Fungal infections - therapeutics
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What is the main target for fungal infections?
Ergosterol
What are fungi?
Eukaryotic organisms that do not contain chlorophyll - can be macroscopic or microscopic but very few cause human disease
how are fungal infections spread?
Inhaling spores or contact with the skin
What are fungal infections known as in humans?
Mycoses
What are the 3 groups for fungi?
Yeasts, moulds and dimorphic fungi
What are yeasts?
Single cells, rounded organisms that multiply by budding or fusion
What are moulds?
Long, tubular filaments that grow by branching and longitudinal extension of hyphae
What are dimorphic fungi?
Exist as yeast or mould dependant on environmental factors e.g, temperature
What are some examples of superficial fungi?
Candida albicans, epidermophyton, malassezia fur fur
What are the main infections of Candida albicans?
Oral thrush, vaginitis, cutaneous candidiasis, onychomycosis
What infections can epidermophytan/microsporum/trichophyton cause?
Tinea (ringworm) of skin and hair, onychomycosis
What is the most common cause of opportunistic fungi worldwide?
Candida
What are the symptoms of candida spp?
Pain and itching with creamy white curd like plaques on mucosal surfaces e.g., tongue, oropharynx, oesophagus and vagina
Where is oral thrush most commonly seen?
Very young, elderly, diabetics, following Abx therapy and immunosuppressed individuals as well as common side effect from incorrect corticosteroid inhalers for respiratory diseases
How does oral thrush occur in incorrect corticosteroid use?
Poor inhaler technique leads to local deposition of corticosteroids on mouth and palate and increases the likelihood of overgrowth of candida
What is common in neutropenic patients?
Systemic invasion of candida
How is oral thrush treated?
Topical imidazoles e.g, clotrimazole, econazole and miconazole, topical terbinafine or nystatin
What does the choice of agent depend on for oral thrush?
Location and severity of the infection
What is nystatin used to treat?
Oral and oesophageal candidiasis
What should be used if symptoms are not responsive to a topical therapy in oral thrush?
Systemically active azole e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole
What is onychomycosis?
Fungal nail infection - invasion of the nail plate by a fungus
What are the risk factors for onychomycosis?
Males more affected than females, prevalence increases with age
What is the main cause of onychomycosis?
Dermatophytes - candida can cause
What are the symptoms of onchomycosis?
DIscoloured nail - white, brown or yellow, thick or brittle nail, can spread to surrounding tissues if untreated, can have some pain and discomfort
What is the treatment of onychomycosis?
Amorolfine, tioconazole and undecaonoate-containing nail lacquers, creams or paints can be used for topical therapy if no more than 2 nails affected
What systemically active drugs can be used for onychomycosis for more advanced infection?
Terbinafine, itraconazole
What can ringworm present as?
Red, scaly patch like lesions that spread outwards and leave a pale, healed centre that is itchy
What can ringworm present as if present on the scalp?
Hair loss and scarring
How are ringworms diagnostic labels characterised?
Site of infection - tinea capitis (head and scalp), tinea corporis (trunk lesion), tinea pedis (athletes foot)
What is the treatment for ringworm?
Topical imidazoles antifungal e.g., clotrimazole, miconazole or shampoo containing ketoconazole - depends on area affected
What is pityriasis versicolour caused by?
Malassezia furfur
What does the infection of the stratum corneum in pityriasis versicolour cause?
Scaly macules with depigmentation - hyper or hypopigmented
What is the treatment of pityriasis versicolour?
Ketoconazole shampoo - systemic azole can be used if this fails
What are the risk factors for invasive fungal disease?
Immunosuppression e.g., organ transplant, systemic corticosteroids e.g., autoimmune conditions like RA, malignancy, severe debilitation e.g., ICU patients, burns, severe trauma, use of broad spectrum antibiotics that is repeated, invasive devices e.g., IV catheters and devices, extremeties of ages and endocrine disorders
Why is diagnosis of a systemic fungal infection difficult?
Symptoms are minimal and non-specific but should always be considered in immunocompromised patients
Why are systemic fungal infections most common in neutropenic patients?
Impairment of defence functions can reduce ability of immune system to clear fungal pathogens
What can candida cause in intensive care patients?
Systemic and line-associated infection following broad-spectrum antimicrobial therapy
What is candidaemia?
Candida in the blood
What can candidaemia result in?
Abscesses or infection in various organs e.g., brain, liver, kidneys, eyes, GI tract and endocarditis
Who do systemic aspergillus infections occur in?
Immunocompromised hosts or immunocompetent individuals with recent tissue damage
What are the 4 aspergillus organisms associated with human infections?
Aspergillus fumigatus, Niger, flavus and terreus
When are aspergillomas formed?
Aspergillus grows in a clump or ball in a lung cavity and invades previously healthy tissue, causing an abscess
What are the common symptoms of aspergillomas?
Persistent productive cough, weight loss, haemoptysis, wheeze and finger clubbing
What are the symptoms of invasive aspergillosis?
Dry cough, fever, pleuritic chest pain and dyspnoea
How are people exposed to cryptococcosis infections?
Soil/dirt containing bird droppings e.g., poultry farm workers or park groundkeepers are at risk of inhaling the yeast
What can cryptococcosis cause?
pneumonia, cutaneous infections or cryptococcal meningitis - seen in advanced HIV infection and presents subacutely
What are pneumocystis jiroveci infections?
Causes pneumonia in the immunocompromised - especially those with CD4 count below 200 e.g, in AIDs
What are the symptoms of pneumocystis jiroveci?
Dyspnoea that develops over days or weeks with a dry, unproductive cough and fever, fine basal crackles may also be heard
What is the treatment of pneumocystis jiroveci?
