Bioenergetics topic 4 biology
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Photosynthesis uses energy to? This takes place in? Energy is transferred to? What kind of process is it?
photosynthesis uses energy to change carbon dioxide & water into glucose & oxygen
takes place in chloroplasts in green plant cells (contain pigment like chlorophyll that absorb light)
Energy transferred to chloroplasts from environment by light
Endothermic → energy transferred from environment in process
Word & symbol equation for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide + water → (light) glucose + oxygen
6CO2+6H2O → (light) C6H12O6+6O2
what do plants use glucose for in 5 main ways
respiration → transfers energy from glucose, enables plants convert the rest into various other useful substances
Making cellulose → converted into cellulose for making strong cell walls (plant)
making amino acids → combined with nitrate ions (absorbed from soil) to make amino acids, then turn to proteins
Stored as oils or fats → turned into lipids for storing in seeds
Stored as starch → turned into starch & stored in roots, stems & leaves ready for when photosynthesis isn’t happening (winter). Starch is insoluble makes better for storing than glucose (cell with lots glucose would draw lots water & swell up)
3 limiting factors for photosynthesis? What are 3 environmental conditions that limit photosynthesis? How can chlorophyll be a limiting factor?
limiting factors (stopping photosynthesis from happening faster) → light intensity, CO2 concentration, temperature
Combined effect on rate of photosynthesis, which limits at particular time depends environmental conditions:
Night → light
Winter → temperature
Warm & bright enough → CO2 concentration
Chlorophyll can be limiting factor → amount affected by disease/ environmental stress (lack nutrients), become damaged/not make enough chlorophyll, rate reduced → cant absorb as much light
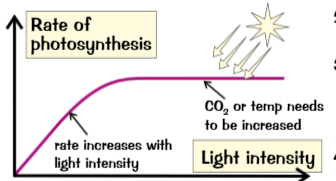
Light provides? Lights level increased? After a while? In a lab? need to measure?
light provides energy (photosynthesis),
Light level raised = rate increases steadily (only to certain point)
light intensity increases = rate no longer increases → either temperature/ CO2 level now limiting factor
in lab can change light intensity (moving lamp)
need measure plant using light meter/ maths to get result

Whats CO2 needed for? What causes the graph to flatten? What would the limiting factor then be?
CO2 = raw materials needed photosynthesis
amount CO2 only increases rate up to point the graph flattens. CO2 increases rate, if no longer increase = CO2 no longer limiting factor
Light & CO2 plentiful supply, factor limiting = temperature
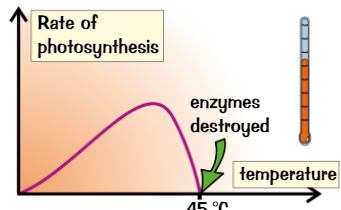
Usually if temp is a limiting factor because? If the plant is too hot?
Usually if temperature is limiting factor becuase too low → enzymes needed photosynthesis work more slowly at low temp
Plant too hot = enzymes needed & other reactions are damaged → happens about 45C
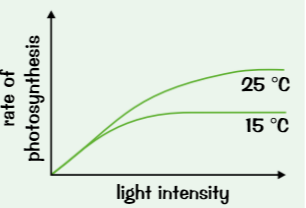
At the start? Lines even off when?
at start both lines show light intensity increase = rate increases steadily
But lines even off when light no longer limiting factor, line at 25C levels of at higher point than 15C, temperature must have been limiting factor at 15C
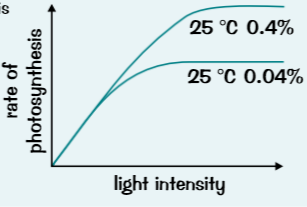
Both lines level off when? compare the 2 lines.
both lines level off when light is no longer limiting factor
line at higher CO2 concentration of 0.4% levels off at higher point than 0.04%, means CO2 concentration limiting factor at 0.04% CO2, aint temperature because same for both lines (25C)
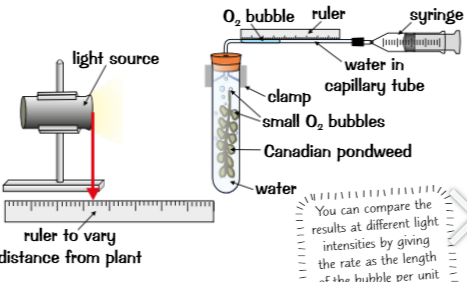
Oxygen production shows rate of photosynthesis practical (Pondweed practical)
Canadian pondweed → measure effect light intensity on rate of photosynthesis, produces oxygen (faster rate oxygen production = faster rate)
Source white light placed at specific distance from pondweed
left to photosynthesise for set amount time, as photosynthesises oxygen released collect in capillary tube
End of experiment, syringe used draw gas bubble in tube alongside ruler & length of gas bubbles measured, proportional to volume of O2 produced
Any variables that affect results should be controlled (temperature & time)
Experiment repeated 2 with light source at same distance & mean volume of O2 produced is calculated
then whole experiment repeated with light source at different distances from pondweed
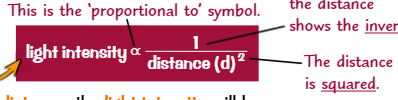
(Pondweed practical) When the lamp is moved away? If the distance decreases? Light intensity decreases in proportion to? Inverse square law?
lamp moved away pondweed = amount of light reaches pondweed decreases
distance decreases = light intensity increases (inversely proportional)
light intensity decreases in proportion to square of distance → inverse square law written → light intensity ∝ 1/ distance (d)2
inverse square law → halve distance, light intensity is 4x greater
ideal artificial environment for plants? Why? Light is always needed for photosynthesis? How do you increase CO2 levels? Keeping plants enclosed means? It costs mean for?
