Tissue and Skin Lab
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
levels of structural organization
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems
histology
study of tissues
tissue
a group of similar cells working together for a common function
organ
2 or more tissue types working together for a particular function
4 primary tissue types
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
epithelial tissue function
Forms boundaries between different environments, protects, secretes, absorbs, filters
nervous tissue function
Internal communication
muscle tissue function
Contracts to cause movement
connective tissue function
Supports, protects, binds other tissues together
nervous tissue locations
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves
muscle tissue locations
Muscles attached to bones (skeletal)
Muscle of heart (cardiac)
Muscle in walls of hollow organs (smooth)
epithelial tissue locations
Skin surface (epidermis)
Lining of GI tract organs and other hollow organs
connective tissue locations
Bones
Tendons
Fat and other soft padding tissue
2 types of epithelial tissue
Covering and Lining epithelia (focus on this more)
Glandular epithelia
simple epithelia
one layer - absorption and secretion
stratified epithelia
2 or more layers - protection from abrasion
squamous epithelia
flat cells
cuboidal epithelia
cubed cells (tall as they are wide)
columnar epithelia
tall cells
transitional epithelium (description)
stratified, multiple cell layers
basal layer - cuboidal or columnar
apical layer (dome shaped) - change shape depending on degree of stretch of the organ, when relaxed cells are rounded dome shaped and dead, when stretched cells flatten
transitional epithelium (function)
stretched to accommodate urine volume changes
transitional epithelium (location)
urinary systems, urthera, olnly found in urinary system
simple squamous epithelium (description)
single layer of flattened cells
simple squamous epithelium (function)
