FNR 201 Midterm #1
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Earth makes up _ percent of the earth’s surface and _ percent of world’s oxygen
71, 50
Three systems that Marine Biology is studied in
physical and chemical processes, organisms, ecosystems/global perspective
First marine biologist
Aristotle
1768
Captain James Cook and crew sailed around the world collecting specimen
1831
Charles Darwin sailed on HMS Beagle as naturalist, writing detailed descriptions
1840s
Edward Forbes, first to study seafloor and discovered species vary depending on depth
Challenger Expedition
First major exploration devoted to marine life - 3.5 years, 19 years to publish 50 volumes
Why is ice less dense than liquid water?
Entrapment of Air
The smaller the sediment particles
the greater water can maintain adhesion properties
Less than what percent of light penetrates deeper than 100 meters
1
Absorbed light energy is converted into
heat
How old is the earth
4.54 billion years
What is earth made of
silicon compounds, iron, magnesium oxide
When did oceans begin to form
4.2 bya and continued to form for next 200 my
What were the oldest known fossils
Marine bacteria - 2.3-4.3 mya
Size of bodies of water in order
Ocean, sea, gulf, bay
Pangaea split into what daughter continents?
Laurasia and Gondwana
Bathygraphic features
Features of ocean bottom similar to geographic features on land
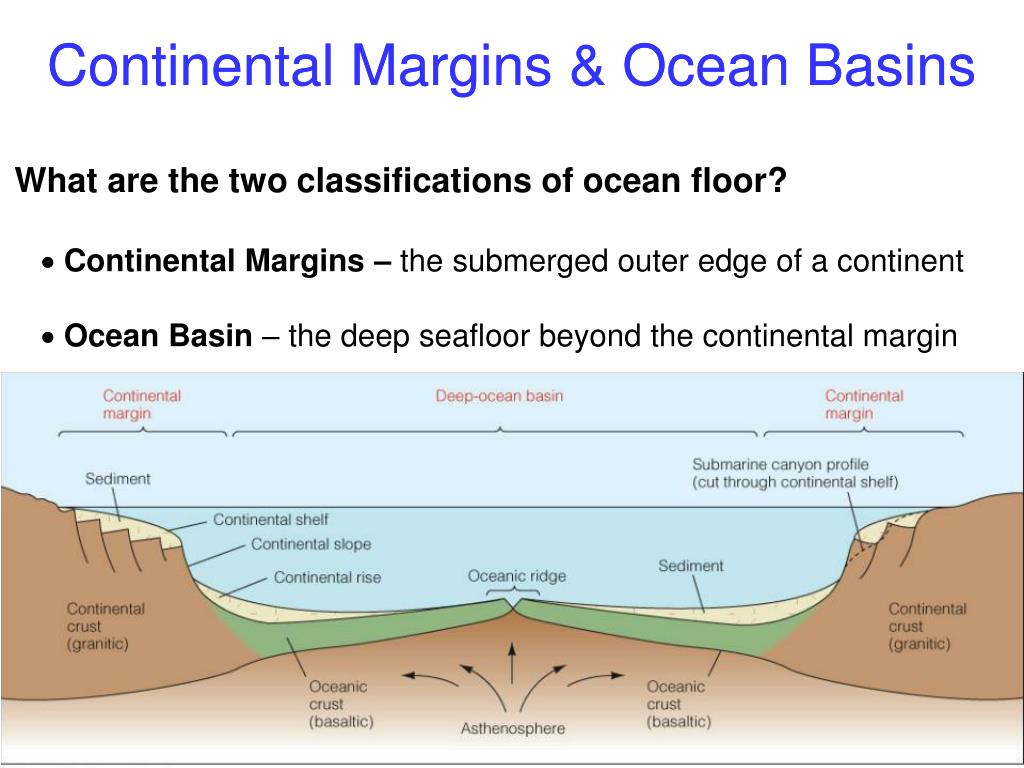
Seafloor split into two divisions:
Ocean Basin and Continental Margin
Continental Shelf
Shallow area of seafloor immediately adjacent to continent - richest area for biodiversity but only makes up 8 percent of oceans
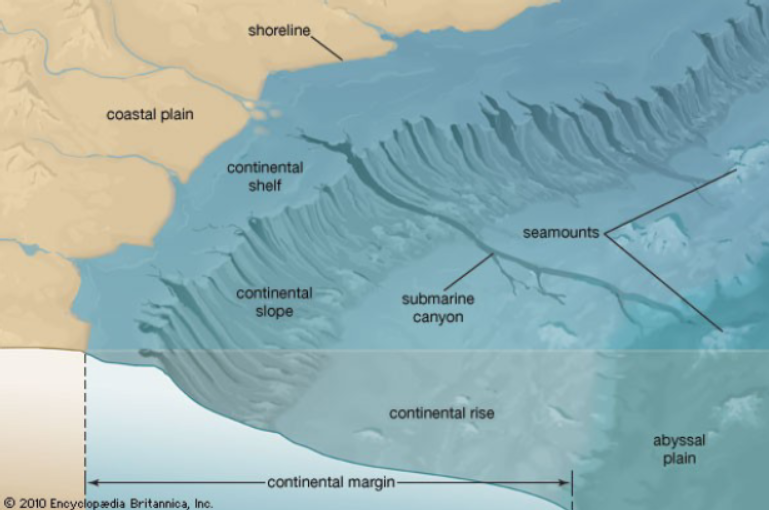
Shelf break
Abrupt change where continental shelf ends and continental slope begins
Continental Rise
