MGMT 311 Final
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Organizational Behavior
Understanding, explaining, and improving the attitudes and behaviors of individuals and groups in organizations
Integrative Model
1. organizational mechanisms
2. group mechanisms
3. individual characteristics
4. individual mechanisms
5. individual outcomes
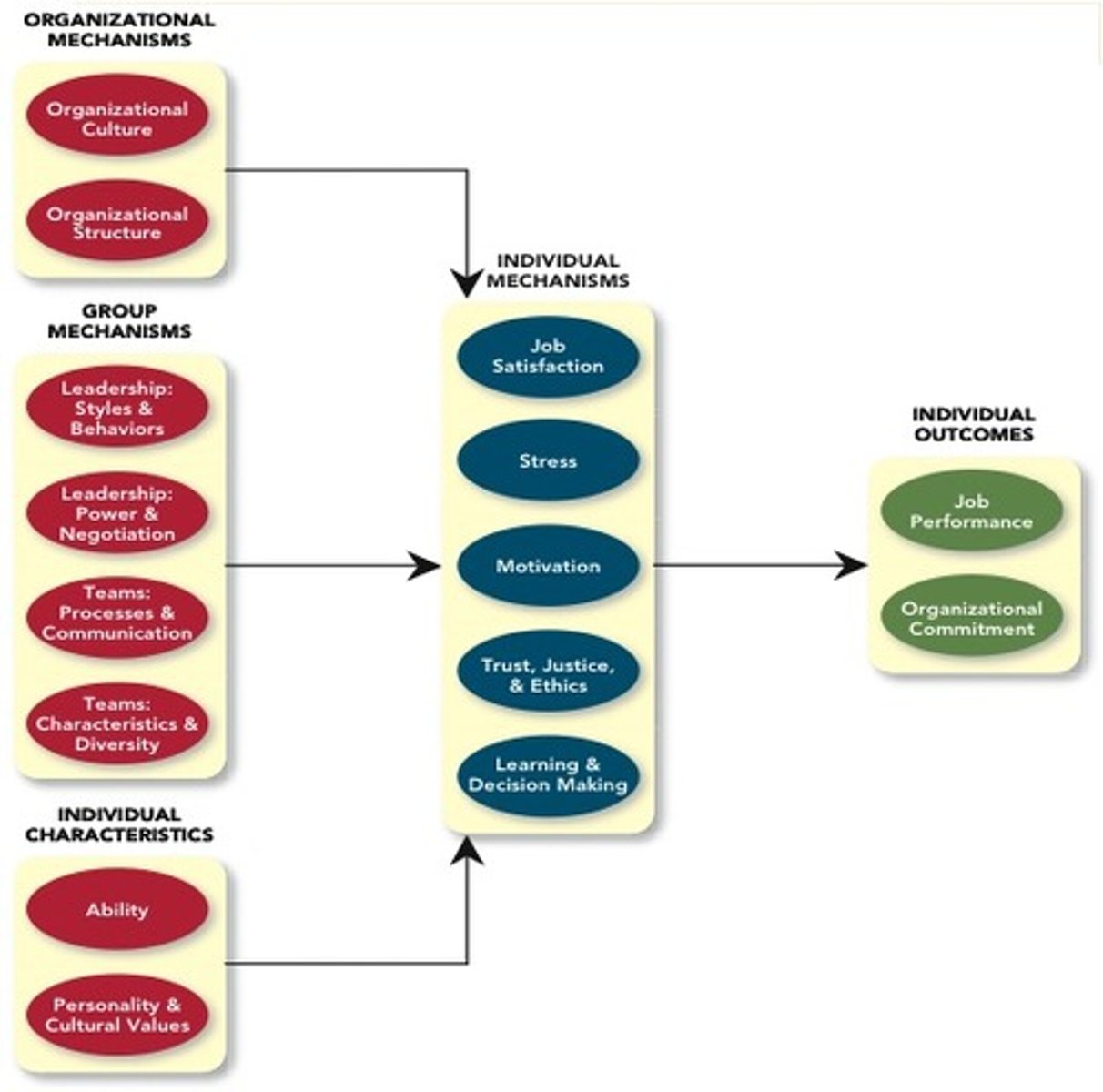
What are the individual Outcomes of the Integrative Model?
