Marketing Instruments product
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Marketing Mix (1) Definition
The set of tactical marketing tools - product, price, place, promotion - that the firm blends to produce the response it wants to achieve in the target market
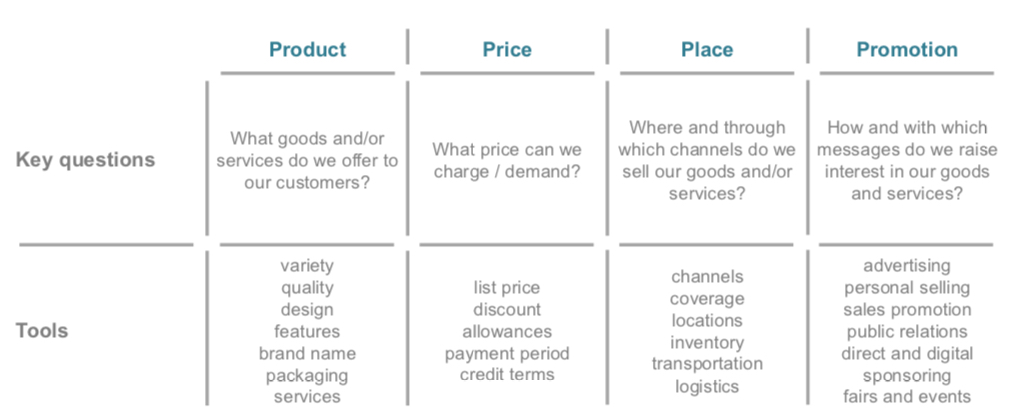
Key questions and tools for the 4Ps
Hierarchy of goals and objectives
Company goals
Marketing goals
Marketing mix goals
Tool objectives
Marketing mix Ziele der 4Ps mit Beispiel
4Ps goals
Production goals: Exclusiveness
Price goals: Price increase
Place goals: Concentration of sales channels
Promotion goals: Awareness
4Ps seller‘s vs. buyers view
Product -acceptability
Price - affordability
Place - accessibility
Promotion - awareness
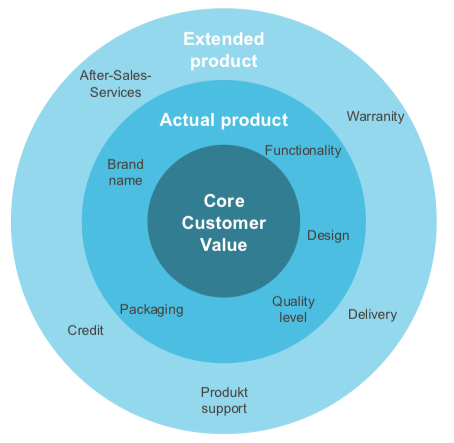
Product Definition
A product is anything that can be offered to a market for atterition, acquisition, use of consumption and is suitable to serve needs and desires. It includes physical objects, services, personalities, places, organizations or ideas.
Product dimensions Schaubild
Unterteilung product types
Products oder services.
Either consumer goods/ consumptive services, or industry goods / buisness services
Hybrid Goods
Goods on the range between tangible and intangible (engraved jewelry)
ENDE VL 1
Buyers market
The buyer decides what to buy from which customer. Options.
