Prokaryotes Part 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is microbial growth?
An increase in a population of microbes due to reproduction of individual microbes.
What is a discrete colony?
An aggregation of cells arising from a single parent cell.
What is a biofilm?
A collection of microbes living on a surface in a complex community.
What are the main nutrients that organisms use for energy and growth?
Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen.
What are autotrophs?
Organisms that obtain carbon from inorganic sources.
What are heterotrophs?
Organisms that obtain carbon from organic sources.
What are chemotrophs?
Organisms that obtain energy from chemical compounds.
What are phototrophs?
Organisms that obtain energy from light.
What is transformation in prokaryotes?
The uptake of prokaryotic DNA directly from the environment.
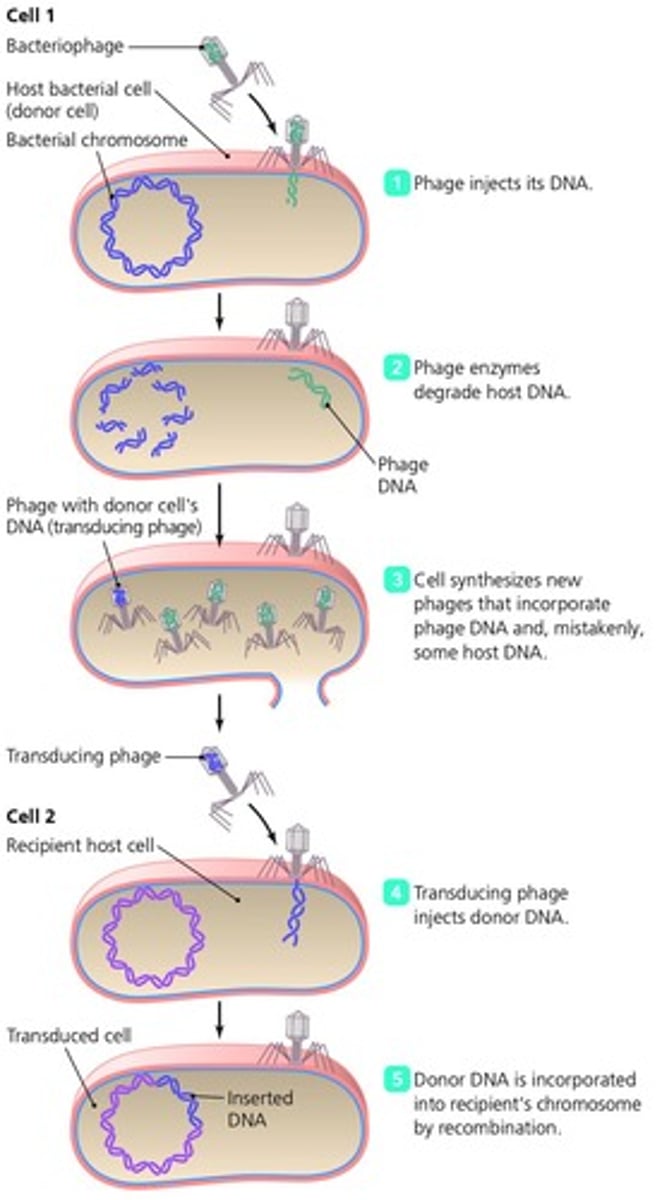
What is transduction?
A process where a bacteriophage injects DNA into a cell, transferring genetic material from one bacterium to another.
