Clinical management of depression and bipolar disorder
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
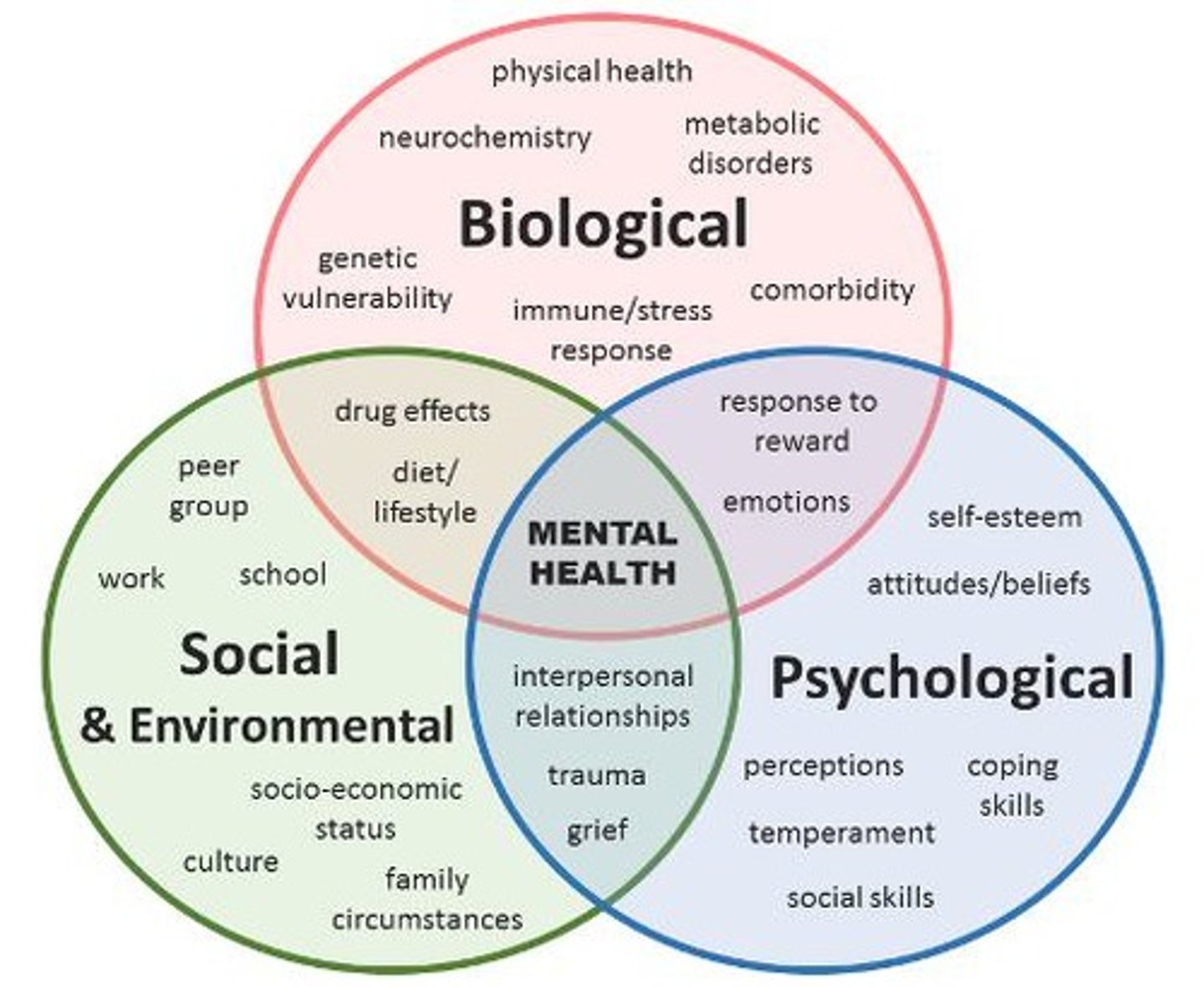
What is the bio-socio environmental model for mental health?
A model which describes the different factors which contribute to mental health including
- biological factors
- social and environmental factors
- psychological factors
What percentage of adults are prescribed antidepressants?
20%
What is the serotonin theory of depression? Why is it wrong?
That depression is chemical imbalance in the brain caused by low serotonin which can be resolved by increasing the level of serotonin.
This is wrong because depression is a complex syndrome caused by both genetic and environmental factors.
What are the aims of depression treatment?
1. Remission
- Symptoms all resolved
2. Relapse Prevention
- Prevent future episodes
3. Restore Function
- Psychosocial
- Physical
What is choice of treatment for depression influenced by?