diffusion/filtration
allows materials to pass by, located at sites where protection is not important
simple squamous epithelium (location)
alveoli (air sacs) of lungs, blood vessels, lining of heart chambers, serosa
simple squamous epithelium
simple cuboidal epithelium (description)
single layer of cube shaped cells
simple cuboidal epithelium (function)
secretion and absorption
cells releasing substances for body functions, while taking substances from the body's outside into the bloodstream or cells
simple cuboidal epithelium (location)
kidney tubules, some glands
simple cuboidal epithelium
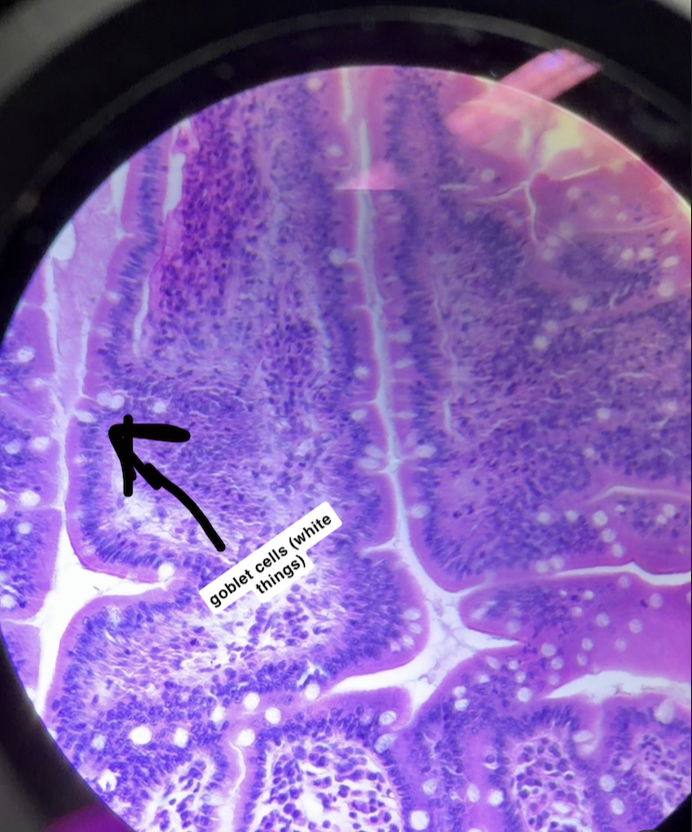
simple columnar epithelium (description)
single layer of tall cells, may have cilia on the apical surface (ciliated), also contains goblet cells
simple columnar epithelium (function)
secretion and absorption
cells releasing substances for body functions, while taking substances from the body's outside into the bloodstream or cells
simple columnar epithelium (location)
jejunum of small intestine, stomach, some glands (non-ciliated), uterine tubes and portion of uterus (ciliated)
simple columnar epithelium
goblet cells
mucous secreting glands, appear as white spheres within the epithelium
cilia
hair-like projections on apical surface of cells, move to propel substances
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (description)
single layer of tall cells that appears stratified since cells vary in height, but not all cells reach the apical surface, also can be ciliated or non-ciliated
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (function)
secretion of substances especially mucous, propulsion of mucus by ciliary action
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (location)
trachea, bronchi, lining respiratory passages (ciliated), male sperm carrying ducts (nonciliated)
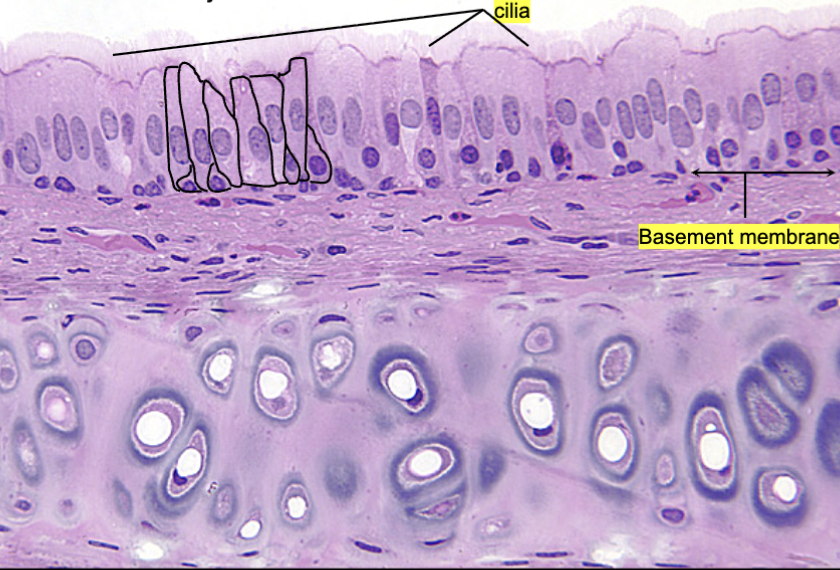
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium (bottom part is hyaline cartilage)