Gentle slope at base of steep continental slope, often containing sediments produced from landslides
Submarine Canyons
Formed by currents that cause underwater landslides, often aligning with terrestrial river mouths
What is the ocean basin comprised of
basalt rock
Abyssal Plain
Flat expanse at bottom of ocean
Abyssal Hill
Formed by volcanic action and plate tectonics
Seamounts
Associated with island arcs and formed by underwater volcanoes
Hydrogenous sediments
Carbonates, phosphorites, and manganese - precipitation of dissolved minerals
Biogenous Sediments
Remains of living organisms
Deep Sea almost all biogenous sediments are from single-celled organisms with silica shell
Terrigenous Sediments
Formed by weathering of continental rocks
Primarily deposited on continental shelves
Cosmogenous Sediments
Iron-rich particles from space
Least common sediment found
Pelagic zone
open water areas
Beritic province
water overlying continental shelves
Oceanic province
Water overlying deep ocean basins
Benthic zone
Layer closest to bottom
Ocean photic zones
Photic zone, midwater zone, aphotic zone
The earth absorbs ___energy at higher latitudes due to the earth’s tilt
less
Earth’s atmosphere ___ more energy than in absorbs
reflects
Earth’s surface ___ more energy than in reflects
absorbs
How does Earth lose energy to the atmosphere?
Radiation (1/3) and Evaporation (2/3)
The greater the temperature the ____ the density
lower
Warm air at equator
rises and moves towards poles
Cold air at poles
sink and move towards equator
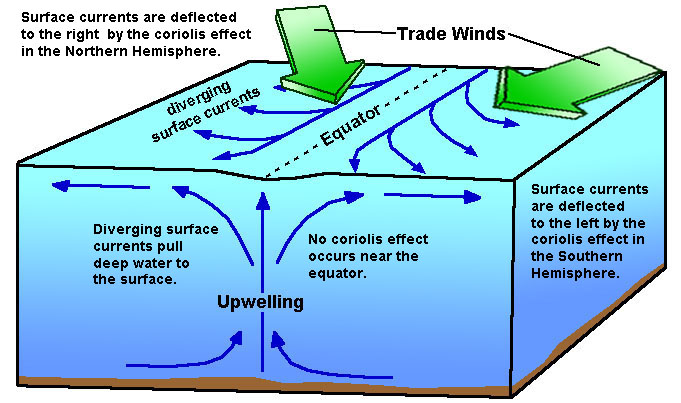
Coriolis effect
Deflection of the paths of winds and currents that results from the rotation of the earth
The 3 cells in each hemisphere
Hadley, Polar, Mid-Latitude
Doldrum
warm, rising air
Horse latitude
Cool, descending air
Which cells are driven by temp?
