Chapter 15, 16, 17 | Eyes, Ears, Nose, Mouth, Throat | NURS 122
1/238
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
239 Terms
flashcard on the cranial nerves?
bony orbital cavity
surrounds the eyes and cushioned the eye with fat
eyelids (palpebrae)
protects the eye and control the light entry
conjunctiva
transparant membrane covering the sclera and lining the eyelids
lacrimal apparatus
system of structures the produces and drains tears to ensure moisture and remove debris
palpebral fissues
elliptical opening between eyelids
canthus
junction of the upper and lower eyelids
inner canthus contains the caruncle which secrete sebaceous materials
caruncle
located in the inner canthus
secrete sebaceous materials
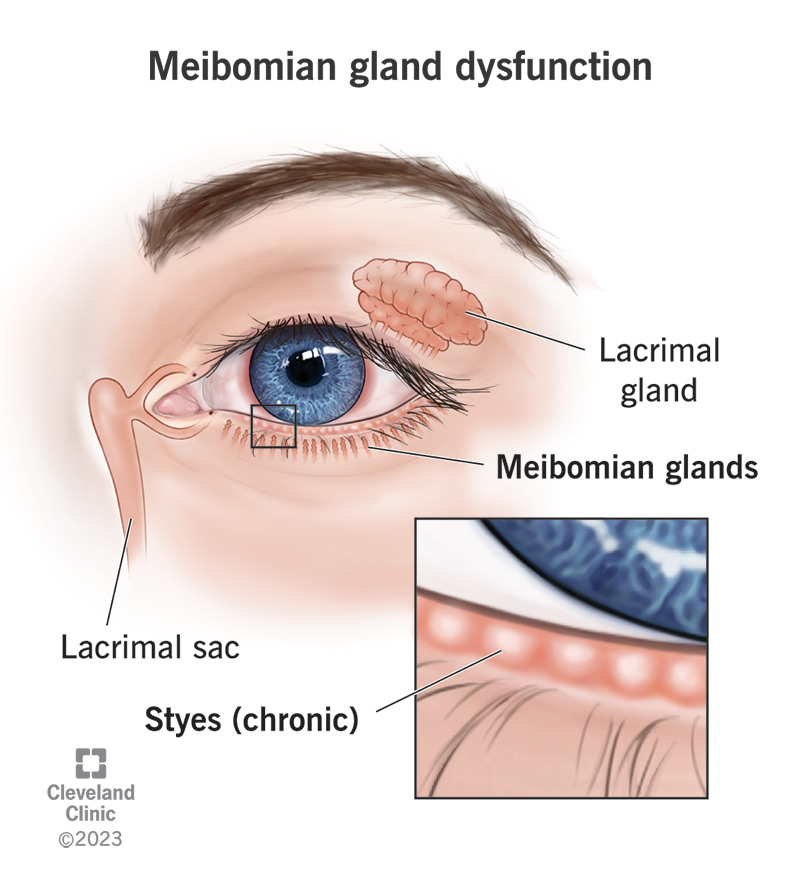
meibomian glands
located in the tarsal plates
secrete oils to prevent tear evaporation
what part of the eyes is involve in light refraction? (outermost to inner most)
cornea
aqueous humor
lens
vitreous humor
what is the neural pathway of the visual pathway starting from the eye to the brain?
retina
optic nerve
optic chiasm (where the fibers cross - lateralization of vision)
occipital lobe
what is the image orientation on the retina?
images on the retina are inverted and reversed
pupillary light reflex
constriction of the pupul in response to light
accomodation (reflex)
adjustments for near and far vision via lens curvature
sherpath
auricle
external ear
vestibule
a space or cavity that serves as the entrance to a passage way (e.g., vestibule of the ear)
semicircular canal
any of the three bony fluid-filled loops in the osseous labyrinth of the internal ear, associated with the sense of balance
cochclear
spiral tunnel with two full and three quarter-turns resembling a tiny snail shells that is associated with the sense of hearing
what are the ossicles of the ear?
malleus
incus
stapes
what are the three antomic division of the pharynx?
