VAS ALL CASE STUDIES
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
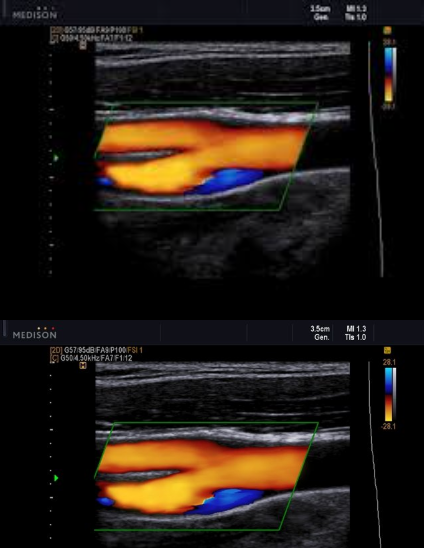
Patient presents with recent history of syncope. New onset of HTN and HX of smoking 1 pack per day (ppd) x 25 years.
Carotid ultrasound exam ordered. Considering following questions and please answer.
1. In patient presentation, which item is the symptom for carotid ultrasound exam?
2. In patient presentation, identify the risk factors for atherosclerosis and carotid artery disease.
3. Consider image, which vessel contain some blue colors?
4. Is the 'blue' pathological?
5. What is the color blue representing?
Syncope
HTN and smoking
Prox ICA (bulb)
no
eddie currents from flow reversal in bulb
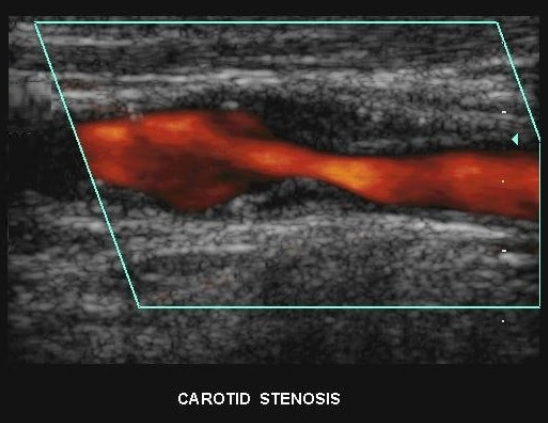
Patient presents to ultrasound department for preoperative work-up. Patient scheduled to have coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) in two days. Patient has HX of peripheral vascular disease, smoking, HTN and hyperlipidemia. You obtain this image. Consider following questions.
1. Is it possible to have plaque producing stenosis without symptoms?
2. What are the risk factors for atherosclerosis in this patient presentation?
3. Is this image diagnostic for hemodynamically significant stenosis? Why or why not.
Yes
Hx of peripheral vascular disease, smoking, HTN, hyperlipidemia. (Also has CAD because they are here for pre op for CABG)
No because power doppler only shows presence of flow and no velocity information
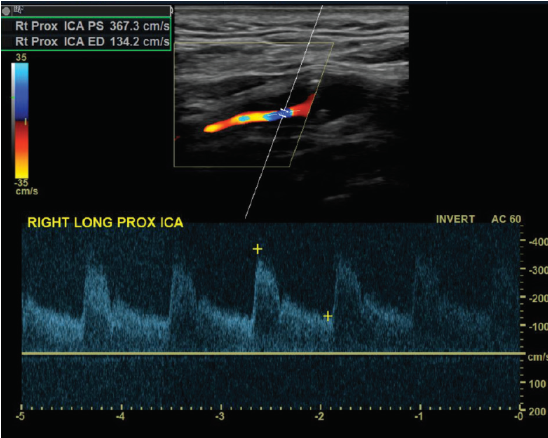
Patient admitted with sudden onset of LT sided weakness and aphasia x 48 hours. Carotid duplex ordered and you obtain this image of RT ICA.
1. Considering patient symptoms, is this a TIA? Why or why not?
2. Considering velocities, what does this image indicate?
3. Describe waveform down stream from this current location.
No because its more than 24 hours
That there is a hemodynamically significant stenosis because the velocities are pretty high at 367.3 cm/s
would be a tardus parvus waveform (slow rise, slow fall)
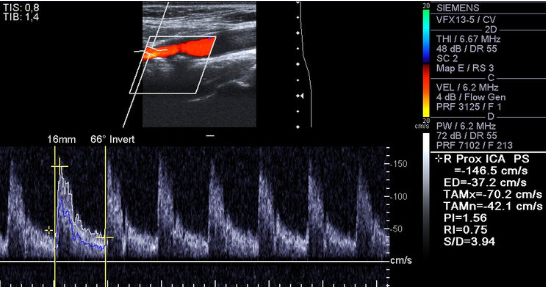
Consider this image.
1. Which vessel is is sample gate positioned?
2. Is the cursor parallel to vessel wall?
3. Is velocity measurement reliable? Why or why not?
4. How would you optimize image? List two items
Rt ICA prox
No
No because the angle is off and its over 60 which will make the velocities higher than they actually are
Decrease depth, move color box up, move sample gate up, fix pw angle, adjust pw ain
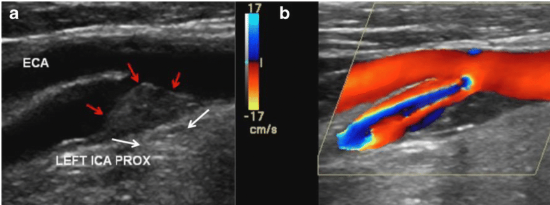
Review ultrasound image and answer following questions:
1. The red arrows indicate what on grayscale?
2. How would you describe surface? How would you describe echogenicity?
3. Color is activated with image 'B', what is term used to describe color patterns center of blood flow? Why is this happening?
4. At which locations will you sample blood flow to determine velocities with this finding? Why will we sample blood flow in these locations?
Plaque
Smooth. Heterogenous
aliasing because the velocities are exceeding the Nyquist limit
Walk sample through stenosis and find the highest velocity. Then grab the prox, distal, and the slow return to laminar.
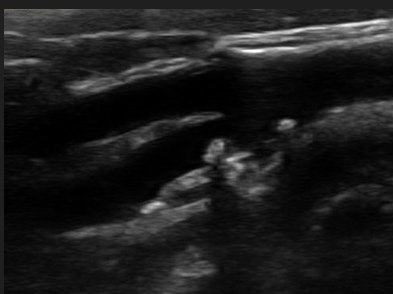
The surface of this plaque is a potential source of emboli.
true (any plaque can break off and go north)
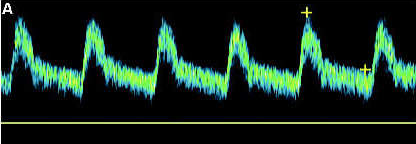
Is this a high resistant or low resistant waveform? Why?
Low resistant because the end diastolic is 30 to 40% of the peak. There is also continued forward flow
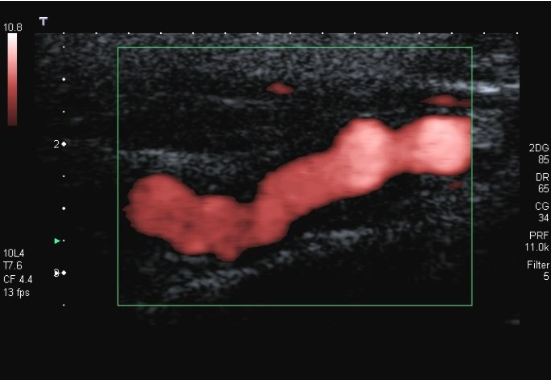
Patient is 38 y/o female with stroke like symptoms. No risk factors or medical history. You take this image of distal ICA.
