Communication Protocols, the world wide web and the Internet.
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
The Client-Server Model
The client-server model is a computing architecture where clients (users or devices) request services or resources, and servers provide them over a network.
Client Server Model steps
1. Client Sends Request:
• The client initiates communication by sending a request to the server. This could be a request for data, a service, or a resource (e.g., a webpage, file, or database query).
2. Server Receives Request:
• The server listens for incoming requests and receives the client’s request. It processes the request by interpreting the data and determining what is being asked.
3. Server Processes Request:
• The server processes the request by executing the necessary actions, such as retrieving data, performing calculations, or accessing stored resources.
4. Server Sends Response:
• After processing, the server sends a response back to the client, which could be the requested resource, confirmation of an action, or an error message.
5. Client Receives Response:
• The client receives the server’s response and uses it accordingly, such as displaying a webpage, storing data, or providing feedback to the user.
6. Communication Ends:
• Once the response is received and processed by the client, the communication ends. If the client requires more resources, the process may repeat from step 1.
Web browser
A software application that allows users to access and retrieve content on the World Wide Web.
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
The address used to identify and access a specific resource, such as a webpage or file, on the Internet.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
A protocol used for transmitting data between a web browser (client) and a server, primarily for accessing and sharing web content.
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure)
An encrypted version of HTTP that ensures secure communication between a web browser (client) and a server using SSL/TLS protocols.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
Handles reliable data delivery. It ensures that the data packets arrive completely and in the correct order.
TCP ensures all data sent is received accurately by using acknowledgments and retransmissions if packets are lost.
TCP numbers packets and reassembles them in the correct sequence on the receiving end, even if they arrive out of order.
IP (Internet Protocol)
A set of rules for addressing and routing data packets across networks to ensure they reach the correct destination.
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity)
A wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide high-speed Internet and network connections without physical cables.
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol)
A technology that enables voice communication and multimedia sessions over the Internet or other IP-based networks.
What is protocol? (In regards to the World Wide Web)
A set of rules describing how to transmit data across a network.
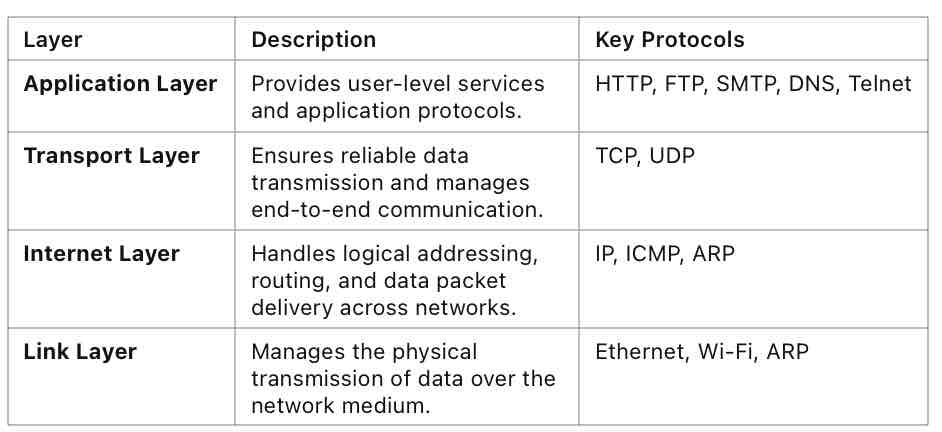
TCP/IP Model
A model designed to standardise computer networking.
TCP/IP model layers
Difference between World Wide Web and the internet.
The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers and servers, while the World Wide Web is a system of websites and online content accessed through the Internet using web browsers.
Peer to peer network
a decentralized type of network where each device (or “peer”) has equal status and can act as both a client and a server.
Differences between a peer-to-peer network and a client-server network
Feature | Peer-to-Peer (P2P) | Client-Server Model |
Architecture | Decentralized | Centralized |
Role of Devices | Each device acts as both client and server | Clients request services, server provides them |
Server Dependency | No dedicated server | Requires a central server |
Cost | Low setup cost | Higher cost (due to dedicated server) |
Scalability | Limited scalability | Highly scalable |
Performance | Can be slower due to shared resources | Generally faster and more efficient |
Security | Less secure, harder to control | More secure with centralized management |
Examples | BitTorrent, LAN file sharing | Websites, email services |
IP address
a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
There are two versions:
IPv4 – Looks like 192.168.1.1 (four numbers, 0–255, separated by dots)
IPv6 – Looks like 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334 (uses hexadecimal and colons)
LAN (Local Area Network)
A network that connects computers and devices within a small geographic area
WAN(Wide Area Network)
A network that connects computers and devices over a large geographic area, such as across cities or countries. The Internet is the largest example of a WAN.
Cloud Computing
The use of remote servers on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, instead of using a local computer or server. Examples include Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive.