RMS - Factorial Design
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
factorial design
A study in which there are two or more independent variables, or factors.
Purpose: test for interactions
Is a factor also a confound?
No, because a confound is both related to dependent and independent variable and therefore affects result
A factor is a variable that relates to dependent variable only.
Advantages of factorial design
• more than one possible main effec
• you can study interaction effects
Disadvantages of factorial design
• you need more participants (at least twice as many) for the same accuracy
interaction effect
A result from a factorial design, in which the difference in the levels of one independent variable changes, depending on the level of the other independent variable → a difference in differences. Also called interaction.
What does it mean when something is a crossover interaction?
When it can be said that: “it depends” for an interaction → e. g. for liking for food and food temperature
→ describes a form of an interaction effect
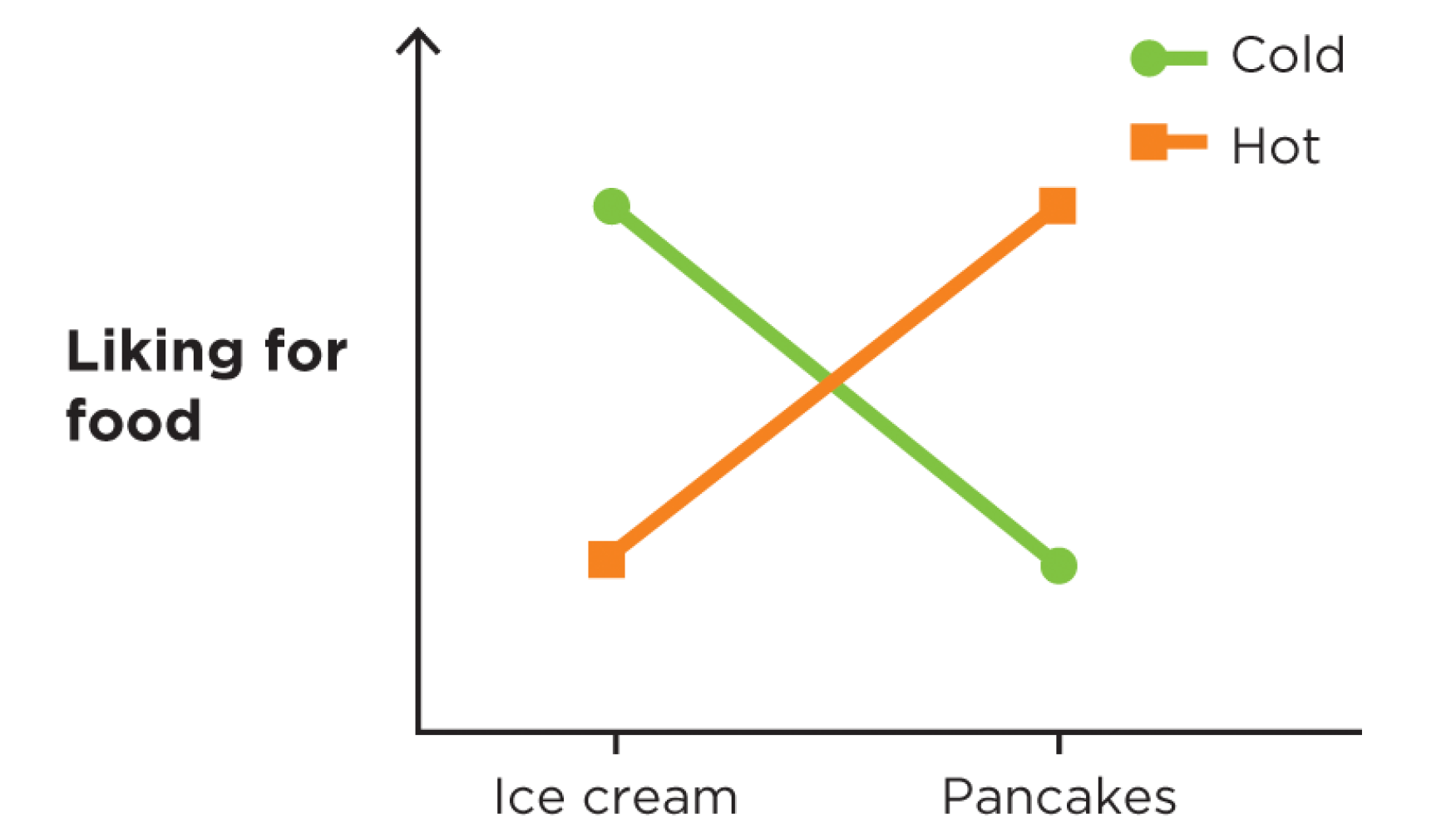
What does it mean when something is a spreading interaction?