1. What is the sonographic description of distal ICA?
2. What does this indicate or what is possible diagnosis?
3. Is this related to atherosclerosis?
4. What is important in patient clinical presentation for possible diagnosis?
5. Which other vessels most likely impacted by this?
string of pearls
FMD
No (congenital abnormality)
young female
Renal artery’s
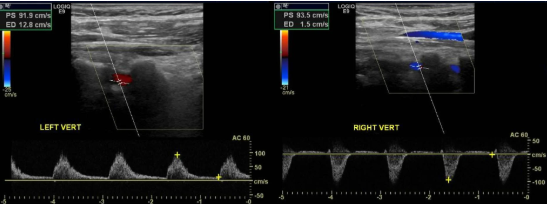
You obtain these images of vertebral arteries.
1. What is this finding right side?
2. What does this indicate?
3. Where is obstruction?
4. Vertebral artery feeds which portion of brain?
5. The two vertebral arteries unite to form?
retrograde flow
subclavian steal
Right subclavian artery that’s proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery
posterior portion
Basilar artery
You are called to bedside to evaluate the Circle of Willis in patient s/p SAH and craniotomy x 7 days. Please consider the following:
1. Which window is this?
2. Which vessels can we visualize or hear with ultrasound through this window?
3. What is a likely finding considering patient history?
4. Which window will provide access to basilar artery?
5. Which calculation will you need to make for this patient?
1. Transtemporal window
2.MCA, ACA, PCA, TICA
3. Vasospasm is likely
4. Suboccipital
5.Lindagard ratio = MCA/ICA ratio
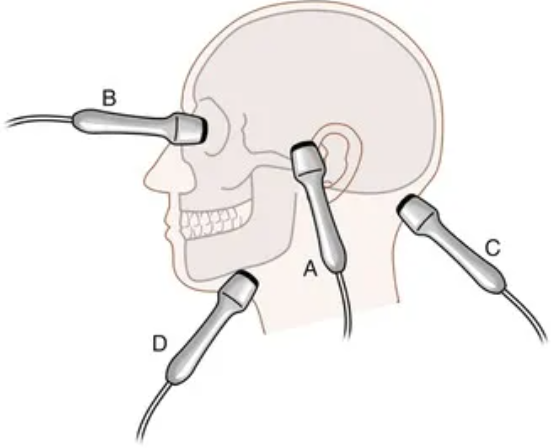
Identify the windows. Discuss how we identify vessels using these windows.
A. Transtemporal
B. Transorbital
C. Suboccipital
D. Submandibular
We use depth and direction and also what window is being used
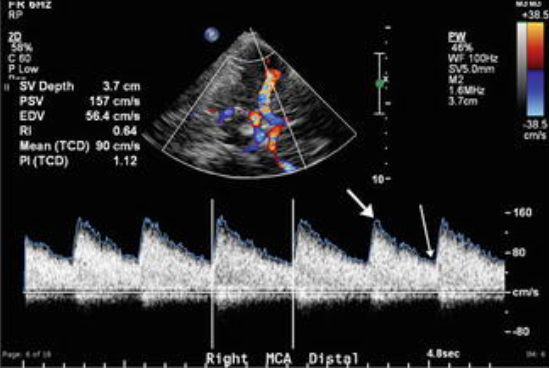
Patient s/p CVA and intracranial endovascular procedures to remove thrombus. Patient in neuro ICU and you are called to bedside to evaluate for vasospasm. You take this image. What does it indicate?
No Vasospasm
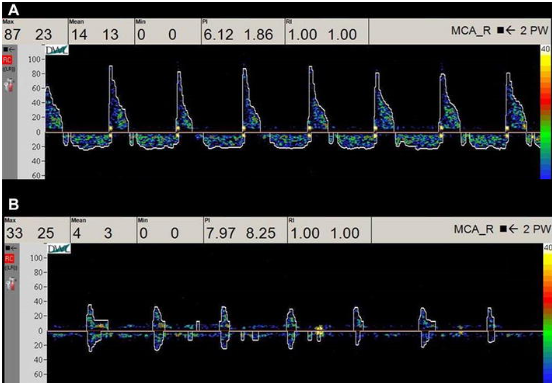
Patient s/p motor vehicle accident (MVA) with head trauma. TCD ordered and you obtain these waveforms. What do they indicate?
Brain death
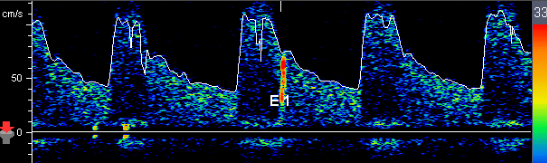
Patient presents with cryptogenic stroke. TCD Bubble Study ordered and you obtain this image with 3rd saline injection. Consider following questions.
1. What does the red item marked 'E1' indicate?
2. Is patient having a stroke with this 'E1'?
3. What is cryptogenic stroke?
4. Provide an example of source of stroke.
1. Embolus
2. one emboli does not equal one stroke so no
3. stroke we do not know where it came from
4. an example of a source of stroke can be carotid artery disease and the build up of plaque, piece of plaque can break off and become and emboli which will travel north and block a smaller artery causing an ischemic stroke.
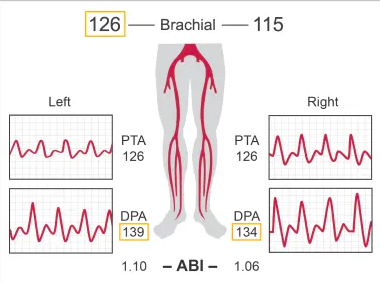
Patient presents to ER via ambulance s/p MVA. ABI obtained in trauma bay by nurse. Is this ABI normal?
Yes
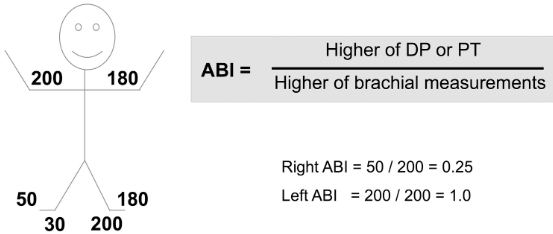
Considering ABI results, which side is abnormal?
right
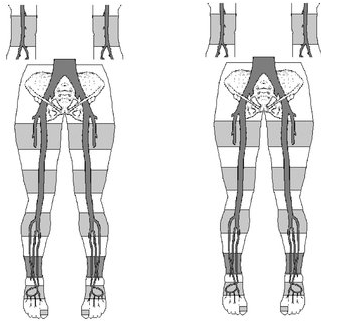
1.Is this a 3 cuff method or 4 cuff?
2.How will the diagnostic criteria change depending on the cuff method?
3.Why do they differ?
1. 4 cuff method
2. the relationship of the thigh cuff to the brachial. With 4 cuff the high thigh cuff needs to be 30mmHg or more than the brachial while with 3 cuff method it is equal to or greater than the brachial
3. Cuff sizes are different. 3 cuff method in the thigh it is 17 cm while the 4 cuff method in the thigh is 12 cm.
When will we obtain toe tracings and TBI?
In patients with DM
Are these waveforms CW Doppler or PVR?