stratified squamous epithelium (description)
multilayers with apical surface cells flattened, basal cells are cuboidal or columnar, can be keratinized (when it is surface cells are dead and full of keratin, basal cells are mitotically active and produce new cells) or non keratinized
stratified squamous epithelium layers
statum corneum (superficial layer, dead flat cells with keratin) stratum basale (deep mitotic layer, single layer of cube like cells) basement membrane
stratified squamous epithelium (function)
protection from friction and abrasion, forming tough barriers on external and internal surfaces
stratified squamous epithelium (location)
epidermis of skin (scalp), esophagus, vaginal lining, oral cavity
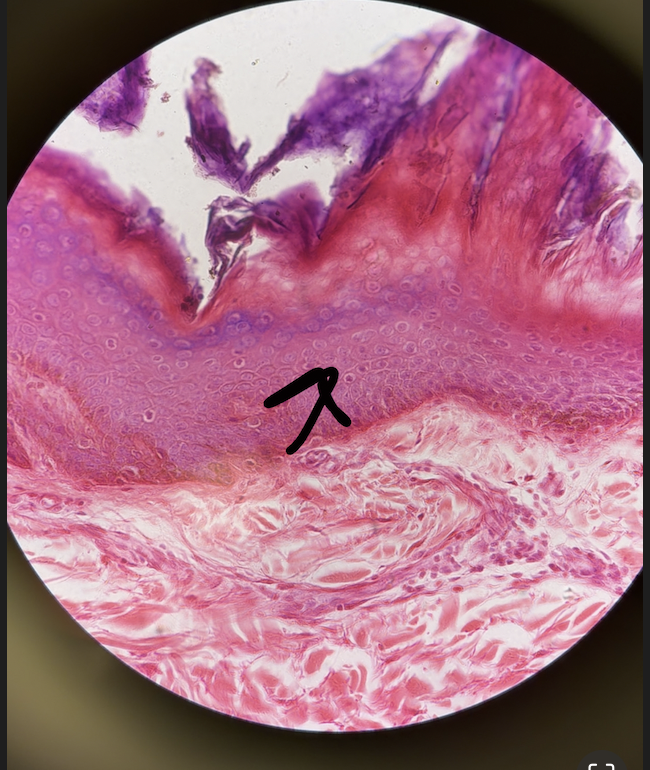
stratified squamous epithelium
keratin (keratinized)
tough, structural protein
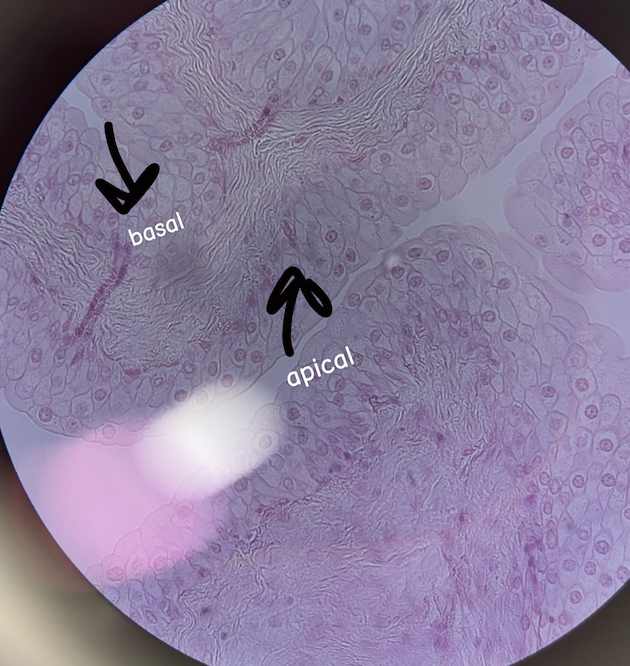
transitional epithelium
connective tissue (3 subclasses)
connective tissue proper, supporting connective tissue, fluid connective tissue
connective tissues (common features)
all derived from the embryonic tissue mesenchyme
all are mostly composed of extracellular matrix (ECM)
extracellular matrix
non-living (protein fibers + ground substance)
It is the composition of this that makes specific tissues so different from each other
areolar connective tissue (description)
Loose connective tissue with a gel-like matrix containing all three fiber types (collagen, elastic, reticular)
fibroblasts
fiber producing cells (main type of cell in areolar connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue)
areolar connective tissue (collagen fibers)
long cable like, strong and flexible, appear thick and pink
areolar connective tissue (elastic fibers)
thin fibers, stretch and recoil, appear as dark thin lines
ground substance
gel like white areas on slide (areolar connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue)
areolar connective tissue (function)
