Kidney failure and dialysis
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
why does kidney sometime stops working?
Often cause by high blood pressure
what happens of our kidney stops working ?
Kindney cannot regulate the balance of electrolytes.
Excess water, waste products like urea / salts are no longer removed from body.
Left untreated , kidney failure → Death
Severity of kidney failure can be measure by ?
Glomerular filtration rate ( GFR)
Glomerular filtration rate ( GFR) units ?
cm3 min -1
what is a normal rate for GFR ?
90-120 cm3 min -1
what rate indicates chronic kidney failure ?
>60 cm3 min-1
what rate indicates kidney failure ?
> 15 cm3 min-1
what are the common cause of kidney failure
Hypertension ( High blood pressure )
Type 2 diabetes
Infections
what are the 2 treatments for kidney failure
Renal Dialysis ( Haemodialysis & peritoneal dialysis)
Kidney transport
Renal Dialysis
Where and how does the waste product / water / excess salt pass from blood
waste product / water / excess salt pass from blood into dialysis fluid across a semipermeable dialysis membrane.
what does the dialysis fluid contains ?
Concentration of solutes that are found in blood
Any substance that is an excess ? what happen to them ?
Diffuses from the blood to fluid
Any substance that is in short supply ? what happen to them ?
Diffuses from the fluid into blood.
what substance does not passes through the membrane ?
Blood cells and plasma proteins
Haemodialysis
what are the steps for Haemodialysis ?
Blood taken from an artery to a dialysis machine. Which contain dialysis membrane to separate the blood from the dialysis’s fluid.
what does the dialysis fluid contains ?
Correct con.c of sugar / salts for normal blood
what is heparin ?
It’s added to the blood to prevent clotting in the machine.
what is a in-line bubble trap used for ?
a in-line bubble trap is present before blood is returned.
what happens when a clap is tightened ?
excess water can be removed from the blood by ultrafiltration.
how often does people with kidney failure need haemodiaylsis ?
3 times weekly in hospital for several hrs
Kidney failure - Peritoneal dialysis
how does Kidney failure - Peritoneal dialysis works?
Uses of peritoneal or abdominal membrane for dialysis
A permanent tube is inserted into the abdomen and used to fill the space between the abdominal wall and organs with dialysis.
After a few hours, the spent fluid is drained and replaced several times.
how often does people with kidney failure need Peritoneal dialysis ?
Dialysis is on a daily basis and can be completed at home or at work.
what are the common problems with Peritoneal dialysis ?
Functional kidney helps to regulate the composition of body fluids by a number of negative feedback mechanism.
These are not possible with renal dialysis, where control is rather crude.
The kidney also performs a number of functions in addition to excretion e.g.; it produces the hormone erythropoietin, which control RBS production.
Dialysis patients are often anaemic as their kidney does not perform this function.
Kidney transplant
how does kidney transplant work ?
Major surgery
Transplants are routine
process of kidney transplant
Donated kidney (either living or cadaver donation) is implanted in the lower abdomen and attached to the blood supply.
The stub of the renal artery is attached to the common iliac artery.
The stub of the renal vein is attached to the common iliac vein and the bladder.
what are the common problems with kidney transplant ?
Main problem: rejection
T-lymphocytes invade organ and destroy it.
what is the rejection determined by?
Rejection can be determined by:
Tissues matching, the donor and recipient closely
Using immunosuppressant or anti-rejection drug
Immunosuppressant drugs are required for life and increases the likelihood of infection.
Urine testing
Basement membrane acts as a filter on substances that have RMM > 69,000
Urine can be tested for a number of substances.
E.g. Human chronic gonadotrophin (hCG)
E.g. Anabolic steroids
what is function of Human chronic gonadotrophin (hCG) and where is it produced ?
Produced by an implanted human embryo in early pregnancy.
Help to maintain the production of progesterone by the ovary and so prevents menstruation.
Small molecule with a RMM of 36,000 so it easily passes into the glomerular filtrate.
Its presence can be detected in urine an over-the-counter monoclonal antibody dip-stick test.