PVR
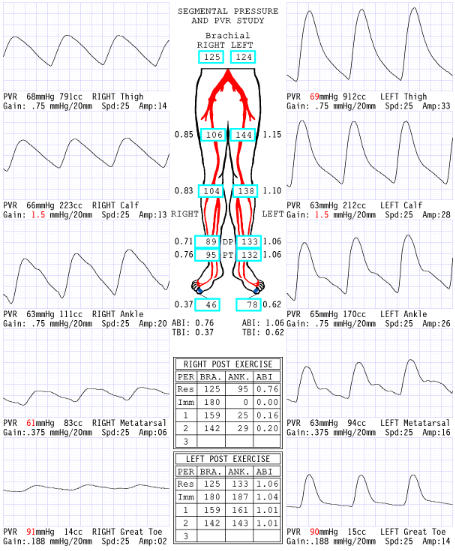
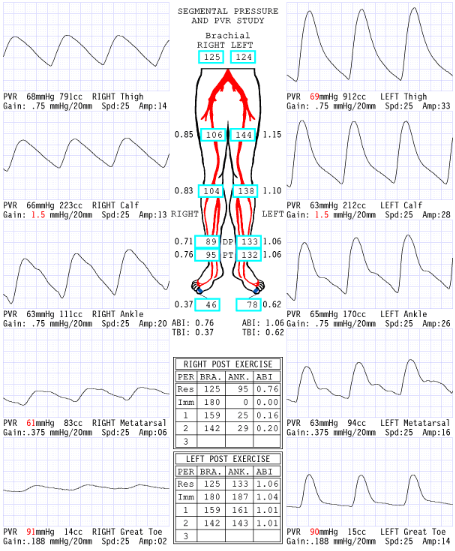
Considering waveforms, which side is abnormal?
Right
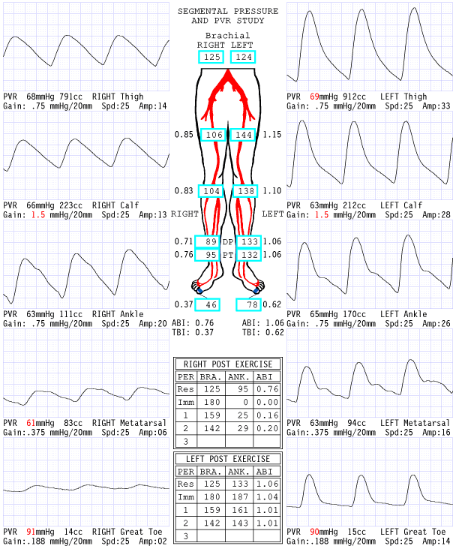
Considering ABI, which side is abnormal?
Right
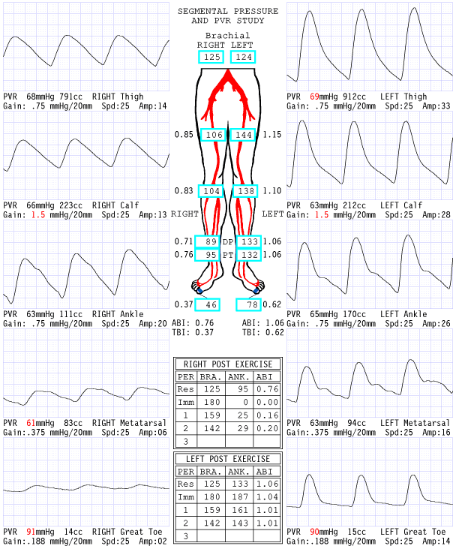
Considering segmental pressures, where is level of disease?
Right inflow
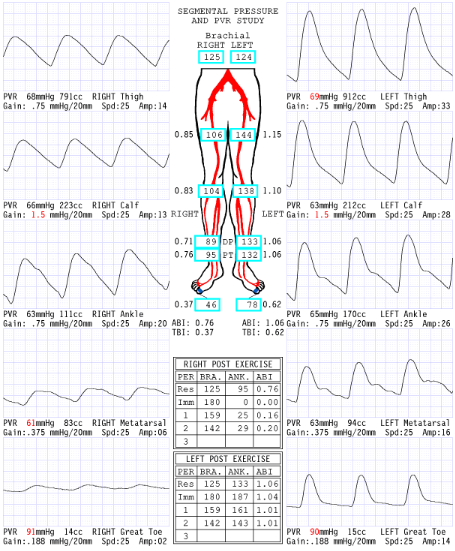
Consider the post exercise results, which side is abnormal?
right
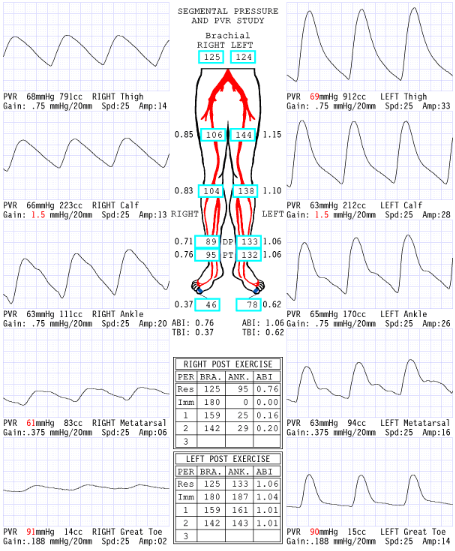
What does the '0' mean at level of ankle immediate post exercise right side?
Severe drop in pressures: No audible pulse, therefore no pressure obtained
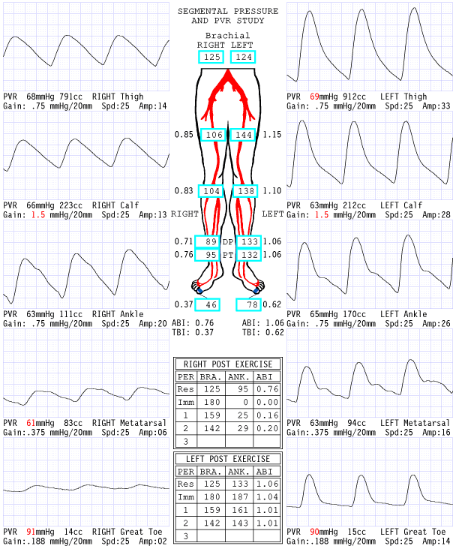
Now that we have dissected results of this report, please describe what you believe are the patient's clinical symptoms for why referring physician ordered exam.
Since the disease is in the right inflow, the symptoms they could have is buttock and hip pain.
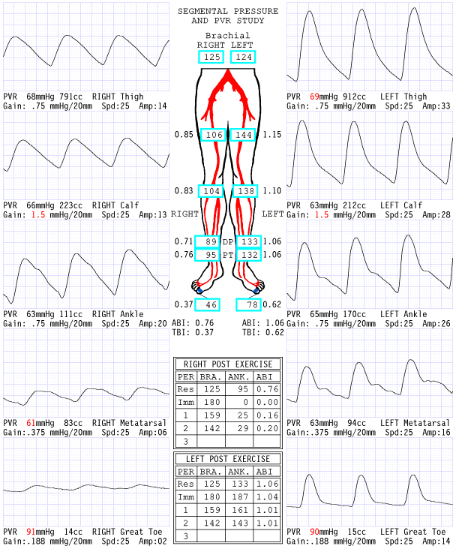
Explain why the ABI is .20 RLE 2 minutes post exercise.
Exercise increases blood flow a significant amount through the narrowing that has a significant pressure drop that causes an extended amount of time to recover
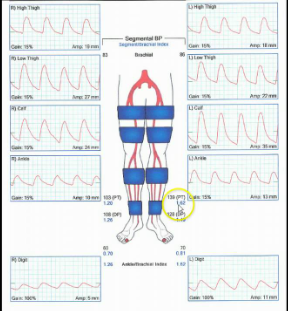
Patient has hx of HTN, CAD, DM and PAD. Please answer following:
1.What are these medical acronyms and why are they important?
2.Considering patient history can we rely on ABI information? Why or why not?
3.Which LE pressures are most accurate for this patient?