When a pattern of an interaction can be described with “especially” → e. g. for toast with bacon/avocado
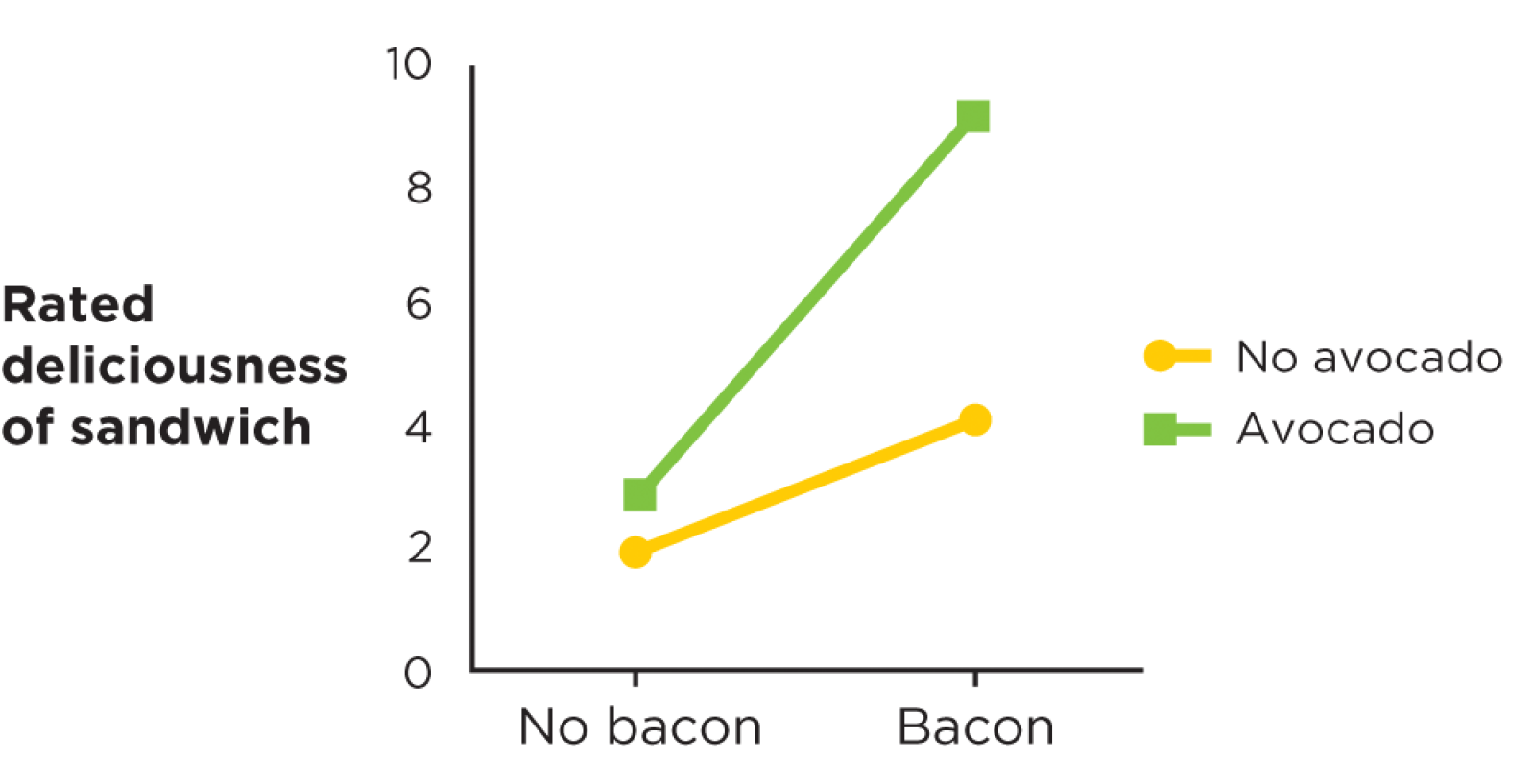
What does it mean when you “cross” two independent variables?
You study each possible combination of the independent variables
cell
A condition in an experiment or in a simple experiment, a cell can represent the level of one independent variable, in a factorial design, a cell represents one of the possible combinations of two independent variables.
What’s a 2x2 (two-by-two) factorial design?
Two levels of one independent variable are crossed with two levels of another independent variable → four cells
participant variable
A variable such as age, gender, or ethnicity whose levels are selected (i.e., measured), not manipulated.
What’s a moderator?
