Chapter 1 Module 2 - Research Strategies
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Scientific Method
a self-correcting process for evaluating ideas with observation and analysis
- Steps: Make and observation, ask a question, form a hypothesis, make a prediction, test prediction, analyze and reconstruct
Theory
explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events
Hypothesis
testable predictions, often implied by a theory
operational definition
carefully worded statement of the exact procedures (operations) used in a research study
Replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
descriptive research
systematic, objective observation of people
- the goal is to provide a clear, accurate picture of peoples behaviors, thoughts and attributes
Case Study
a research in which detailed consideration is given to the development pf a particular person, group, or situation over a period of time
- can not be used to generalize conclusions
Naturalistic Observation
a research method that involves observing subjects in their natural environment without influencing their behaviors
- describes but does not explain behavior, can be revealing
Interview
a way to gather information about a persons thoughts, experience's, and behaviors through conversation
Survey
a research toll that can be used to gather information about a group of peoples opinions, behaviors, or characteristics
Correlation
A measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other. Correlation does NOT lead to causation
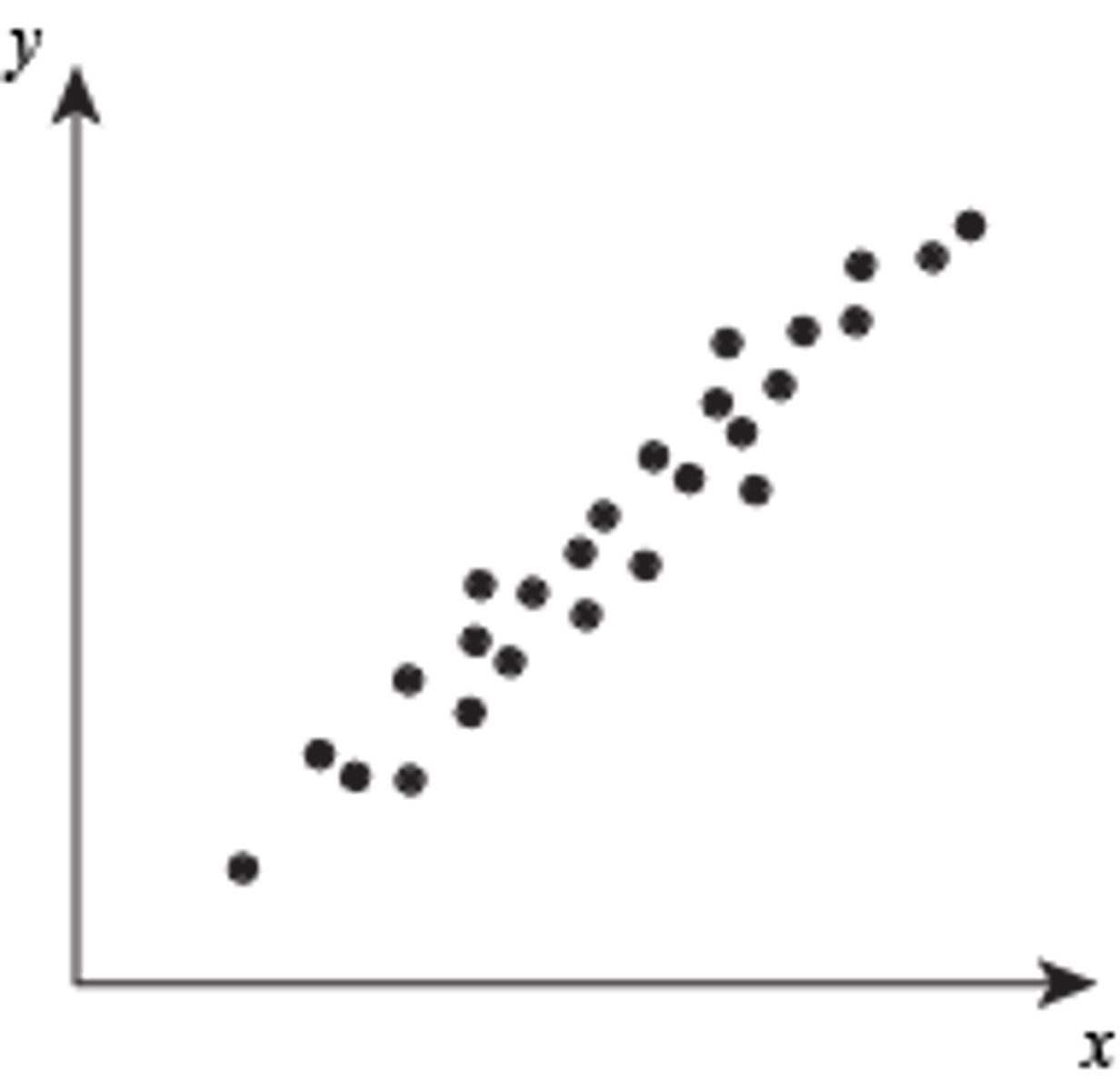
positive correlation
when one variable increases, the other variable increases
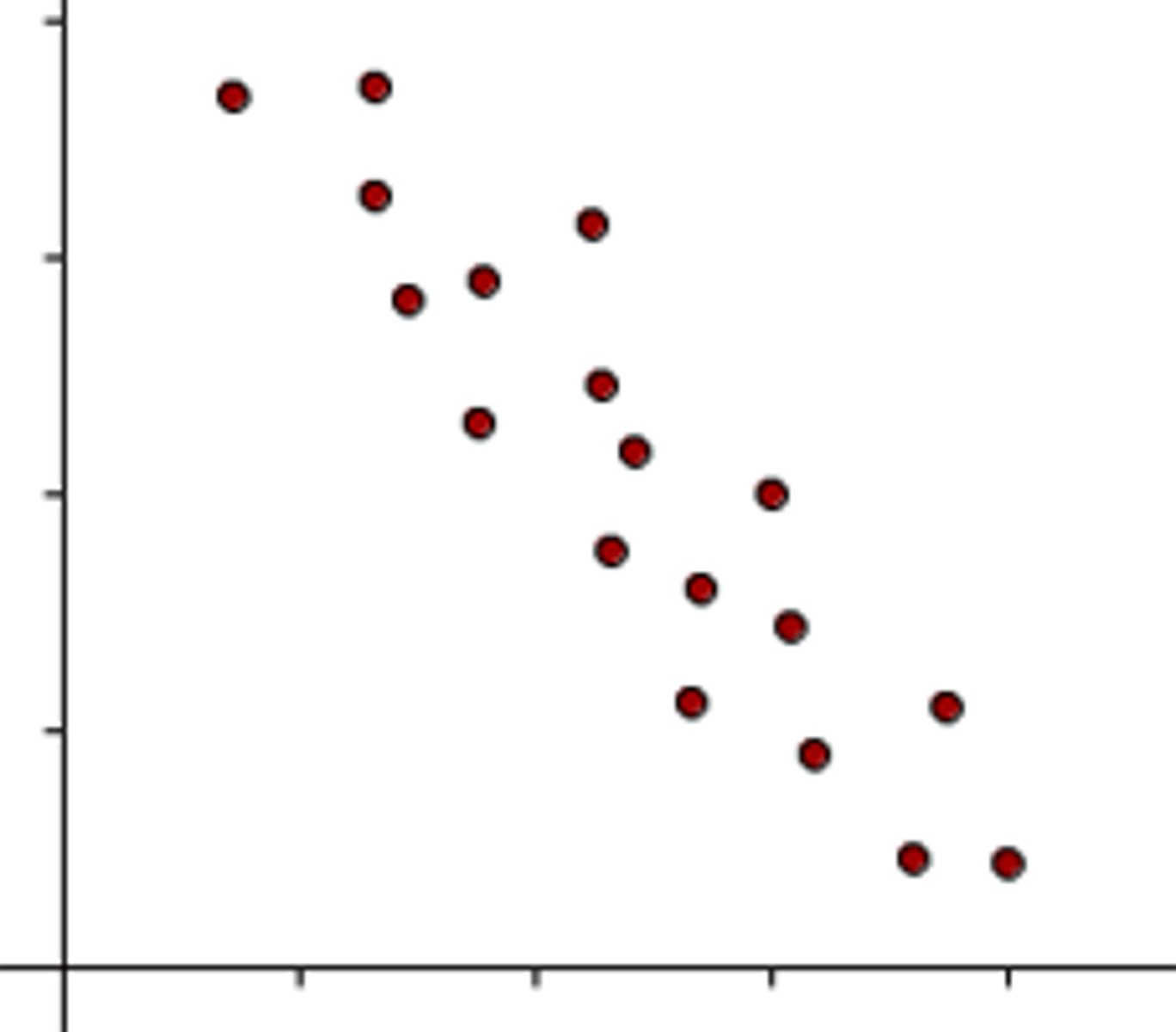
Negative Correlation
when one variable decreases, the other decreases
Experimental Studies
a type of research where researchers introduce a treatment or intervention and observe the results
Experimental manipulation
The deliberate alteration of the independent variable in an experiment in order to learn about its effects on the dependent variable.
independent variable
a variable that is manipulated by a researcher to see if it changes the dependent variable
dependent variable
a variable that is expected to change as a result of the manipulation of an independent variable
confounding variable
influences both independent and dependent varibale in a study, potentially distorting the observed relationship between them making it difficult to accurately determine the true cause and effect relationship between the primary variables