1.HTN=hypertension, CAD= coronary artery disease, DM= Diabetes mellitus, PAD = Peripheral artery disease. they are all risk factors
2. No because diabetic pt can have calcified arteries
3. The TBI is most accurate for pts with DM
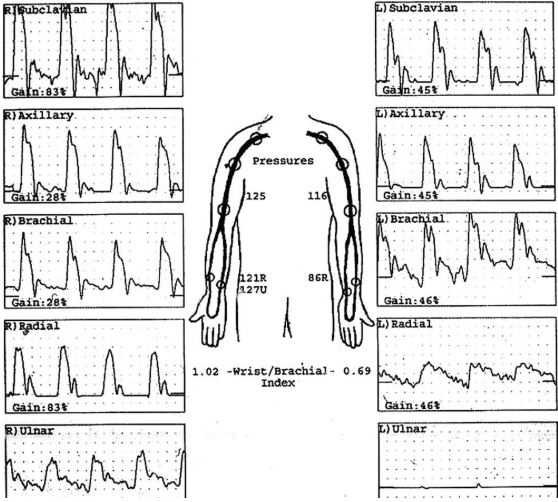
Considering segmental blood pressure report, which side is abnormal?
Left
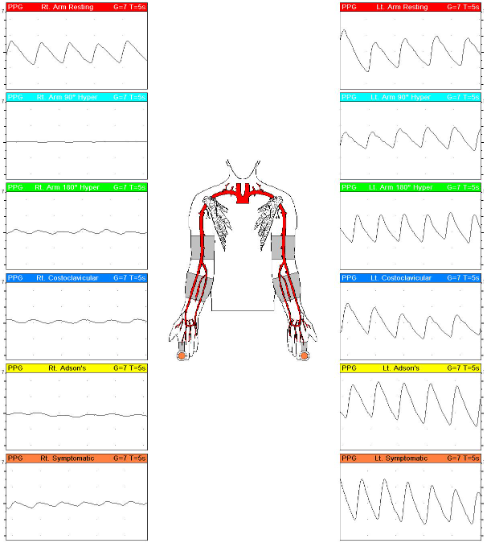
30 y/o male patient presents with tingling and pain RUE in specific positions. No medical history. Indirect UE testing ordered and you obtain these results with PPG sensor and PRV waveforms.
1.What is possible diagnosis?
2.Which position causes cessation of blood flow?
1.agnosis is thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS).
2.Right arm 90 degrees hyper extended (light blue one)
Patient presents with c/o LT calf pain after walking two blocks. Pain is relieved with rest. Select medical term for this symptom.
intermittent claudication
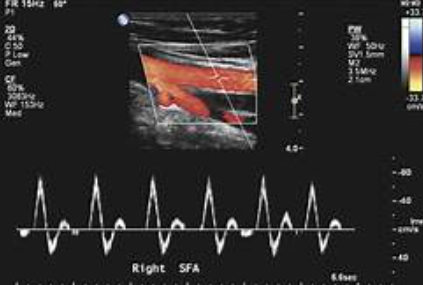
Which type of waveform is this?
triphasic
Patient c/o pain in RT calf after walking 2 blocks. Pain is relieved by rest. Referring physician ordered segmental blood pressure with arterial duplex imaging if needed.
Segmental blood pressure exam demonstrated:
RT high thigh pressures as 166
RT low thigh pressures as 90
High calf pressure 89
Ankle pressures at 80
1.Where is possible stenosis?
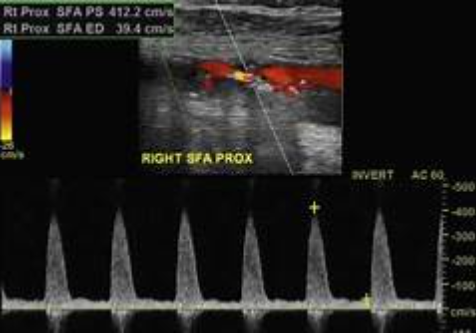
Because of the results you obtained with segmental blood pressures, imaging performed to visualize obstruction and you take this image in proximal SFA. Consider velocities.
2.What does image indicate?
3.Describe waveforms you will obtain at SFA mid thigh (distal to area) because of this finding.
4.Does this finding explain the pressure gradient and patient symptoms?
1. Mid thigh for possible stenosis
2.Image indicates a hemodynamically significant stenosis
3. will see post stenotic waveforms or tardus parvus.
4.yes because of its location
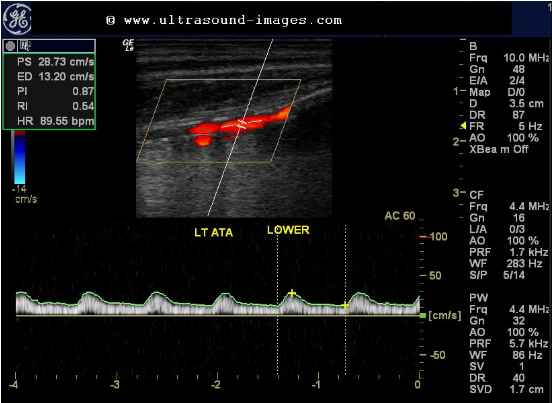
Considering artery, location of sample volume and waveform, is this a normal waveform?
1.If disease is present, where is it?
2.Proximal or distal to sample volume?
1.No it is not because we need to see a triphasic high resistance waveform for the anterior tibial artery
2. it would be proximal because this is a post stenotic waveform
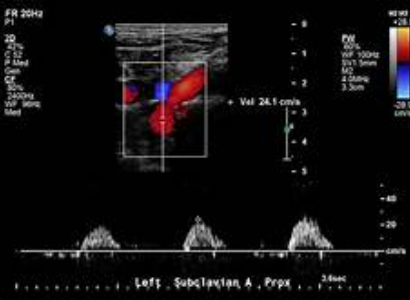
Consider this LT sided subclavian artery waveform. Where is obstruction?
With this finding, what might you find in the ipsilateral vertebral artery?
1. proximal to the sample volume
2. retrograde flow for subclavian steal
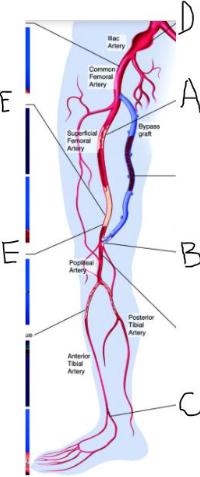
Your patient has significant peripheral arterial disease and treatment! Label the structures and pathology identified by letters.
What is the name of the bypass graft?
Include laterality.
1.A=right mid SFA stenosis
B=right fem pop distal anastomosis stenosis
C=Right DPA occlusion
D=Right Common illiac aneurysm
E=right distal SFA occlusion
2. right fem pop
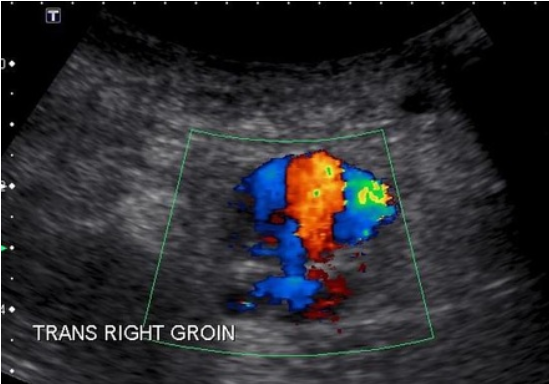
Pt is s/p cardiac catherization RT groin x 2 days. Patient presents with pain, palpable pulsatile mass RT groin. Duplex arterial ultrasound ordered to evaluate area of pain. Consider this image taken in area of pain.
1.What is most likely diagnosis?
2.What is important in patient history supporting diagnosis?
3.It is possible to have another vascular finding with this patient history and diagnosis. What is it?
