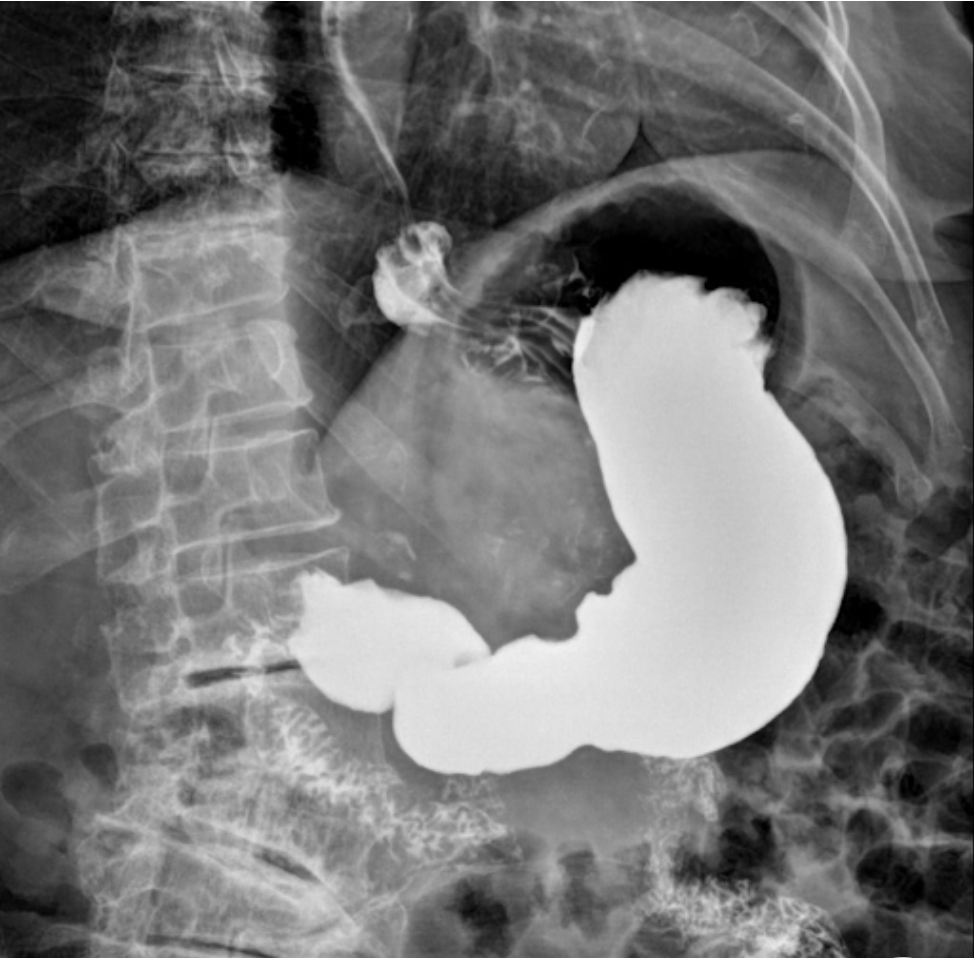
which fuck ass position was this shot? barium in the body, air in the fundus
RAO
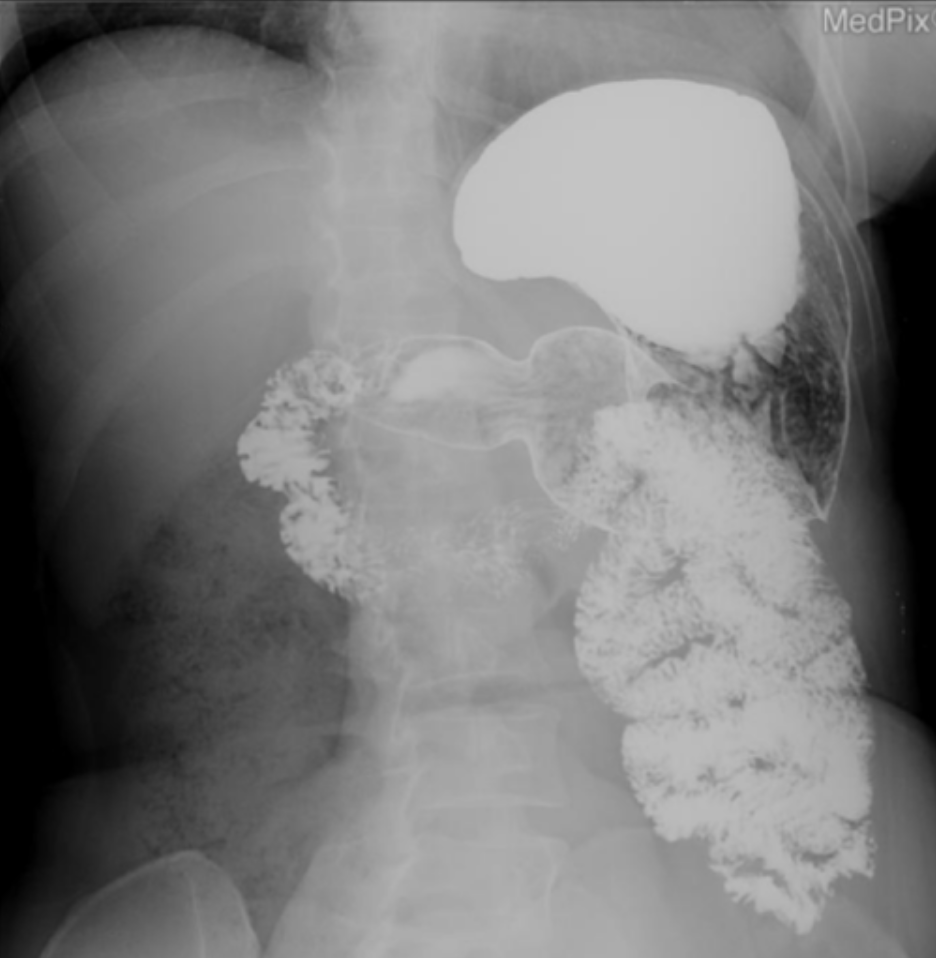
which position to visualize barium in the fuck ass fundus
LPO
What complication does GERD cause (starts with a B)
Barret’s, lazy cardiac sphincter lets chyme go up and it fucks up the espophagus tissue.
esophagus ends at wgich thoracic vert?
t11 esoph ends at 2nd to last t vert and spine cord ends at 2nd to last l vert
achalasia is when the inferior _______ sphincter fails to relax
esophageal
schatzki rings are in the _______
esoph
fundus is inferior/superior to cardi orifice
super
duodenum then ileum/jejunem, then,ileum/jejunem
duo, jej, ile doojie illy
tortuous veins in esoph are called
varices v for veins and varices
where are the haustra?
colon
which organs are retroperitoneal?
Suprarenal organs - adrenals
Aorta and super/inf vena cava
Duodenum
Pancreas
Ureters
Colon - ascending Descending
Esophagus
Rectum
small bowel follow thru is done for these three disorders . Sword song
Merckel’s divert, Celiac and Crohn’s
length of esoph is typically. really long dick but not too long
10”-12”
loop of duodenum encircles the…..
panc
what causes esophageal varices
portal hypertension
order of pharynxes (NOLE)
naso, oro, laryngopaharynx, esoph
sternocalvicular joint is a ______ ________type of joint
synovial gliding
degree of rotatage for RAO sternum?
15-20, just enough to get vert away
what is emyema
how should technique change for it?
pusy lungs
crank the kVp
what type of joint is the FIRST sternocostal joint?
immovable
what is atelectasis?
how should technique change for it?
collapsed lung
crank the kVp
where is jug notch on a sthenic pt?
t2-t3
which part of rib articulates with the tranny process of T verts?
tubercle
you would perform a lat chest with suspended expir to look for
suspected pneumothorax
draw the lungs
when doing a cross tabl lat cervy spine line up CR so you dont get _____cutoff
grid cutoff
dont remove pt from a trauma backboard until all _______have been _____ ______
fracs have been ruled out
scoli pt - stitch images together. no answer to this one
intervertebral articulations are what kind of joint?
symphysis
at what level does spine cord terminate?