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
the bony arch of the hard plate and the soft palate from the _______ of the mouth
roof
the tongie is secured to the oral cavity by the __________
frenulum
nares
anterior opening of the nose
septum
cartilaginous divider between the two anterior cavities (vestibules)
choana
posterior opening leading to the nasopharynx
turbinates
parallel curved bony structures covered by a vascular mucous membrane which forms the lateral walls of the nose and protrude into the nasal cavity
cribriform plates
bony plate on the roof of the nose
kiesselbach plexus
convergence of small fragule artries and veins in the nasal septum
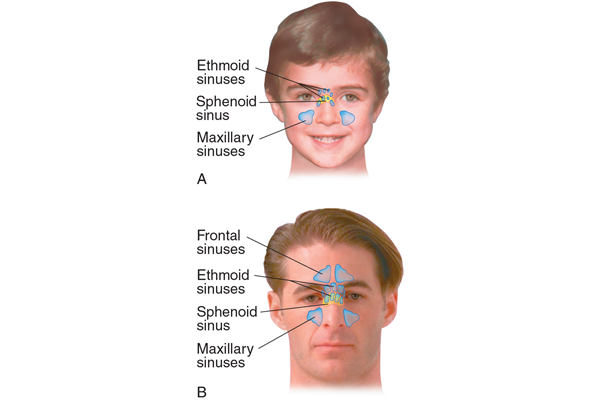
what are the four paranasal sinuses and their general functions
maxillary
frontal
ethmoid
sphenoid
all of these provide humidification, filtration, voice resonance, skull lightening, thermal insulation, and shock absorption
on the _________ and the ________ sinuses are accesible for examination
maxillary; frontal
what are the main functions of the ears and associated structure)?
transmission of sounds impulses (cochlear)
responding to changes in movement vestibule of inner ear)
interpretation of sounds waves (tympanic membrane
drainage of fluid into the posterior aspect of the inferior nasal turbinate (eustachian tube)
what are the function of the nose?
olfaction
respiration
warming of air
humidification of air
filtering of the air
resonance of laryngeal sounds
which part of the pharynx does food, saliva, and liquid pass through on its way to the stomach?
oropharynx and laryngopharynx
what is the function of the salivary glands?
identify fastes
moisten the mouth
reduce the incidence of dental caries
start digestion of starch
The inner ear is composed of which of the following structures?
Auricle
Cochlea
Tympanic membrane
Stapes
cochlea
when asking about a patient history of present illness in relation to the ear, nose and mouth, what are the factors that the student should inquire the patient about?
symptoms (onset, duration, location, associated symptoms)
aggravating/alleviating factors
effort to treat
medication (e.g., analgesic, NSAIDS, narcotics, etc)
characteristics/severity/predisposing factors of the illness
what are some type of medication that can help alleviate symptoms of ear and nose illness?
analgesics
NSAIDs
narcotics
thyroid preparation
what are some type of medications that can help alleviate symptoms of the mouth and oropharynx illness?
analgesics
NSAIDs
narcotics
phenytoin
cyclosporine
calcium channel blockers
mouth rinse
lozenges
when asking about the patient’s medical-surgical history regarding the ears, what should the student nurse ask about?
history of ear infections
history of surgery to the ea
history of labyrinthitis (inflammation or dysfunction of the labyrinthine canals of the inner ear - resulting in vertigo)
when asking about the patient’s medical-surgical history regarding the nose, what should the student nurse ask about?
history of previous nasal trauma/fracture
history of chronic nosebleeds
history of pharyngitis
history of nasal surgery
history of postnasal drip
history of recurrent or chronic sinusitis
history of recurrent/chronic sinusitis
history of allergies
when asking about the patient’s medical-surgical history regarding the mouth/throat, what should the student nurse ask about?