4.Why is sonographer using abdominal curved probed?
1. pseudoaneurysm
2. pt had recent right groin vascular access
3. yes, a hematoma
4. Increased penetration
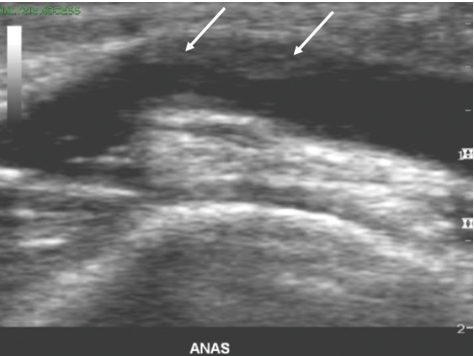
Patient is s/p LE bypass graft x 3 years. Patient has not had previous ultrasound exam for 2 years.
You obtain this image and the white arrows most likely indicate which of the of following?
progression of artherosclerosis
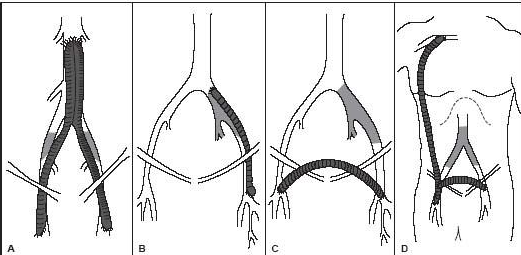
Recall that the inguinal canal is the point at which the iliac artery becomes the common femoral.
Name the bypass grafts.
A. aorto bi femoral bypass graft
B. left ilio fem bypass
C. right to left fem fem bypass graft
D. Right axillo bi fem bypass graft or right axillo fem bypass graft with right to left bypass graft
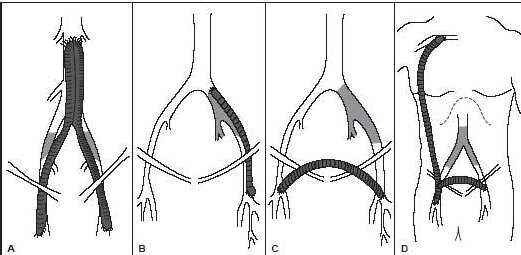
What is the proximal anastomosis for graft type A?
Aorta
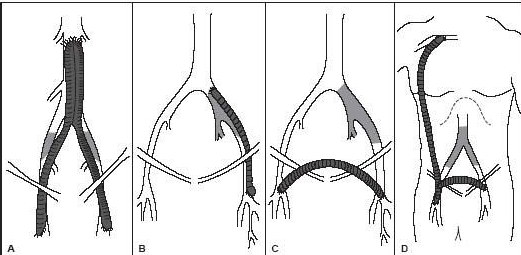
What is the proximal anastomosis for graft type D?
Axillary
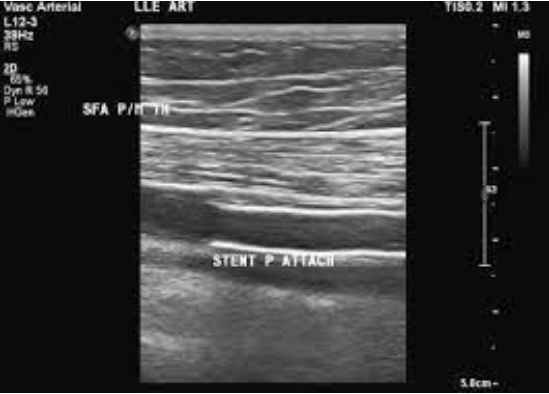
Patient presents for f/u ultrasound exam. She is s/p stent placement x 3 weeks.
Describe your imaging protocol.
Mid stent
color doppler
velocities proximal and distal stent edge
PW doppler and psv
grayscale assessment
proximal to and distal to stent edge
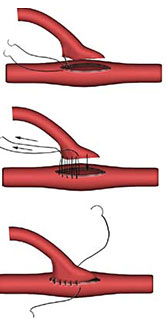
What type of anastomosis is this?
end to side
Patient in the ER with cold left leg. Patient has history of vascular disease with revascularization however he is a poor historian and cannot provide valuable surgical information. Ultrasound is ordered STAT.
What are your next steps to prepare for patient?
Look at leg for proximal and distal linear incisions
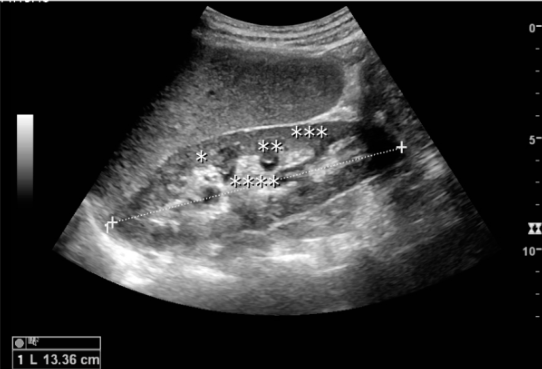
You are measuring right kidney as you prepare to complete the renal artery Doppler. Convert measurement to millimeters. Select best answer
133.6mm
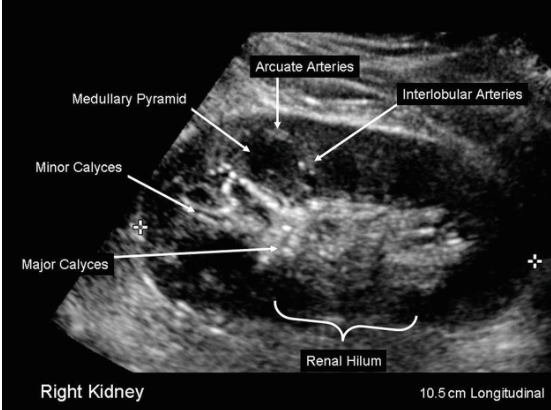
In your assessment of the intrarenal arteries at level of arcuate or interlobular arteries, is it necessary to angle correct? Select best answer.
No. As we scan the kidney, the angle is closer to zero degrees with position of probe and arteries traveling towards transducer.
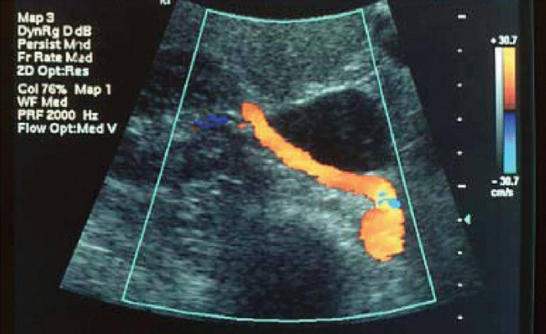
In this image, the RRA is seen from aorta to hilum of kidney. Which portion of RRA is proximal and which is distal?
Proximal is at aorta; distal at hilum
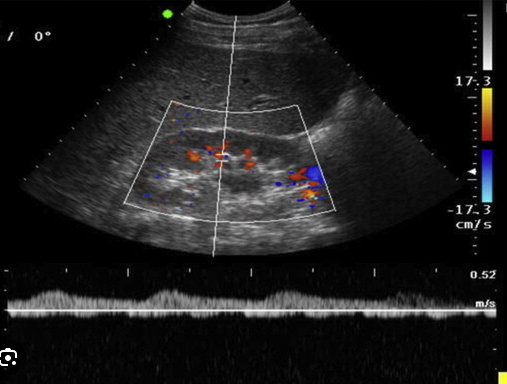
Your patient is 63 y/o with hx of HTN, DM, smoking, carotid artery disease and RLE bypass graft. He presents with uncontrolled hypertension.