ideal artificial environment for plants to grow in greenhouse
help trap suns heat & make sure temperature doesn’t become limiting. winter = too cold (use heater keep temperature at ideal level), summer = too hot (use shades & ventilation)
Light always needed photosynthesis, often supply artificial light after sun sets (+ quality photosynthesis time)
increase CO2 level (paraffin heater heat greenhouse, as burns = makes CO2 by-product)
Keeping plants enclosed = free from pests & diseases, add fertilisers to soil (provide minerals healthy growth)
Costs money → keep conditions just right photosynthesis = plants grow faster & decent crop harvested + often = sold), important not more light, CO2, nutrients than plants need (waste money)
Whats respiration? Where does it happen? What kind of reaction is it?
Respiration → process of transferring energy from (breakdown of) glucose (sugar) & goes in every cell in body continuously
Happens in plants too all living organisms respire → how they transfer energy from food to cells
Exothermic → transfers energy to environment
3 examples of why respiration transfers energy
build up large molecules from smaller ones (proteins from amino acids)
in animals → used to allow muscles to contract (move about)
in mammals & birds → used to keep body temperatures steady in cooler surroundings
What happens in cells? Many reactions are linked together to? What is the sum of all those reactions called?
in cells → lots chemical reactions happening all time, controlled by enzymes
many reactions linked together to form bigger reactions:
reactant — (enzyme) → product — (enzyme) → product — (enzyme) —> product
Sum of all those reactions that happen in cell or body is called metabolism
3 substances that lots of small glucose molecules are joined together to make? What are lipid molecules each made from? What is a protein made from?
lots small glucose molecules are joined together in reactions to form starch (storage molecule in plant cells), glycogen (storage molecule in animal cells) & cellulose (component of plant cell walls)
Lipid molecules each made from one molecule of glycerol & 3 fatty acids
glucose combined with nitrate ions to make amino acids, then made into protein
Glucose is broken down in respiration which produces? Excess protein is broken down to produce?
Glucose broken down in respiration → transfers energy to power all reactions in body that make molecules
excess protein is broken down in reaction to produce urea → then excreted in urine
What’s the most efficient way to transfer energy from glucose? Goes on all? Most of reactions happen in? Word & symbol equation
Most efficient way to transfer energy from glucose is aerobic respiration
goes on all the time in plants & animals
Most of reactions in aerobic respiration happen inside mitochondria
Word & symbol equation:
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O
Whats anaerobic respiration? word equation? doesn’t transfer nearly as much? Only used in?
Anaerobic → without oxygen = incomplete breakdown of glucose making lactic acid
Word equation:
Glucose → lactic acid
doesn’t transfer nearly as much energy as aerobic, because glucose isn’t fully oxidised (don’t combine with oxygen)
only used in emergencies
Plant & yeast cells respire without oxygen? word equation? Whats anaerobic respiration called in yeast cells? In the food & drinks industry used to make? In bread-making what makes it rise? Whats beer & wine-making?
plant & yeast cells respire without oxygen but produce ethanol (alcohol) & carbon dioxide
Word equation:
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
anaerobic respiration in yeast cells → fermentation
food & drinks industry, fermentation by yeast = great value used make bread & alcoholic drinks (beer & wine)
bread-making → carbon dioxide from fermentation that makes bread rise
beer & wine-making → fermentation process produces alcohol
Muscles need energy from respiration? Increased respiration in cells means? What increases? Really vigorous exercise means? Not best way to transfer energy because? Long periods of exercise cause?
muscles need energy from respiration (contract). exercise → muscles contract more frequently than normal = need more energy →> from increased respiration
increase respiration in cells means need more oxygen
breathing rate & breath volume increases (+oxygen into blood) & heart rate increases to get oxygen faster round body. Remove CO2 quicker at same time
Really vigorous exercise (sprinting) body cant supply oxygen to muscles quick enough → start respiring anaerobically
Not best way to transfer energy from glucose, lactic acid builds up in muscles (painful)
Long periods of exercise → muscle fatigue → muscles get tired & stop contracting efficiently
When you stop exercising? Why do we repay oxygen? What does this mean? Why do pulse & breathing rate stay high? Whats another way of coping with high levels of lactic acid?
when stop exercising → oxygen debt → amount of extra oxygen body needs to react with build up of lactic acid & remove from cells (oxygen +lactic acid → CO2 + water)
have to repay oxygen didn’t get to muscles in time because lungs, heart & blood couldn’t keep up with demand
means have to keep breathing hard for awhile after stop to get more oxygen into blood → transported to muscle cells
pulse & breathing rate stay high = high levels of Lactic acid & CO2
Another way of coping with high levels lactic acid → blood that enters muscles transports lactic to liver, lactic acid converted back to glucose
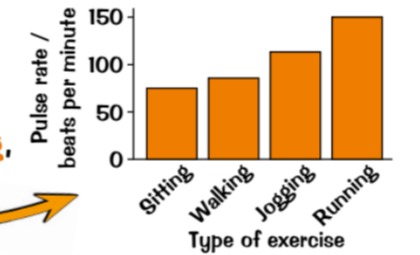
How do you measure the breathing rate? If the pulse rate increases? How to reduce effect of random errors?
measure breathing rate by counting breaths & heart rate by taking pulse & plot bar chart
pulse rate increases =more intense exercise is, body need more oxygen to muscles & take more CO2 away
Reduce effect of random errors on results, do as group & plot average pulse rate for each exercise