Cushions organs, holds tissue fluids, binds different tissues together while allowing flexibility
areolar connective tissue (location)
Under the skin (subcutaneous layer); surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs
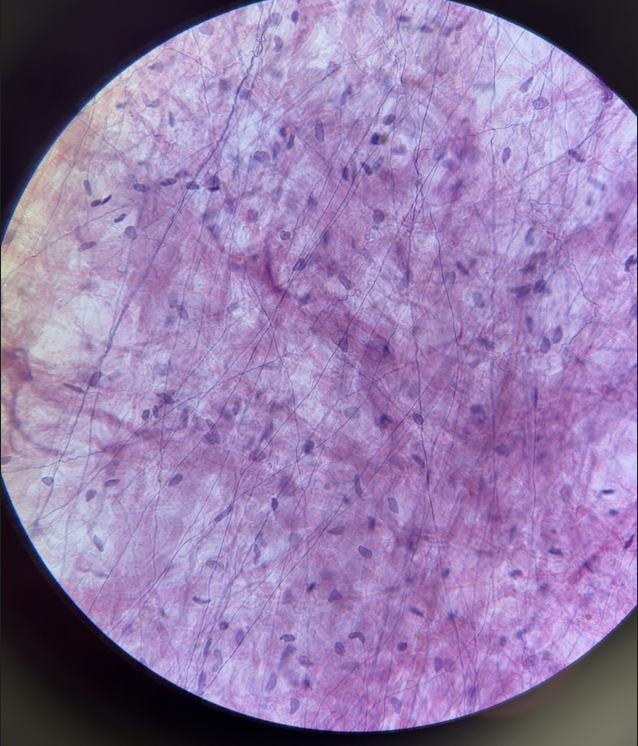
areolar connective tissue (dark spots fibroblasts nuclei, thin dark lines elastic fibers, lighter thick lines collagen fibers, white space ground substance)
adipose tissue (description)
loose connective tissue made mostly of fat-storing cells
adipose tissue (adipocytes)
main type of cell in this tissue, appears as large empty-looking cells due to lipid storage, the middle is the fat storage area
adipose tissue (signet ring nucleus)
the nucleus of adipocytes, pushed to the side of the cell
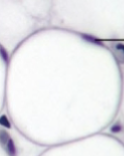
adipose tissue (function)
Stores energy, insulates the body, and cushions/protects organs.
adipose tissue (location)
Beneath the skin (hypodermis), around kidneys, behind the eyeballs, in breasts
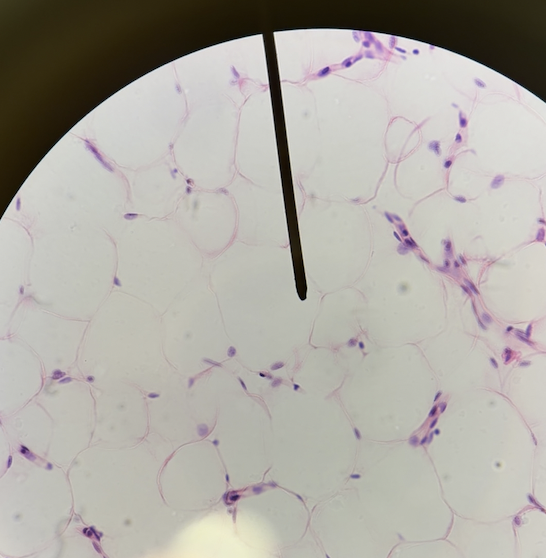
adipose tissue
dense irregular connective tissue (description)
Densely packed collagen fibers running in many directions; few cells (mainly fibroblasts)
dense irregular connective tissue (collagen fibers)
dominant fiber type, irregularly arranged bundles, pink colors
dense irregular connective tissue (function)
Provides strength and resists tension from multiple directions
dense irregular connective tissue (location)
Dermis of skin, fibrous capsules of joints and organs (e.g., kidney capsule)
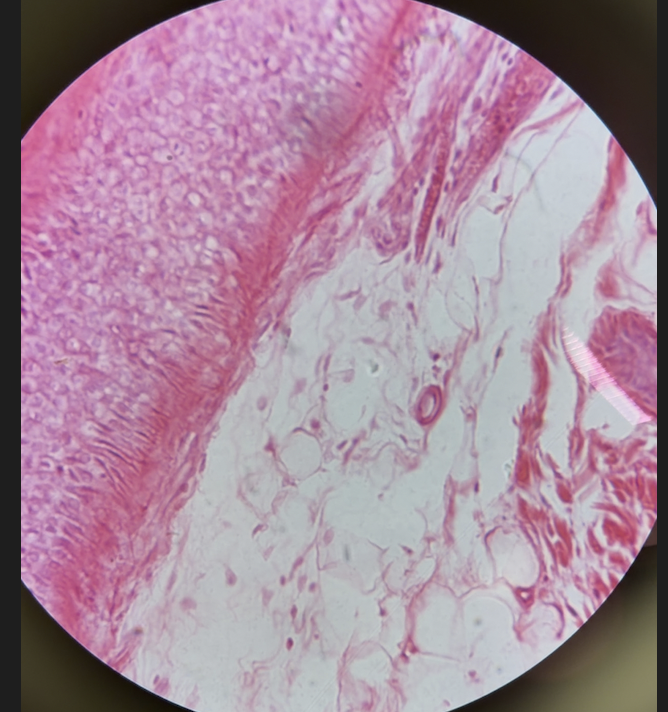
dense irregular connective tissue
hyaline cartilage (description)
Firm yet flexible connective tissue
hyaline cartilage (chondrocytes)
cartilage cells, major cell type of this tissue
hyaline cartilage (lacuna)
open spaces in tissue containing chondrocytes
hyaline cartilage (ECM)
frosted glass appearance, fibers not visible
hyaline cartilage (function)
Provides support and reduces friction between bony surfaces; resists compressive forces.