Job Performance
Organizational Commitment
Resource Based View
Competitive Advantage comes from (valuable) resources that are rare and inimitable & is socially complex which all contribute to a firm's profitability
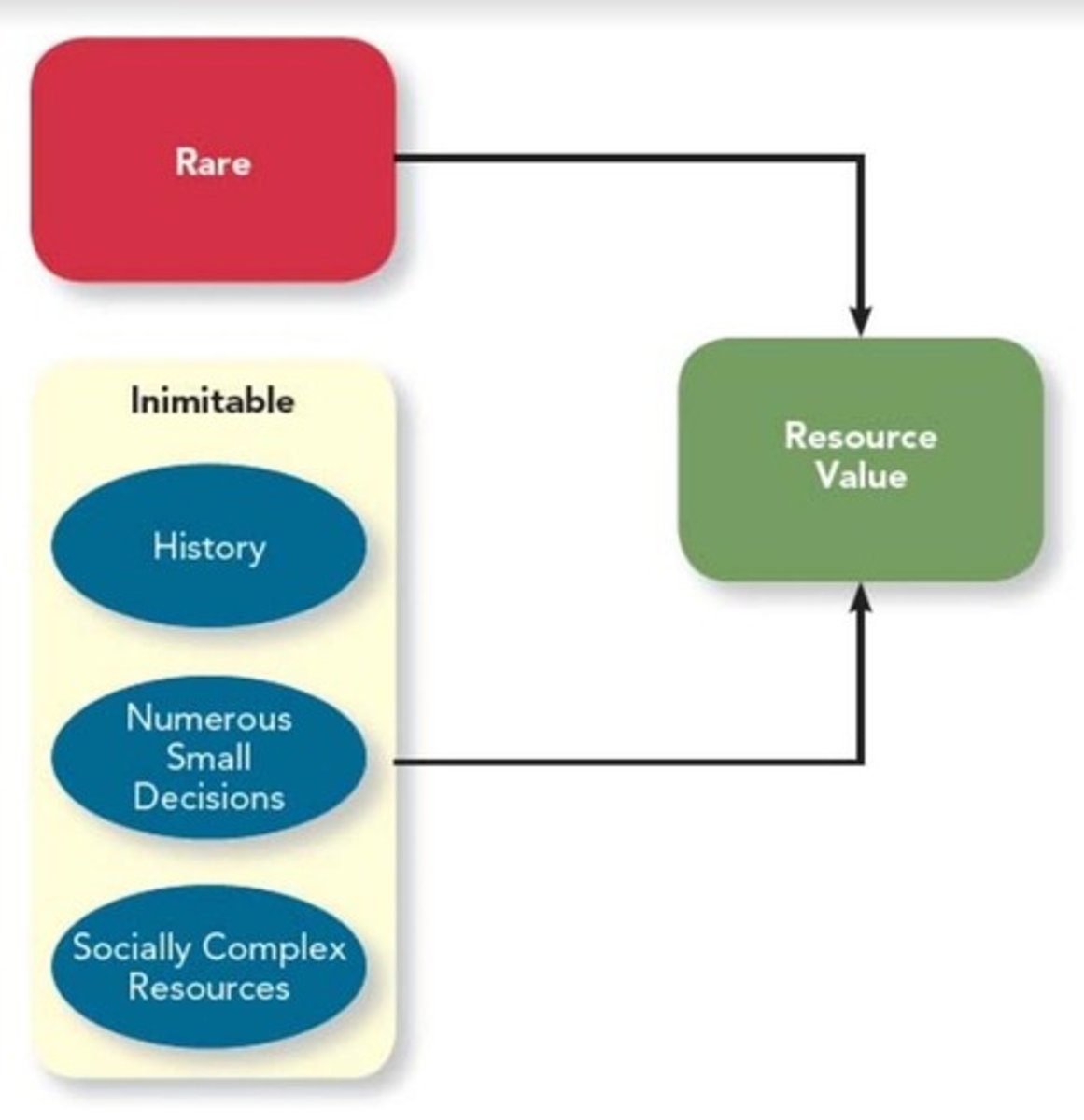
Socially Complex Resources
Intangible resources which include culture, trust, and teamwork. Difficult to imitate due to the amount of time and numerous small decisions that must be put into creating them
The Rule of One-Eighth
Only about 1/8 of companies truly excel at managing people - Organization Behavior gives you the edge
Job Performance
The value of behaviors that contribute the organizational goals
3 Major Categories Relevant to Job Performance
Task Performance
Citizenship Behavior
Counterproductive behavior
Types of Citizenship Behavior
Organizational (Voice, Civic Virtue, Boosterism)
Interpersonal (Helping, Courtesy, Sportsmanship)
Both Forms are voluntary
Voice
Speaking up and offering constructive suggestions to
improve unit or organizational functioning or to address problems
Civic Virtue
Participating in the company's operations at a deeper-than-normal level
Do you offer stability? Doing more than job functions of your job
Boosterism
Representing the organization in a positive way when out of the office
How do we identify relevant behaviors?