• moderator = independent variable that changes relationship between another independent variable and a dependent variable
• → moderator results in an interaction
How can you determine an interaction by looking at a line graph?
• whenever you have parallel (or “parallel-ish”) lines, it means that there is no interaction
Main effect
In a factorial design, the overall effect of one independent variable on the dependent variable, (averaging over the levels of the other independent variable) → simple difference
What’s a marginal mean?
Arithmetic means for each level of an independent variable, averaging over levels of the other independent variabel
How can you determine a main effect?
• Marginal means → calculate means for both conditions separately
• if they differ, there is a main effect
• or look at the graph
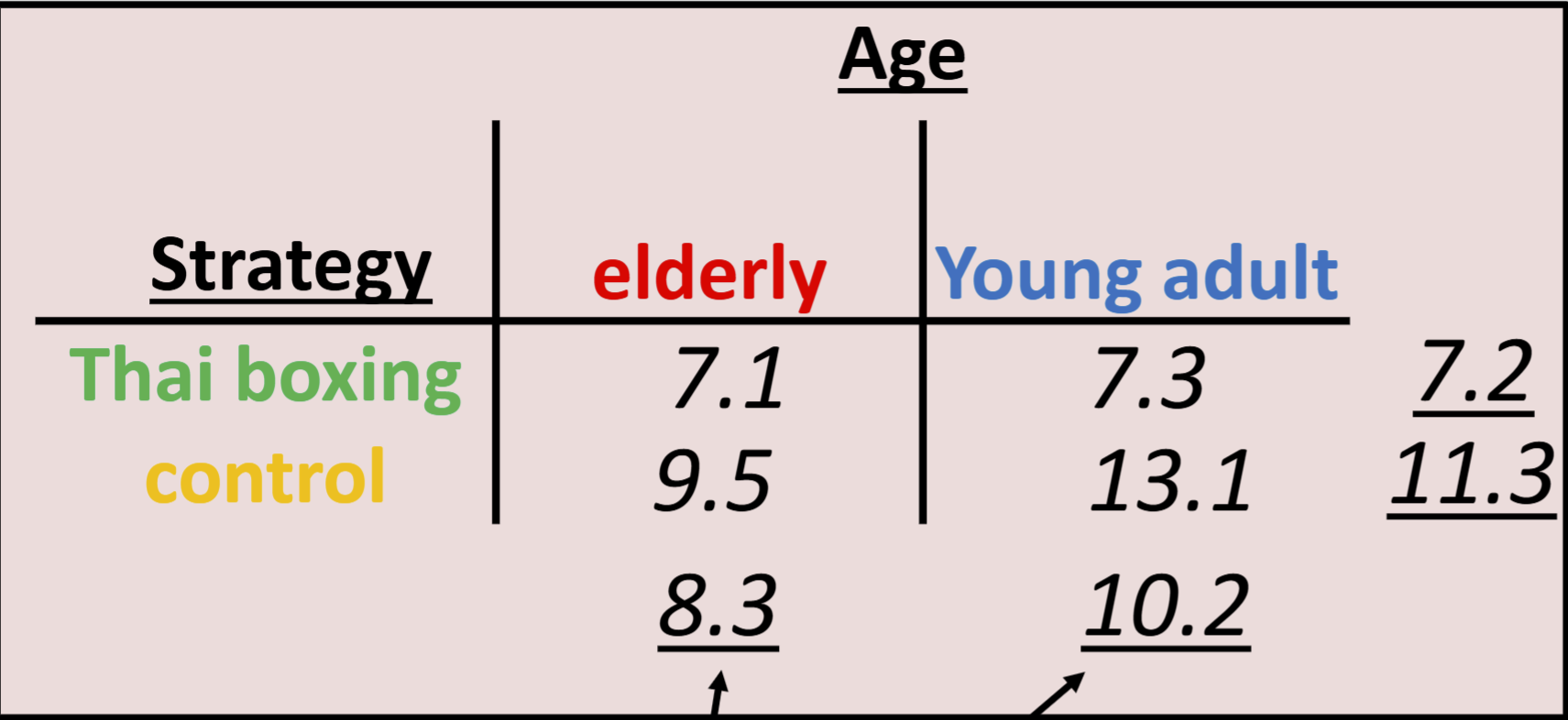
How can you estimate how large each main effect is?
• calculate difference between marginal means
• compute 95% confidence interval of this difference → if it doesn’t include zero, then difference between marginal means is “statistically significant main effect”
How can you determine an interaction by using the marginal means?