hyaline cartilage (location)
Nose, trachea, larynx, ends of long bones, costal cartilage (connecting ribs to sternum).
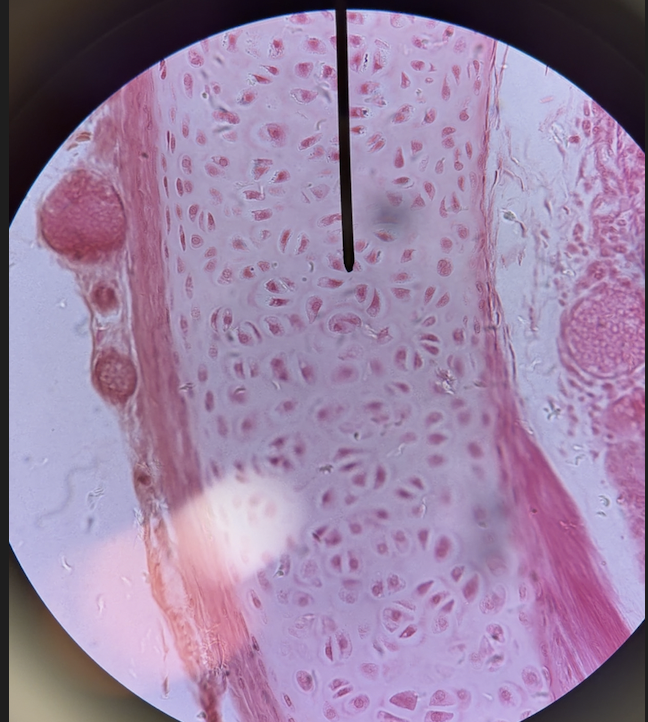
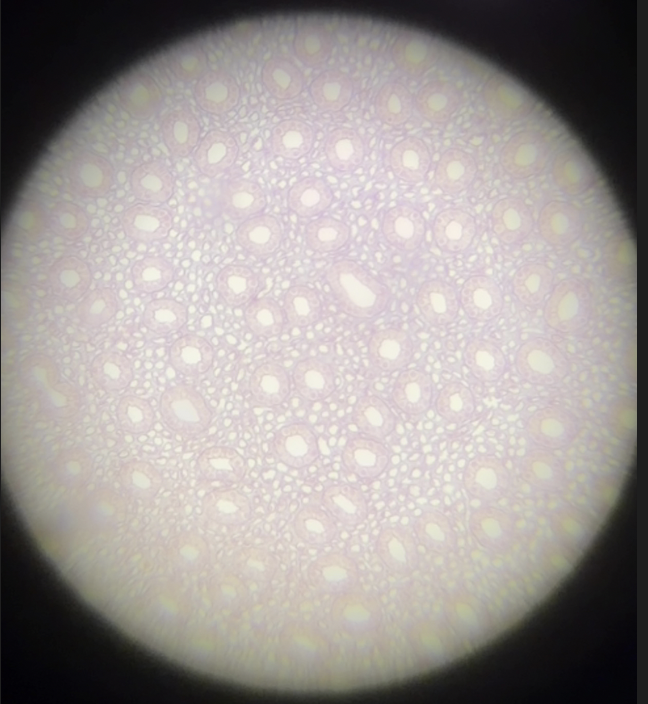
hyaline cartilage, dark spots are chondrocytes, lacuna is the open space where the cell sits, and matrix is around it
bone (compact bone) (description)
Hard, calcified matrix with osteocytes in lacunae; highly vascular (packed with an extensive network of blood vessels that keep the tissue alive)
bone (compact bone) (osteocytes)
bone cells, major type of cell in this tissue
bone (lacuna) (description)
open spaces in matrix that houses the osteocytes
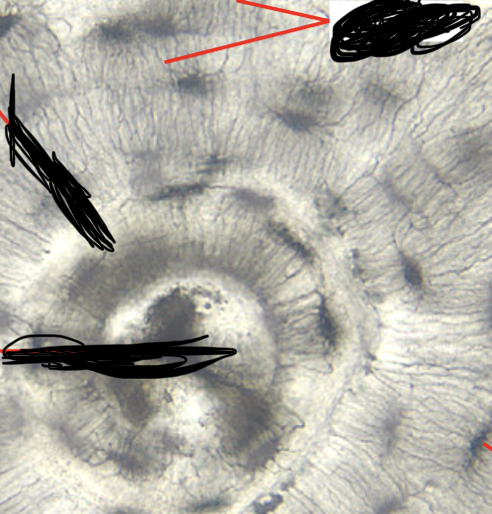
bone (compact bone) (osteon/haversian system)
circular structural units of compact bone, comprised of multiple concentric layers of calcified matrix (lamellae) surrounding a central canal

