AP Bio Unit 1; Chp 1-5
1/103
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Organic Compound
made of carbon & hydrogen, may include elements like oxygen, nitrogen & sulfur
Isomer
molecules w/ the same chemical formula, same number of atoms but different structures
Structural Isomer
Same empirical formula, different shape
Sterioisomer
Same empirical formula, same shape, different arrangement
Enantiomer
molecules that are mirror images of each other
Cis-Trans Isomer
Atoms differ in spatial arrangements due to inflexibility in double bonds
Hydrocarbon
organic compounds composed solely of hydrogen and carbon atoms, hydrophobic
Functional Group
Behavior of organic molecules depends on it, they're specific clusters of atoms within a longer molecule, dictating chemical properties & reactivity
Hydroxyl Group
functional group consisting of -OH
Carbonyl Group
functional group consisting of C=O
Carboxyl Group
functional group consisting of -COOH
Amino Group
functional group consisting of -NH2
Sulfhydryl Group
functional group consisting of -SH or HS-
Phosphate Group
functional group consisting of -PO3
Methyl Group
functional group consisting of -CH3
Aldehyde Group
type of carbonyl groups: functional group at the end of a carbon chain
Ketone Group
type of carbonyl groups: functional group at the middle of a carbon chain
Hydrolysis
Chemical reaction where water is added, causing it to split (opposite of dehydration synthesis)
Dehydration Synthesis
formation of large molecules via removal of water molecules
Polymer
Many units, many monomers
Monomer
Single subunit of a polymer
Macromolecule
large molecules or carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins
Monosaccharide
monomer of carbohydrate, typically 6 carbons, simple sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose)
Disaccharide
formed by a dehydration reaction between two monosaccharides, e.x., sucrose
Polysaccharide
Polymers with a few hundred to thousands of monosaccharides joined by glycosidic linkages - lots of sugar molecules bonded together
Glycosidic Linkage
Bonds between sugar molecules, between monosaccharides through dehydration synthesis
Glucose
primary energy source for the body, monosaccharide, level is low we feel hunger
Fructose
isomer of glucose, fruit of sugars
Sucrose
Disaccharide formed from glucose and fructose - held by a glycosidic linkage
Glycogen
carbohydrate found in animal tissue, a ton of branches of glucose chains - big boost of energy and then dropped
Amylose
edible starch, found in plants, alpha linkage, the simplest branch of a glucose chain
Cellulose
found in plant cell walls, non-edible starch, polysaccharide, beta linkage
Starch
polymers of glucose molecules, energy storage for plants, alpha linkage
Chitin
found in shells of arthropods and in cell walls of fungi, structural polysaccharide, beta linkage
Lipid
includes fats, oils, waxes; even distribution of electrons, hydrophobic, no monomer
Fatty Acid
long carbon skeleton, usually 16 or 18 carbon atoms in length, with a carboxyl group at the end
Saturated Fatty Acid
contains as many hydrogen atoms as possible, no double bonds between carbon atoms
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
contains one or more double bonds, with one fewer hydrogen atom on each double-bonded carbon
Triacylglycerol (Triglyceride)
formed by a dehydration reaction between three fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule
Phospholipid
similar to triglycerides but has only 2 fatty acids attached to a phosphate group
Steroid
lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
Cholesterol
type of steroid, crucial molecule in animals, found in animal cell membranes
Peptide
short chains of amino acids, typically less than 20
Peptide Bond
bond between amino acids formed by a dehydration reaction
Polypeptide
polymer of amino acids, typically folded into a specific shape
Amino Acid
monomer of protein, organic molecule with both an amino group and a carboxyl group
Nucleic Acid
macromolecule, includes DNA, RNA, ATP
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acid, consisting of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogenous base
DNA
contains instructions to make proteins, double-stranded, AT & GC
RNA
single-stranded, can leave nucleus and make proteins, AU & GC
Pyrimidine
type of nitrogenous base with one six-membered ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms, cytosine & thymine& uracil