L3-L4
what angel and where is the CR centered for AP SI joints
30-35, 2”below ASIS
atlas superior articular facets are concave/convex shaped
concave
cant get decent t spine images with severe kyphotic pt, so do a bunch from multiple ________and stitch em
angles
AP oblique of c spiune would demonstrate 2things
intervert foramina, zygopop joints
breathing for lat lumbar
hold ex
stetcher method for scaphoid:
_______deviation and
______° tube tilt toward_______
ulnar
20, elbow/head
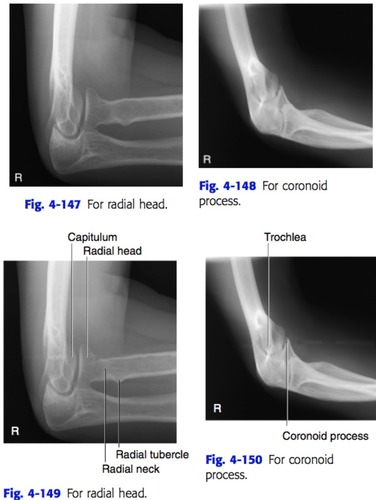
medial rotation of the elbow best shows the_____ process
lateral rotation best shows the _____ ____and_____
coronoid process
radial head and neck
Coyle method for elbow
to see radial head, point tube 45° toward/away from shoulder
to see coronoid proc, point tube 45° toward/away from shoulder
toward
away
grashey is AP or AP oblique of shoulder joing?
Ap oblique
Neer or supraspinatus outlet - how many fuck ass degrees of tilt and where do you point the fuckin ray?
10-15 caudal at humeral head.
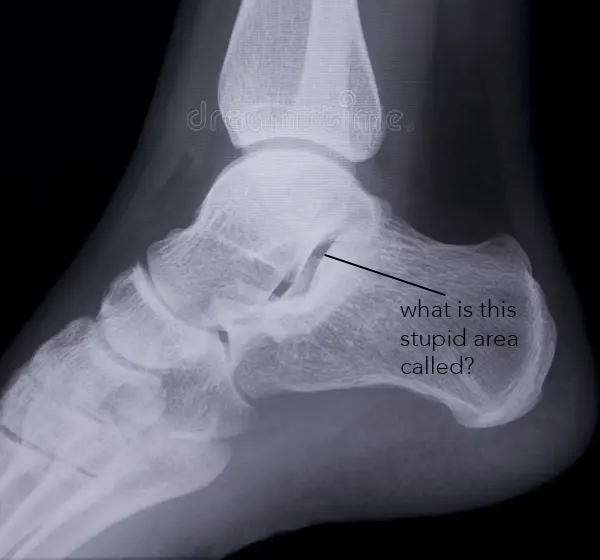
what other joint space is open?
tibiotalar
pic-sustenaculum tali
what joint space is open on a 45° medial rotation ankle besides tibio fibular?
fibulotalar ( is that even a thing? idk, i dont give a fuck)
tube angle for settegast/sunrise
20-25
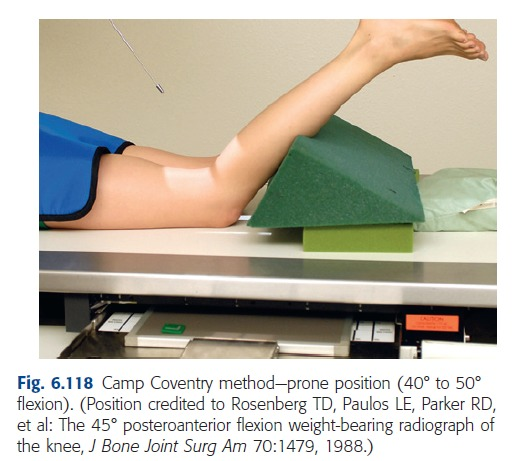
what stupid exam is this?
what does it look at? (inter____ ____)
what’s the leg angle?
what is the CR perp to?