history of frequent, documented strep infections
history of tonsillectomy (surgical excision of the palatine tonsil)
history of adenoidectomy (surgical removal of the lymphoid tissues in the nasopharynx)
why would someone chose to have a tonsillectomy?
some people may chose to remove their palatine tonsil to prevent recurrent tonsillitis
why would someone chose to have a adenoidectomy?
removal of the lymphoid issues in the nasopharynx may be performed because the adenoids are enlarged, chronically infected or causing obstruction
what are the factors that the student nurse should ask about when inquiring about patient’s family history of ears, nose, and throat illness?
allergies
hearing loss (e.g., Meniere disease)
hereditary renal diseases
what are some personal/social history that might predispose the patient to higher likelihood of developing ears, nose, and/or thorat infections?
environmental hazards (e.g., chemical exposure
nutritions
oral care patterns
tobacco/alcohol use
recreational drug use
protective devices
The nurse should ask the patient with ear pain about which associated symptoms as part of a history of present illness?
Select all that apply.
Fever
Ear drainage
Decreased hearing ability
Previous ear pain
Association with exercise
Fever
The nurse should ask about fever as part of the history of present illness related to the patient’s ear pain.
Ear drainage
The nurse should ask about any ear drainage as part of the history of present illness related to the patient’s ear pain.
Decreased hearing ability
The nurse should ask about the ability to hear as part of the history of present illness related the patient’s ear pain.
Previous ear pain
Previous ear pain is part of the medical-surgical history, not history of present illness.
Association with exercise
Association of the ear pain with exercise is part of the personal/social history, not history of present illness.
Which questions should the nurse ask a patient with hearing loss regarding timing of symptoms as part of the history of present illness?
Select all that apply.
“Did the hearing loss begin suddenly?”
“How long has the hearing loss lasted?”
“Are you sensitive to loud noises?”
“Are you experiencing any pain?”
“Is the hearing loss constant or intermittent?”
“Did the hearing loss begin suddenly?”
The nurse should ask whether the hearing loss was sudden or gradual when assessing the timing of symptoms as part of the history of present illness.
“How long has the hearing loss lasted?”
The nurse should ask how long the hearing loss lasted when assessing the timing of symptoms as part of the history of present illness.
“Are you sensitive to loud noises?”
The nurse should ask about sensitivity to noise to assess associated symptoms, not the timing of symptoms.
“Are you experiencing any pain?”
The nurse should ask about pain to assess associated symptoms, not the timing of symptoms.
“Is the hearing loss constant or intermittent?”
The nurse should ask whether the hearing loss is constant or intermittent when assessing the timing of symptoms as part of the history of present illness.
The nurse should ask the patient presenting with dental pain which questions as part of the history of present illness?
Select all that apply.
“Do you wear dentures?’
“Have you noticed any areas of irritation?”
“How long have you had the pain?”
“Do you have any family history of dental disease?”
“How often do you see a dentist?”
“Do you wear dentures?’
The nurse should ask the patient with dental pain if he or she wears dentures as part of the personal/social history.
“Have you noticed any areas of irritation?”
The nurse should ask the patient with dental pain about any irritation he or she is experiencing related to the dentures as part of the history of present illness.
“How long have you had the pain?”
The nurse should ask the patient with dental pain about the duration of the pain as part of the history of present illness.
“Do you have any family history of dental disease?”
Asking the patient with dental pain about a family member’s dental disease is part of the family history and is not a part of the history of present illness.
“How often do you see a dentist?”
The nurse should ask the patient with dental pain about his or her dental visits as part of the personal/social history, not history of present illness.
The nurse should ask the patient presenting with nasal drainage which questions regarding the history of present illness?
Select all that apply.