bone (compact bone) (central/haversian canal)
opening in the center of each osteon, space for the passage of blood vessels and nerves
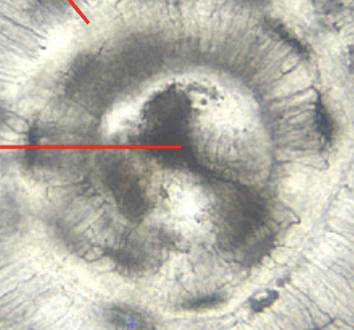
bone (compact bone) (lamellae)
rings/layers of calcified matrix around the central canal
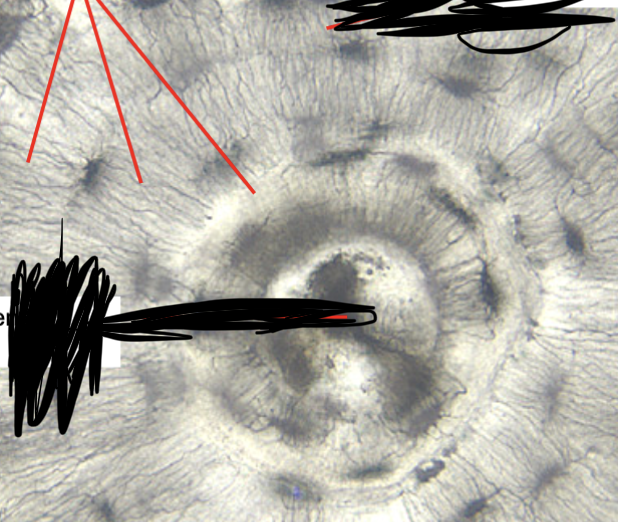
bone (compact bone) (canaliculi)
small canals through matrix, appear as cracks, connect lacuna and osteocytes together
bone (compact bone) (function)
Supports body, protects organs, stores minerals, produces blood cells
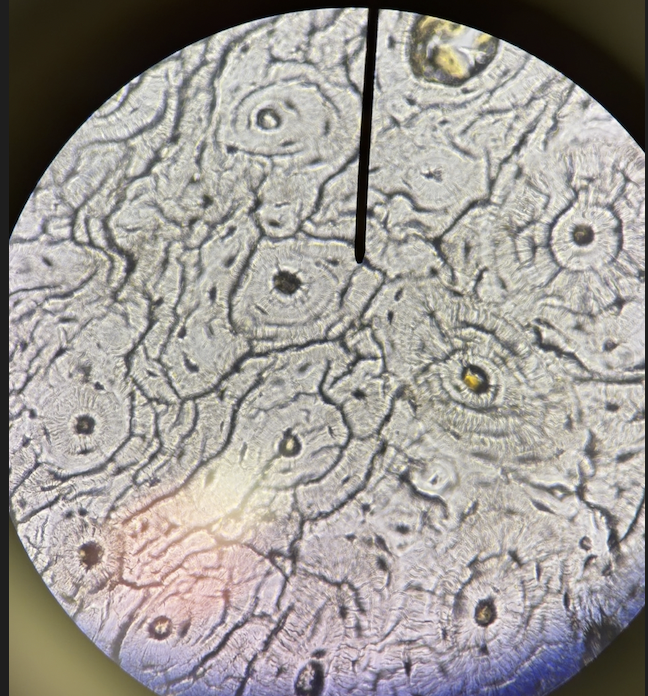
bone (compact bone)
blood (description)
Fluid connective tissue with plasma matrix; contains Erythrocytes (red blood cells), Leukocytes (white blood cells), and Thrombocytes (platelets)
blood (plasma)
fluid ECM, white areas of slide
blood (erythrocytes)
red blood cells, look like little pink dots without nuclei