camp coventry
intercondylar fossa
40-50°
lower leg
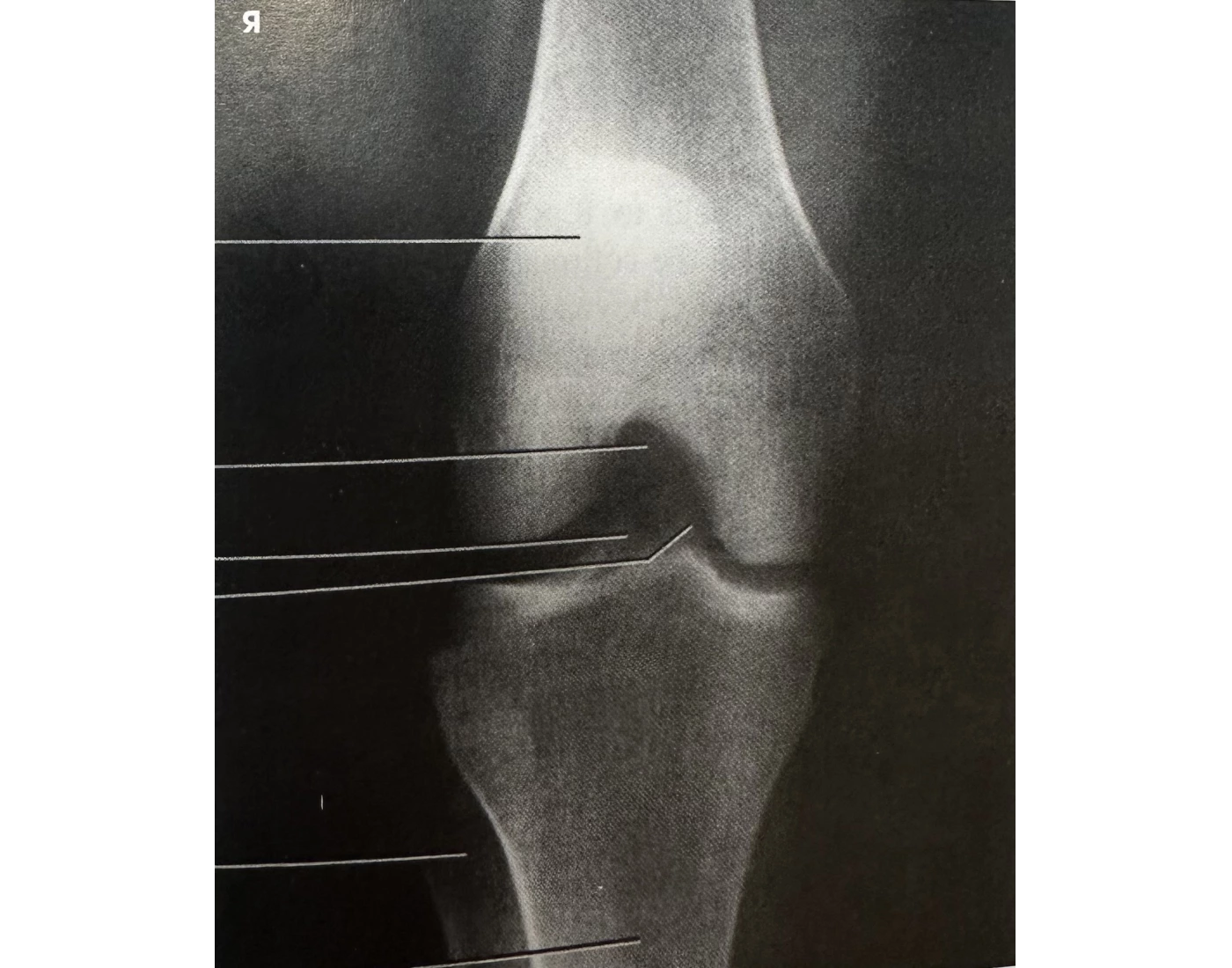
if patient’s asis is between____ and______cm high, you can shoot an AP knee with no angle
What angle for fat asses?
19-24
5° cephy
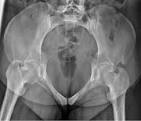
what view is this? what’s the tube angle?
pelvic inlet, 25-40° crawdad (ischial rami are perp to IR)
what view is this? tube angle
pelvic outlet , 30-45° cephy (ischial rami are parallel to IR)
Name the spinal cord layers from outer to inner
Where is contrast for myelography injected?
Dura mater, Arachnoid membrane, Pia mater
Subarachnoid space
Colles fracture involves breakage of the distal _______
And can also involve the distal __________because of severe abduction of hand
distal radius
distall ulna
Cholangiography is used to see ______ducts
contrast is injected into the ________________
bile
liver
Body habitus gen description, guts orientation and percentage
Hypersthenic -
Sthenic
Hypostenic
Asthenic
Short and fat, guts horizontal, 5%
Average, guts normal, 50%
Slender, guts long, 35%
Super skinny, super long guts, 10%
Does SID affect scatter?