Hadley and Polar
What are currents driven by
Trade winds, Coriolis effect, Position of Land Masses
Currents result from
wind blowing against the oceans surface
Gyre
Circular current pattern around edge of ocean basins (5 major ones exist)
Western boundary currents
Fastest and deepest, moving warm water to poles. Low Productivity and low nutrients but increased oxygen
Eastern Boundary Currents
Slow moving, move cold water toward the equator, high productivity and mix nutrients into surface waters
Traverse Currents
Connect the western and eastern boundary currents
How long does ocean conveyor take for one full circuit
1000 years
Ekman transport
Wind moves water at surface. Due to friction, moving water at surface moves other water deeper
Horizontal friction
Does not move water in same direction, results in spiral of vertical movement
Density is driven by
Temperature and Salinity
Ocean layers from most shallow to deepest
Surface layer (0-100m), Thermocline (temp decreases rapidly and depth and width varies seasonally), Deep Water (100m+ - cold, stable temp)
Equatorial Upwelling
Currents on either side of equator deflect surface water away from poles, replaced by nutrient rich deep water
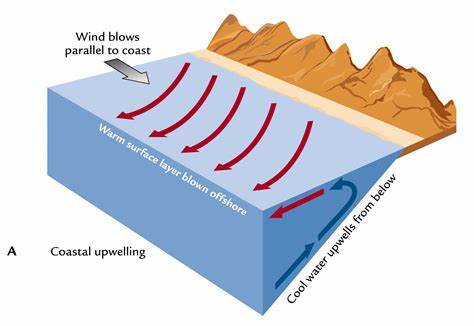
Coastal Upwelling
Winds parallel to coast or away from coast - nutrient rich deep water rises
Coastal downwelling
Wind blows water towards coastline, forcing it to return to ocean
Wave
Flow of energy or motion
Generating Force
Force that generates waves (winds, geological events, ships)
Restoring Force
Force that restores water to undisturbed state (surface tension, gravity)
Small waves are called
Capillary waves
Progressive wave
Wave generated by wind, restored by gravity
Forced Waves
Increase in size due to storms energy
Free Waves
No external energy generating force
Swell
Patterns of wave crests on ocean’s surface that are uniform for long period

Amplitude
Height of wave crest starting from water surface
Wavelength
Distance between two wave peaks
Higher frequency
slower waves
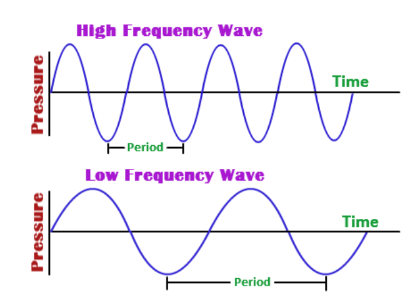
Trough
Lowest point of a wave
Deep water wave
Water depth is greater than ½ wavelength
Wave height is dictated by
wind speeds, wind duration and fetch
Fetch
Distance of water that wind blows over
Shallow water waves
When water depth is less than ½ wavelength
Tsunamis are long waves with ____ periods and ____ height
Long, low
Tides
Periodic change in water level along coastline due to gravitational pull from sun and moon
More about tides
The gravitational pull from the Moon causes a bulge of water on the side of the Earth facing the Moon. Simultaneously, there is another bulge on the opposite side of the Earth due to the centrifugal force resulting from the Earth-Moon gravitational interaction. This creates two high tide areas on opposite sides of the planet.
High tide
bulging wave
Low tide
Area between bulges
Spring tides
Largest difference between high tide and low tide, occurring during full and new moon
Neap tides
Occur during 1st and 3rd quarter moon
Diurnal tide
1 high and 1 low tide each day
Semidiurnal tide
2 high and 2 low tides each day (common)
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration
Nucleus
Contains the chromosomes
Golgi Complex
Manufacture, package, and transport cellular products such as protiens
Natural selection has ____ in traits
High variation
Allopatric speciation
Gradual process by which populations evolve into different species due to geographic changes
Fitness
Measured by number of organism’s own genes present in next gen
Sympatric Speciation
New species from surviving ancestral species while both continue living in same region
Phylogenetics
Study of evolutionary relationships between organisms
Taxonomy order
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family genus, species
Ectotherms (most marine organisms)
Generate body heat metabolically but lose head rapidly - match surrounding environment
Endotherms
Retain most metabolic heat and body temp stays higher than surronding environment
Regional Endothermy
Internally heat key parts of body (tuna, sharks, etc)
Pressure at ocean surface is
1 ATM