Orgo Reactants
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
LDA
Performs E2 reactions
N takes the H - makes N neutral charged
Electrons attached to H go to the C-C bond
LG takes its electrons
>-:N:--< Li+

Conc HCl & heat
Performs SN1 reactions
Can react multiple times
Can have carbocation rearrangement

HCl
Performs addition
Epoxide opening
O takes the H
Break bond to make the most stable carbon
Can also do normal addition

conc H2SO4 & heat
Performs E1 reactions with OH
Both E and Z products
H attaches to OH, making H2O
H2O leaves, causing + charge
O on the nuc takes an H, and its electrons form a double bond, getting rid of the + charge
Basically, OH becomes a double bond between the carbon with OH and the most stable carbon
NaH
Forms epoxides
H reaches out and takes the H attached to an OH group
Basically, electrophile with OH and a good LG reacts with this to form an epoxide
a) NaH
b) R-LG
Adds a carbon chain to an O
When electrophile has an OH
R = carbon chain
Excess NaNH2, heat
Elimination reaction
Forms a triple bond
Will react until it can’t
Nuc reaches out and takes an H
LG leaves
Move electrons accordingly
a) NaNH2
b) R-LG
Adds a carbon chain to terminal alkyne
Br2
Adds nuc to both carbons in a double bond (on opposite stereochem)
Double bond reaches out and takes one part, leaving a + charge
The other part attaches to where the + charge is; OPPOSITE stereochem
(±)
Br2, H2O
Adds nuc to least substituted carbon and OH to most substituted carbon (on opposite stereochem)
a) Hg(OAc)2, H2O
b) NaBH4
Addition reaction
Follows normal rules
Adds OH to most substituted carbon
Does NOT do carbocation rearrangement
a) R-Li
b) H+
Can do SN2 and E2 reactions
Adds carbon chain to molecule
Epoxide opening
Electrons attaching Mg to C take C chain and attach to one part of epoxide
O takes its electrons and epoxide opens, leaving O with a - charge
O takes H+ to make OH
Can also do non-epoxide reactions which would be (±)
LiAlH4
Turns a group into another group
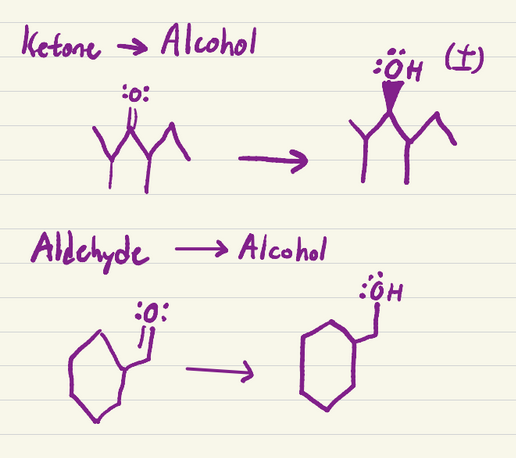
Aldehyde → alcohol (primary)
Ketone → alcohol (secondary)
Carboxylic acid → alcohol (primary)
Esters → alcohol (primary)
Amides → amines
Nitrile → amines (primary)
Epoxides → alcohols
Alkyl halides → alkanes
Basically turns Os into alcohols
a) NaBH4
b) H+
Turns aldehydes and ketones into alcohols
mCPBA
Makes alkenes into epoxides
Turns double bond into epoxide
a) BH3
b) HOO-
Adds OH to alkenes
Addition
Puts OH on LEAST substituted carbon
(±)
a) O3
b) DMS
Cuts at the double bond and puts oxygen at the end (both ends)
Can “cut” hexanes
a) OsO4
b) NaOH, H2O
Adds 2 OH groups to alkene; same stereochem (±)
CH2N2
Turns alkene into a 3 carbon triangle
Like an epoxide but no “O”, just carbons
(±)
H+, H2O, heat
Turns alkyne into ketone
Or HgSO4, H2SO4, H2O
a) Hb(Sin)2
b) HOO-
Turns alkyne into aldehyde
Br2 + light
Radical reaction
Adds ___ to the molecule on the MOST substituted carbon
H leaves; one of its electrons goes in on itself, creating a radical

Cl2 + light
Adds ___ to molecule, does not have regiospecificity so it will cause a mixture
HBr + ROOR + light
Adds ___ to LEAST substituted carbon of a double bond
H2, Pd
Turns alkynes and alkenes into alkanes
Gets rid of double and triple bonds
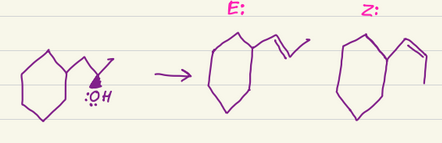
H2, Lindlars
Turns alkynes into Z alkenes
Does not react with alkenes
Li, NH3 (I)
Turns alkynes into E alkenes
Does not react with alkenes
Mg and Li
Makes Grignard with carbon chains that have leaving groups Br, Cl, or I
Mg sticks itself between a halogen and the C attached to it
Li replaces halogen
KCN (or HCN, NaCN, etc), H2O (or HCl, HBr, etc)
CN- is a bullet nucleophile
Only does SN1
Called “cyanohydrin formation”
Whatever is in front of CN- is positively charged and not part of the reaction