external forces
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
kinetics
analysis of the forces
produce, arrest, modifies motion
force
push or pull that changes the motion of the object
results to rotation motion
contact force
direct contact between two objects
applied forces, friction
long range forces
forces that can act over distances
gravity, EMF
displacement
vector that points an object from initial position to final position
equilibrium
no movement due to equal forces
1º source of force
muscles
gravity
externally applied resistance
friction
mass
amount of matter
weight
force of gravity acting on the object
moment
result of force acting at a distance
M = d x F
1st law of motion
law of inertia / equilibrium
A body at rest will remain at rest unless otherwise an external force acted on it
2nd law of motion
law of acceleration / mass
A change in the acceleration of a body occurs in the same direction as the force that caused it
the acceleration of a body is proportionate to the magnitude of the net forces acting on it and inversely proportionate to the mass of the body
EX. deadlift
3rd law of motion
law of action & reaction
for every action there is an opposite & equal reaction
force system
identification of all forces acting on the object
linear force system
all forces are in the same line
parallel force system
two or more parallel forces acting at some distance from each other
center of gravity
females have slightly higher COG than males
adult: slightly ant to S2
pregnant: anterior & superiorly
infant: xiphoid process
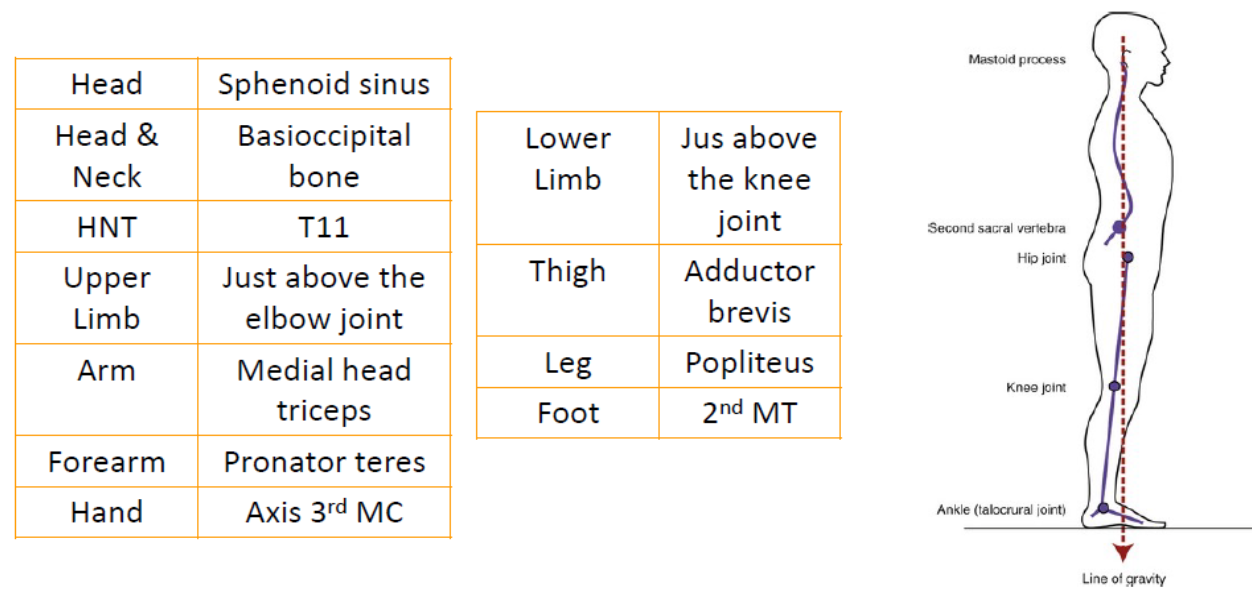
to enhance equilibrium, maximize stability, & achieve balance
lower COG
> weight
larger BOS
line of gravity / weight line
line from COM to the center of the earth
ground reaction force
forces applied to the ground by the foot & vice versa
3rd law of motion
moment
resultant force
force application distant to the center of rotation
types of forces
tension
compression
shear
torsion
bending
tension
traction / distraction
applied perpendicularly to the surface
compression
approximation
applied perpendicularly to the surface
direction of force is towards one another
shear
applied parallel to the surface
- through moving one object along the surface of another
friction
parallel to contacting surface but opposite to the direction of shear
torsion
rotation / twisting
rotation of a segment around its long axis
bending
parallel forces applied to unsegmented object = equilibrium
translation / rotation
bending force is applied on unconstrained object