L13 Recombinant DNA and Nucleic Acid Structure
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is Next Generation DNA Sequencing?
-Massively Parallel sequencing of many DNA's concurrently
-Can produce 1.2 billion reads of ~100 base pairs each in single experiment
-Responsible for current explosion of genetic and genomic data
What is the Human Genome?
-3.2 billion nucleotides
-finished in 2001-2004
What main conclusions have come from the human genome?
-about half is various sequence repeats
-~80% is transcribed to RNA
-!1.2% encodes for protein
-Contains ~21,00 protein-encoding genes (Open reading frames, ORFs)
-Only a fraction of protein encoding genes are unique to vertebrates
-Most humans differ on average by about 1 nucleotide per 1000
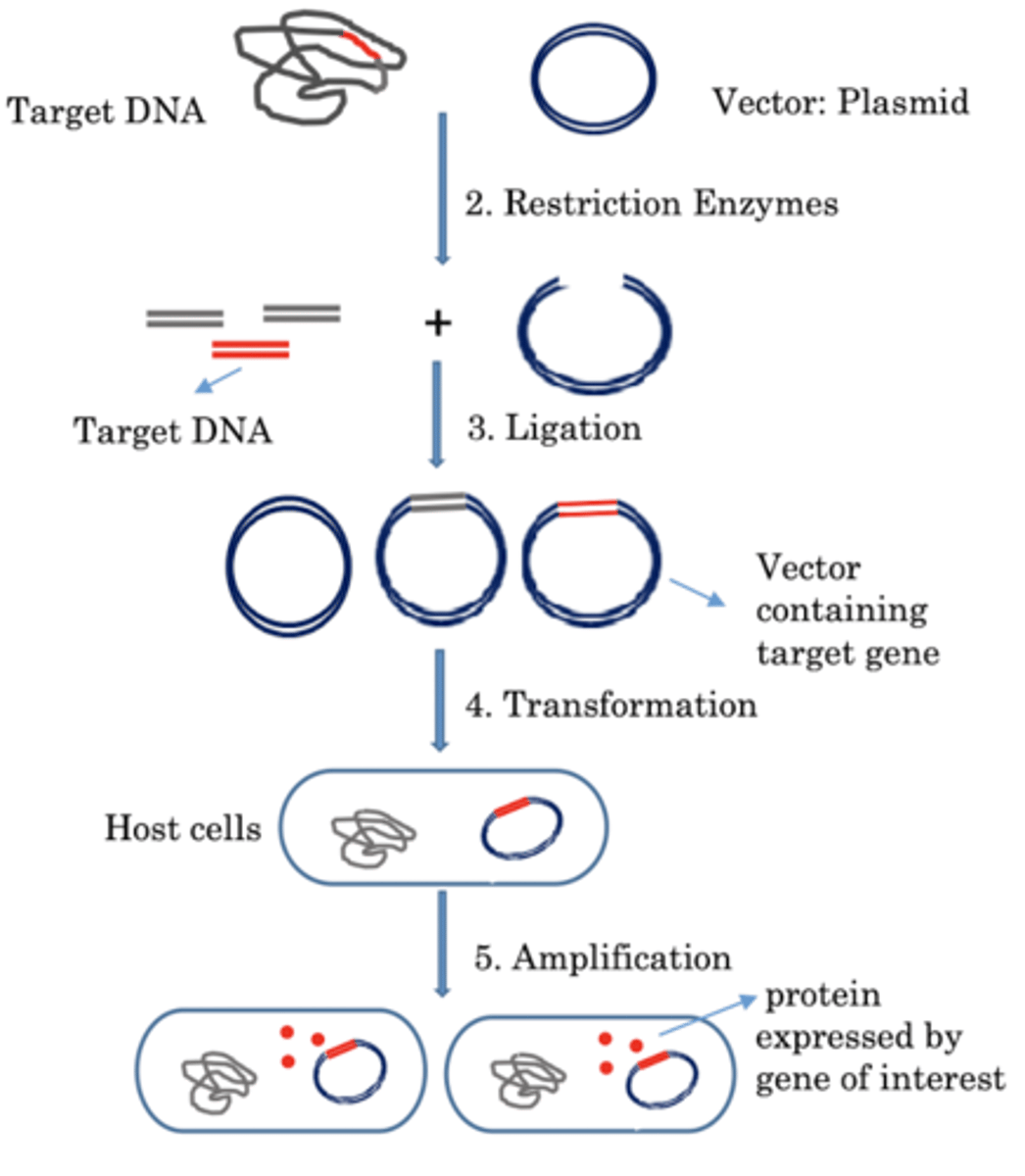
Explain the construction of recombinant DNA molecules
So basically theres this circle and its called the cloning vector. And then theres this straight line called the foreign DNA. The cloning vector and foreign DNA are cut with restriction endonuclease to generate sticky ends. The sticky ands are covalently joined by DNA ligase. And the result is a chimeric DNA containing a portion of foreign DNA inserted into the vector.