No
In what position do you view sternum and why
RAO, becasue you want it superimped on heart shadow cuz of uniform tissue density or some bullshit.
What are the three main joint types? and what do they mean?
diarthrotic/synovial - freely moveable
amphiarthrotic/cartilaginous - slightly moveable
synarthrotic/fibrous - not moveable
Diana’s Amphitheatre is in a Synchole
4 examples of synarthrotic joints
bones of the skull
sternocostal joint
teeth-gomphosis
syndesmoses - between tib and fib and ulna/radius
2 exmples of amphiarthrotic/cartilaginous joints
intervertebral discs
pubic symphysis
2 ball and socket joints
3 hinge joints
1 saddle joint
2 plane joints
2 pivots
3 condyloid
synovial gliding
shoulder and hip
elbow ankle knee
carpometacarpal
AC, subtal
prox and dist radioulnar joints
wrist MCP, MTP
costotransverse
syndesmoses joints are held together by a _________membrane
2 examples
syndchondroses joints are held together by_________, example
fibrous,middle radioulnar and tibfib joints
hyaline cartilage, daiphysis and epiphysis
Name the 6 diarthrotic/synovial joints
Bald, Sad Plumbers Hinge and Pivot on the Conduits
ball n socket
saddle
plane
hinge
pivot
condyloid
what angle for both Judet hips (typical)
45°
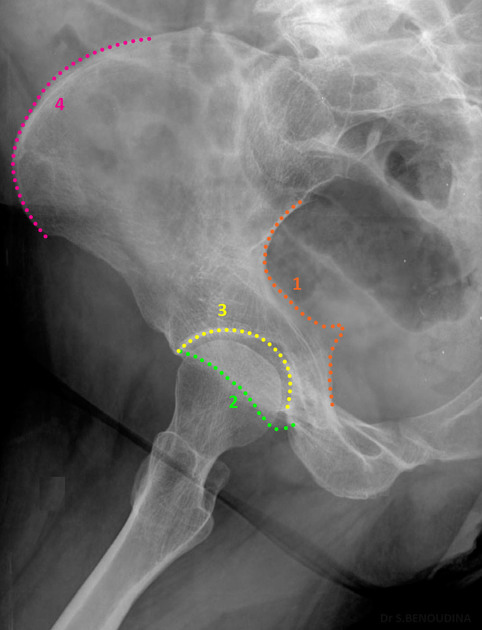
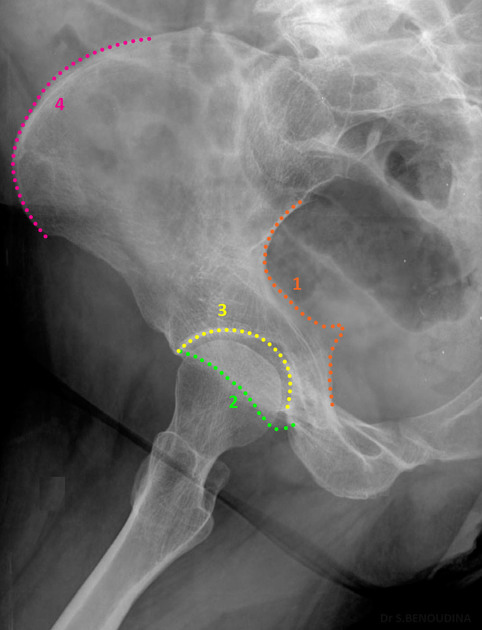
Judet hip - iliac view
affected/unaffected side of the pelvis is rotated 45 degrees anteriorly, allowing visualization of the 1 and 2
1 - posterior column, 2 anterior wall and rim
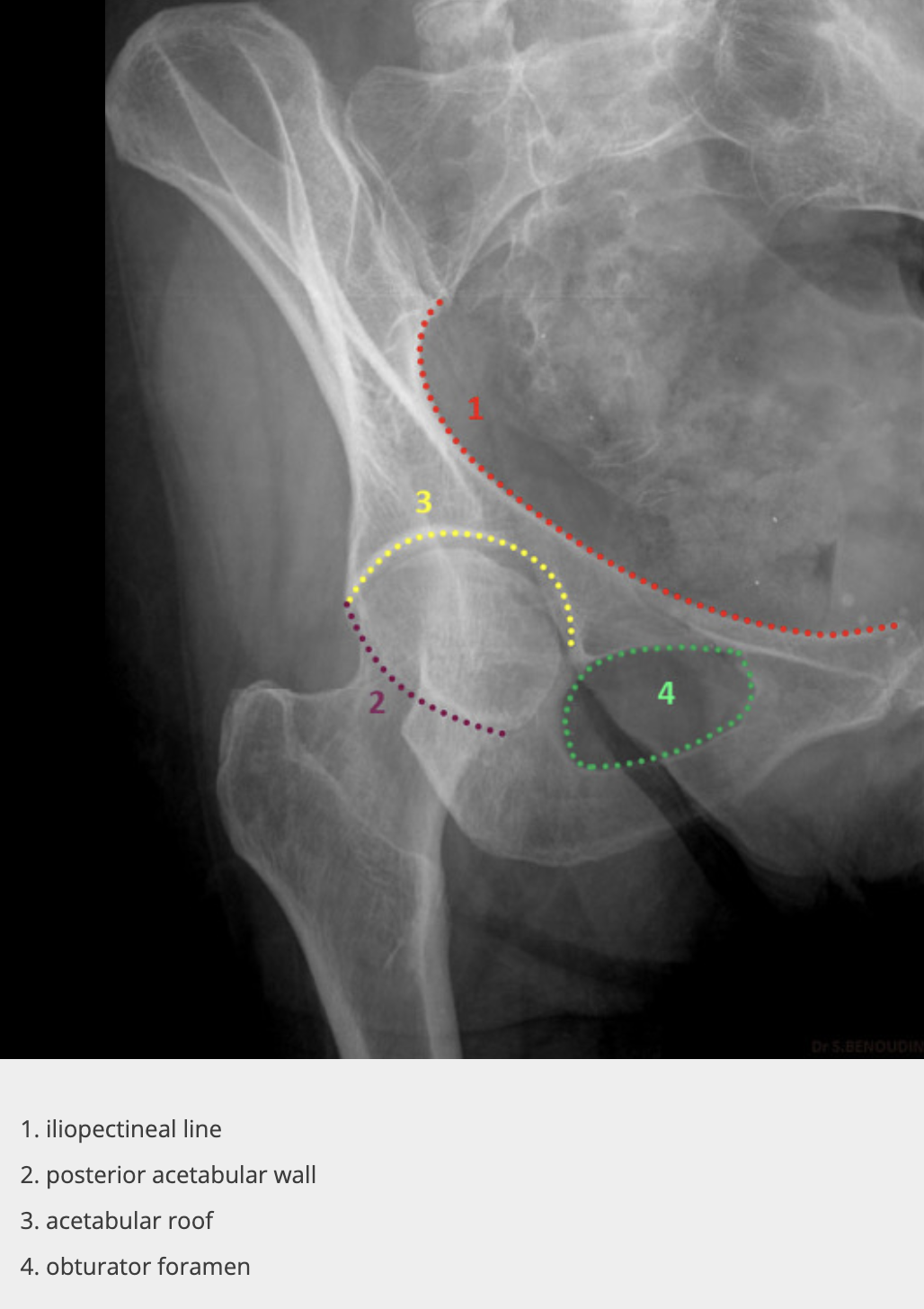
Judet obturator view
unaffected/affected side of the pelvis is rotated 45 degrees anteriorly, allowing visualization of the 1 and 2
affected
obturator ring, posterior wall
centering for AP sacrum
centering for coccyx
between pubi symp and asis
2” above pubic symph
Si joint AP tube angle
male- _____
female-_______
centering?
30
35
2” below asis
SI oblique position angle?
CR center
25-30 up
2.5cm medial to ASIS
top of iliac crests are at the top of L__
5
RAO lumbar spine will show right or left facet joints
left
zygopops visible in lateral or oblique of c spine
interveetebral foramina visible in….
lateral
oblique
C spine -
zygopops lateral
foramina oblique
T-Spine
zygopops and foramina lateral
L spine
zygopops - oblique
foramina - lateral