Coasts
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are two types of weathering?
Chemical Weathering - Carbonic acid in rainwater reacts with rocks and eats away at the surface (Decomposition).
Mechanical Weathering - Temperature variations cause water to freeze in cracks expanding it. Thawing allows the water to then travel deeper before the cycle is repeated. This repetition is called Freeze-Thaw (Disintegration).
What are 3 types of mass movement?
Sliding - Rain infiltrates the soil and percolates down into a cliff. This make the rock heavier and if support is removed from the base a landslide occurs.
Slumping - The ground becomes saturated and cliff material slowly sags away.
Rock Fall - Bare rock is prone to freeze-thaw and the rock loses contact with the cliff.
What are the 3 types of coastal erosion?
Hydraulic action - Force of waves breaking against the coast, putting pressure on the rock.
Abrasion - Waves carrying and hurling rock fragments against the coast.
Attrition - Rocks and pebbles carried by waves collide and wear each other down.
What are the 4 types of transport?
Solution - Soluble materials dissolved in the water.
Traction - large rocks rolled along the seabed.
Saltation - smaller stones bounced along the seabed.
Suspension - Small particles carried along in the water.
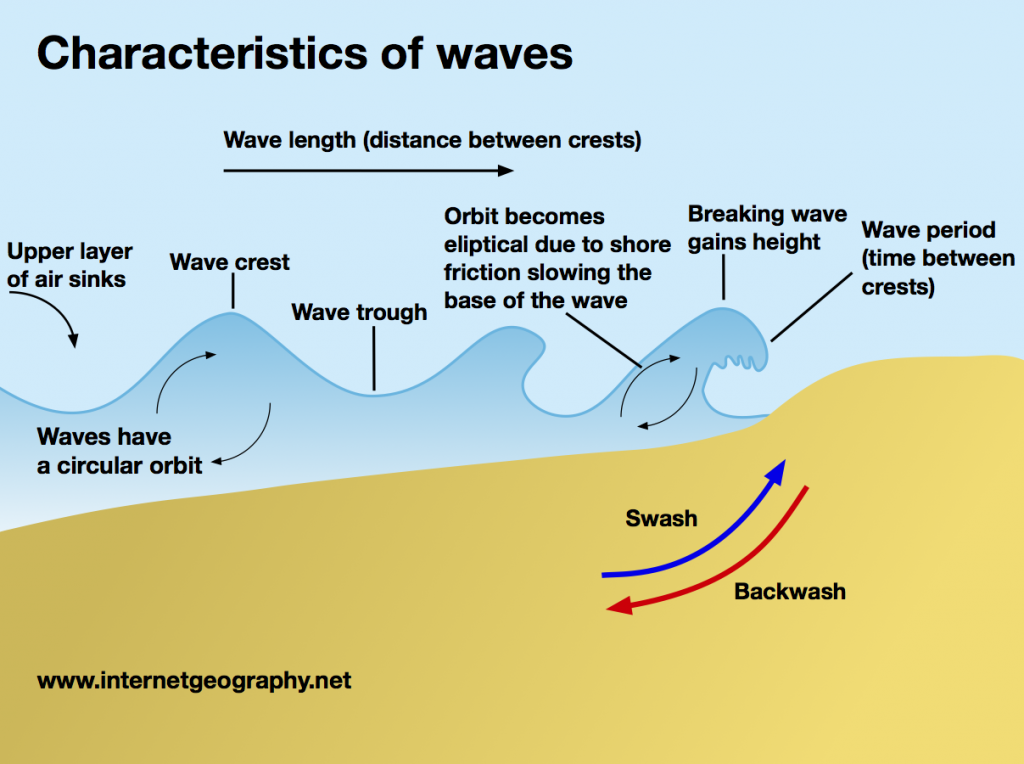
What dictates wave power?
Fetch
Wind Strength
Wind Duration
What are different wave characteristics?
Constructive:
Low Height
Long Length
Spilling
Strong Swash, Weak Backwash
Sediment Gain
Destructive:
High Height
Short Length
Plunging
Weak Swash, Strong Backwash
Sediment Loss
What is Longshore Drift?
Longshore Drift - a coastal process where the prevailing wind carries sediment along the coastline in a zigzag direction.

What are Concordant and Discordant Coastline?
Concordant - alternating bands of hard and soft rock parallel to the coast.
Discordant - Alternating bands of hard and soft rock which can cause headlands and bays to form.