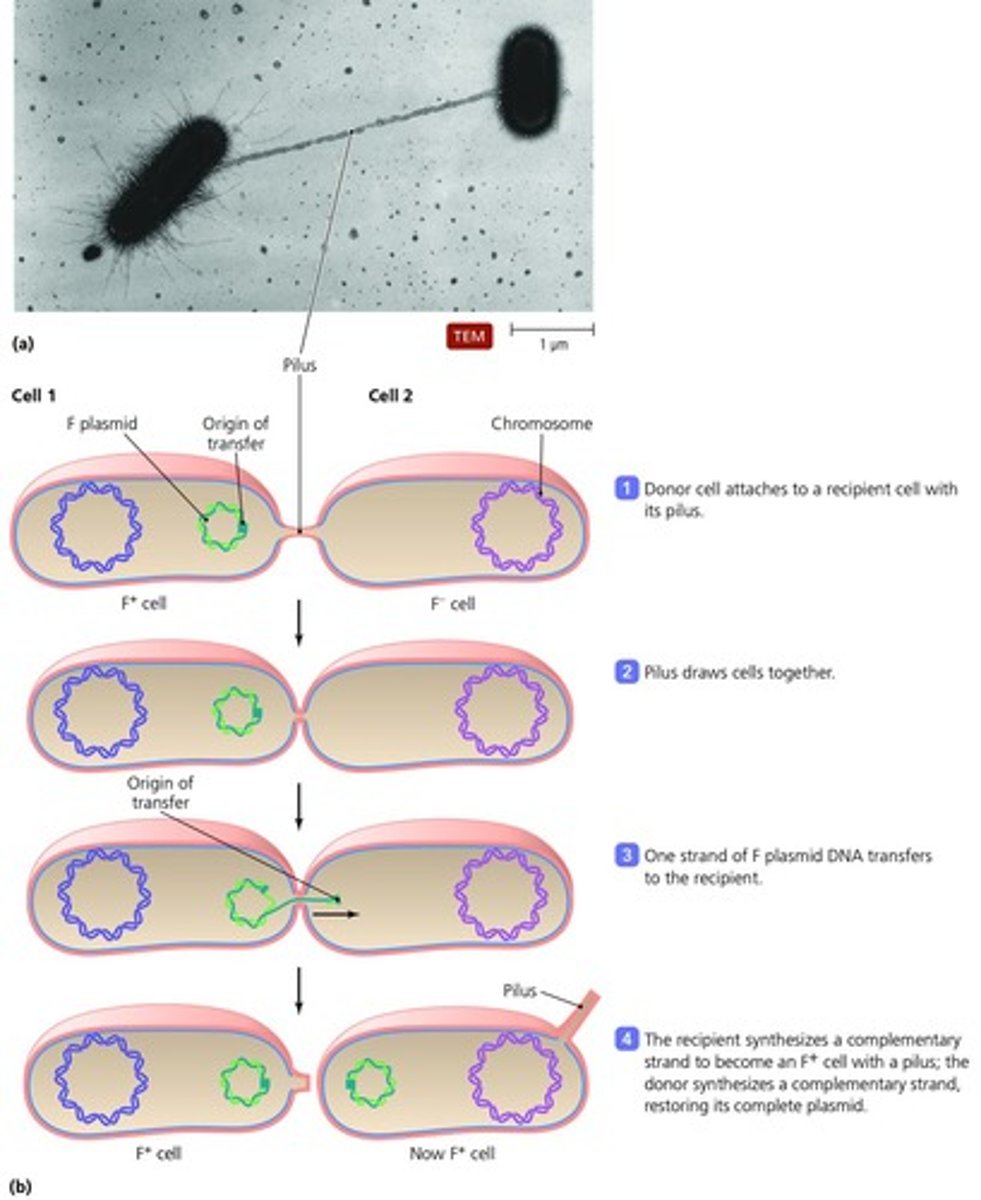
What is conjugation?
The transfer of DNA from one cell to another via a pilus that connects the two cells.
Who conducted the famous transformation experiment with Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Frederick Griffith.