(a) determine the requirements associated with the specific job
(b) rate the tasks on frequency & importance
(c) Use most frequent and important tasks to define task performance
What key tool is used for job analysis?
O*NET Database -> used to identify important tasks and required knowledge, skills, abilities and other characteristics for thousands of jobs
3 Categories of Task Performance
1. Routine Task Performance
2. Adaptive Task Performance
3. Creative Task Performance
Team
People who work interdependently to accomplish common goals (teams and work groups are different)
Types of teams
Work Teams, Management Teams, Parallel Teams, Project Teams, Action Teams
Types of Task Interdependence
Pooled, Sequential, Reciprocal, Comprehensive
Pooled interdependence
Members work independently and then pool the results
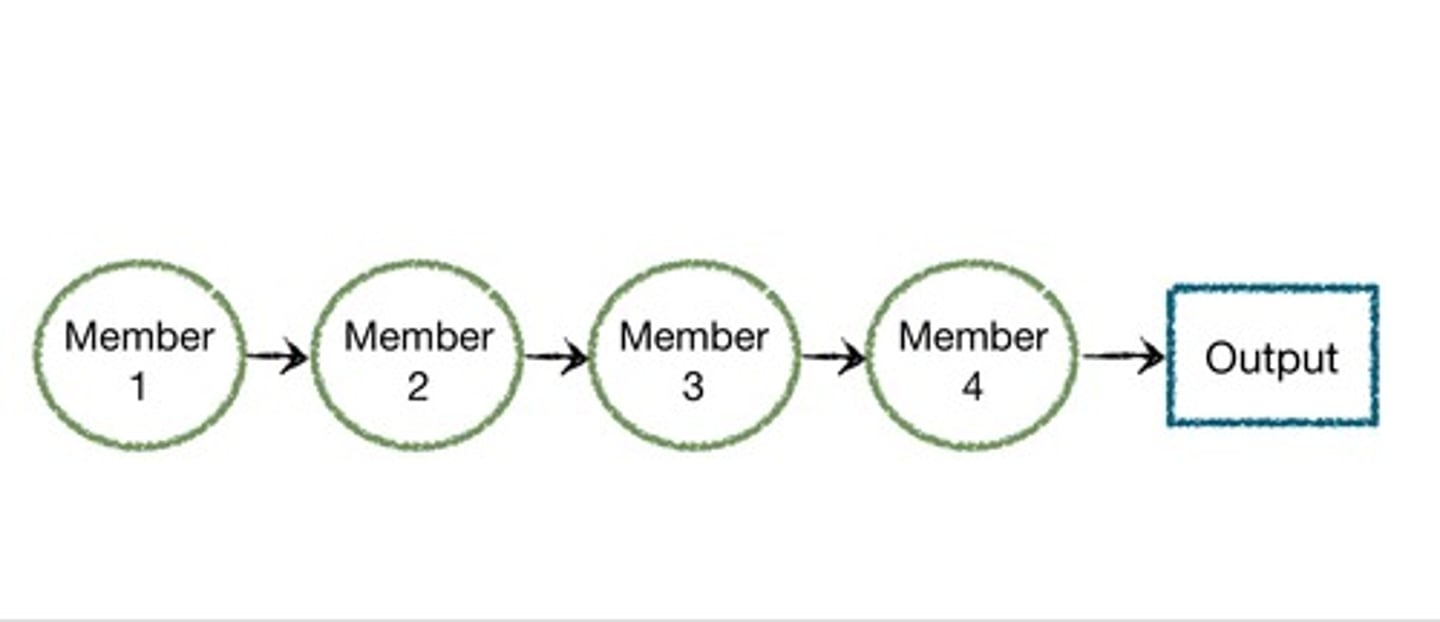
Sequential Interdependence
Members work on specialized tasks in a prescribed order
Reciprocal Interdependence
Members perform specialized tasks and then interact with other members to complete work
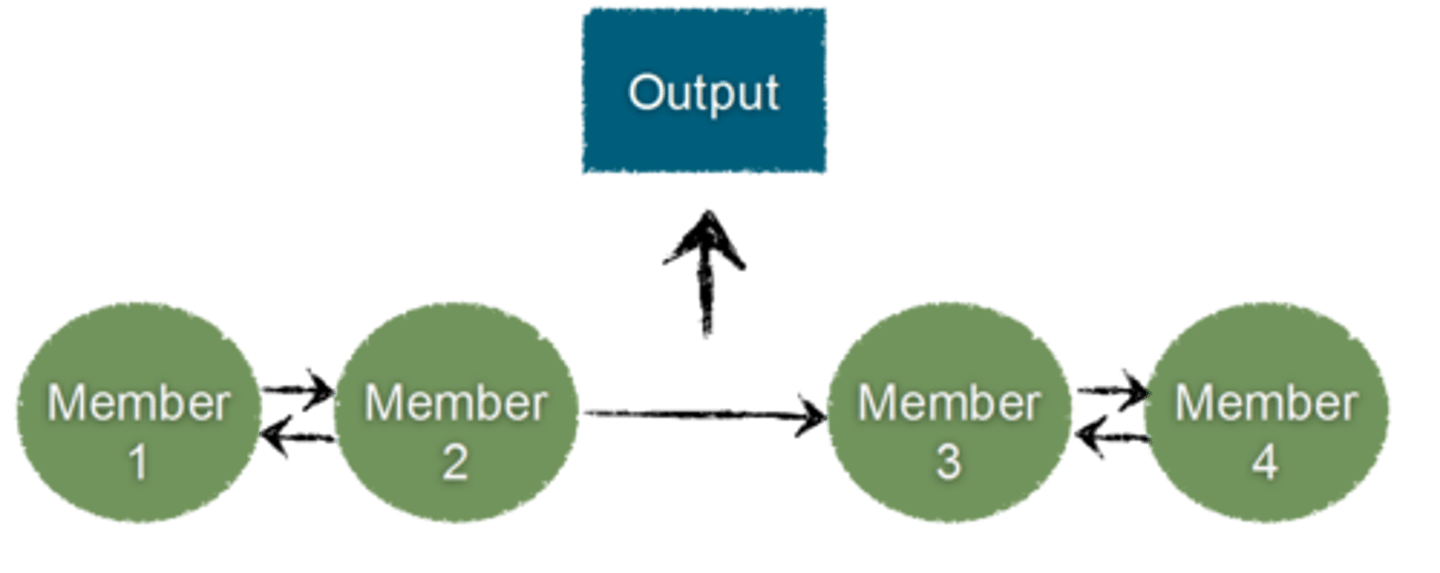
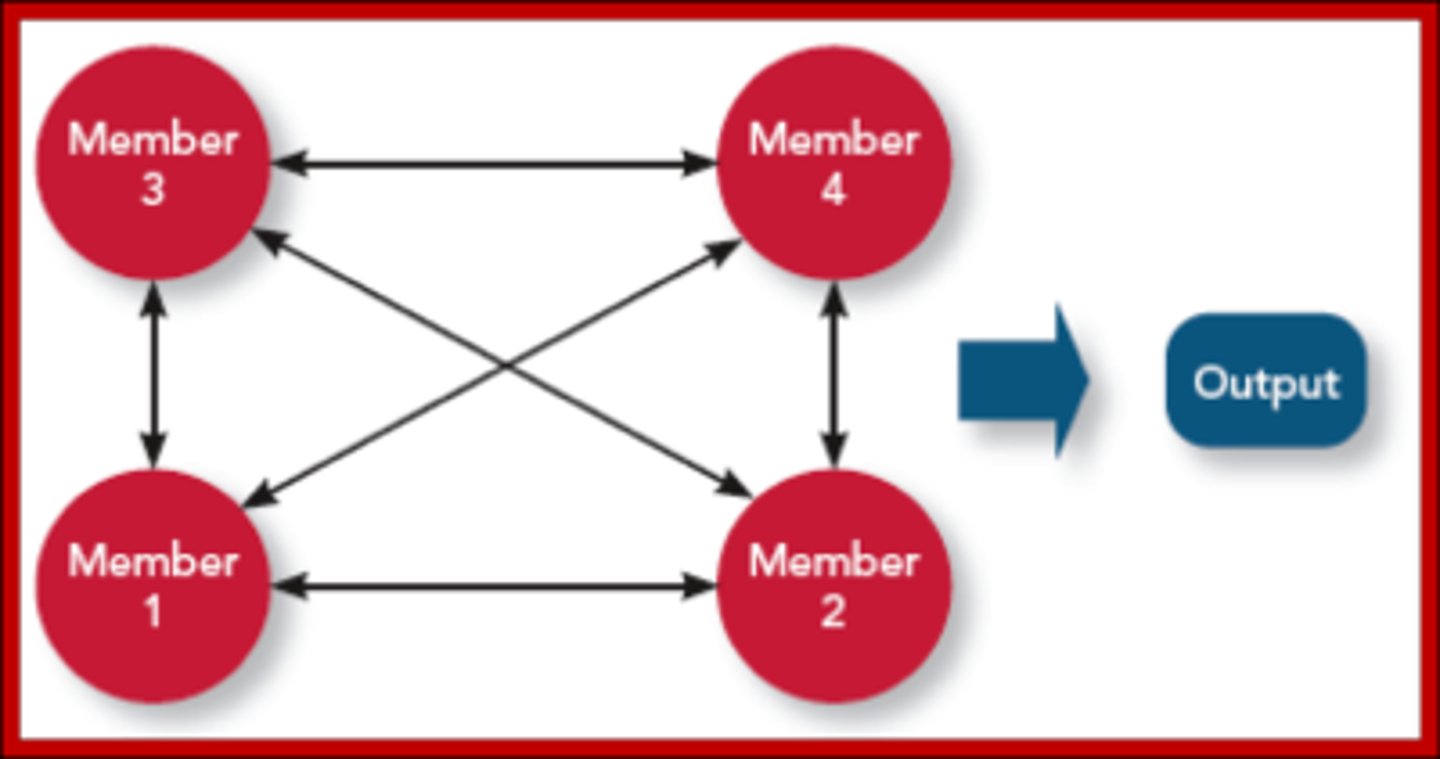
Comprehensive Interdependence
Members interact to a high degree to coordinate and perform tasks
Surface Level Diversity
Diversity of observable attributes such as race, gender, ethnicity, and age
Deep Level diversity
Diversity of attributes that are difficult to observe initially but can be inferred through direct experiences such as personality, values, and attitudes
Ideal Team size for satisfaction
4-5
Team Stages
forming, storming, norming, performing, adjourning
Organizational Commitment
The desire of an employee to remain a member of an organization (based on either want, need, or feeling of obligation)
What are the three types of organizational commitment?
Affective commitment (emotional attachment)
Continuance Commitment (cost of leaving is perceived)
Normative Commitment (Feeling of obligation)
Withdrawal
A set of actions that employees perform to avoid the work situation (Ie Coffee Breaks)
Withdrawal is the opposite of Commitment (Inverse)
Embeddedness
Links, Fit, and Sacrifice. Increases the likelihood of staying with the organization
Job Satisfaction
An enjoyable emotional state as a result of appraisal of one’s job
Value-Percept Theory
Job satisfaction depends on whether you perceive that your job supplies the things or certain aspects that you value
What are the job characteristics that are correlated with overall satisfaction?