1. Considering patient history and clinical presentation, is suspected disease related to atherosclerosis or FMD?
2. You started your exam with measurement of RT kidney and assessment of interlobular arteries. You take this image. Is this waveform normal? Which term best describes it?
3. Considering patient history and reason for exam, where might you stenosis?
4. Your patient has extensive bowel gas obstructing main renal artery. Is this waveform with measurements you have obtained diagnostic?
5. If we use the waveform and measurements obtained in the arcuate arteries to diagnose RAS without evaluating main renal artery, which type of assessment is this considered? Direct or indirect?
1.Atherosclerosis
2. not normal because of delayed upstroke. tardus parvus waveform.
3. Origin or the proximal portion
4. This is still diagnostic
5. Indirect
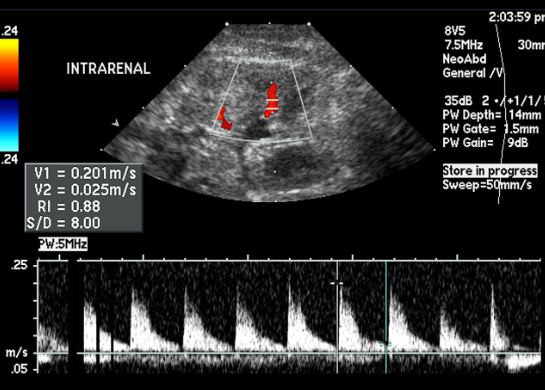
Considering the RI on this image, which is most likely the diagnosis?
Medical renal disease
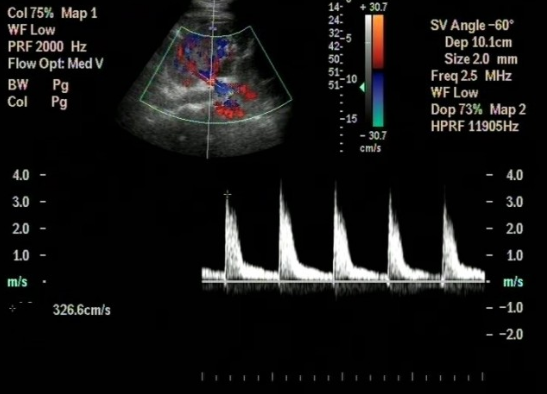
Is this a normal PSV?
No (Too high)
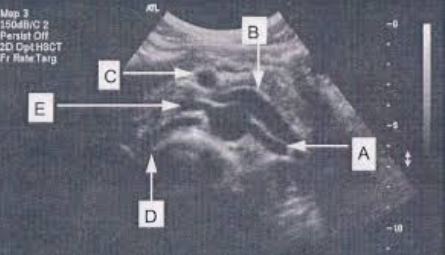
Identify structures:
A=Left renal artery
B= Left renal vein
C= SMA
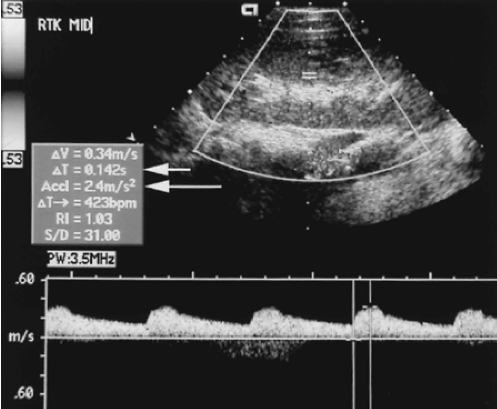
Is the sonographer correct documenting the RI is 1.03? Please explain.
If we estimate the EDV is 14 cm/sec, what is the RI using RI formula. Please include formula in your answer.
1.No because they put one of the calipers at the wrong spot at the baseline of the waveform instead of the EDV
2.
Formula = S - D / S = RI
34 - 14 / 34 = 0.59
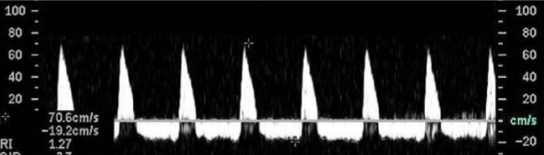
This is a waveform from mid portion of MRA. What does this waveform indicate?
Renal vein thrombosis
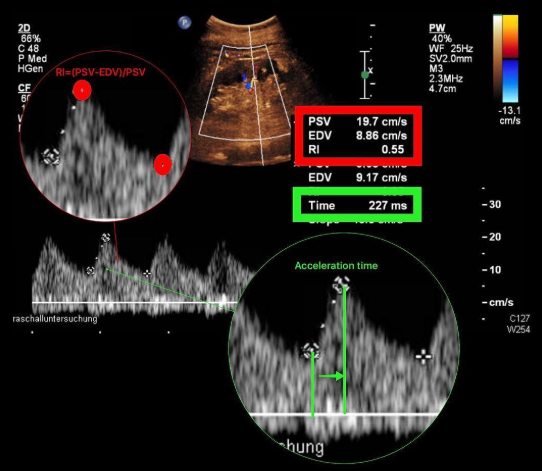
Is the acceleration time on this waveform normal?
no (Too slanted/time wrong)
Case Study: The RT Kidney is measuring 9.72 cm. However, the LT Kidney is measuring 5.4 cm in your 76 y/o patient w/ c/o uncontrolled HTN.
What does the difference in renal length possibly indicate?
Lt hemodynamically significant stenosis
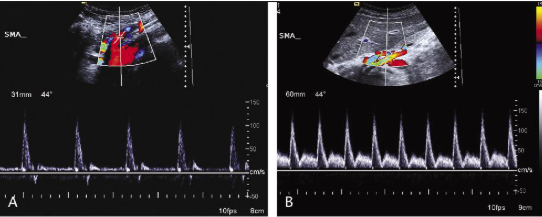
Which SMA waveform is post-prandial?
B
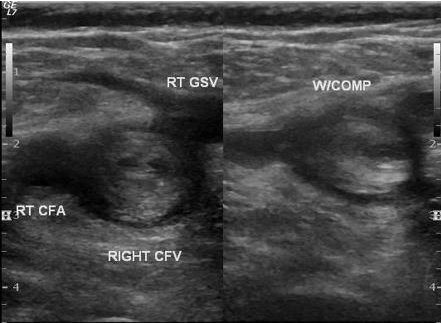
Patient diagnosed with acute DVT. As scanning sonographer, you obtained this image. Select appropriate sonographic findings for acute thrombus.
Dilated vein
hypoechoic
isoechoic
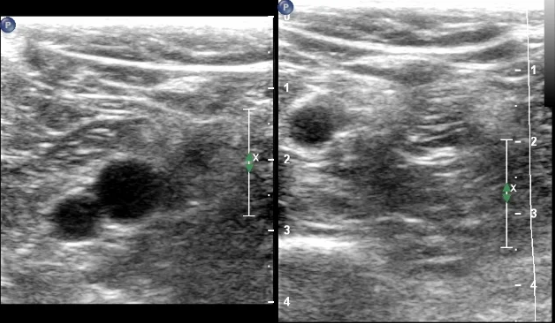
This image indicates a complete compression.
True
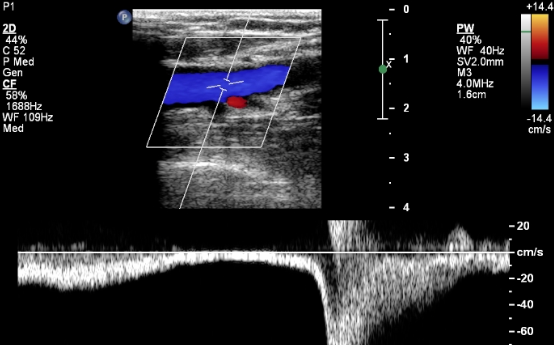
This waveform indicates
Augmentation
SAG compressions of the venous system is necessary to exclude presence or absence of thrombus.
