SBI4UI - Cellular Respiration Review
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
kinetic vs potential energy
kinetic: the energy possessed by a moving entity
potential: stored energy that will be released when a chemical reaction occurs
exergonic vs endergonic reactions
exergonic: reactions that release free energy
endergonic: reactions that absorb energy
catabolic vs anabolic pathway
catabolic: complex molecules are broken down into simpler compounds — exergonic rxn
anabolic: builds complex molecules from simpler ones — endergonic rxn
how do our cells harness energy? (3)
macromolecules fuel chemical reactions → contributes to making of energy.
harnessed by:
forming new bonds as new compounds are created
moving electrons between different molecules (using electrons to help complete chemical reactions)
making & breaking down ATP
what is ATP
main source of energy
what does phosphorylation mean?
the gaining of a phosphate group
reduction reaction
molecules that gain electrons are reduced
oxidation reaction
molecules that lose electrons are oxidized
what do our cells use ATP for? (3)
chemical reactions — helps complete an endergonic reaction
movement, motion, mechanical work — helps move cell parts, chromosomes, & muscle fibre contraction
moves substrates into & out of the cell
what happens during substrate level phosphorylation?
enzyme transfers a phosphate group to an ADP directly. ADP → ATP
where does substrate level phosphorylation occur?
glycolysis: cytoplasm
krebs cycle: mitochondria matrix
pros and cons of substrate level phosphorylation
pro: simple process (fast)
con: very few ATP made
what happens during oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)?
multi-step chemical reactions which uses energy harnessed in electrons (from redox reactions)
where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
mitochondria
pros and cons of oxidative phosphorylation
pro: produces a lot of ATP
con: very complex
what is the purpose of glycolysis?
to break down a 6 carbon molecule into 2 smaller pyruvate molecules (3 carbon molecules)
where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
what is coming and going during glycolysis?
input: glucose, 2 ATP
output: 2 pyruvate molecules, 2 NADH, 2 ATP
Products of glycolysis (what is the function/destiny of each product)
2 pyruvate molecules → mitochondria for pyruvate oxidation
2 NADH → Electron transport chain
2 ATP → net
what is the purpose of pyruvate oxidation?
break down 3 carbon pyruvate molecules into 2 carbon Acetyl CoA molecule to release all available energy
where does pyruvate oxidation occur?
mitochondrial matrix
what is coming and going out at each step during pyruvate oxidation?
input: 2 pyruvate molecules, NAD+, 2 CoA (added to acetyl molecule)
output: 2 Acetyl CoA, 2 CO2, 2 NADH
Products of pyruvate oxidation (what is the function/destiny of each product)
2 Acetyl CoA → enters kreb’s cycle
2 CO2 → gets released as waste
2 NADH → electron transport chain
what is the purpose of krebs cycle
complete oxidation of Acetyl CoA made during pyruvate oxidation
where does krebs cycle occur
mitochondrial matrix
what is going in and out during the krebs cycle
input: 2 Acetyl CoA