3 parts of an attractive market offer
Product, service, brand
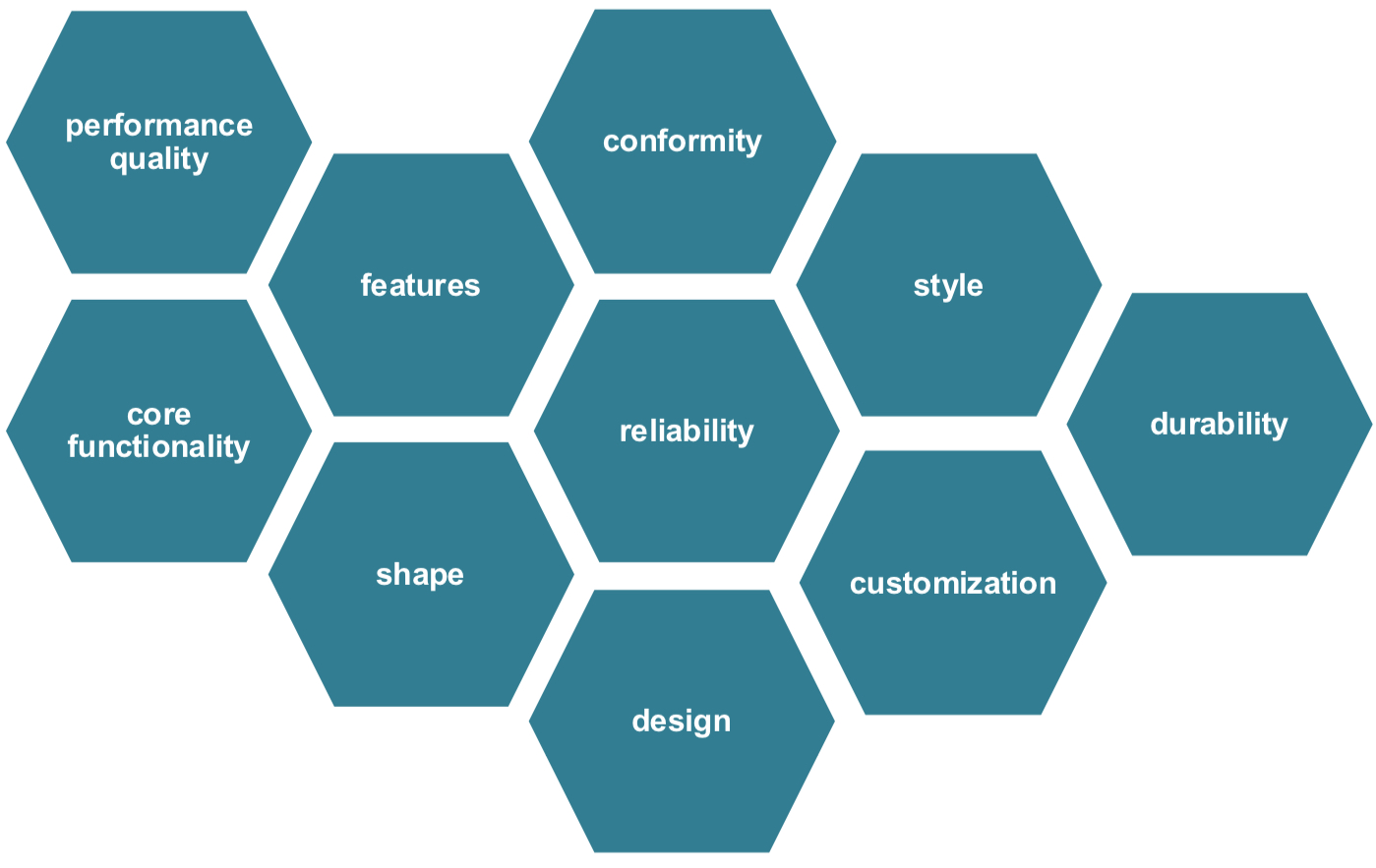
Product differentiation Schaubild (2-3 Wissen)
Services Definition
Services are intangible benefits from a supplier to the customer, without any transfer of ownership of an item. The creation may be associated with tangible goods.
The four service characteristics
Intangibility: Can’t be seen, felt usw.
Variability: Quality depends on who, when, where and how.
Inseparability: Services cannot be separated from providers.
Perishabilty: Services cannot be stored and sold later.