Associated symptoms of sneezing and congestion
Parent or family member with seasonal allergies
Color and amount of drainage
Unilateral or bilateral
Seasonality
Associated symptoms of sneezing and congestion
The nurse should ask about associated symptoms as part of the history of present illness.
Parent or family member with seasonal allergies
The nurse should ask about seasonal allergies but as part of the family history, not history of the present illness.
Color and amount of drainage
The nurse should ask about drainage characteristics as part of the history of present illness.
Unilateral or bilateral
The nurse should ask about laterality as part of the history of present illness.
Seasonality
The nurse should ask about seasonality as part of the history of present illness.
what factors should he student nurse note when inspecting the auricles and mastoid?
size, shape, symmetry
color
positions
preauricular area
external auditory canal
what factors should he student nurse note when palpating the auricles and mastoid?
mobility
consistency
what factors should he student nurse note when examining the inside of the ear?
audiotory canals
landmarks, color, contour, and mobility of the tympanic membrane
what are some different hearing examination that can be done?
whispered voice
Weber test
Rinne Test
the use of ________ is the preferred screening for hearing loss
audiometry
what are the different factors that the student nurse should assess for when examining the mouth and lips?
symmetry
color
condition
what are the different factors that the student nurse should assess for when examining the teeth and tongue?
occlusion
color
conditions
size
symmetry
color, coating, size, and presence of ulcerations of the dorsal surface of the tongue
ventral surface and floor of the mouth
lateral borders
number of teeth
texture
movement
what are the different factors that the student nurse should assess for when examining the oral mucosa and gums?
color
sweeling
symmetry
ulcerations
conditions
bleeding
loose teeth
tenderness
what are the different factors that the student nurse should assess for when examining the uvula and oropharynx?
color
landmark
movements
tonsils
posterior wall of pharynx
The nurse should assess for which findings by palpating the nose?
Select all that apply.
Masses
Tenderness
Nasal flaring
Shape and size
Position of bones and cartilage
Masses
Tenderness
Position of bones and cartilage
When inspecting the dorsum of the tongue, the nurse should note which features?
Select all that apply.
Size
Color
Coating
Ulcerations
Tenderness
Size
Color
Coating
Ulcerations
what are the normal assessment findings for inspection of the ears?
auricles equal size/similar appearance
Darwin tubercle
same color as facial skin
top of auricle aligns or above inner canthus of the eye
auricle in vertical position
preauricular pits
skin tags
smooth skin
no discharge or odor
what are the normal assessment findings for the palpation of the ears?
firm and mobile auricle
flexible auricle readily recoil
no tenderness in postauricular or mastoid area
pre/postauricular lymph nodes not palpable
what is the normal assessment findings for otoscopic examination?
minimal cerumen (color/texture varies)
visible umbo, handle of malleus, and light reflex
translucent, pearly gray tympanic membrane
tympanic membrane slightly conical, concave umbo
tympanic membrane moves in and out with positive and negative pressure from pneumatic attachment
wha is the normal assessment findings for hearing screening?
patients respond appropriately to questions
patient repeats whispered words, numbers, letters more than 50% of the time
what is the normal assessment finding for the Weber Test?
sound heard equally in both ears when ears not occluded, sound heard better in non occluded ear
what is the normal assessment finding for the Rinne Test?
measurement of air conduction twice as long as measurement of bone conduction
what is the normal assessment finding (inspection & palpation) for the nose?
smooth
columella (directly midline, width not greater than diameter of naris)
color same as facial skin
nares oval shapes, symmetrical
patent bilaterally
firm, stable
patient is able to smell
what is the normal assessment finding (inspection & palpation) for the nasopharynx?
close to midline
thicker anteriorly than posteriorly
inferior and middle turbinate visible
possible film of clear discharge on septim
hairs in vestibule
what is the normal assessment finding (inspection & palpation) for the nasopharynx?
nontender
no swellng
what are the normal assessment findings for the teeth?