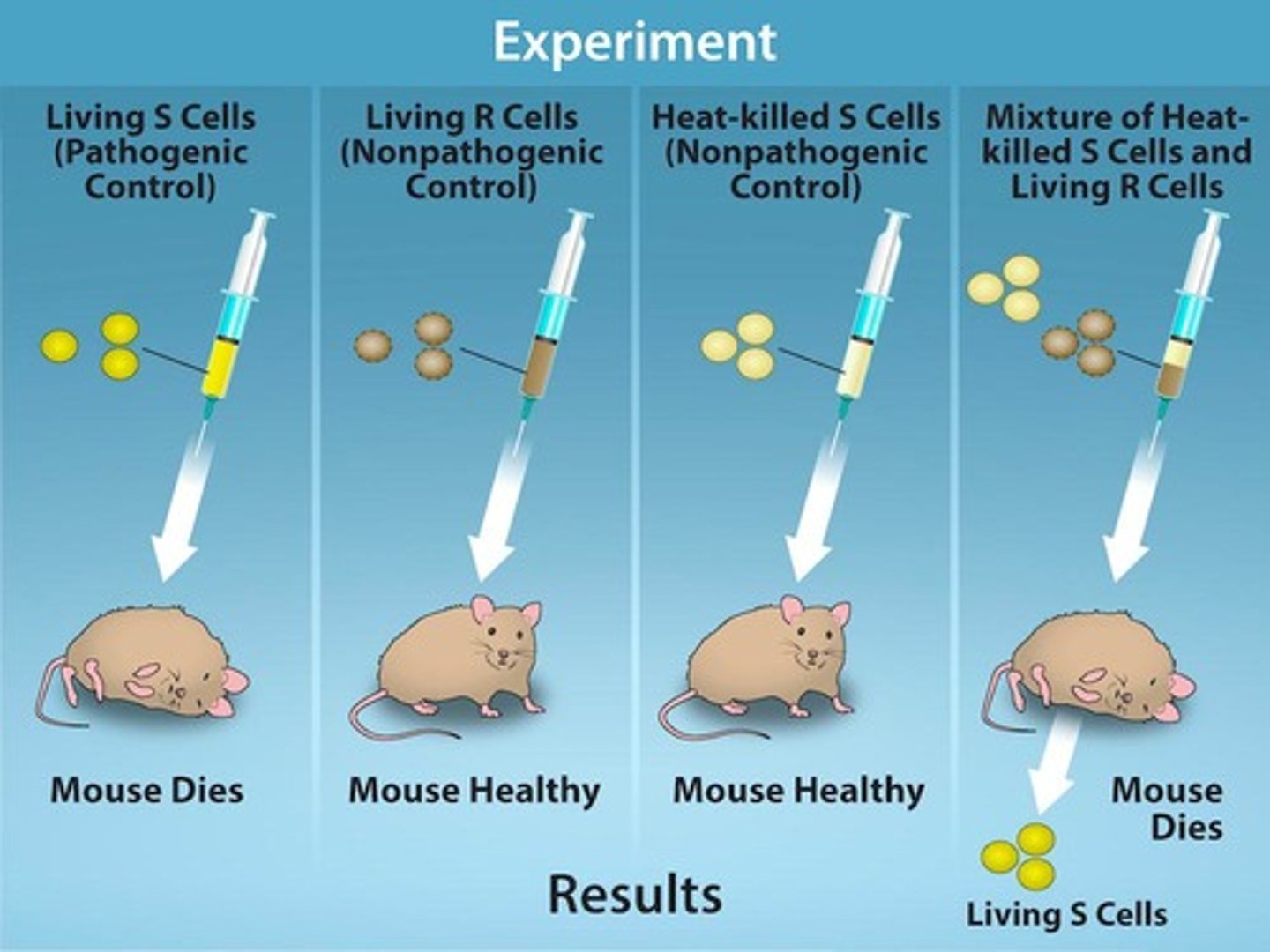
What did Griffith conclude from his experiment with S and R strains of S. pneumoniae?
Something had passed from the heat-killed S strain to the R strain, transforming the R strain into S strain.
What did Lederberg and Tatum discover in their work with E. coli?
Genetic transfer between different strains of E. coli occurred, resulting in new genotypes.
What did Bernard Davis's U-Tube experiment demonstrate?
Direct cell-to-cell contact is required for bacterial conjugation.
What happens during bacterial transformation?
The cell takes up DNA from the environment, which may remain as plasmid DNA or be incorporated into the host genome.
What are the steps in bacterial transduction?
1. Phage injects DNA. 2. Host DNA is degraded. 3. New phages are synthesized. 4. Transducing phage injects donor DNA. 5. Donor DNA is incorporated into the recipient's chromosome.
What is the F plasmid?
A fertility factor in E. coli that allows for conjugation.
What did Antoni van Leeuwenhoek contribute to microbiology?
He made and used simple microscopes to visualize microorganisms, calling them 'animalcules.'
What was the purpose of Pasteur's swan-neck flask experiment?