1. Severity of problems: implication on daily life
2. Past experiences of medication and treatment
3. Person's preferences
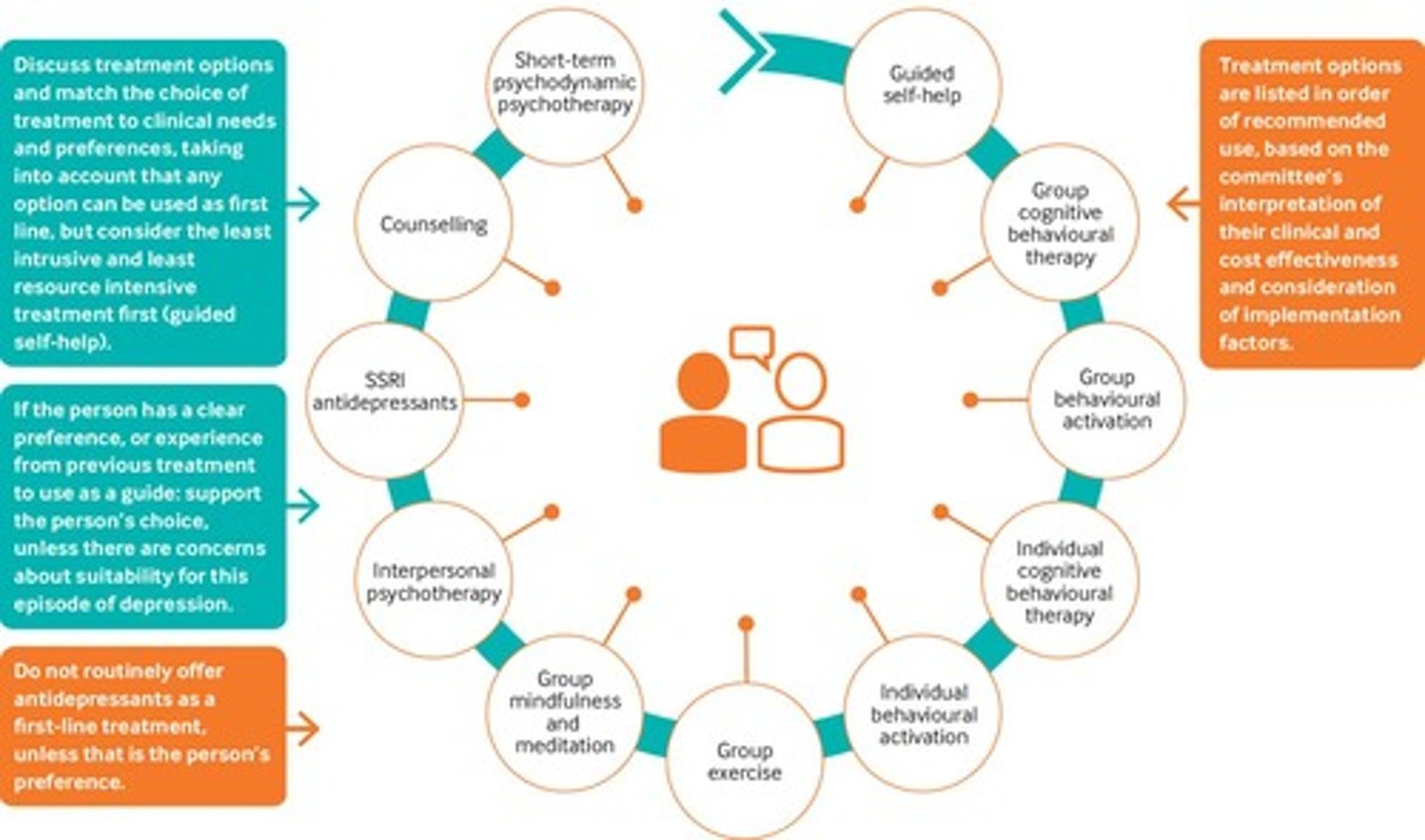
What are the (in order) treatment options for less severe depression?
Priorities high or low psychological OR psychosocial interventions
1. Guided self help
2. Group cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT)
3. Group behavioural activation
4. Individual CBT
5. Individual behavioural activation
6. Group exercise
7. Group mindfulness and meditation
8. Interpersonal psychotherapy
9. SSRI antidepressants
10. Counselling
11. Short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy
- Any treatment option can be chose first-line but first consider the least intrusive and least resource intensive treatment.
- In less severe depression, the risks outweigh the benefits for medication (antidepressants). Would prefer other interventions first.