False
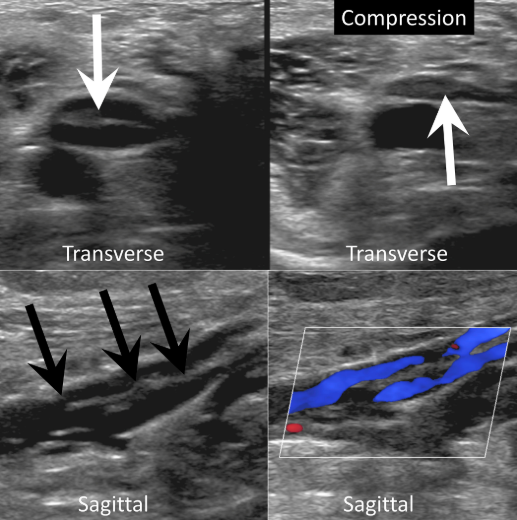
This image indicates
Chronic thrombus
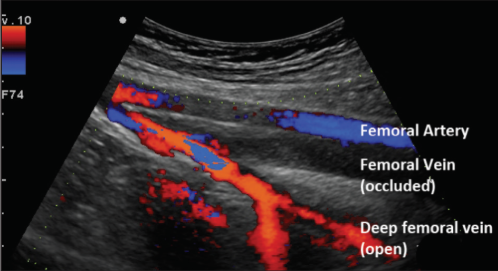
Is this image sufficient to diagnose DVT? Explain
No, we need a TRV with compression image
Which items will help identify whether a vein is superficial or deep?
presence or absence of adjacent artery
vein in superficial fascia
vein in muscular compartments
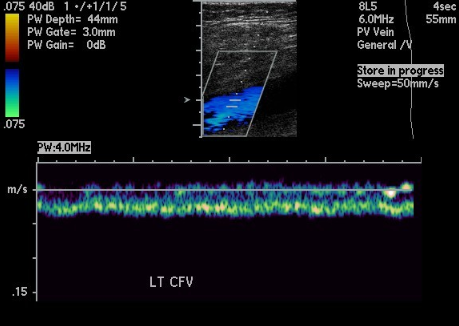
This waveform indicates
Proximal obstruction
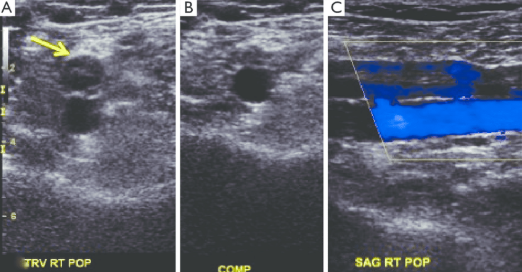
Identify the following statements that describe this image obtain in patient with c/o periodic swelling RLE x 6 months with HX of DVT x 6 months ago post RT knee surgery.
Partial compression
Chronic DVT
Hyperechoic intraluminal echoes
Recanalized
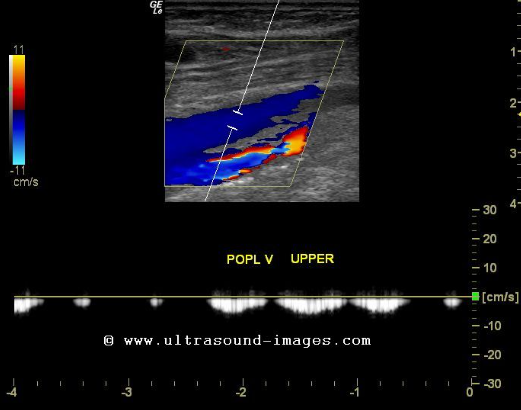
This waveform indicates
Phasic

Which column associated with chronic thrombus?
B
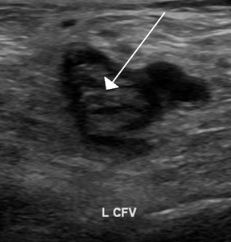
The findings in this image indicate
Acute thrombus
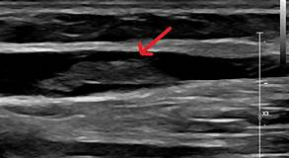
Patient presents with RUE swelling x 2 days. You obtain this image in the basilic vein. Is this a DVT?
no
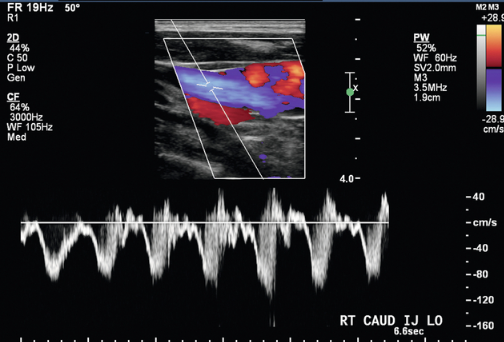
In your UE venous exam, you obtain bilateral IJ waveforms as indicated in this ultrasound image. These waveforms indicate that
SVC patent
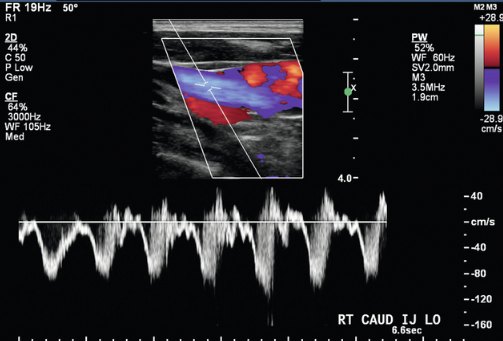
Select the best description for this IJ waveform.
Pulsatile
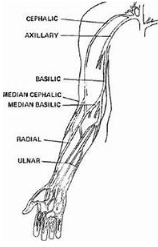
The cephalic vein is
Lateral
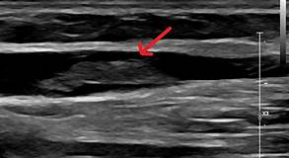
Patient presents with RUE swelling x 2 days and recent antibiotics administered through peripheral IV in the right arm.
What is most likely cause of thrombus formation?
Vessel wall injury
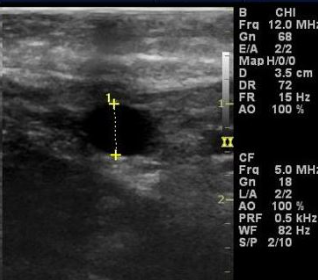
This is AP diameter measurement of the vein.
Yes
The axillary vein is considered proximal or distal to radial vein.
Proximal
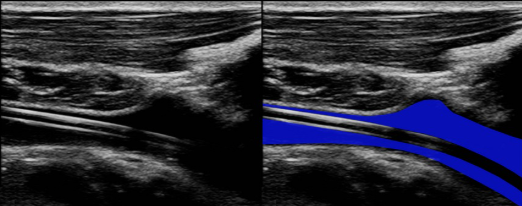
This ultrasound image demonstrate intraluminal catheter. Color is traveling around catheter. Considering catheter placement, patient is at a higher risk for developing thrombus.
Yes
All of the following are symptoms of venous thrombosis EXCEPT:
Cold leg
The basic vein is considered
Medial
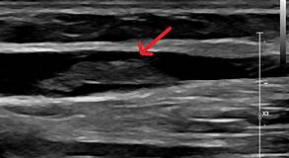
This would be characterized as acute appearing thrombus in the basilic vein.