To determine whether microbial life spontaneously generates.
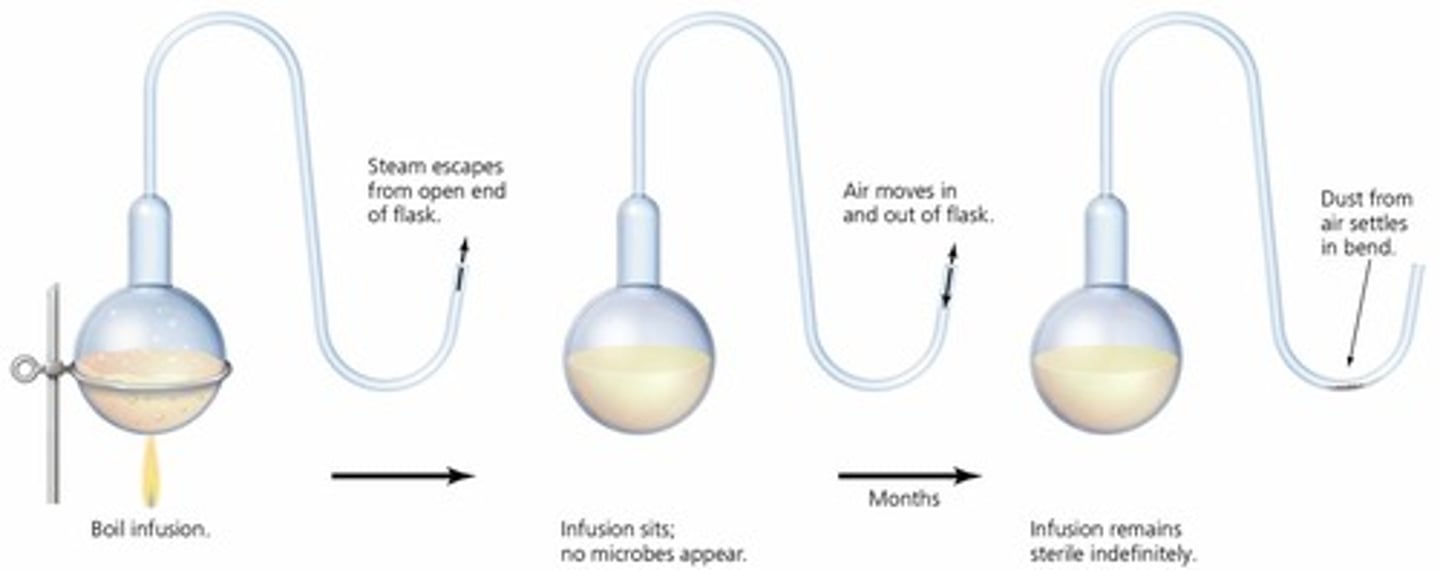
What were the results of Pasteur's swan-neck flask experiment?
No microbial growth occurred in upright flasks, but microbial growth appeared when dust entered tilted flasks.
What is the significance of understanding microbial nutrient utilization?
It helps in understanding how microbes obtain energy and build organic molecules and cellular structures.
What is the role of plasmids in bacterial conjugation?
Plasmids may encode advantageous information and can be transferred between bacteria during conjugation.
What is the difference between natural and artificial transformation?
Natural transformation occurs in many bacterial species, while artificial transformation can be accomplished in the lab using methods like heat shock or electroporation.
What is a high frequency of recombination (Hfr) cell?
A cell in which the F plasmid has integrated into the bacterial chromosome, allowing for more efficient gene transfer.
What are Koch's Postulates?
Four criteria to establish a causal relationship between a microorganism and a disease.
