Animal Cells and Tissues
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Define hemostasis
Homeostasis-homeo [similar] + stasis [condition] - maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in their external environment
examples of the body maintaining a stable internal environment
sweating/shivering
insulin/glycogen
osmoregulation
What is the biological hierarchy in animals
Cell→Tissue→Organ→Organ System→Organism
purpose of digestive system
Conversion of food to energy
purpose of nervous system
Responsible for communication, control, coordination
purpose of Muscular system
Movement
(true/false) No organ system works in isolation
true
Define cells
the basic building blocks of life
Define
Specialized cells
What are the 4 primary tissues
Epithelial tissues
connective tissue
Muscle tissue
Nervous tissue
purpose of Epithelial tissues
line body cavities
purpose of connective tissues
bind other tissues together
purpose of muscle tissues
specialize in contraction
purpose of nervous tissues
conduct impulses
structure of epithelial tissue
Sheets of epithelial cells that cover body surfaces and forming barriers
allow for Secreting, absorbing, excreting, and transporting other molecules
Types of cell layers
simple (one layer)
Stratified (multiple layers)
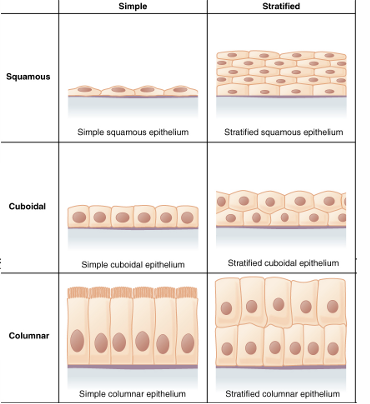
types of cell shapes
Squamous (plate-like)
Cuboidal (cube-like)
Columnar (cylindrical)
Special types of cell
Pseudostratified - essentially simple but in different sizes and shapes
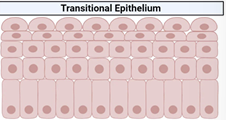
Transitional - are stratified, however When they receive a lot of pressure they can extend until their simple

transitional
are stratified, however When they receive a lot of pressure they can extend until their simple
Purpose of connective tissue
tissue that supports, binds, and protects other tissues and organs. Characterized by having relatively few actual cells
Describe Skeletal muscle tissues
majority of muscle
Voluntary contraction
Ability to control it
Multinucleated – many nuclei
Cell has the ability to get bigger and smaller
Most are really big
Ability to repair itself
Describe Cardiac muscle tissues
Only found in heart
Involuntary contraction
Branched and connected by intercalated discs
Mononucleated
Heart doesn’t need to get bigger
Not anticipating heart damage
describe nervous tissues
Tissues that are responsible for communication, control, coordination
triggers a series of reaction that allow the muscle to contract
How do the 4 primary tissues work together in the stomach?
Epithelial tissue - lines the inside, secreting gastric juices and mucus
Muscle tissue - smooth muscle contracts to churn and move food
Connective tissue - provides elasticity and strength
Nervous tissue - regulates muscle contractions and secretion
How do the 4 primary tissues work together in the skin?
Epithelial tissue- outer protective barrier and glands
Connective tissue- provides elasticity and strength
Nervous tissue- sensory receptors for touch, temperature, and pain
Muscle tissue- small muscles cause hair to stand up