High dose co-trimoxazole or IV pentamidine - prophylaxis can also be given with oral co-trimoxazole for those at high risk
What is selection of antifungals dependant on?
Indication, site of infection, patient comorbidities and local guidelies
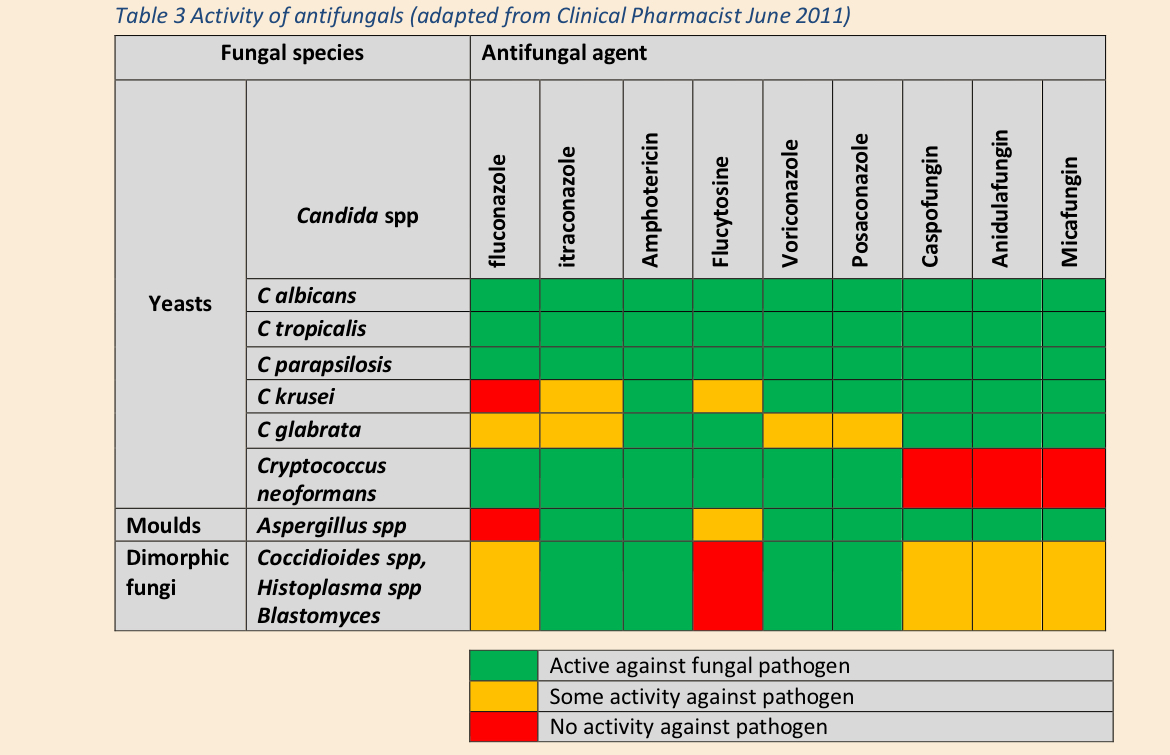
What is a table comparing fungal species and appropriate antifungals?
All can be used for C albicans, tropicalis and parapsilosis, more selectivity for others
What is the mode of action for azoles - imidazoles and triazole derivatives?
Targets Ergosterol by inhibiting the fungal cytochrome p450 enzyme 14-alpha-demethylase and prevents conversion of lanosterol to Ergosterol and inhibits fungal growth and replication
What are the main uses of imidazoles and triazoles?
systemic infections and superficial infections
What is the MOA of polyenes - topical nystatin and amphotericin?
Interacts with Ergosterol at the cell membrane and causes an increase in membrane permeability and leakage of cellular components
What are the main uses of amphotericin and topical nystatin?
broad spectrum antifungals agents
What is the MOA of terbinafine?
Inhibits squalene epoxidase - essential in Ergosterol biosynthesis and leads to deficiency of Ergosterol in membrane which destroys the cell
When is terbinafine used?
Dermatophyte infections of the nail, tinea infections
What is the MOA of echinocandins - caspofungin etc?
Inhibits synthesis of Beta 1-3 glucan synthase and is fungicidal against candida spp, but fungistatic against aspergillus
What is the main uses for echinocandins?
Invasive aspergillosis or candida
What is the MOA of flucytosine?
Competitive inhibitor of uracil metabolism - converted to 5-fluorouracil in susceptible fungal cells and incorporated into fungal RNA to exert its effects
What is the main use flucytosine?
Cryptococcal meningitis in combination with amphotericin
What is the potential MOA of griseofulvin?
Inhibits fungal mitosis
What are the main uses of griseofulvin?
Dermatophyte infections of skin, hair and nails
Why is nystatin not used systemically?
Too toxic
What is amphotericin used for?
Suspected fungal infections in immunocompromised patients - affinity for cholesterol found in mammalian cells so is quite toxic, minimised by putting into lipid formulation
What is griseofulvin?
Well absorbed orally and incorporated stratum corneum of the nail - used to treat fungal nail infections
Why is terbinafine used instead of griseofulvin?
Griseofulvin is quite toxic and teratogenic and fetotoxic should be avoided pregnancy during and 1 month after treatment and men should avoid fathering children during treatment and 6 months after
What are some side effects of terbinafine?
GI disturbances
What are examples of imidazole antifungals?
Ketoconazole and miconazole
What are examples of triazole antifungals?
Fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole and voriconazole
What is fluconazole useful for?
Prophylaxis of fungal infections in neutropenic patients
What triazole antifungals penetrate the blood brain barrier?
Fluconazole and voriconazole
What are the side effects of flucytosine?
Bone marrow-suppression, thrombocytopenia and abnormal liver function tests