Service Profit chain
The chain that links service firm profits with employee and customer satisfaction
Five links of service profit chain
Internal service quality (Good employees, train them etc)
Satisfied and productive service employees
Great service value
Satisfied and loyal customer
Healthy service profits and growth
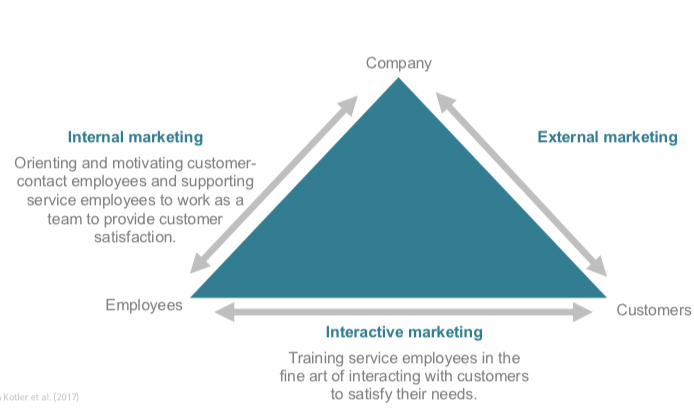
3 types of services marketing Schaubild
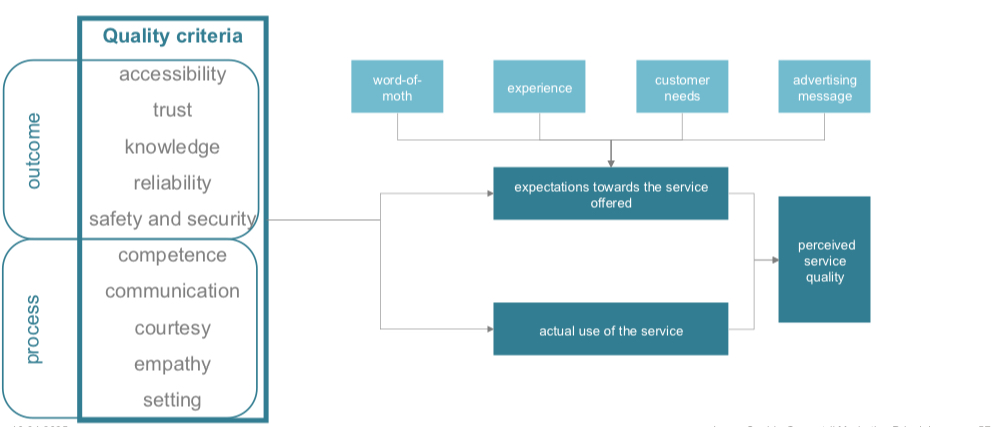
Management of service quality
Quality of a service is based on the difference between expectations and the actual service.
Service recovery is so important, it generates more customers than without recovery
Common attributes of successful service providers
Customer orientation
Monitoring
Customer feedback
Complaint management
Perceived service quality Schaubild
Services in differentiation. Risks and options
Risks: More difficult to compare service than product
Threat of price competition
Innovations in the service sector can be copied
Options: Employees, Processes, physical facilities
Fundamentals in brand management
Brand positioning
Brand name selection
Brand sponsorship
Brand development
Three level of Brand positioning
Product attributes
Benefits
Beliefs and values
Brand name selection
Should:… suggest sth. about the products
Easy to pronounce and recognize
Easy to translate
Brand sponsorship
Manufacturers brand (BMW)
Store brand (Ja!)
Licensing: Brand use for fee (Joop!, Löwenbräu in USA)
Co-Branding (GucciXAdidas)
Brand development strategies Schaubild

ENDE VL 2
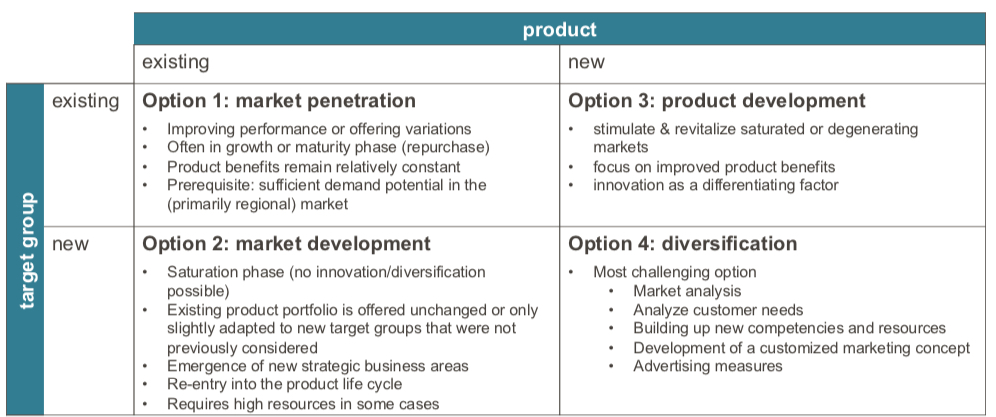
Ansoff Matrix Schaubild
Product portfolio Beispiel Schaubild
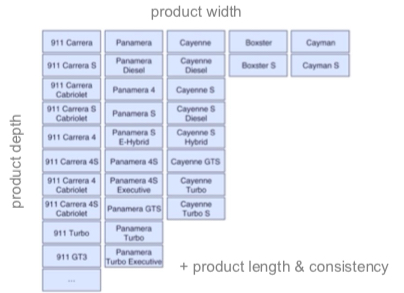
Portfolio Design options
Strategic portfolio design Optimization of product lines
Operational portfolio design: Optimization within the product line
Portfolio management decisions
New product (increasing product depth and width)
Modification of existing products
Elimination of existing products
Consistency of the product mix…
Refers to how closely related product lines are in production, use, distribution channels etc.
