IPC EXAM 2
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 13.1 13.2 13.3 14.1 14.2 14.4 15.1 15.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
how does pressure exerted by the atmosphere change as altitude increases?
air pressure decreases as altitude increases
How is pressure distributed in a fluid?
It is exerted equally in all directions of the fluid
pressure
result of a force distributed over an area
a fluid
substance that assumes the shape of its container
according to pascal’s principal…
a change in pressure at any point is transmitted equally and unchanged in all directions throughout the fluid
hydraulic system
device that uses pressurized fluid acting on pistons to change a force
How can a hydraulic lift system increase force?
a constant fluid pressure is exerted on the larger area of the output piston
How are fluid speed and fluid pressure related?
As the speed of a fluid increases, the pressure within the fluid decreases
a lift
when the air-travel over the wing is moving faster than the air-travel under the wing, creating an upward force
buoyancy
fluid’s ability to exert an upward force on an object placed in it
What affect does buoyancy have on an objects weight?
objects inside a fluid have an apparent lose in weight
buoyant force
when a submerged object is acted upon by an upward force, making the submerged object easier to lift
Archimedes principal
the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object
How can you tell if an object will float or sink in a fluid?
an object less dense than it’s fluid will float, an object more dense than the fluid its in will sink
units for pressure
pascal (Pa)
units for density
g/cm³
the object will be suspended
when it has the same density of the fluid it is in
density formula
density = mass / volume
work
the product of force and distance
if there is no motion
there is no work
for a force to do work on an object
some of the force must act in the same direction as the object moves
any part of a force that does not act in the direction of motion does no work on a object
true
work formula
work = force x distance
units for work
joule (J)
power
the rate of doing work
doing work at a faster rate requires
more power
to increase power
increase amount of work done in a given time
power formula
Power = work/time
One horsepower
746 watts
units for power
watt (W) = 1 Joule per second
machine
devise that changes work
how do machines make work easier?
they change the size, direction, or distance the force acts over
input force
force exerted on a machine
output force
force exerted by a machine
the distance the input force acts through
input distance
work input
work done by input forcing acting on input distance
output distance
distance output force is exerted through
how many types of simple amchines are there?
6
fixed point the the bar rotates around
fulcrum
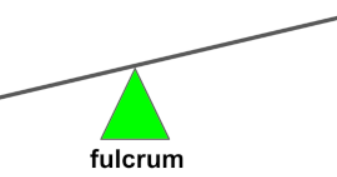
To calculate ideal mechanical advantage of any lever…
divide input arm by output arm
example of a first class lever
opening paint can using a screw driver
example of a second class lever
wheelbarrow
example of a third class lever
someone sweeping, input force is hand on middle of broom, fulcrum is the hand on the top of broom, and output force is the broom sweeping
to calculate ideal mechanical advantage of a wheel and axle
divide radius where input force is exerted by radius where output force is exerted
Does a thick wedge or a thin wedge have a greater mechanical advantage? (they are the same length)
thin wedge
screws with threads closer together have a ____ mechanical advantage
greater
it takes energy to do…
work
Elastic potential energy
energy of an object that is stretched or compressed
work is a transfer of…
energy
energy of motion
kinetic energy
Potential Energy
energy stored as a result of position or shape
gravitational potential energy
PE that depends on an object’s height
mechanical energy
sum of an objects PE and KE
Chemical energy
energy stored in chemical bonds
electrical energy
energy associated with electric charges
an object’s gravitational PE depends on its…
mass, height, and acceleration due to gravity
electromagnetic energy
form of energy that travels through space in the form of waves
nuclear energy
energy stored in atomic nuclei
energy conservation
changing energy from one form to another
einsteins equation states that energy and mass…
are equivalent and can be converted into each other
Einstein’s equation
Energy = mass x constant for speed of light
constant for speed of light
3 × 108 m/s