Pregnancy testing
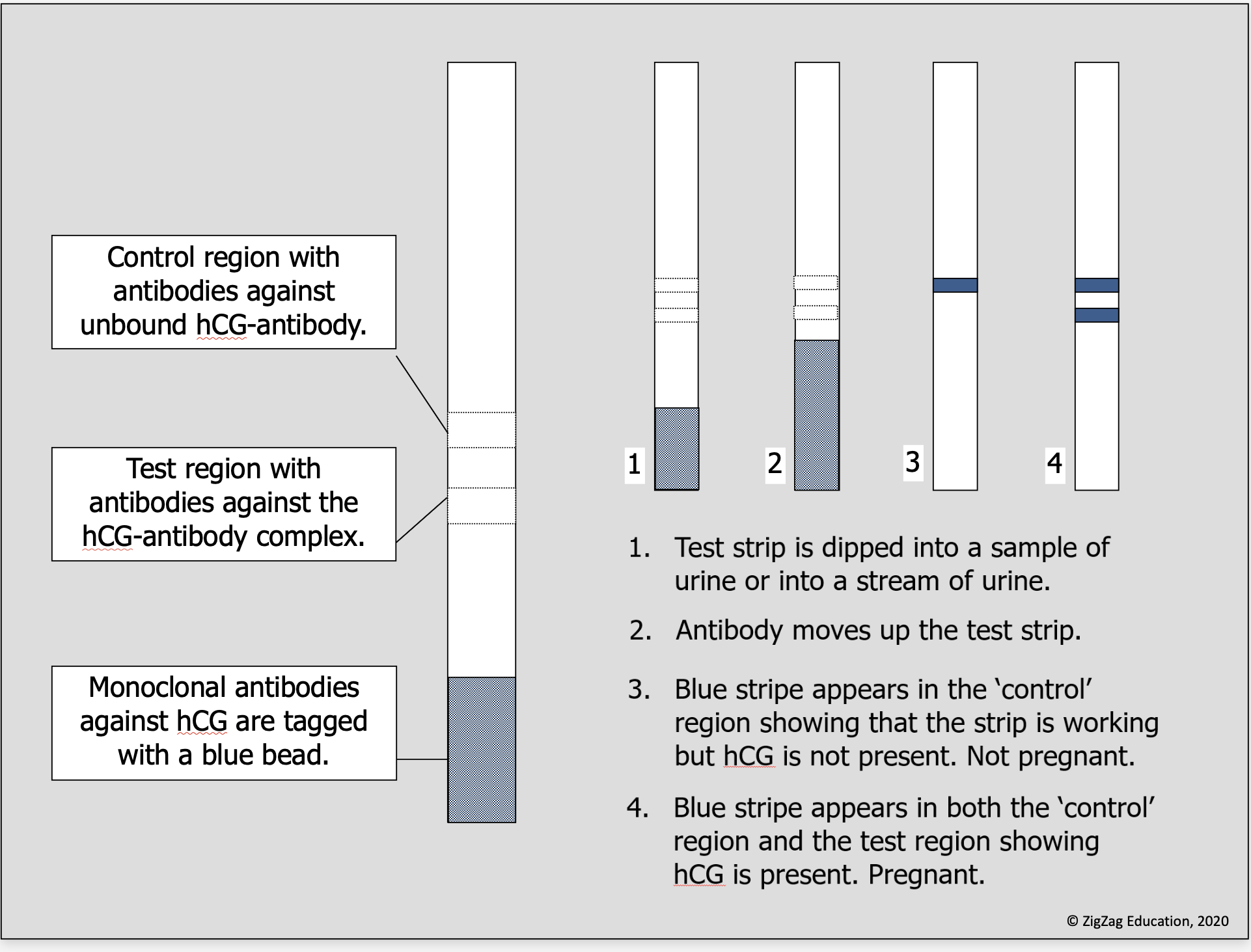
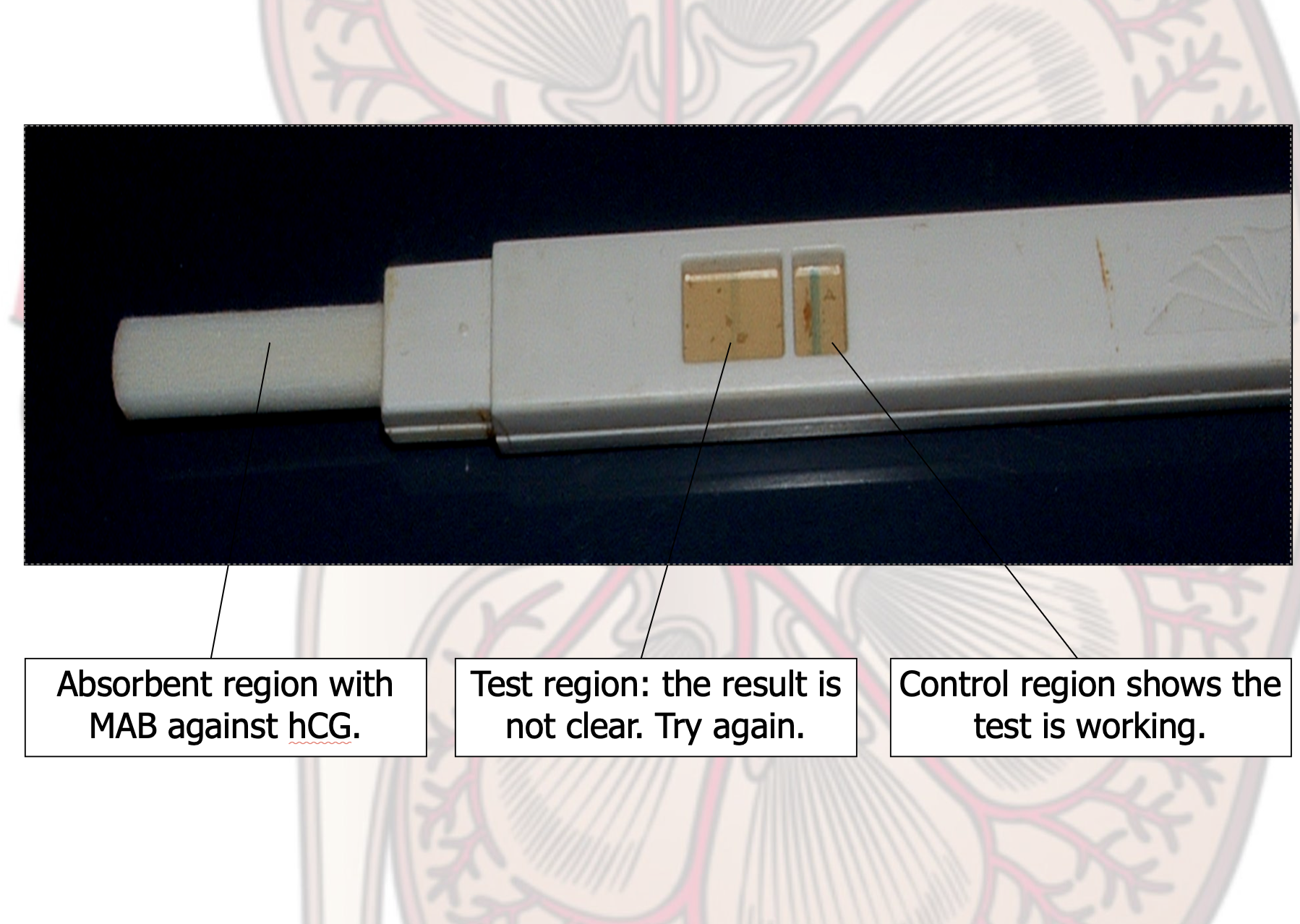
what does Pregnancy testing contains ?
The test strip contains monoclonal antibodies that are specific for:
HCG alone
The hCG antibody complex
Unbound hCG antibody
How does Pregnancy testing work ?
The hCG specific antibody is tagged with a blue dye and is mobile.
The antibodies against the hCG antibody complex and against the unbound hCG are immobilised in separate sites at one end of the strip.
Any hCG in the urine binds to the hCG specific antibody, forming a hCG antibody complex.
The complex moves along the test strip until it trapped by a ban of immobilised antibodies against the hCG antibody complex and a blue line form.
The unbound hCG specific antibody also moves up the strip and is also trapped by immobilised antibodies.
Antibodies against unbound hCG specific antibodies are in a different position.
Blue line indicate test worked properly.
Monoclonal antibodies
what is Monoclonal antibodies used for ?
Use in pregnancy test
They are pure and can be made to bind to anything you want, to:
Detect / identify hormones/ drugs/ disease
Dliver drugs to specific cells
what is Monoclonal antibodies made from ?
Made by a single clone of B cells hybridised with myeloma cells.
B cells themselves will secrete antibodies but not divide well in culture.
Myeloma cells will divide but will secret antibodies.
Anabolic steroids
Functions of Anabolic steroids
Increase protein synthesis in cells, esp. muscle cells
Their used is banned in most sport because:
They give an unfair advantage.
They have dangerous side effects, including liver cancer, heart disease and testicular atrophy.
is Anabolic steroids big or small molecules ?
They are relatively small molecules with a relative molecular mass of < 69,000 so they are excreted in urine.
Remain detectible for a few days after their use had stopped.
how to test for Anabolic steroids ?
Urine Sample by Gas chromatography
Urine Sample by Gas chromatography
A sample of urine is vaporised and passed with a solvent into the gas chromatography tube.
Different substances have different retention times in the chromatography tube.
Used to identity the substance.