What is a vector?
A DNA molecule capable of carrying a foreign DNA sequence and replicating in a host cell
Describe the steps of molecular cloning.
1.Isolate DNA from and DNA source
2.Use a restriction enzyme to generate fragments of DNA
3.After separation of the DNA fragments, each can be used to generate a recombinant molecule
4.Introduce recombinant molecule into new host
What is the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
-Convenient way of obtaining large numbers of copies of a specific DNA sequence
-Uses two synthetic ssDNA primers
-Anneal to each strand at the ends of the region to be amplified
What are the 3 steps of PCR
1.Heat to melt apart DNA
2.Cool to anneal primers
3.Intermediate temperature to extend the primers
*facilitated by the use of heat-stable DNA polymerase from thermophilic organisms
PCR amplification
-amplification of template is exponential
-template can be dsDNA or ssDNA
-Mar be present down to a single molecule
-30 cycles yields 1 billion-fold amplification
iClicker Question:
If PCR amplification using human genomic template is working properly, it produces a lot of
the human DNA that is in between the sequences that are complementary to the primers used
What is a transgene?
a transplanted foreign gene
What does transgenic mean?
a multicellular organism expressing a gene from another organism
What is gene knockout?
the use of genetic engineering to inactivate or remove one or more specific genes from an organism
What is DNA Fingerprinting?
-Forensic DNA testing
-Relies on DNA sequence variations (polymorphisms) among people
-Short tandem repeat (STR) sequences occur at various lengths
iClicker Question
Blood from a crime scene and 4 suspects was PCR amplified with fluorescent primers associated with 3 STR loci: D3S1358, vWA, and FGA. Electrophoretograms are shown. Who did it.
Suspect 3 (the one that matched the blood stain)
B-DNA Structure
-Most common biologically relevant form
-Two antiparallel polynucleotide strands wound in a right-handed helix of 20 angstroms
-planes of nucleotide bases occur in H-bonded pairs are nearly perpendicular to helix axis
-Each base pair has approximately the same width
-Canonical B-DNA helix has ~10 base pairs per helical turn and has a pitch of 34 angstroms per turn
Alternative DNA Conformations
-Forms do not freely interconvert
-physical conditions or protein binding
-DNA has limited flexibility
-X-ray structures of B-DNA shows that individual residues can depart from the average B form values
B-DNA
(sodium salt) (Watson-Crick structure) hydrated form
A-DNA
-partially dehydrated DNA duplexes
-DNA:RNA heteroduplexes
-dsRNA
-20 degree tilt of base pairs
Z-DNA
(zigzag conformation) left-handed helix formation occurs in transcription due to torsion
What is supercoiling of DNA?
-supercoiling facilities the biological processes:
-packaging of DNA
-replication
-transcription
-linear and circular DNA can be relaxed or supercoiled in shape
What happens when DNA is underwound?
-it twists to the right
-most naturally occurring DNA is negatively supercoiled
What creates positive supercoils?
Overwinding in the direction of the helix
Supercoiled DNA topology
L=T+W
L
-L=linking number
-number of times one DNA strand winds around the other
T
-T=twist
-Number of complete revolutions one strand makes around the duplex axis
-normally # of bp;s divided by 10.5
W
W=writhing
-Number of turns duplex axis makes around the superhelix axis
Number of coils in DNA cannot be altered without____________.
cleaving at lease one of its strands
Topoisomerase I
creates transient single-strand breaks
Topoisomerase II
transient double strand breaks
Forces that stabilize nucleic acid structure
-Hydrogen bonding of bases
-Stacking interactions
-Cations shield repulsive forces of negative charges
What is hydrogen bonding of bases?
-thought to be the "glue" to hold the 2 strands together
-contributes only weakly to stabilization
-bases form H-bonds to water in denatures form
-some non-Watson-Crick base pairs possible
-occur in RNA
What are stacking interactions?