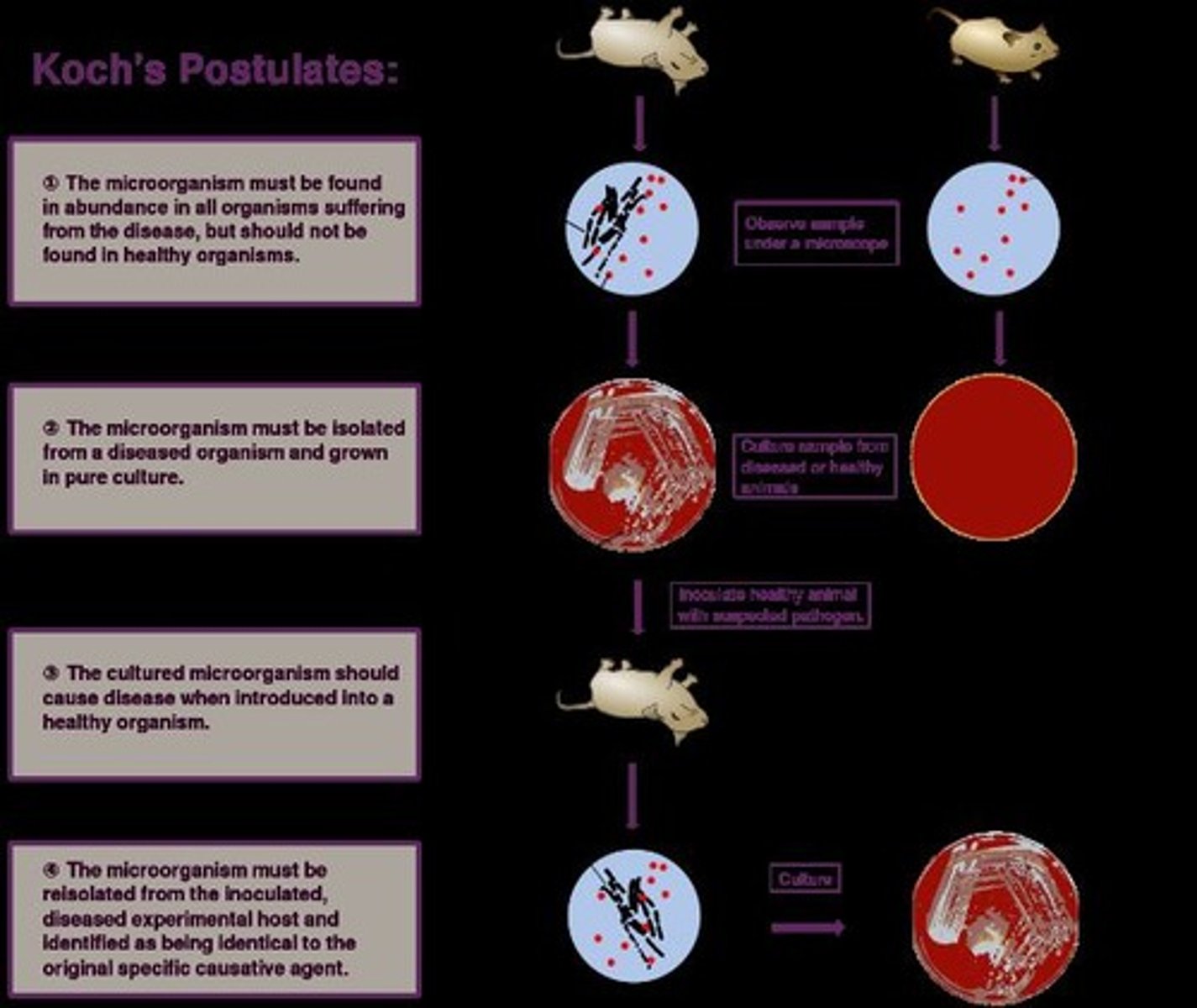
What is the first postulate of Koch?
The suspected causative agent must be found in every case of the disease and absent from healthy hosts.
What is the second postulate of Koch?
The agent must be isolated and grown outside the host.
What is the third postulate of Koch?
When the agent is introduced to a healthy, susceptible host, the host must get the disease.
What is the fourth postulate of Koch?
The same agent must be found in the diseased experimental host.
What are pathogenic bacteria?
Parasitic microbes that cause disease symptoms.
Name three diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria.
Cholera, pneumonia, and Lyme disease.
What is the role of beneficial bacteria in the environment?
They support essential life processes, such as nutrient production and decomposition.
What is the causative agent of the Bubonic Plague?
Yersinia pestis, a Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium.
How is the Bubonic Plague transmitted?
Through the bite of an infected flea, which is infected by a rodent.
