memory
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
input
process of receiving info through 5 senses
processing
operations we perform on sensory info in our brain
storage
retention of info in our memory
encoding
turning sensory info into a form that can be used
retrieval
recall of stored memories to our conscious
MSM model structure
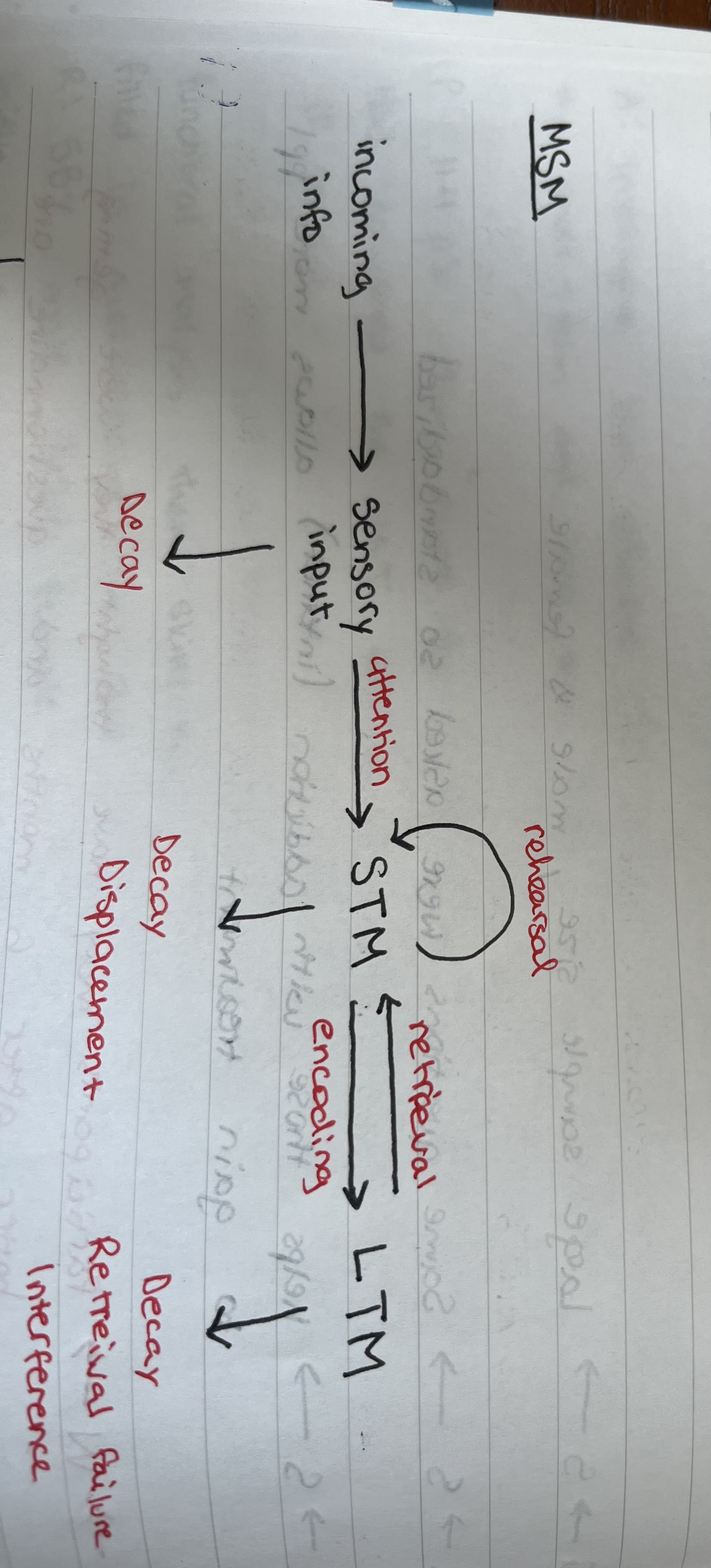
3 registers
encoding | capacity | duration | |
sensory | 5 senses | unlimited | 2 seconds |
STM | acoustically | 5-9 items | 15-30 seconds |
LTM | semantically | infinite | lifetime |
strengths of MSM
lots of experiment to support 3 separate stores
practical application for student revision
inspired further research
weakness of MSM
too simplistic
overstates role of rehearsal
reconstructive memory
refers to how memory is not an exact copy but is influenced by our schemas
omissions
when we leave out unfamiliar details
transformation
when details are changed to make them more rational and familiar
familiarisation
when we change out unfamiliar details to align with our schemas
rationalisation
when we add details to give more meaning
retrograde amnesia
when you don’t remember what happens before the injury but can make new LTM
anterograde amnesia
when you remember what happened before injury but unable to make new LTM
Peterson and Peterson: Aim+ procedure
investigate the duration of STM when rehearsal is prevented
24 uni students volunteers
lab experiment
trigrams
had to recall trigram after counting backwards in 3s or 4s for an interval of 3,6,9,12,15,18 secs
Peterson &Peterson Results & Conclusion
3sec-80% recalled
6 secs- 50% recalled
18secs - less than 10%
STM has duration of 18 secs when rehearsal is prevented
Peterson and Peterson GRAVES
G-24 uni students -small sample size-same age
R-lab experiment-replicable-no EVs
A-helpful for revision
V-artificial setting and task
E-volunteers so consent given