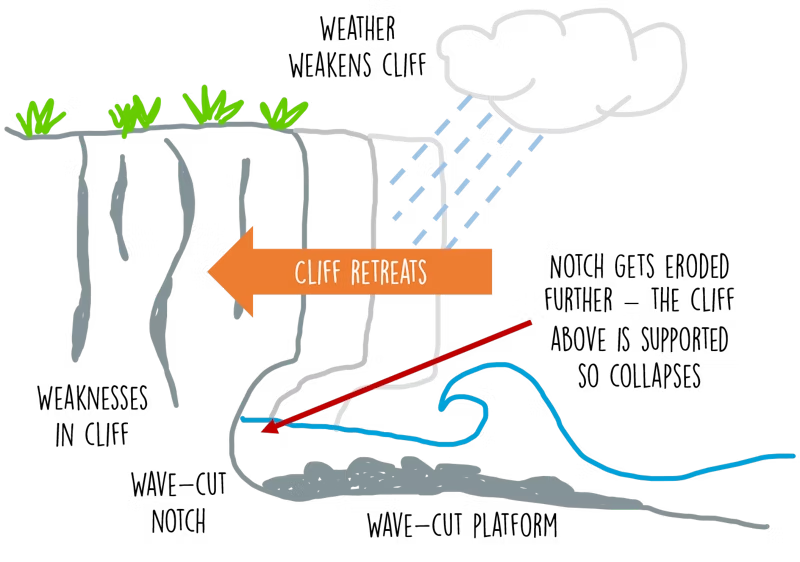
How does a wave-cut platform/wave-cut notch form?
The sea attacks the base between high and low tide.
A Wave-cut Notch forms by abrasion and hydraulic action at the level of high tide.
As the notch increases, the cliff becomes unstable and collapses/retreats.
Attrition breaks away the eroded material leaving a Wave-cut Platform.
This process repeats as the cliff retreats.
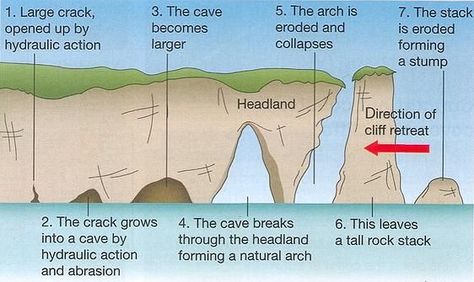
How do Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps form?
There is a crack in the headland caused by hydraulic action and abrasion, which slowly widens over time.
Over time a cave will form as the rock are broken away.
The cave is eroded away at both sides forming an arch.
The base of the arch if further eroded until gravity forces it down making a stack.
The stack is undercut until it collapses forming a stump.
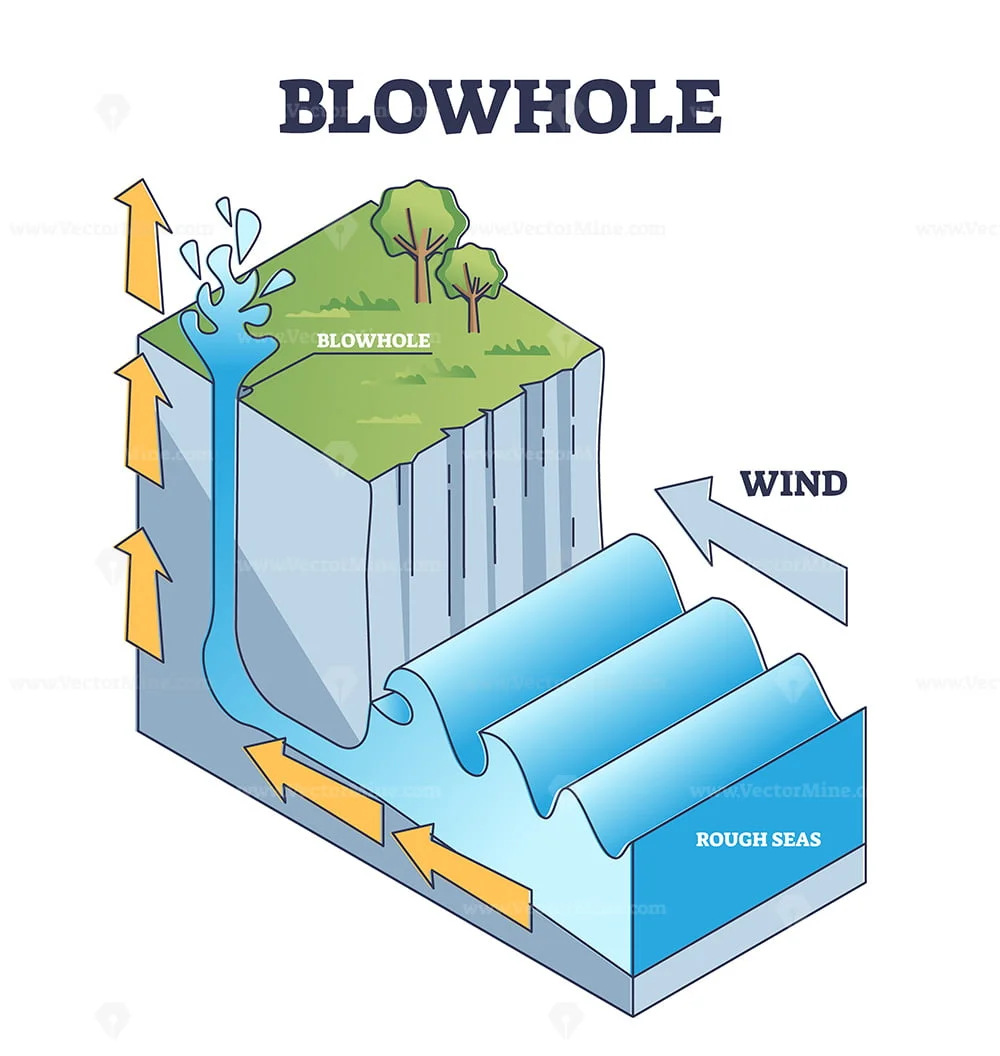
How does a Blowhole form?
