DT: TOPIC 4
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
228 Terms
what will a business aim to experience as it grows in size and produces more unit of output?
falling average costs of production - economies of scale
what is craft production?
makes a single, unique product from start to finish.
labour intensive
highly skilled
small scale
centred on manual skills
what are the pros and cons of craft production?
pros: locally based, allows direct conversation between clients and manufacturers
cons: slow, designers have to be multidisciplined, high cost
what is mechanised production?
a volume production process involving machines controlled by humans - less labour intensive than craft production
what is automated production?
the fastest way of mass producing goods and services. a volume production process involving machines controlled by computers.
what are the pros and cons of automated production systems?
pros: automated systems can make complex decisions far more quickly than/beyond the capacity of people
cons: routine, boring jobs for humans (on assembly lines), simple and repetitive, struggle maintaining focus
what is assembly line production?
a volume production process where products and components are moved continuously along a conveyer. as the product goes from one workstation to another, components are added until the final product is assembled
what is mass production?
the production of large amounts of standardised products on production lines, permitting very high rates of production per worker
what is mass customisation?
a sophisticated CIM system that manufactures products to individual customer orders. the benefits of the economy of scale are gained whether the order is for a single item or thousands.
what is computer numerical control (CNC)?
the computer control of machines for the purpose of manufacturing complex parts. machines are controlled by a program called “G code”, where each code assigns a particular operation or process, pertaining to movement and feed speeds,.
what does design for manufacture (DfM) mean?
designing specifically for the optimum use of existing manufacturing capability. designers need to consider designing products so that they can be easily and efficiently manufactured with minimal impact on the environment. can be a constraint on the design brief.
what are the four aspects of design for manufacture?
design for processes
design for materials
design for assembly
design for disassembly
what is design for materials?
designing in relation to materials during processing.
the selection of materials is important to consider
it can affect environmentally-friendliness at each stage of the product cycle from pre production to disposal
minimising the amount of materials and using non-toxic or biodegradable alternatives can reduce the impact on the environment
what is design for process?
designing to enable the product to be manufactured using a specific manufacturing process
designers should consider how the manufacture of the parts and components can be achieved efficiently and with minimal waste
what is design for assembly?
taking into account assembly at various levels: component to component, component to sub-assembly, sub-assembly to product
designers must consider how to optimise these levels of assembly to make them as efficient as possible, incurring the least costs
by minimising components, assembly can be made quicker and more efficient.
using standard components can decrease manufacturing time
what is design for disassembly?
designing a product so that when it becomes obsolete it can easily and economically taken apart, the components reused or repaired, and the materials repurposed or recycled.
different materials should be able to be separated (for recycling)
repair and reconditioning should be easy (less to landfill)
what three step workflow do rapid prototyping processes follow?
first, a model is created in cad software which contains information about the physical form, shape and dimensions of a product
the 3d model is then processed by slicing software. this takes the model and slices it into layers. parameters such as layer thickness, wall thickness and infill can be set here.
the sliced file is then sent to the rapid prototyping device for manufacture. in most cases, this will involve the device cutting or depositing material in the pattern set by the slicer software.
what is paper-based rapid prototyping (PRP)?
in this process, layers of paper are cut and then glued together to create a 3d shape. this is cost-effective and useful in producing presentation models. it is also more environmentally friendly than other plastics-based rapid prototyping methods.
what is laminated object manufacturing (LOM)?
uses thin layers of polymer which are cut and layered together. this process is used to create scale and presentation models which can be used to gather client/user feedback on form.
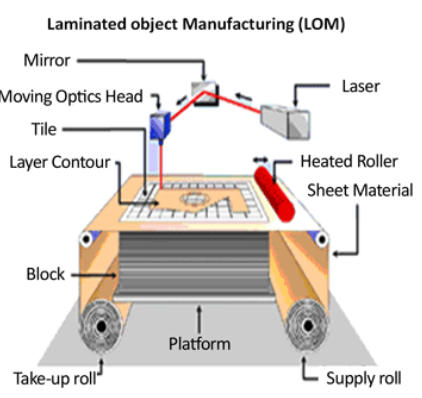
what is stereolithography (SLA)?
in this process an object is created by selectively curing a thin layer of liquid resin with a laser. a laser heats selected areas of the resin, turning it into a solid. this process continues until the piece is completed.
what is fused deposition modelling (FDM)?
the most accessible type of 3d printing technology, involving laying down thin layers of material, usually a type of plastic. the filament is heated in a nozzle and then “drawn” on layer-by-layer.