blood (leukocytes)
white blood cells, look like larger cells with dark staining nuclei
blood (thrombocytes)
platelets, looks like really tiny specks/dots
blood (function)
Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, wastes; immune defense, clotting.
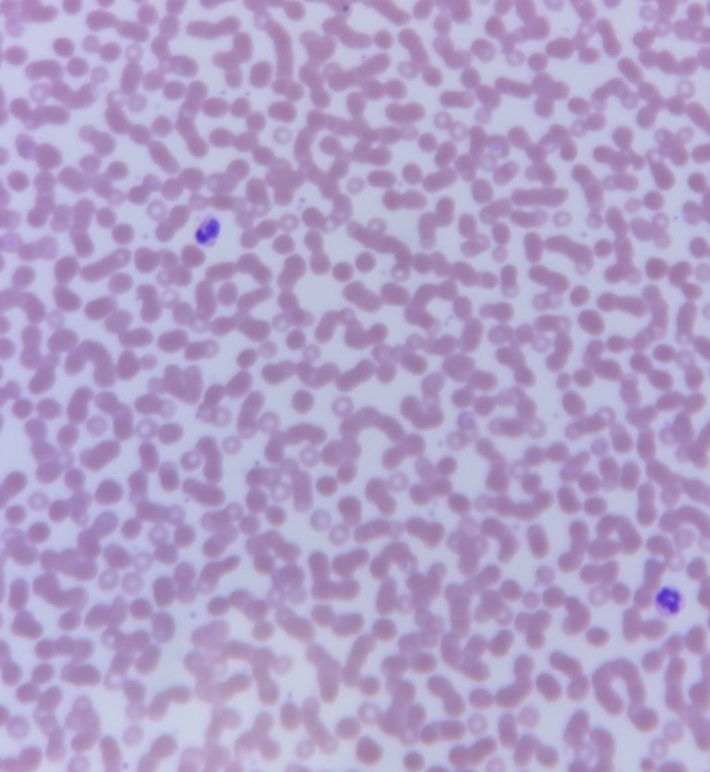
blood, erythrocytes=pink, leukocytes=purple, thrombocytes=tiny
loose connective tissue proper types
areolar connective tissue, adipose tissue
dense connective tissue proper types
dense irregular connective tissue
supporting connective tissue
hyaline cartilage, bone (compact) tissue
fluid connective tissue
blood
muscle tissue types
skelatal, cardiac, smooth
skeletal muscle (description)
Long, cylindrical, multinucleated cells with striations; under voluntary control.
skeletal muscle (function)
Voluntary movement, posture, heat generation
skeletal muscle (location)
Muscles attached to bones