-Hydrophobic interactions
-Van der Waals stacking interactions
-enthalpically favorable
-differs from hydrophobic effect driving protein folding
-may be due to increased polarity of bases
-stacking energy is sequence dependent
-G-C base pairs are more stable die to improved stacking
-nearest neighbor
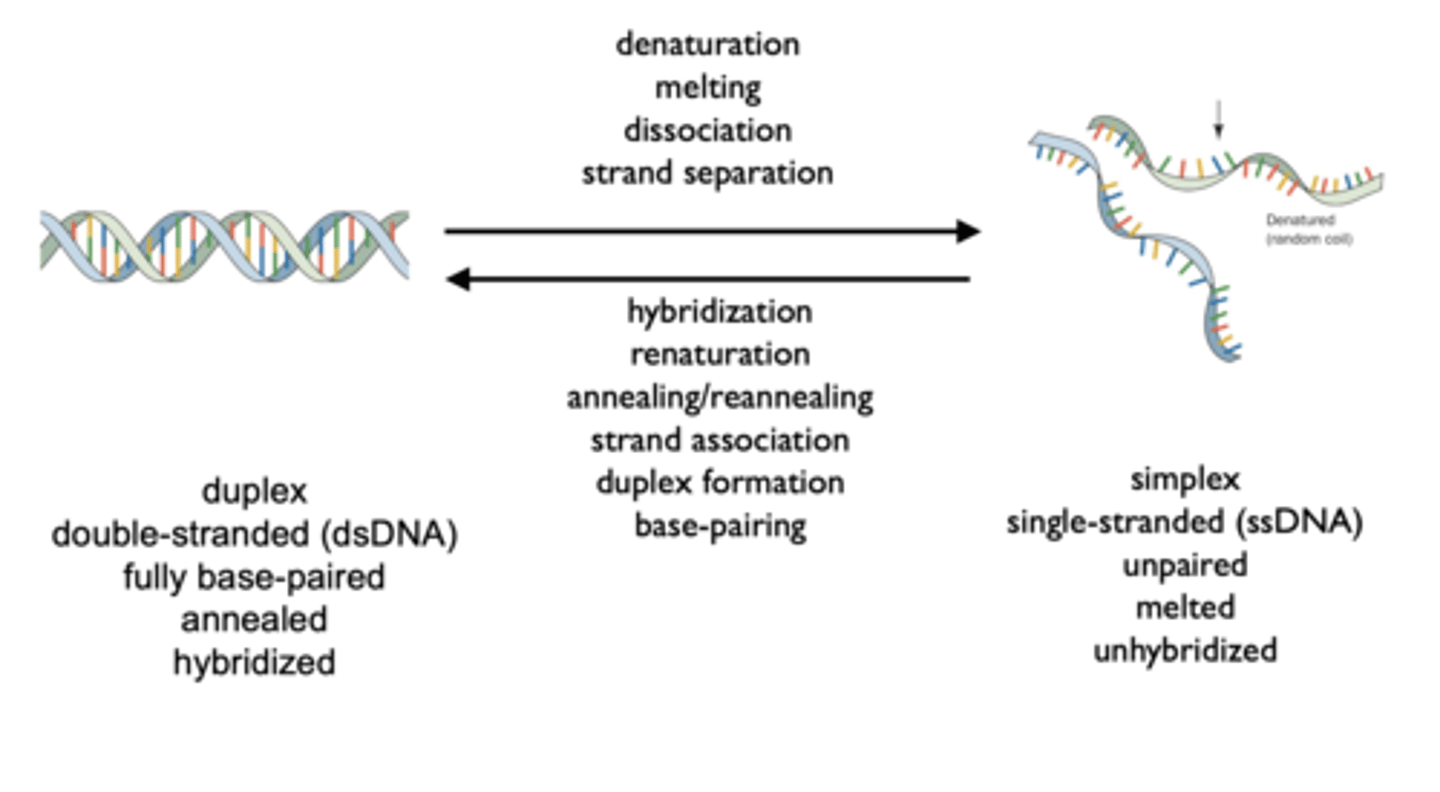
Terminology of dsDNA versus ssDNA
Mechanisms of Stabilization/Destabilization of Duplex Nucleic Acids
-Temperature
-Ionic strength (monovalent cations)
-pH
-hydrogen bonding
-Denaturants
-Polyvalent cations
Temperature
-higher temp. reduce hydrophobic base stacking interactions (Higher temp. destabilizes duplex, lower temps stabilize)
Ionic strength (monovalent cations)
-low ionic strength enhances charge repulsion (destabilizes
-high ionic strength reduces charge repulsion (stabilizes)
pH
-acidic pH removes phosphate charge repulsion (precipitates)
-neutral pH allows for normal phosphate charge repulsion and base pair
Hydrogen bonding
-(stabilizes)
-Alkaline pH destabilizes baise pair hydrogen bonds (destabilizes)
Denaturants
(urea, formamide)
-Increase solubility of bases (reduce stacking energy)- destabilizes duplex
Polyvalent cations (Mg2+, Ca2+, polyamines)
-decreases charge repulsion (stabilizes duplex) - in low concs
At what wave length do purines and pyrimidines strongly absorb UV light?
around 260nm
Does base stacking increase or decrease UV aborbance?
decrease
Does denaturation increase or decrease UV aborbance?
increase
Is dsNA more or less colored that ssNA?
less colored, hypochromic
Does RNA ever contain double stranded segments?
Yes, frequently
How many of 5S rRNA bases are paired?
about 2/3
tRNA
-contains several unusual H-bonding of bases
-Post-transcriptionally modified bases