They are former caves where the ceiling has been eroded so it looks like a blowhole. The pressure of the waves push water up eroding the rock as it emerges.
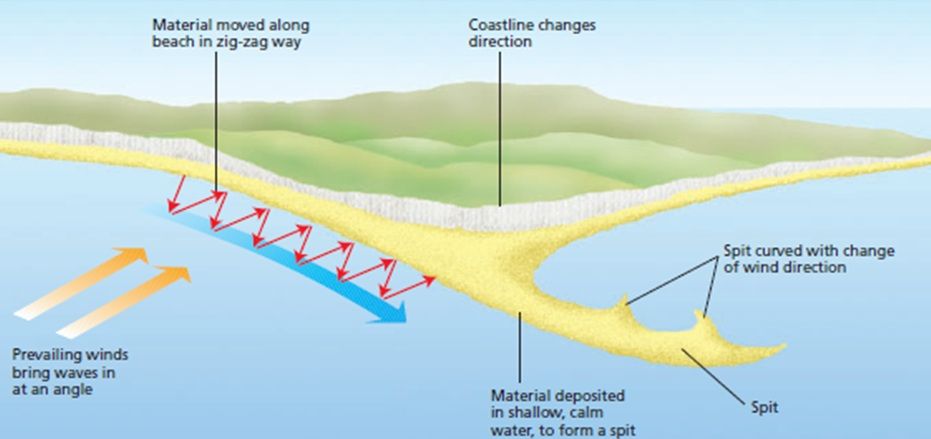
How does a Spit form?
A spit forms when longshore drift carries sediment along a coast due to prevailing wind.
It then carries on into the sea due to a sharp bend in the coast.
It eventually becomes too deep so the spit curves creating a hook.
Behind the spit is a sheltered area where a salt marsh forms.
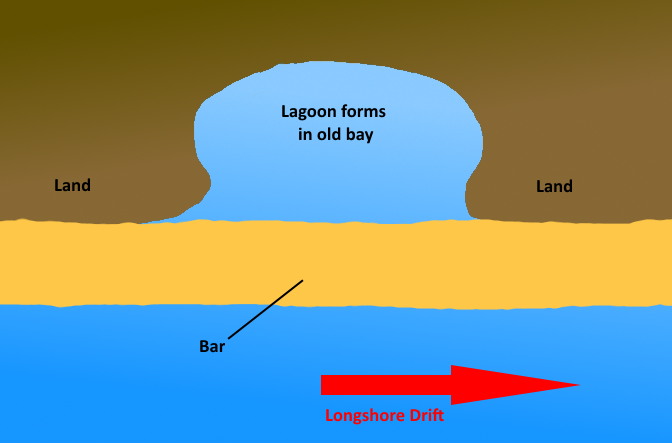
How does a Bar form?
When longshore drift carries sediment across between two headlands and the bay gets cut off from the sea. This forms a lagoon behind.
What are the two types of Beaches?
Sand Beach:
Sheltered Bays
Constructive Waves
Wide
Gently Sloping
Pebble Beach:
Exposed Coast
Destructive Waves
Narrow
Steep Slope
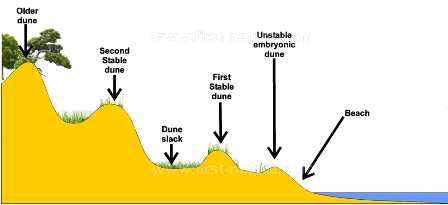
How are Sand Dunes formed?
An obstacle like driftwood decreases wind speed so sand is deposited, forming an embryo dune.
More sand will then form behind creating a foredune.
A dune slack will then occur behind.
Another older dune will form with Marram grass holding it together and stabilizes the dune.
What are 4 types of Hard Engineering?
Sea Wall - Concrete wall which reflects waves back to sea. Prevents erosion and flooding. Very expensive and unnatural.
Gabions - Cages of rocks that support cliffs or buffer the sea. Cheap and absorbs wave energy. Very ugly and corrode over time.
Rock Armour - Piles of boulders along the coast. Quite cheap and absorb wave energy. Need to be replaced often.
Groynes - Traps sediment and prevents longshore drift. Bigger beaches and cheap. Starves other beaches and unattractive.
What are 4 types of Soft Engineering?
Beach Nourishment - Builds up sand taken away from the beach. Creates bigger beaches for tourists. Expensive as done often and disrupts sea shore habitat.
Beach Reprofiling - Redistribution of sand to buffer the sea. Cheap and simple. Done multiple times.
Dune Regeneration - Creating and restoring dunes. Natural and popular with wildlife. Needs fencing off and time consuming.
Managed Retreat - Letting nature take away the land. No defence needed and helps nature. Land is lost and landowners need to be compensated.