What distinctive sign often indicates Lyme disease infection?
A bullseye rash.
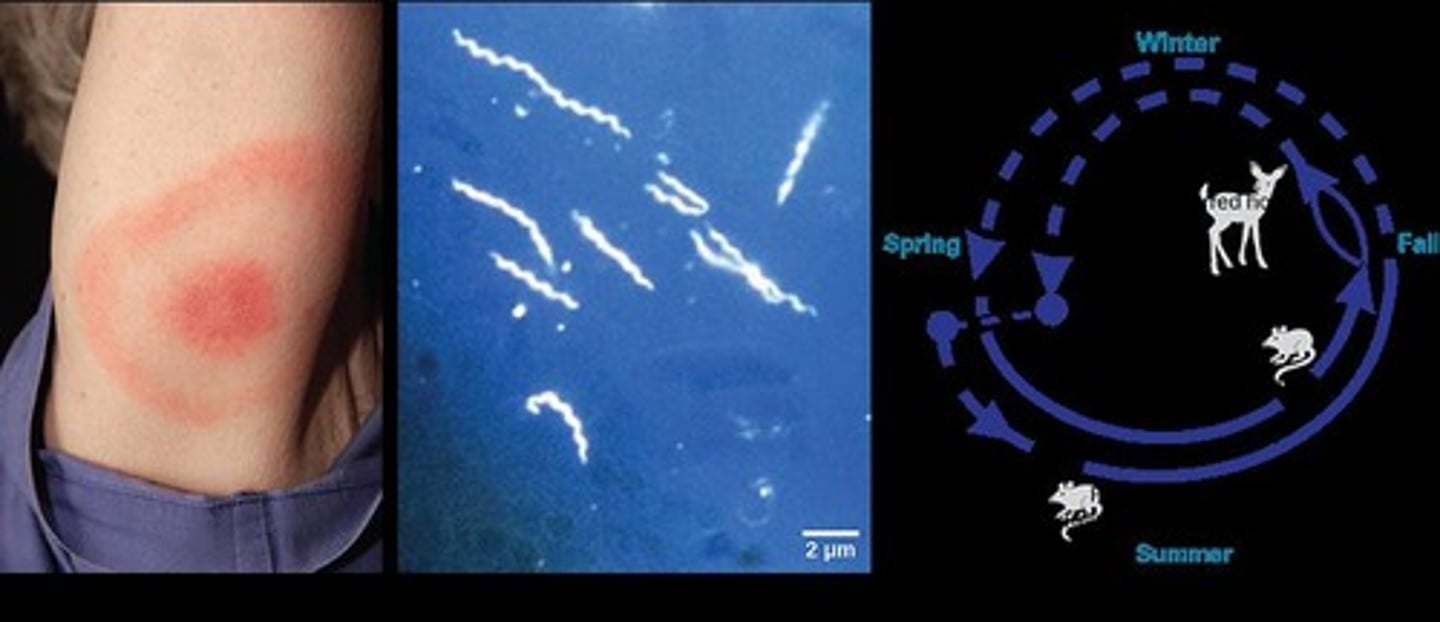
What is the causative agent of Lyme disease?
Borrelia genus, a Gram-negative spirochete.
