Lesson 2.6: Changes in Supply and Supply Curve Shifts
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on supply curve shifts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
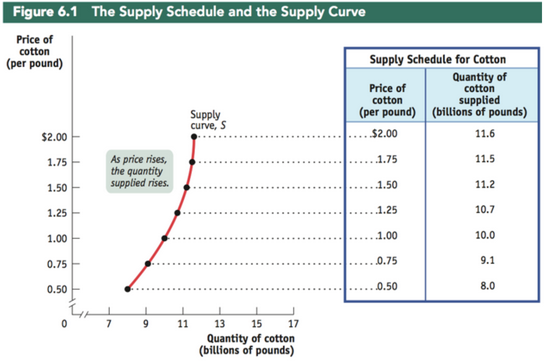
Supply curve
The graphical representation of the supply schedule, showing how much of a good or service producers are willing to supply at different prices
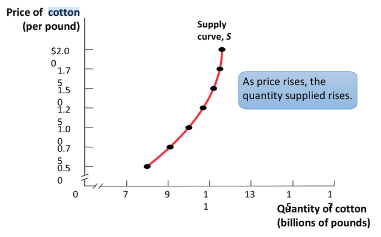
Law of supply
Law that states that all other things being equal, the price and quantity supplied of a good are positively related
Profit maximization
The goal for suppliers, done through matching marginal revenue to marginal cost
Lower marginal costs stop short of maximizing resource allocation and total revenue
Higher marginal costs lose money when sold on the market
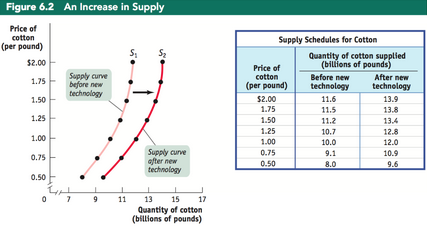
Supply curve shift
A change in the quantity supplied at any given price, represented by the movement of the original supply curve to a new position as a result of a change in overall supply
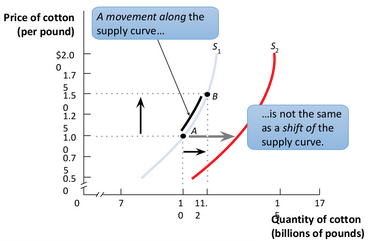
Supply curve movement
A change in the quantity supplied of a good that is a result of a change in price, not overall supply
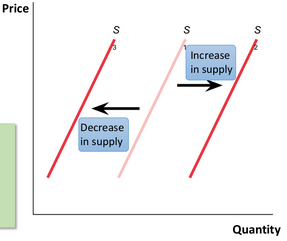
Decrease in supply
A decrease in total levels of supply across the market at all prices, leading to a leftward shift of the supply curve
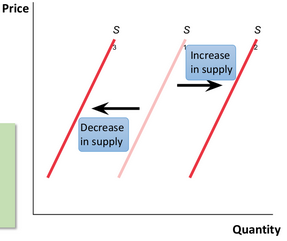
Increase in supply
An increase in total level of supply across the market at all prices, leading to a rightward shift of the supply curve
Supply curve shift factors
Represented by the mnemonic I-RENT:
Input prices
Related goods or services prices
Expectations of producers
Number of producers
Technology changes
Input price changes
Factor in the shift of a supply curve based on a good or service used to produce the end product
An increase in the price for sugar and cream will lead to lower ice cream supply
A decrease in the price of oil will lead to higher airline fuel and ticket supply
Related goods or services price changes
Factor in the shift of a supply curve based on substitute or complement price shifts
Substitute: Less supply in one leads to higher demand (and thus higher prices and supply) in the other
Complement: An increase in the price of one leads to more supply in the other
Substitutes in production
Products as part of a product’s related goods and services that can shift the supply curve as an increase in the price of one product causes suppliers to supply less of the other (and vice versa)
Higher heating oil prices and lower gasoline prices will lead producers to supply less gasoline, shifting gasoline’s supply curve to the left
Lower heating oil prices and higher gasoline prices will lead producers to supply more gasoline, shifting gasoline’s supply curve to the right
Complements in production
Product as part of a product’s related goods and services that can shift the supply curve as an increase in the price of one causes suppliers to supply more of the other (and vice versa)
Natural gas is a byproduct of crude oil drilling
Higher natural gas prices will cause suppliers to supply more crude oil and natural gas
Lower natural gas prices will cause suppliers to supply less crude oil and natural gas
Expectations of producers
Factor in the shift of a supply curve based on a supplier’s beliefs of price movement in the future as anticipated higher prices in the future may cause a decrease of supply today (and vice versa)
Gasoline prices can peak in the summer, leading producers to supply less gasoline in the spring
Heating oil prices may go down in the spring, leading producers to supply more heating oil in the winter to sell more at higher prices
Number of producers
Factor in the shift of a supply curve based on how many suppliers are in a market
More widget producers entering the market shifts the supply curve for widgets to the right
Many widget producers going out of business shifts the supply curve for widgets to the left
Technology changes
Factor in the shift of a supply curve based on production efficiency with new advancements
A new innovation in gadget production speed can shift the supply curve for gadgets to the right
The restriction of a pesticide in cotton farming can reduce cotton output, shifting the supply curve for cotton to the left
Governmental policies
Additional factor in the shift of a supply curve based on governmental power to raise or lower the costs of production, thus encouraging or discouraging production abroad
Subsidy
A governmental payment that supports a business or market, thus lowering costs of production and increasing supply
Excise tax
A governmental tax on the production or sale of a good, thus increasing costs and lowering supply
Regulation
A governmental intervention in a market that affects the price, quantity, or quality of a good
Foreign changes
Another determinant of supply curve shifts based on changes in the global economy
A strike in workers for carpet production in India can reduce the supply of carpets to the United States, shifting the supply curve to the left
A discovery of oil abroad in Russia can increase the supply of oil to the United States, shifting the supply curve to the right