Elements of Computer Architecture - INFS 1101
1/77
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Hardware
is comprised of physical, tangible parts
Software
is comprised of programs and operating systems
Programs
composed of collections of instructions and procedures that perform specific tasks on a computer
Computers
follow instructions
algorithm
A list of steps to solve a problem or perform a computation
software program
An algorithm written in a language that the computer understands
Windows Command line also known as cmd.exe or CMD,
is the command-line interpreter for the Windows operating system. It is a text-based interface that allows users to interact with the computer by typing text-based commands
WMIC which stands for Windows Management Instrumentation
is a terminal utility on Microsoft Windows operating systems that allows users to access system resources and settings. You can use it to query system settings, set system properties, and perform system actions via the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) framework
Binary
Computer use a _________ system
Passing current or no current (5V or 0V)
For Binary
Binary
1 or 0
1 or 0
Called a Bit
states
By combining bits, we can form ________
2² States
2 bits can have
2³ States
3 bits
2^4 States
4 Bits
RAM (Random Access Memory)
Program stored is in ____________
Memory Cells (for RAM)
are identified by an address, which is a binary number
RAM (Random Access Memory)
It occupies a list of memory cells
CPU
orchestrates program execution
CPU
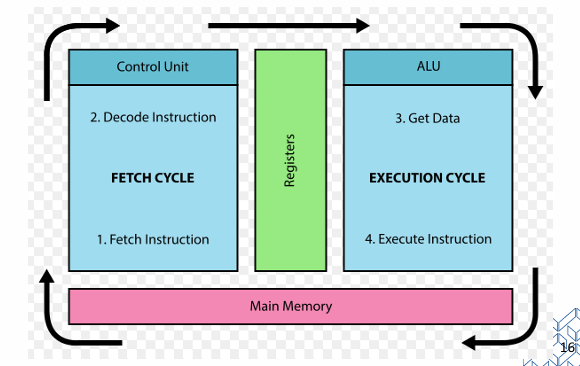
Performs fetch-decode-execute cycles
Von Neumann Architecture
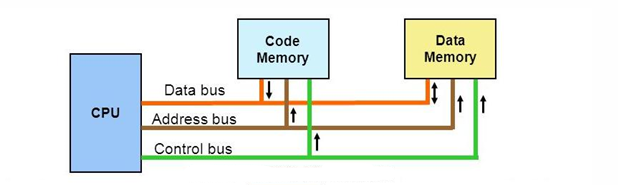
Harvard Architecture
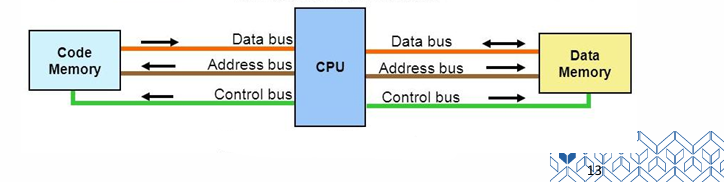
Von Neumann
One shared memory unit for program instructions and data, and one bus for memory access.
Von Neumann
One arithmetic unit and one program control unit.
Von Neumann
Instruction is fetched from memory and decoded, then relevant data is fetched, then instruction is executed
Von Neumann
Requires at least two clock cycles to execute an instruction
Von Neumann
Most commonly used in PCs.
Von Neumann
Due to single memory unit and single bus, limited bandwidth causes a bottleneck situation.
Harvard
Two separate memory units: one for program instructions and one for data.
Harvard
A set of address and data buses to read and write data to memory, and another set of address and data buses to fetch instructions
Harvard
Can fetch instruction and data simultaneously
Harvard
Can execute an instruction in only one clock cycle
Harvard
Faster and no bottleneck issues
Harvard
Requires more memory and hardware.
Harvard
Most commonly used in embedded devices and signal processing.
Harvard
More and more modern computers are using Harvard architecture
Fetch Decode Execute
Algorithm
“a process or set of rules to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations, especially by a computer”
Plain English
Pseudo-code
Flowchart
The algorithm can be described in a variety of ways
Pseudocode
an artificial and informal language that helps programmers develop algorithms.
Pseudocode
is a "text-based" detail (algorithmic) design tool.
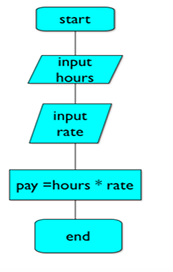
A flowchart
a picture of the separate steps of a process in sequential order.
Pseudocode
These include while, do, for, if, switch
Pseudocode
The rules of _________ are reasonably straightforward.
Pseudocode
All statements showing "dependency" are to be indented.
A flowchart
It is a generic tool that can be adapted for a wide variety of purposes,
A flowchart
can be used to describe various processes, such as a manufacturing process, an administrative or service process, or a project plan
Flowchart
Pseudocode

Program code
Implementation of an algorithm in a programming language
programming language
is a formal language comprising a set of strings that produce various kinds of machine code output
High level languages
C & Python
Binary
Add two numbers (0010)
Machine code
Native language of the processor
Machine code
Operations and operands all in binary (or hex
Machine code
Operations and operands all in binary (or hex) Not human readable
Low-level languages
Machine code & Assembly
Assembly
Each line can be associated to as single instruction
Assembly
Human readable (but tedious and long)
An assembler
An ___________ converts assembly code to machine code
Machine Code and Assembly
Both are CPU-specific (non portable)
High Level Languages
Human readable (English keywords)
High Level Languages
Portable: same code can be used on different computers
High Level Languages
Differ in the level of control / automation they provide
High Level Languages
C, C++, Java, Rust, Go, Python, Javascript, PHP, Ruby
Compiled
converts the whole program to executable (machine code) before running.
Compiled
Runs faster and compiler not required to run the executable, but is more complex to develop.
Compiled
Allows the developer to have more control over hardware specs, i.e., memory management, CPU usage.
Interpreted:
converts the program to machine code instruction by instruction
Interpreted
Easy to debug but a little slower - always requires interpreter to run
Interpreted
More flexible, offer dynamic typing and smaller program size
Interpreted
Examples: Python, Javascript, PHP, Ruby
Hybrid
Java
Strongly typed
A language that requires variable and object data types to be specified (integer, string, float). Allows for more structure, but less flexible.
Loosely typed
A language that does not require variable and object data types to be specified. More flexible and faster, but errors are more likely to occur.
Loosely typed
Examples: JavaScript, Perl, Python, Ruby
Strongly typed
Examples: C++, Java, C#.