Pay, Promotion, Supervision, coworker & the work itself
Which job characteristics has the strongest correlation?
Work Itself (0.70)
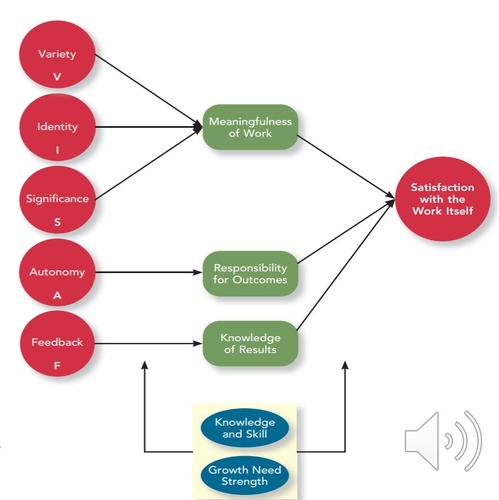
Job Characteristics Theory (VISAF)
Skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback
*** 3 of them are associated with meaningfulness of work
Skill Variety
The degree to which a job requires using a range of different skills and talents.
Task Identity
Completing a whole, identifiable piece of work from start to finish.
Task Significance
The job's impact on other people's lives or work (clients, colleagues, or the organization)
Autonomy
The freedom and discretion an employee has in scheduling work and determining procedures
Feedback
Receiving direct, clear information about the effectiveness of one's performance
What are the moderators in the job characteristics theory?
Growth needs strength and Knowledge and skill
Motivating Potential Score (MPS)
(Variety + Identity + Significance)/3 * Autonomy * Feedback
Job Satisfaction itself is most strongly correlated with
Life Satisfaction, health, and lower counterproductive behavior
Team processes include
Different types of activities/interactions to work toward a goal through communication and task interdependence. These processes can be observable or less visible
Process Gain
Getting more from the team than you would expect according to the capabilities of individual members, also known as snergy
Motivational Loss
Process loss due to lack of effort from team members. Social loafing is an example of motivational loss
Taskwork Processes
Creative behavior, decision making and boundary spanning
Teamwork Processes
Transition, action, and interpersonal processes
Transition teamwork process
Focus on preparation for future work
• Mission analysis involves an analysis of the team’s task, the challenges that face the team, and the
resources available for completing the team’s work.
• Strategy formulation refers to the development of courses of action and contingency plans, and then
adapting those plans in light of changes that occur in the team’s environment.
• Goal specification involves the development and prioritization of goals related to the team’s mission and strategy.
Action Team Process
Important as taskwork is being accomplished
• Monitoring progress toward goals involves recording accomplishments on a progress chart or something similar.
• Systems monitoring involves keeping track of things that the team needs to accomplish its work.
• Helping behavior involves members going out of their way to help or back up other team members.
• Coordination refers to synchronizing team members’ activities in a way that makes them mesh effectively and seamlessly.
Interpersonal Team Process
These are important before, during, or between periods of taskwork, and they relate to the way in which team members manage their relationships.
Motivating and confidence building refers to things team members do or say that affect the degree to which members are motivated to work hard on the task.
Affect management involves activities that foster a sense of emotional balance and unity.
Conflict management involves activities that the team uses to manage conflicts that arise in the course of its work.
• Relationship conflict: Disagreements among team members in terms of
interpersonal relationships or incompatibilities with respect to personal values or
preferences
• Task conflict: Disagreements among members about the team’s task
Communication in Teams
Communication is dense, centralized, and has a network structure
Cohesion
When team members develop strong emotional bonds to other members of their team and to the team itself, forming a sense of unity. Has the chance to increase motivation and performance when the goals align
Mental Model
Shared understanding amongst team members with regard to important aspects of the team and tasks
Transactive memory should:
Possess both specialized knowledge that is useful to the team and meta-knowledge regarding who knows what
Team potency
Degree to which members believe that the team can be effective across a variety of situations and tasks
Stress
A psychological response to demands that tax or exceed a person’s capacity or resources
Transactional Theories of Stress (Stressors)
Hindrance is a negative stressor that can lower performance whereas challenge stressors can be good and raise performance
Hindrance Stressor Example
Work-family conflict, Financial uncertainty, Negative life events
Challenge Stressors Example
Time pressure
Work complexity
Work responsibility
Family time demands
Personal development
Positive life events
Transactional Model
Primary Appraisal: Is it stressful?