- Do not routinely offer antidepressants, unless it is the person's preference.
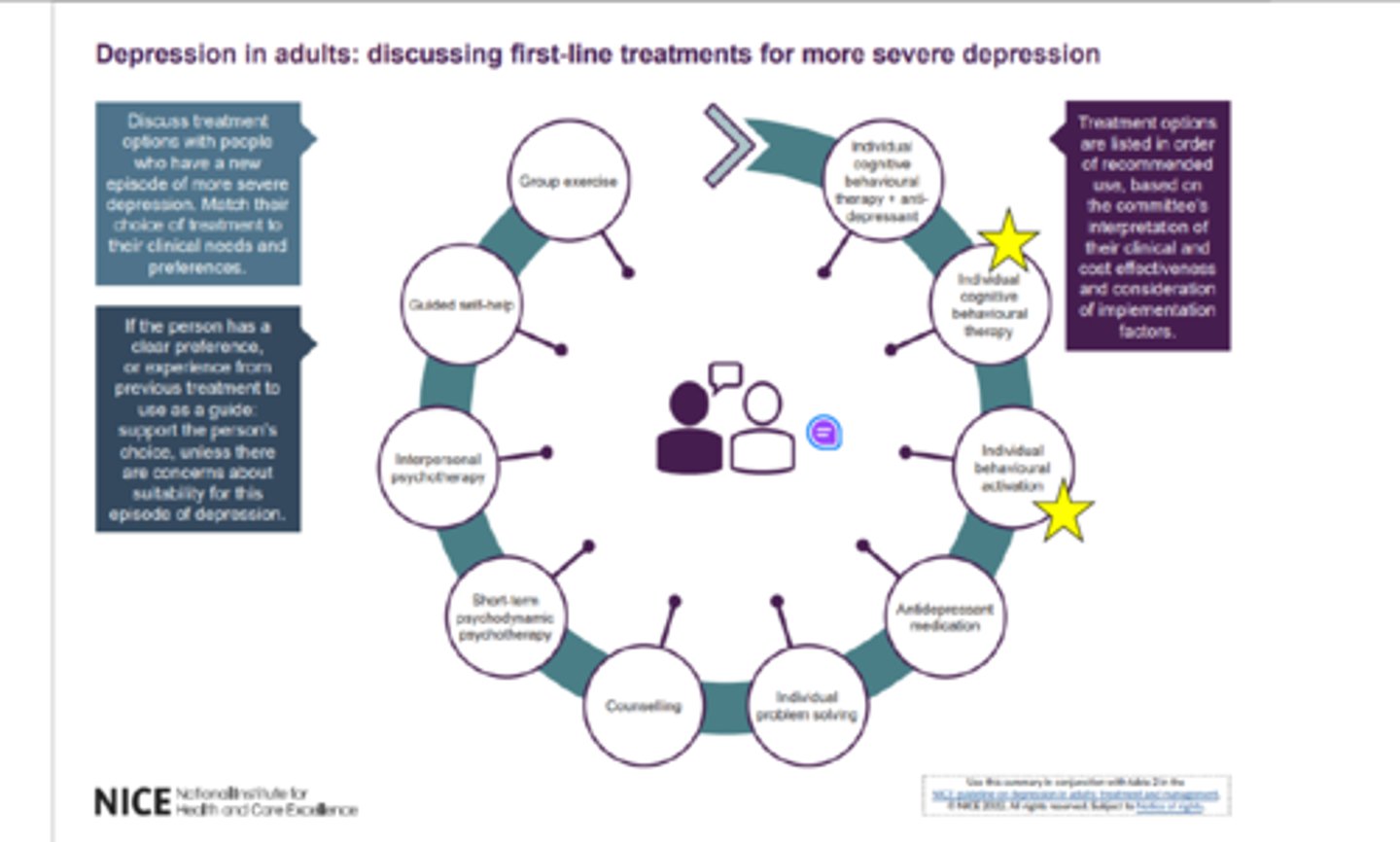
What are the (in order) treatment options for more severe depression?
Prioritises medication THEN psychosocial/ psychological intervention
1. Individual cognitive behavioural therapy + anti-depressants
2. Individual cognitive behavioural therapy
3. Individual behavioural activation
4. Antidepressant medication
5. Individual problem solving
6. Counselling
7. Short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy
8. Interpersonal psychotherapy
9. Guided self-help
10. Group exercise
What class of antidepressant is considered first line?
SSRIs
Give examples of SSRIs
Sertraline, escitalopram
What pharmacological treatment is considered if first line treatment fails for depression?