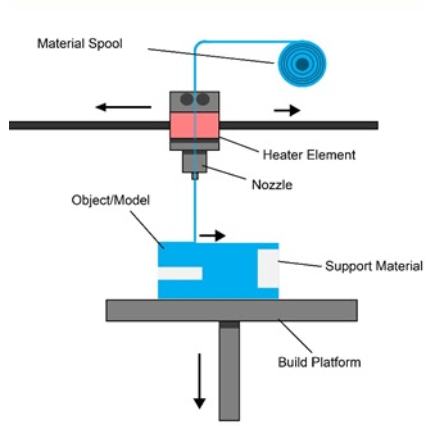
what is a subtractive manufacturing technique?
when material is cut away to create a product or component
what is machining?
a process whereby a cutting tool moves across and around the surface of a material. the machines can be CNC controlled or operated by a user.
what is turning?
rotating a material along a horizontal axis while a cutting tool is moved along the surface to remove material.
what is milling?
the movement of a rotating bit over the surface of a material, moving on a vertical axis. the material is fixed to a work surface, and the rotating bit is moved up and down and around the material.
what is drilling?
involves a spinning bit moving up and down the z-axis to create a hole in the material
what is abrading?
the process of using an abrasive to grind or rub away material. compounds that are used to grind, sand or polish a material - they can be used to remove material for shaping or to create a smooth surface. abrasives need to be harder than the material they are being used on in order for them to be effective.
what are abrasive grades?
the coarseness of an abrasive will affect how much material it removes as well as the smoothness of the surface. a coarse adhesive will remove material quickly, whereas a fine abrasive will remove material slowly and leave a smooth surface.
what is a grinder?
an abrasive compound embedded in a spinning disc. the material is held against the spinning disc and ground away. this process is used for shaping a form and removing marks from manufacturing.
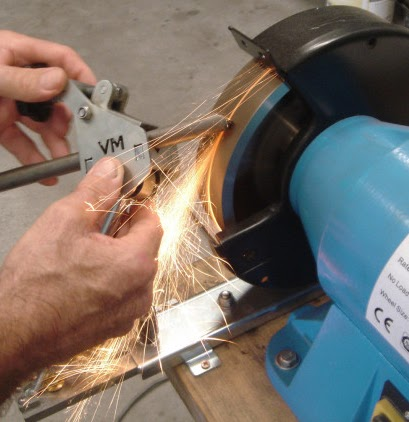

what is a sander?
uses abrasives attached to a moving surface. the material is held against the surface and ground away. this process is used for shaping a form and removing marks from manufacturing.

what is polishing?
involves the use of compounds to achieve a very smooth surface with particular aesthetic qualities.

laser cutting…
injection moulding…
what do shaping techniques involve?
modifying the shape of a material using heat, pressure, and other forms of mechanical manipulation
what is a mould?
a hollow form into which a material like plastic, glass or metal is injected or placed. moulds allow for the accurate production of a product. designers need to consider the material and scale of production and match it to they type of moulding process.
what is injection moulding?
parts are produced by injecting a liquid material into a mould. as the material is heated and then cooled, it takes on the form of the mould. there is very little waste with this process. most commonly used with plastic, but also glass and metals also.
what is a use case for injection moulding?
solid forms, simple or complex shapes
most common type of plastic production method
what are the advantages and disadvantages of injection moulding?
advantages: highly accurate, fast production
disadvantages: requires expensive equipment, restrictions on part dimensions and forms
what is blow moulding?
the process of inflating a hot hollow plastic inside a mould. the heated material takes the form of the mould. also can use glass.
what are the use cases of blow moulding?
hollow forms such as drink bottles and containers
what are the advantages and disadvantages of blow moulding?