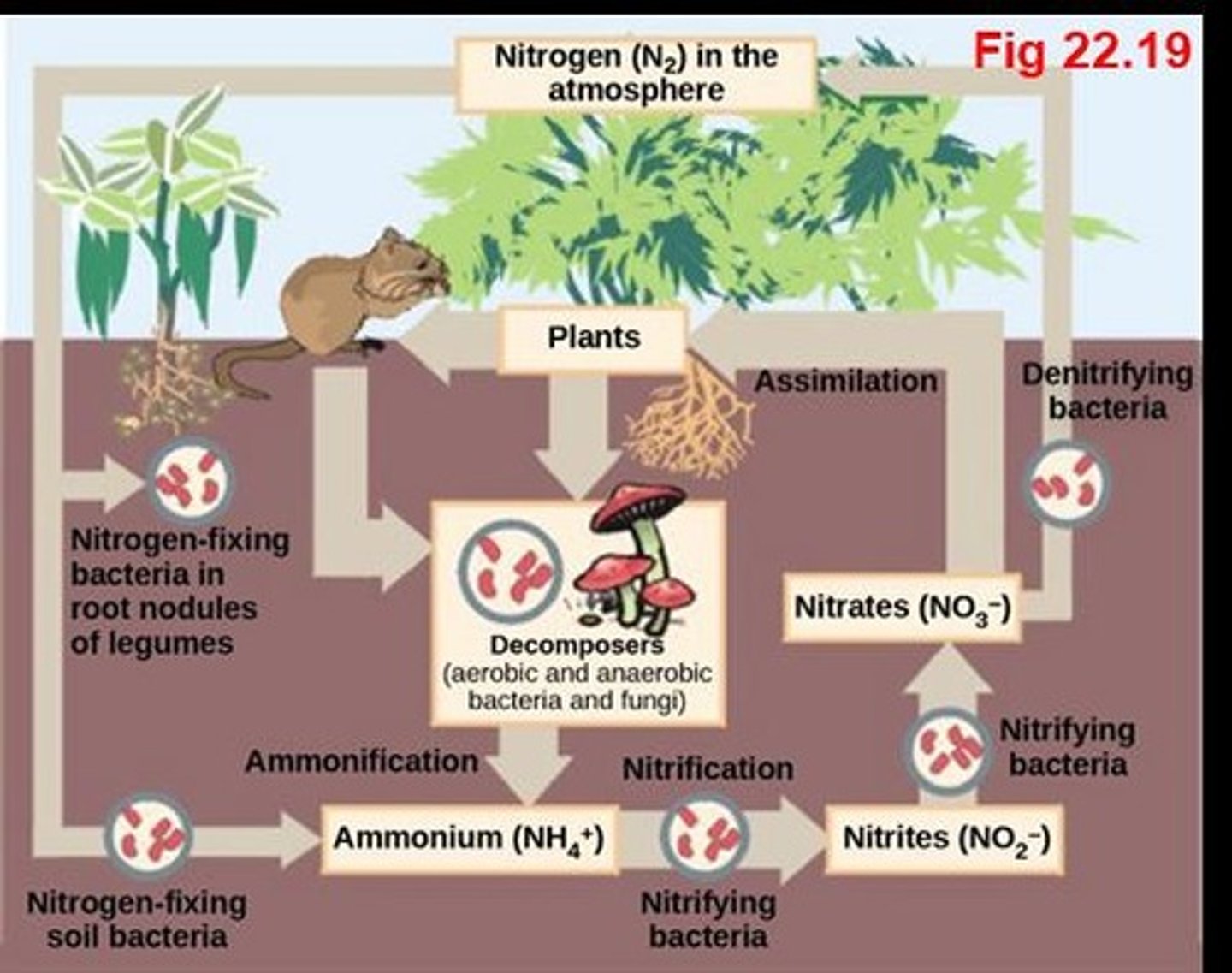
What are nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Bacteria that convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3).
What is the significance of cyanobacteria?
They added oxygen to the atmosphere, enabling life as we know it.
What is bioremediation?
The use of bacteria to remove pollutants from the environment.
What is one example of a product derived from beneficial prokaryotes?
Yogurt.