More common approaches:
1. A different SSRI or SNRI or mirtazapine
2. A recognised antidepressant combination
3. Adding a mood stabiliser or antipsychotics - specialist intervention
(Less common approaches)
1. Vortioxetine
2. Tricyclic antidepressant (TCA)
3. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
How do we monitor patients who are on antidepressants?
Monitor
- Duration: how long they've been on the medication
- Efficacy: is it working for the patient?
- Side effects: what ones have they experienced? How severe have they been?
- Re-enforce self-care advice
- Review diagnosis
- Review adherence: have they been taking it?
- Ask patient if they are interested in talking therapies
What are side effects of SSRIs?
1. Gastrointestinal - nausea, diarrhoea, decreased/increased appetite
2. Sexual dysfunction
3. Insomnia and agitation
4. More rarely bruising and bleeding
Rarer side effects:
- Hyponatraemia - low Na+
- Withdrawal syndrome
What is serotonin syndrome?
A predictable reaction when two or more agents increase levels of serotonin are prescribed.
The onset is very rapid - it occurs within minutes - hours of increased serotonin levels.
What are symptoms of serotonin syndrome?
A triad of symptoms:
1. Cognitive
headache, agitation, hypomania, mental confusion, hallucinations, coma
2. Autonomic
shivering, sweating, hyperthermia, vasoconstriction, tachycardia
3. Somatic
myoclonus (muscle twitching), hyperreflexia, tremor
How do you manage serotonin syndrome?
Stop medication causing rise in serotonin
- Support organ function
- Manage temperature
- Agitation and muscle twitching use benzodiazepines
- Serotonin antagonist cyproheptadine can be used
What counselling should be given to patients beginning antidepressant therapy?
1. Symptoms may feel worse in the first week - 10 days (increased anxiety and suicide ideation). Feel more vulnerable but for most people it resolves very quickly.
2. Brief conversation about how long the anti-depressant will be taken for - continued for at least 6 months to prevent relapse as depression often reoccurs (people often don't need lifelong treatment)
3. Awareness that they can cause withdrawal symptoms so they may need to be tapered down
4. Allow patients time to consider whether they want to start their medication
5. Not everyone respond to their first antidepressant - may require switching to different class of antidepressants or different class if adverse effects
How often does antidepressant medication need to be reviewed?
Every 6 months
What percentage of people never respond to antidepressants?
20% of people never respond to antidepressants
What fraction of people will not respond to their first antidepressant?
1/3 of people
What is bipolar disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a recurrent and sometimes chronic mental illness. It is characterised by alternating periods of abnormal mood elevation (mania) and low mood (depression). This is associated with a change or impairment in functioning.
What medication can be used for the management of bipolar disorders?
1. Mood stabilisers
2. Lithium
3. Anti-convulsant medications e.g. valproate or lamotrigine
4.Antipsychotics
5. Benzodiazepines
- Beware dependence
6. Antidepressants
- A controversial treatment option - can make things worse
What is first line pharmacological treatment of bipolar disorder?
Lithium for first line, long term pharmacological treatment for bipolar disorder
Describe how lithium should be taken
- Lithium should be taken regularly - if lithium is taken erratically then it can be worse for the patient than not taking any medication.
- Lithium is good for the management of depression and mania
- A single daily dose regimen is associated with less polyuria, a reduction in permanent renal damage and better compliance
Describe monitoring for lithium
Lithium must be heavily monitored
It has a narrow therapeutic window. Needs to be within 0.4 - 0.8 mmol/L.
Many drugs have interactions with lithium
Renal function should be measured at least every 6-months for patients on a stable dose
- It should be measured every 3 months in higher risk groups
What classes of drugs have interactions with lithium?
ACEI, diuretics and NSAIDs, some OTC preparations
What are the different chemical compounds of lithium and their formulation?
Solid dose form - lithium carbonate
Liquid dose form - lithium citrate
When should serum-lithium concentration be measured?
Therapeutic serum-lithium concentration should be taken 12 hours post-dose window.
What are signs of acute toxicity with lithium?
- Gastro-intestinal disturbances (vomiting, diarrhoea),
- Visual disturbances
- Polyuria
- Muscle weakness
- Fine tremor increasing to coarse tremor,
- CNS disturbances (can be confused with symptoms of bipolar)
- Confusion and drowsiness increasing to lack of coordination, restlessness, stupor
- Abnormal reflexes, myoclonus
What concentration of lithium is associated with serious toxicity?
Concentrations >2 mmol/litre
What is the purple book?
A record book for lithium therapy