ivory, yellow-stained or brown
32 teeth firmly anchored
what are the normal assessment findings for the tongue?
midline, no fasciulations
dull red color, moist, glistening
anterior: smooth with papillae and small fissures
posterior: slightly uneven.rugose, thinner mucosa
ventral surface: pink, smooth, large veins visible
wharton ducts on either side of frenulum
patient can taste
what are the normal assessment finding of the buccal mucosa?
whiteish yellow or whitish pink Stense duct
fordyce spots may be present
what are the normal assessment findings of the palate of the mouth?
hard palate: whitish, dome-shaped, tranverse rugae
soft palate: pinker, continuous with hard palate
uvula midline
torus palatinus: bony protuberance at midline
soft palate rises symmetrically with “ah”
uvula remains midline with “ah”
what are the normal assessment finding fo the throat and tonsils?
tonsils blend into pink pharynx
possible crypts in tonsils for debris collection
posterior oropharynx: smooth glistening pink
small lymphatic tissues spots and blood vessels
gag reflex present bilaterally
what are some mouth and throat changes associated with aging?
decreased salivary flow
thinning buccal mucosa
fissures/varicosities on tongue
malocclusion, missing teeth, dentures
the sense of taste begins to deteriorate at 50 years of age
what are some ear/nose changes associated with aging?
may have hearing aid
coarse hair on auricle
scleroic changes to tympanic membrane
presbycusis (conductive hearing loss)
cerumen impaction
nose/sinuses
dry mucosa
increased hairs on vestibules
decreased sense of smell in adults over age 60
true or false: nose flaring on inspiration is an abnormal finding?
true
true or false: polyps of the nose or sinuses is an abnormal finding
true
hyperemia
an excess of blood in part of the body caused by increase blood flow as in inflammatory response, local relaxation of arterioles, or obstruction of the outflow of blood from an area
rhinorrhea
AKA runny nose - excessive nasal discharge
During the examination of the ears, which finding is expected?
Auricle scales
Low-set ears
Flexible earlobes
Tenderness on palpation
Flexible earlobes
What ear assessment finding should be considered part of the normal aging process?
Tinnitus
Epistaxis
Angioedema
Presbycusis
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, is an unexpected finding at any age.
Epistaxis
Epistaxis, or nasal bleeding, is not part of the ear assessment and not a normal part of the aging process.
Angioedema
Angioedema is not part of the ear assessment and not a normal part of the aging process.
Presbycusis
Presbycusis, or sensorineural hearing loss, is an expected finding in older adults.
Which of the following are normal findings of a mouth and throat examination?
Select all that apply.
Uvula at midline
Dorsal surface of tongue glistening
Lips symmetrical vertically but not horizontally
Hard palate continuous with soft palate
32 teeth, firmly anchored
Uvula at midline
Dorsal surface of tongue glistening
Hard palate continuous with soft palate
32 teeth, firmly anchored
Which of the following are normal findings of a nose examination?
Select all that apply.
Columella directly midline
Septum thicker posteriorly than anteriorly
Hairs in vestibule
Inferior and middle turbinates visible
Nares asymmetrical
Columella directly midline
The columella should be directly midline.
Septum thicker posteriorly than anteriorly
The septum should be thicker anteriorly than posteriorly.
Hairs in vestibule
There should be hairs in the vestibule.
Inferior and middle turbinates visible
The inferior and middle turbinates should be visible.
Nares asymmetrical
The nares should be symmetrical.
Which mouth and throat assessment findings should be considered abnormal?
Select all that apply.
Nodule on the palate, not at the midline
Tonsils that project beyond the tonsillar pillars
Intact gag reflex
Asymmetrical lips
Red spots at the Stensen duct
Nodule on the palate, not at the midline
A nodule on the palate that is not at the midline is an abnormal finding in an assessment of the mouth and throat.
Tonsils that project beyond the tonsillar pillars
Tonsils that project beyond the tonsillar pillars is an abnormal finding in an assessment of the mouth and throat.