• calculate difference between groups within factors
• there is an interaction effect, if the values differ → for more than two factors, it’s enough if at least one variable differs
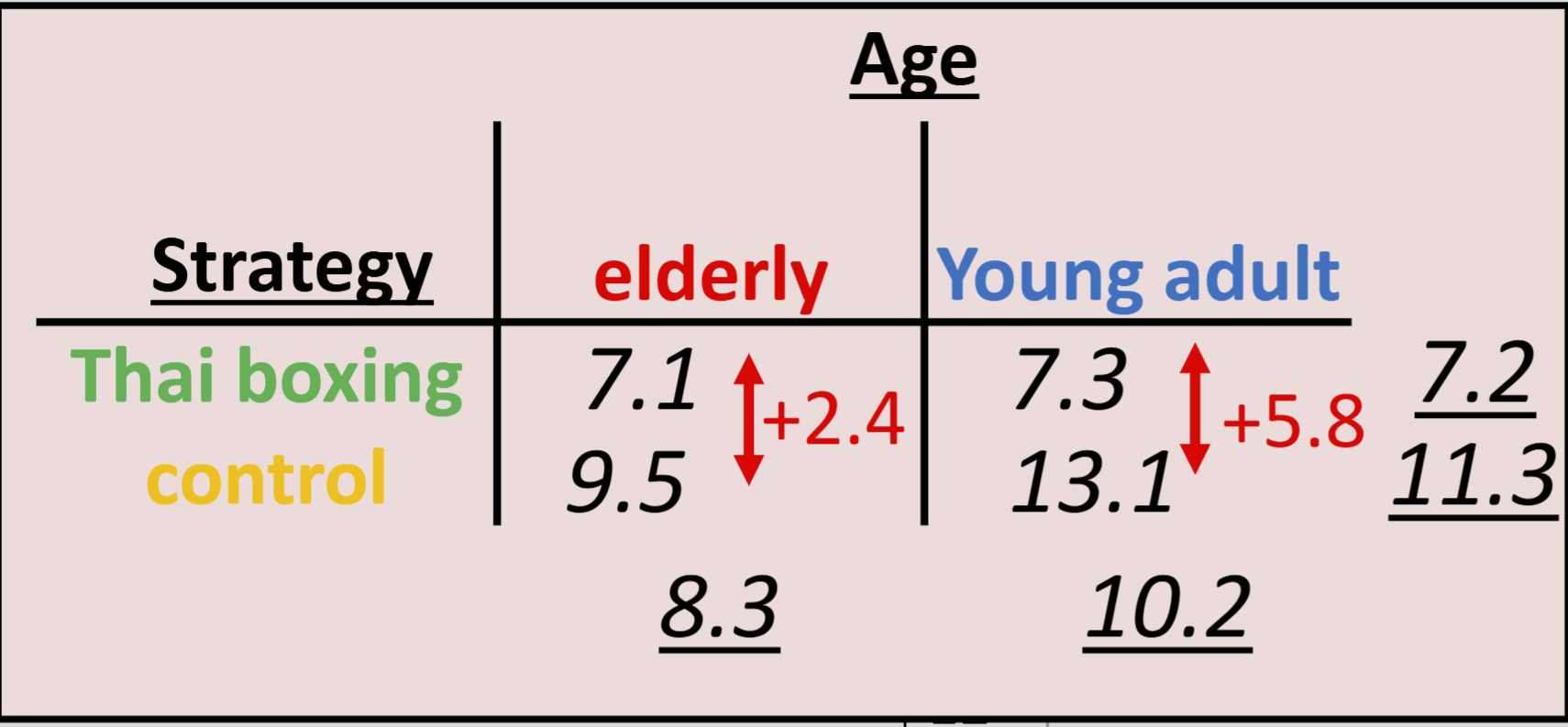
What’s more important: an interaction or a main effect?
Interaction almost always more important
What happens in a mixed factorial design?
One independent variable is manipulated as independent-groups and the other is manipulated as within-groups
Which pattern does the notation for factorial designs follow?
• __ x __
• quantity of numbers indicates number of independent variables
• value of each of number indicates how many levels there are for each independent variable
• when you multiply numbers, you get total number of cells in design
What’s a 2x2x2 factorial design?
When you have 3 independent variables
What’s a 2x3 factorial design?
When you have two independent variables, but one has two levels and the other has three levels
When do designs with more than two groups/conditions not have an interaction effect?
• When all the lines in a graph are parallel
• When the differences between all the means in one margin are equal → you have to calculate the differences between each values, so for 3 conditions there are 2 differences, for 4 conditions there are 3 differences, …
How does the 2x2x2 factorial design influence the tables?