Product Similarities
Shared production. Shared materials
Shared reason. Coffe, beans, etc
Shared sales. ATU car things
Product line definition
A group of products that are closely related because they function in a similiar manner. (Consistency)
Analysis tool: product landscape
Analysis of product line: competitive landscape. Schaubild (Verstehen)
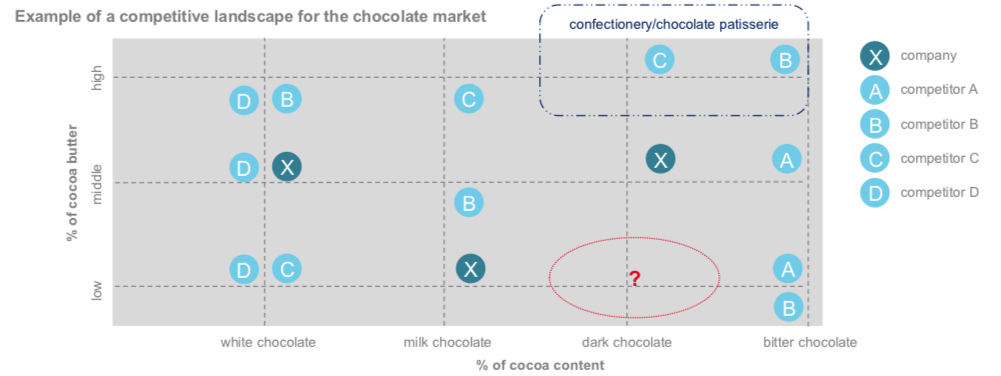
Extent of the product line Schaubild
Company goals impact product length
Possible objectives like: upwelling, crossselling, risk diversification
Options for extending a product line: expanding the line, filling up the product line
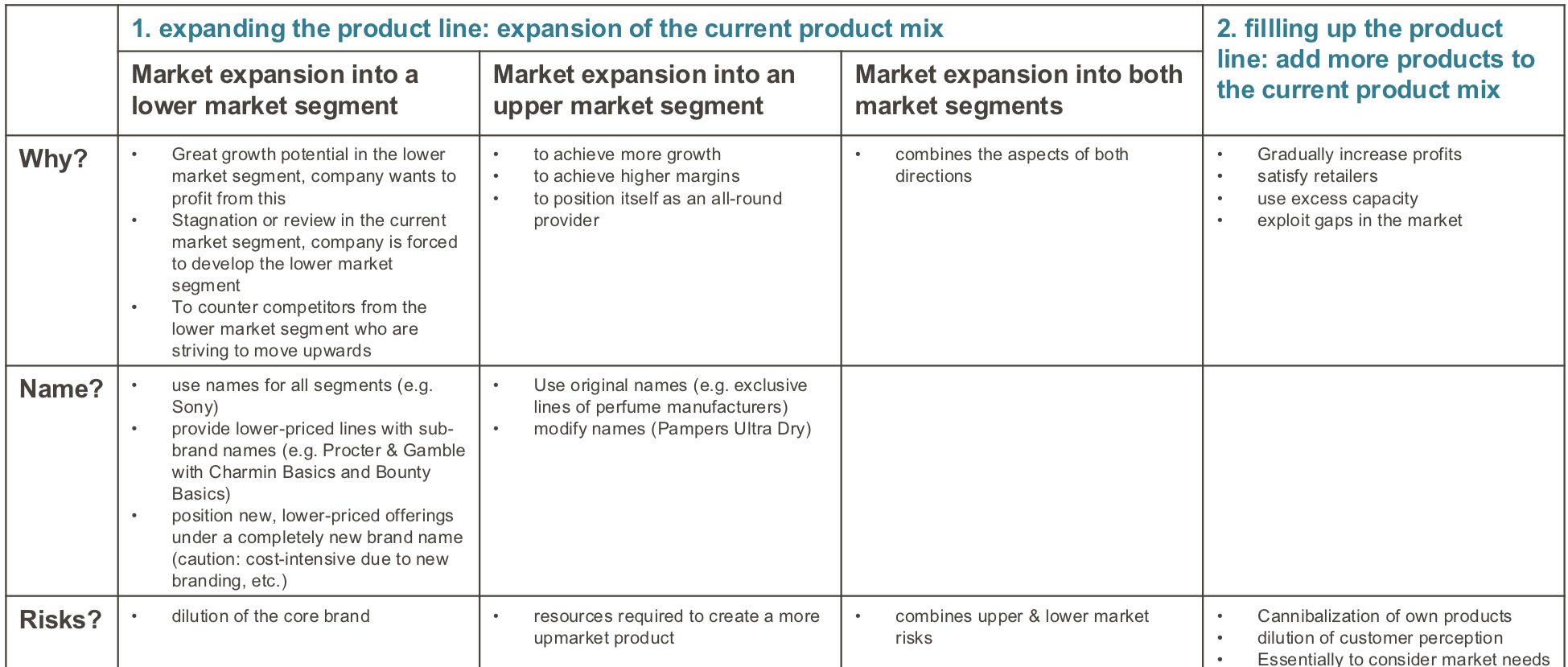
Reasons why products fail
Market size overestimated
Wrong market research
Poor design
Overpriced
Departements that may create a new product
Departments for existing product
Departments for new market offerings
Innovation centers
Venture teams
Stage gate approach
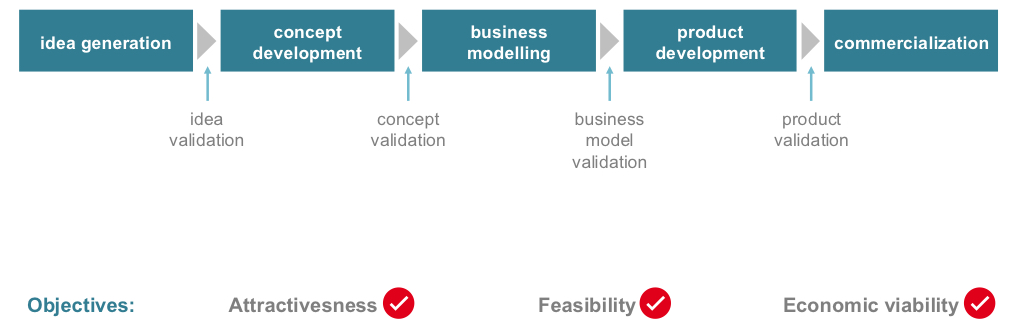
Idea generation
Direction: top-down / bottom-up
Sources: internal / external
Uncover unfulfilled customer wishes (Explorative market research)
Going into details (can we/our partner even fulfill the wishes)
Validations
Explorative market research (part of idea generation)
employee survey
Customer observation
Customer survey
Expert survey competitor analysis
Concept development
Product concept leads to prototype
Then, Alpha and Beta testing
Then, concept validation (technological feasibility and attractiveness for customer)
Business modelling
Identification of target market
Formulating the value proposition
Description of the most important features of the market offer
Is there value for, target customer, partners, company ?
Business model validation
Analysis of ability to generate market value through:
Attractiveness: desirable for customer?
Feasibilty: Able to offer all functions desired by customer?
Economic viability: Can it generate value?
Forecasting: forecasting the fundamental demand
Forecasting the demand
What consumers say
What consumers do
What consumers have done
Product development, 2 phases
Developing core resources. Having everything you need, can be generated in-house or with partners
Design a concrete market offer. Transforming the prototype into a real product. Real product or test product.
Two decisions for commercialization
When? Dependent on economic, competitive situation
Where? Locations and scale of roll-outs