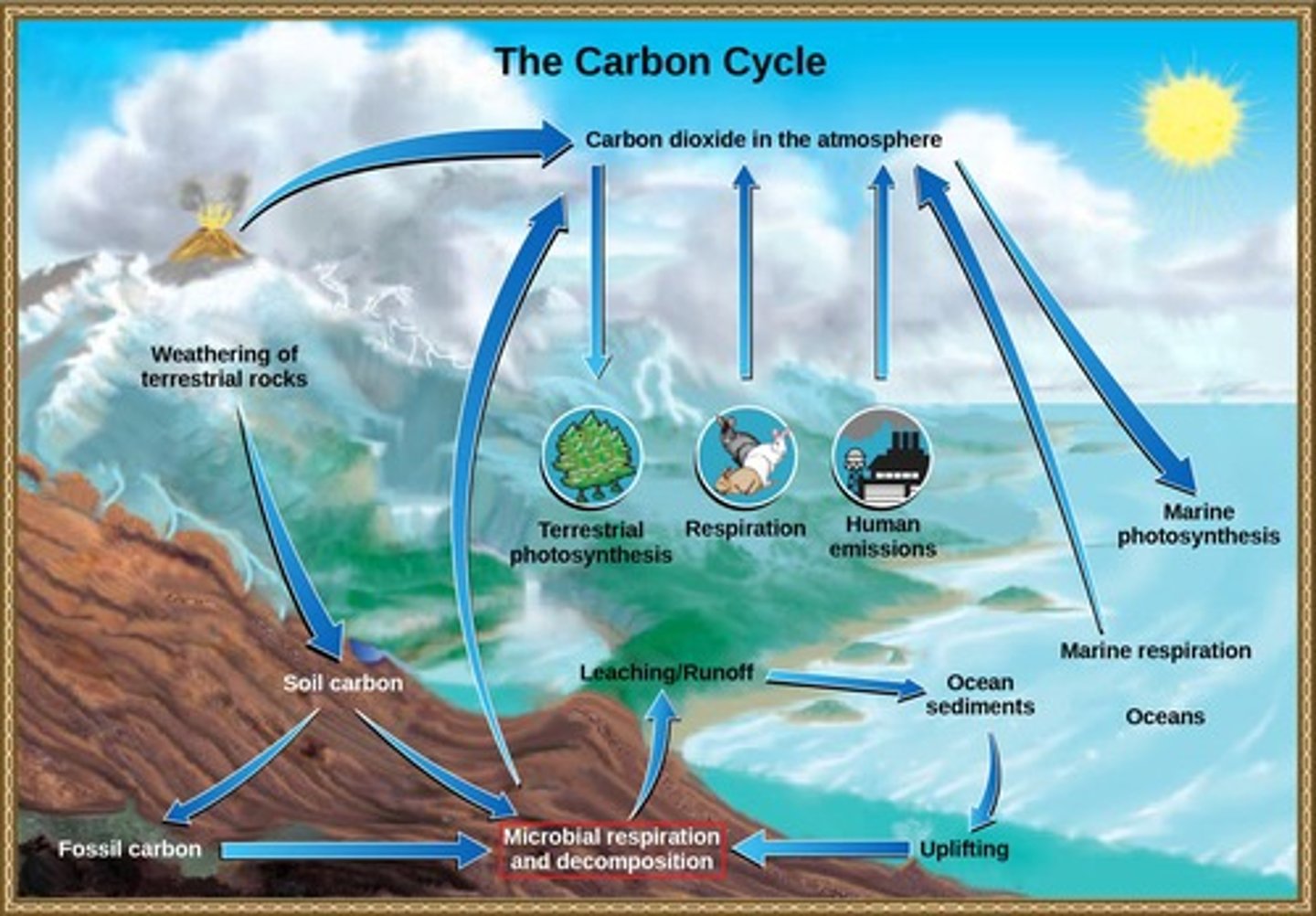
What role do decomposers play in the carbon cycle?
They break down dead organisms, contributing to atmospheric CO2.
What is the role of Rhizobium in the nitrogen cycle?
It is essential for plant growth by fixing nitrogen in the soil.
What are the long-term effects of untreated Lyme disease?
Chronic neurological, ocular, articular, and cardiac issues.
What historical event is associated with the Great Plague of London?
It killed an estimated 200,000 people, about 20% of the city's population.
What is the role of bacteria in genetic engineering?
They act as biofactories producing various chemicals, including insulin.
What is ammonification?
The process of decomposition that releases ammonia from nitrogen-containing organic compounds.
What is nitrification?
The conversion of ammonium to nitrite and then to nitrate by bacteria.
What is denitrification?
The process by which denitrifying bacteria convert nitrate back to gaseous nitrogen forms.
What is one consequence of oil spills that bacteria can help mitigate?
Damage to fauna, which can be reduced by bacteria that degrade oil.
What is the role of bacteria in the carbon cycle?
They convert carbon between inorganic and organic forms, cycling through various environments.
What is the significance of the term 'bioenhancement' in bioremediation?
It refers to adding nutrients to encourage the growth of naturally occurring microbes.