Yes
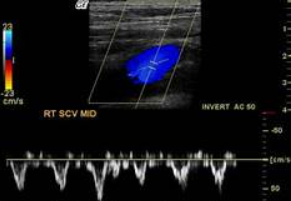
This is a normal subclavian waveform.
Yes
Which type of thrombus formation is more common in the upper extremities, superficial thrombus or deep vein thrombosis?
Superficial
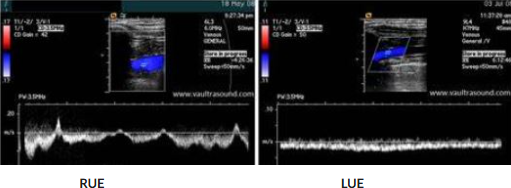
Patient presents with LUE arm swelling x 3 days. Consider waveforms.
What is the finding?
Obstruction proximal to left subclavian vein
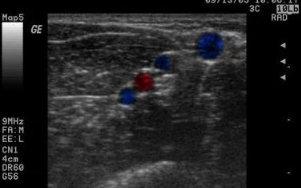
This is an image of the RUE. Which vessel is medial?
Basilic vein
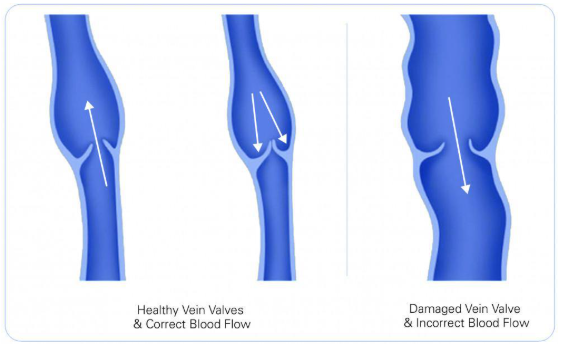
Identify what is true in this condition represented in image with damaged valves.
Venous ulcers indicate severe venous disease
Blood flow moving in both directions
Dilated veins
Increase venous volume
Increase venous pressure
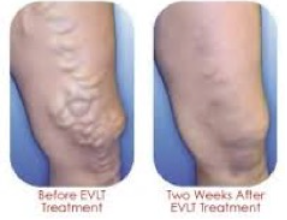
In this image of patient pre and post endovascular ablation, is the vein medial or lateral leg?
medial
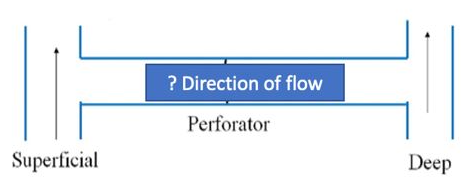
Which direction is venous flow?
Superficial to deep system
Which statement is not true?
Thrombus in the GSV is considered deep vein thrombosis.
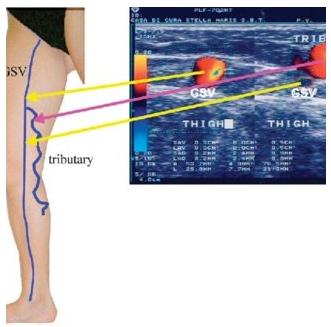
Which vessel is the common location for venous incompetency to form?
Tributary
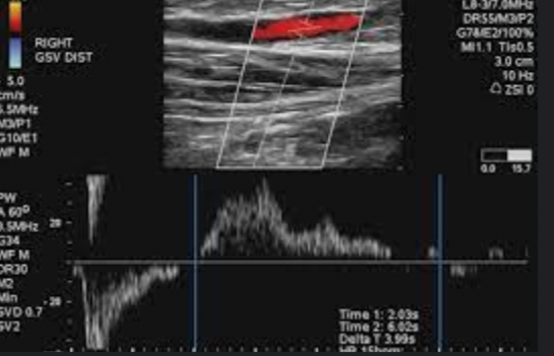
Patient c/o heavy, tired RLE with persistent swelling relieved with elevation of leg. Will this ultrasound finding explain symptoms
yes
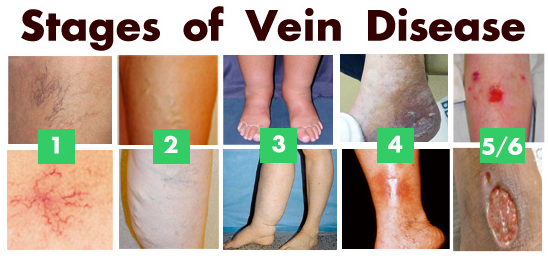
Which numbers indicate severe venous disease?
5/6
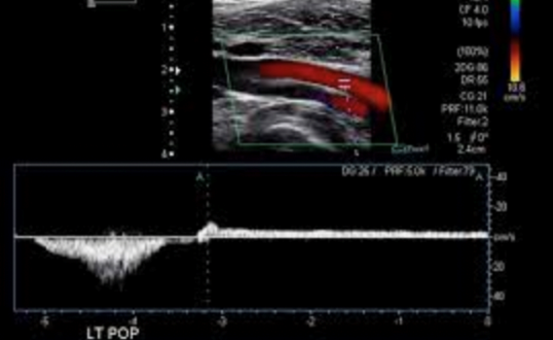
What does this image indicate?
Deep vein valvular insufficiency
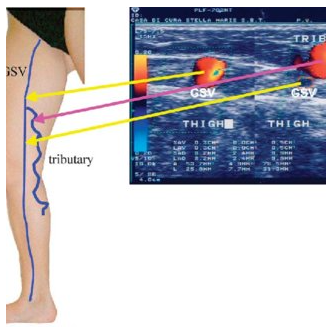
Tributary is a superficial vein.
true
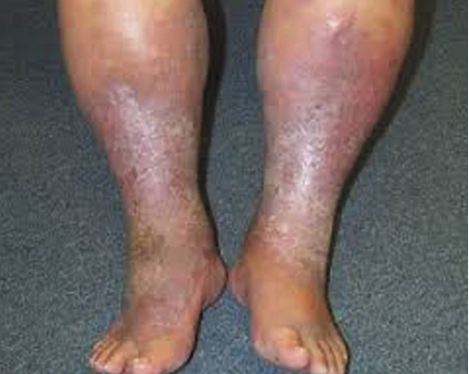
Which condition is most likely cause of patient's symptoms seen in this image?
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
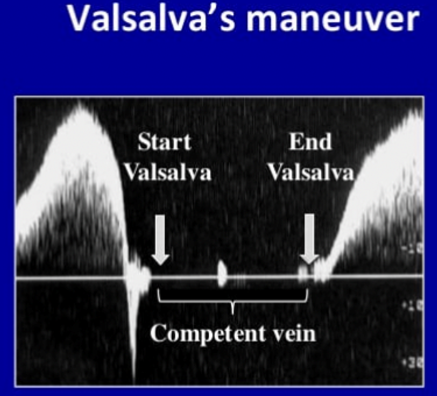
What is occurring during the Valsalva Maneuver?
Valve closure
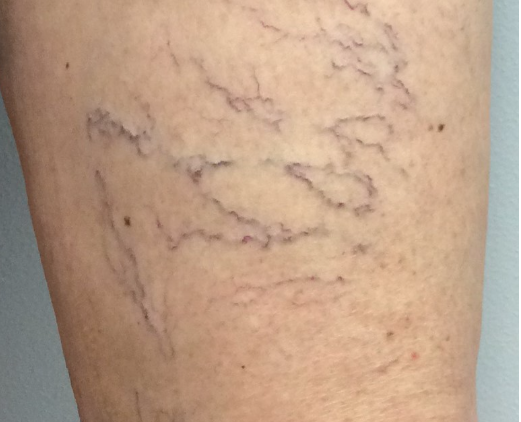
Which is the best term to define veins in this image?
Spider veins