Secondary Appraisal: Do I have the resources to cope?
3 Facets of Strain
Medical/Physiological, psychological, behavioral
How do people cope with stressors?
Problem focused or Emotion Focused
Problem Focused Coping
Behavioral methods: Working harder, seeking assistance, acquiring additional resources
Cognitive Methods: Strategizing, Self-motivating, Changing priorities
Emotion Focused Coping
Behavioral Methods: Engaging in alternative activities, Seeking support, Venting anger
Cognitive Methods: Avoiding, distancing, ignoring, looking for the positive in the negative, reappraising
Stress Management and Instrumental Support
Includes tangible help and resources to reduce strains
Motivation
Energetic forces that initiate work-related effort. It determines direction, intensity, and persistence
Expectancy Theory
Motivation is fostered when employees believe that effort results in performance, performance results in outcomes (instrumentality), and those outcomes will be valuable (valence)
Expectancy can be shaped by self-efficacy through
Past accomplishments, vicarious experiences, verbal persuasion, and emotional cues
Goal Setting Theory
Goals must be specific and difficult
Equity Theory and Sensitivity
Motivation is enhanced when the ratio of outcomes to inputs is compared to others. Equity sensitivity involves differences in reactions to perceived equity
Psychological Empowerment is fostered by
Meaningfulness, self-determination, competence, and impact
Trust
The willingness to be vulnerable
Trust is rooted in
Disposition based, Cognition based, Affect Based Factors
Cognition based Trust
The characteristics or attributes of a trustee that inspire trust (ability, benevolence, integrity)
Types of Justice
Disruptive, Procedural, Interpersonal, Informational
Disruptive Justice
Reflects perceived fairness of decision-making outcomes
• Gauged by perceived fairness of outcomes such as pay, promotions, and assignments
• Equity typically the norm (that is, more inputs typically lead to more outcomes)
Procedural Justice
Fairness of the decision-making processes used to arrive at outcomes.
Interpersonal Justice
The degree to which individuals are treated with respect, kindness, and dignity in interpersonal interactions. High levels of organizational justice lead to increased employee commitment, job performance, organizational citizenship behaviors, and customer satisfaction
Informational Justice
the principle that people should receive fair and accurate information about decisions that affect them, including clear explanations for why certain procedures or outcomes were chosen
Ethics
Behaviors of an authority are in accordance with generally accepted moral norms
Categories of Ethical Decision influences
Moral intensity, Moral Principles, Moral Outcomes
Moral intensity includes
Specific Effect, Magnitude of consequences, probability effect, temporal immediacy, and concentration of effect
Stages of Moral Judgement
Preconventional, Conventional, Principled

Components of Corporate Social Responsibility Pyramid
Economic, legal, Ethical, Social, and philanthropic responsibilities
Learning
Reflects permanent changes in knowledge/skill that result from experience
Expertise
The knowledge or skills that distinguish experts from less experienced people
Two Types of Expertise (Knowledge)
Explicit and Tacit
Explicit
Easy to communicate and teach
Tacit
More difficult to communicate, gained with experience
Reinforcement
Method of learning also known as operant conditioning
Contingencies of Reinforcement
Positive Reinforcement, Negative reinforcement, Punishment & Extinction
Positive Reinforcement
Positive outcome follows a desired behavior
3 Facets of Goal orientation
Learning orientation, Performance-prove orientation, performance-avoid orientation
Bounded Rationality
Not having the ability or resources to process all available information and alternatives which leads to satisficing
Personality
Propensities inside a person that explain their thought, emotion, and behavior
Characteristics of The Big Five Taxonomy
Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, Neuroticism, openness to experience, extraversion
Which characteristic of the Big Five is the strongest predictor of performance?
Conscientiousness
Positive Affectivity
A tendency to experience pleasant moods such as enthusiasm, excitement and elation that is commonly linked to extraversion
Locus of Control
A personality trait where people attribute the causes of events to themselves or the external environment