output: 6 NADH, 2 ATP, 2, FADH2, 4 CO2 gets released as waste
krebs cycle — major molecules: what happens to Acetyl CoA, what is oxaloacetate & citrate
Acetyl-CoA (2C) + Oxaloacetate (4C) → Citrate (6C)
Products of Krebs cycle (what is the function/destiny of each product)
4 CO2 → exhaled
6 NADH, 2 FADH2 → electron transport chain
2 ATP → useable energy
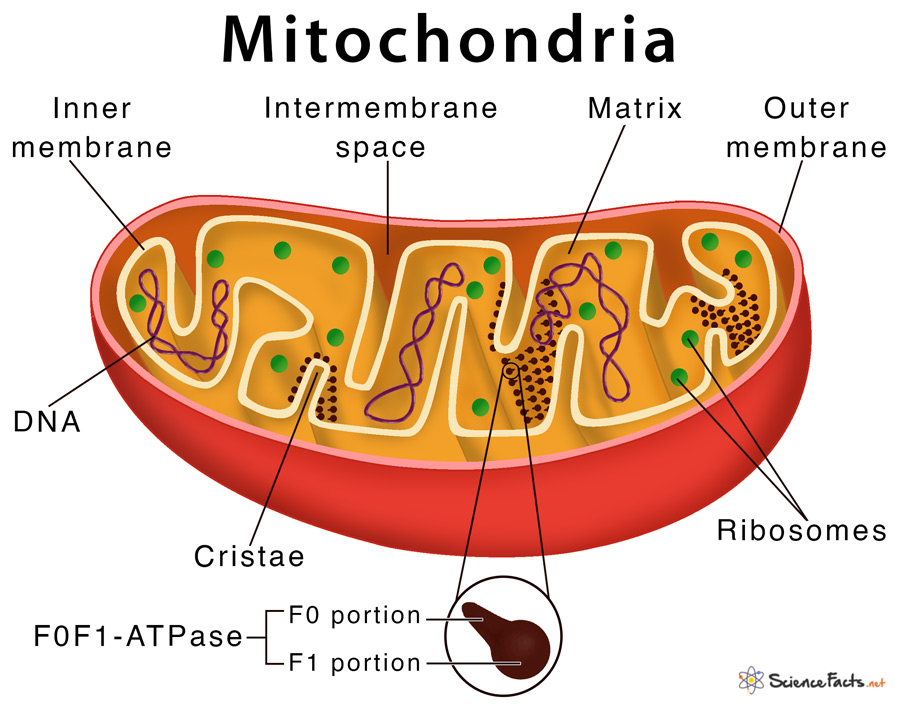
where does the electron transport chain occur
mitochondrial matrix
across the inner mitochondrial membrane
what is the purpose of the electron transport chain
to harness energy from NADH and FADH2 to pump H⁺ and drive ATP production.
what is coming in and out of the electron transport chain
input: 10 NADH, FADH2, O2, H+,
output: ATP, H2O, NAD+, FAD
what are the steps of the electron transport chain?
(where electrons come from and are transferred to)
as electrons from NADH and FADH2 move through the components of the ETC, energy is released
what are the steps of the electron transport chain?
(how do the electrons drive hydrogen movement)
the energy release from electrons pumps H+ across the INNER membrane space → INTER MEMBRANE space
what are the steps of the electron transport chain?
(why is hydrogen movement important)
the high amounts of H+ create a H+ gradient, which drives ATP production
how does chemiosmosis work?
H+ ions move down their concentration gradient back into the matrix through AN ATP synthase channel.
ATP synthase produces ATP by phosphorylation (ADP + Pi → ATP)
what are the products of electron transport?
ATP, H2O, NAD+, FAD
how many ATP is produced per 1 electron carrier?
H+ = 1 ATP
1 NADH → 3 H+ → 3 ATP
1 FADH2 → 2 H+ → 2 ATP
what is the role of oxygen in cellular respiration (4)
no final acceptor of electrons
no new electrons can go in
inhibits electron flow
NAD cannot be NADH (vice versa) & FAD cannot be FADH2 (vice versa)
what is the role of water in cellular respiration
produced when O₂ combines with electrons + H⁺.
what is protein catabolism?
what is the waste product and what happens to the remaining molecule
the break down of amino acids for energy via cellular respiration
NH3 → waste product & remaining amino acid enters cellular respiration pathways
what is lipid catabolism?
what happens to the glycerol backbone? what happens to the fatty acids?
glycerol → glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and continues through the cellular respiration pathway
fatty acids → Acetyl + CoA → Acetyl CoA
how is aerobic respiration regulated?
regulated by oxygen.
No O2 = no final electron acceptor = electrons entering & exiting = inactive ETC = no ATP
anaerobic processes — what is fermentation?
uses an organic molecule as a final electron acceptor but does not use an electron transport chain so it is not considered a form of respiration
anaerobic respiration — what is lactate fermentation?
glucose stays in glycolysis stage & regenerates NAD+
NADH transfers its electrons directly to pyruvate
generates lactate as product
anaerobic respiration — what is ethanol fermentation?
yeast and alike organisms produce energy without oxygen and generates CO2 and ethanol as a product
Aerobic vs. anaerobic
what is required and what they produce
aerobic uses oxygen and produces 32 ATP and water