You draw two tables in which the same 2 factors are presented, the third factor influences which each table is for → one condition for each table
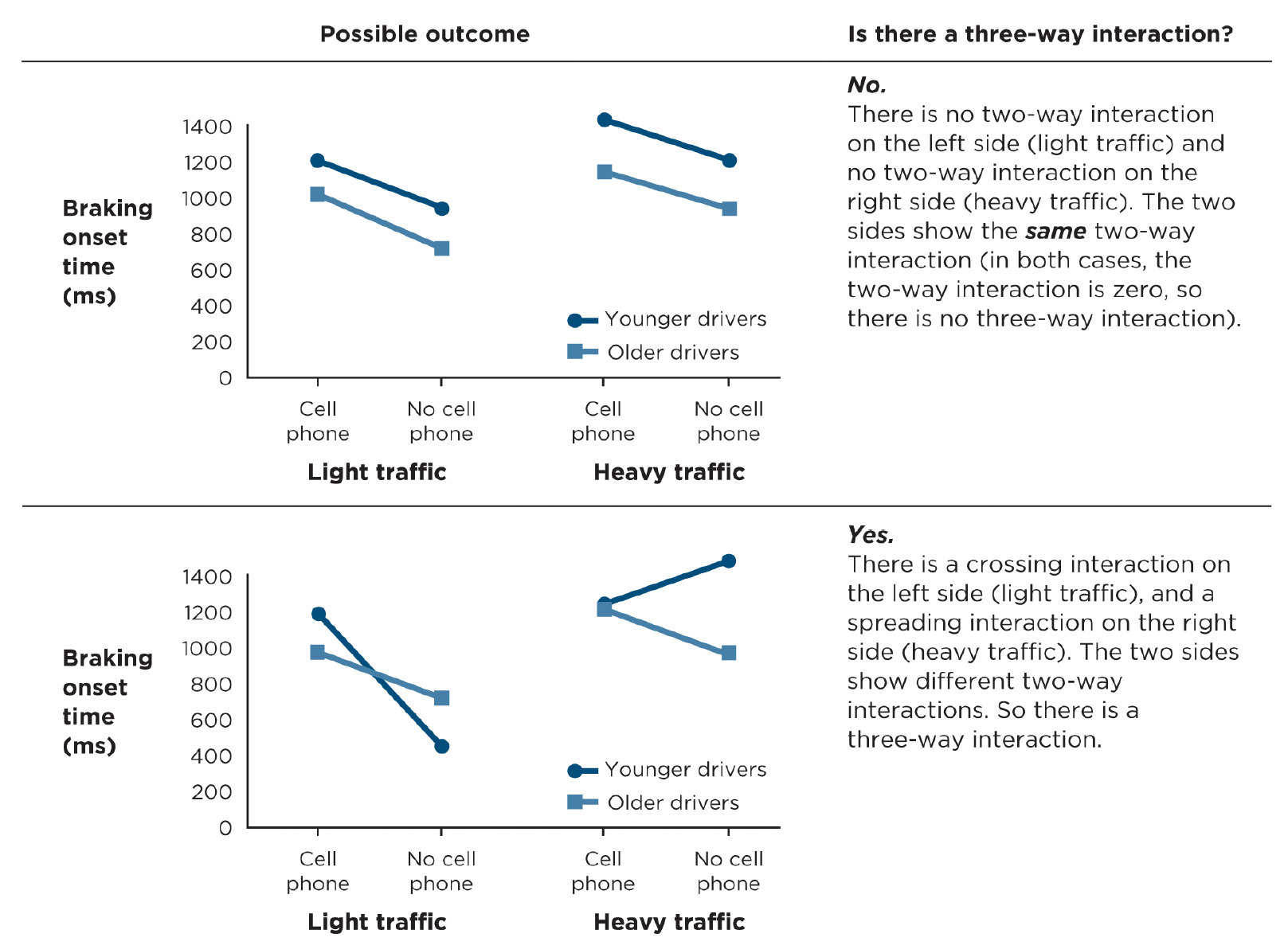
What’s a three-way interaction?
When the two-way interaction between two of the independent variables depends on the level of the third independent variable
How can you determine a three-way interaction based on a graph? → 2 options
• when there is a two-way interaction for one level of a third independent variable but not for the other
• when a graph shows one pattern of two-way interaction on one side but a different pattern of two-way interaction on the other side
What are different types of factorial variations?
• between-groups factors
• you can also use within-groups factors
• if you have both independent-groups and within-groups factors: mixed factorial design
What’s a prerequisite to be able to make inferences from the marginal mean?
Size of all the groups must be equal