Intact gag reflex
Intact gag reflex is a normal finding in an assessment of the mouth and throat.
Asymmetrical lips
Asymmetrical lips are an abnormal finding on assessment of the mouth and throat.
Red spots at the Stensen duct
Red spots at the Stensen duct is an abnormal finding on assessment of the mouth and throat.
vertigo
illusion of rational movement by a patient, caused by disorder of the inner ear
should documentL spontaneous episode of dizziness that is severe, difficulty walking, nausea and vomiting, and headaches
Meniere disease
sudden onset of vertigo
hearing loss
whistling/roaring sound in the affected ear
sensitivity to sound
fullness in ears
nausea and vomiting
what are some behavior associated with conductive hearing loss?
turns volume up on TV, radio
speech sounds muffled in noisy environment
asks to have information repeated
speaks softly
what are some behavior associated with sensorineural hearing loss?
people mumble
difficulty understanding speech
speaks loudly
unable to hear in crowded room
The nurse assesses a patient complaining of difficulty swallowing that began 1 month ago. The nurse notes the presence of enlarged tonsils, dry mucous membranes, and white spots on the tonsils. Which assessment information should the nurse document as history of present illness related to the ears, nose, and throat (ENT) assessment?
Select all that apply.
Enlarged tonsils
Difficulty swallowing
White spots on the tonsils
Dry mucous membranes
Difficulty swallowing
Dry mucous membranes
A patient with a history of dental caries reports pain with chewing. The patient smokes 1 pack of cigarettes each day and reports no dental visits for several years. The nurse notes a foul odor from the mouth and multiple discolored teeth. Which subjective assessment data should the nurse document as personal/social history related to a mouth assessment?
Foul mouth odor
Pain with chewing
History of dental caries
Patient’s cigarette habit
Patient’s cigarette habit
Which information suggestive of a thyroid condition should be documented under family history?
Tachycardia
Neck pain on palpation
Spouse with Graves disease
Father with Graves disease
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is objective data, not part of the family history.
Neck pain on palpation
Neck pain on palpation, as determined by the nurse, is objective data, not part of the family history.
Spouse with Graves disease
The patient’s spouse with Graves disease is not considered part of the family history because there is no genetic relationship between the patient and his or her spouse.
Father with Graves disease
The patient’s father with Graves disease is family history suggestive of a thyroid condition.
The nurse has a 36-year-old patient who is complaining of ear pain and difficulty hearing. The patient reports a family history of hearing loss. The patient has ear drainage and a retracted tympanic membrane on examination. Which should the nurse document as objective data related to the ear assessment?
Difficulty hearing
Ear pain
Ear drainage and retracted tympanic membrane
Family history of hearing loss
Ear drainage and retracted tympanic membrane
A patient with a history of ear trauma complains of right ear pain and muffled hearing. The nurse notes loss of high- and low-frequency sounds. Which objective information should be documented as a part of the ear assessment?
Select all that apply.
Ear pain
Muffled hearing
History of ear trauma
Loss of low-frequency sounds
Loss of high-frequency sounds
Ear pain
The patient’s ear pain is history of present illness, not objective data.
Muffled hearing
The patient’s muffled hearing is history of present illness, not objective data.
History of ear trauma
The patient’s history of ear trauma is medical-surgical history, not objective data.
Loss of low-frequency sounds
Loss of low-frequency sounds, as determined by the nurse, is objective data related to the ear assessment.
Loss of high-frequency sounds
Loss of high-frequency sounds, as determined by the nurse, is objective data related to the ear assessment.
_____ to _____ mm is considered to be the most normal size pupil
2; 3
true or false: pupil are equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodating
true: PERRLA
fixation
a reflex direction of eye toward an object attrating a person’s attraction
slide 12
diabetic retinopathy
abnormal growth of blood vessels in the retina obstructing vision