Purine
type of nitrogenous base with two rings, a six-membered ring fused to a five-membered ring, adanine & guanine
Oligosaccharide
short chain of carbohydrates (3-10) - functions like cell recognition
Cis functional group
functional group on the same side of a carbon structure
trans functional group
functional group on opposite sides of a carbon structure
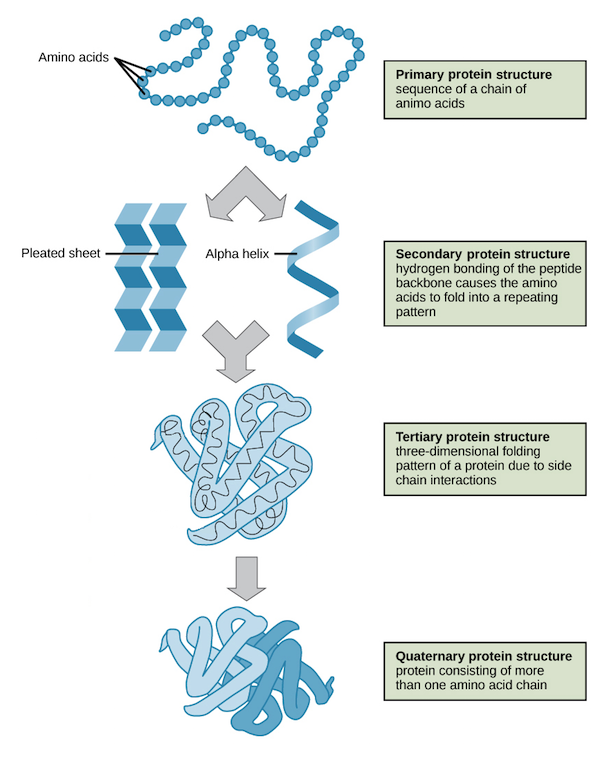
primary structure of a protein
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure of protein
alpha helices and beta sheets formed by the backbone
tertiary structure of protein
shape of the amino acid chain
quaternary structure of protein
shape/interaction of more than one amino acid chain
mass number
number of protons+neutrons for an atom
valence electrons
electrons found in outermost orbital - bonding sites
polar covalent bond
bond between atoms where electrons are shared but not evenly distributed - creates charged sides; i.e. water
elements
substances that cannot be broken down into other substances by a chemical reaction
-atom with specific amount of protons
dalton
unit of measurement for atomic mass
1 proton = 1 Dalton
1 electron = (1/2000) Dalton
Potential Energy (PE)
energy matter has due to its position or structure/phase
Non-Polar covalent Bond
bond between atoms where they share electrons evenly, meaning the charge is the same all the way around the molecule
Compound
substance consisting of 2 or more unique elements combined in a fixed ratio
different characteristics from parent elements
isotope
when element contains a different number of neutrons from protons
protons stay the same and determine type of element
behave identically in chemical reactions
typically more neutrons than protons
orbital
3D region around an atomic nucleus that contains the electrons
Cation
positively charged ion
Proton
positively charged particle found in nucleus of an atom
radioactive isotope
Isotope where nucleus is unstable and spontaneously decays, giving off energy
Covalent Bond
bond between atoms where electrons are shared
Anion
negatively charged ion
neutron
neutral particle found in nucleus of an atom
contains both positive and negative charge
half-life
the time it takes for half of a parent isotope to decay
only applies to radioactive isotopes
molecule
2 or more atoms that are covalently bonded
ionic bond
electron is transferred between two atoms
creates 2 ions with opposite charges that are now attracted to each other
weaker than covalent bond
electron
negatively charged particle found outside the nucleus of an atom
radiometric dating
used to calculate the number of half-lives that have passed since organic matter has been fossilized
single bond
one pair of shared electrons
double bond
2 pairs of shared electrons
triple bond
3 pairs of shared electrons
hydrogen bond
covalently bonded H atoms are partially positive, resulting in an attraction to electronegative particles
attraction is the H bond
easily broken
Atomic nucleus
densely packed protons and neutrons found at the center of an atom
energy
capacity to do work (cause change)
electronegativity
measure of how strongly an atom attracts electrons (mainly in chemical bonds)
high electronegativity = stronger pull on electrons
Van der Waals Reaction
caused by randomly moving electrons creating regions with +/- charges that enable atoms to stick together
-individually weak bonds that happen in close proximity
Specific heat
The resistance to change in temperature
Product
The resulting material in a chemical reaction
Reactant
Starting material in a chemical reaction
Acid
High level of hydrogen ions (H+) and low levels of hydroxide (OH-)
pH under 7
Base
Low levels of hydrogen ions (H+) and high levels of hydroxide (OH-)
pH over 7
Creation of Hydroxide
when H+ ion in water bonds to another water molecule leaving behind a water molecule that lost a proton (OH-) with a charge of 1-
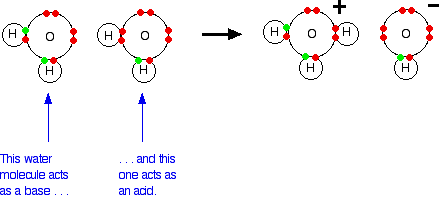
Buffer
substance that minimizes changes in concentration of H+ and OH- by accepting H ions from solution when there is an excess and donating when H+ has been deplted
i.e. carbonic acid in the blood
pH scale
reverse logarithm measure of H+ ions in an aqueous solution
Solution
Homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances
Solvent
dissolving agent in a solution
Solute
the substance being dissolved in a solution
hydrophilic
water loving
polar molecules (ions)
dissolve in water