advantages: highly accurate, suitable for mass production, very low waste
disadvantages: high cost of equipment
what is compression moulding?
a heated sheet of thermoset plastic is places into a mould, the mould then applies pressure to shape the plastic.
what are the use cases of compression moulding?
flatware, tableware, electric plugs
what are the advantages and disadvantages of compression moulding?
advantages: lower production costs compared to other methods, ideal for high production costs, suitable for products requiring thick walls
disadvantages: limited to relatively simple forms
what is rotational moulding?
where a heated hollow mould is rotated as thermoplastic is poured in. the liquid plastic takes the form of the mould as it moves around the interior.
what is the use case for rotational moulding?
large hollow forms such as floats and toys where the inside surface is not important
what are the advantages and disadvantages of rotational moulding?
advantages: moulds are lower cost to produce, ideal for large forms, ideal for rigid and flexible shapes, low waste
disadvantages: material costs can be higher
what is thermoforming?
involves the heating of a sheet of thermoplastic to the point that it becomes pliable and soft. it is then placed into a mould to be formed into a shape. commonly uses vacuum forming.
what are the use cases of thermoforming?
disposable cups and containers, clamshell packaging and blister packaging, body parts for cars, machines or products.
what are the advantages and disadvantages of thermoforming?
advantages: high production speed, cost effective, low tooling costs
disadvantages: limitation on size and shapes
what is laminating?
the laying down of thin layers of materials joined with an adhesive
what are the use cases for laminating?
wood furniture, glass windows and plastic
what are the advantages and disadvantages of laminating?
advantages: cost effective, high strength to weight ratio, range of veneers can be applied
disadvantages: time consuming, bending requires special equipment and techniques
what is casting?
the pouring of molten metal into a mould. the shape that is produced is called a casting.
what are the use cases for casting?
cars, machine parts, heavy duty equipment
what are the advantages and disadvantages of casting?
advantages: complex shapes, range of scale
disadvantage: labour and energy intensive, may require finishing
what is a joining technique?
involves permanently or temporality connecting two or more similar or dissimilar materials
what are adhesives?
chemical substances that when dried creates a bond between two surfaces. needs to be carefully matched to the materials and use situations.
what is welding?
using high heat to join two similar metals together. their bond is very string. the high heat results in greater energy used and can deform the metal. great skill and specialised equipment is required.
what is brazing?
uses a (lower) heat and a filler metal to join two different metals together. uses less energy than welding and won’t deform the metal.
what is a permanent fastener?
a nail or rivet that binds two or more pieces together
what are the advantages and disadvantages of permanent fasteners?
advantages: low cost, easy to apply, create a strong mechanical bond
disadvantages: cannot be removed without damage, not for design for disassembly contexts
what are temporary fasteners used for?
used to join two or more dissimilar materials together, or in cases where pieces need to be joined and later separated.
what is design for manufacturing (dfm)?
refers to the manufacturing process driving the design process. as such, designers seek to optimise the process. when designers are selecting processes they should consider: material properties, cost and scale of production.
What should designers consider with regards to robots in automation?
The benefits of increased efficiency and consistency, but also a responsibility to consider the moral and ethical issues surrounding increased use of automation.
What are the four main types of robots?
Single-task
Multi-task
Teams
Machine to machine
What is a robot?
A machine controlled by a computer that is used to perform repetitive jobs automatically
What is the impact of robotics on people (negative)?
Often makes skilled workers redundant in favour of a technician who can maintain and equip a large number of robots.
What are the three generations of robots?
1st generation: simple robots that can do one task - programmed to do one thing and cannot respond to changes in their environment (no sensors)
2nd generation: make use of sensors to respond to their environment. Complex code uses these sensors to guide the robots to operate autonomously.
3rd generation: make use of AI to process the world around them and to accomplish tasks. They are able to learn and operate without human supervision.
What is the work envelope of a robot?
the 3D space a robot can operate within, considering clearance and reach. Defined by length of arms, range and number of axes. 3D printers have 3 axes (X, Y and Z), whereas CNC routers can have four or five axes, allowing it to reach up, behind and around forms.
What is the load capacity of a robot?
The maximum load it can manipulate
What is the difference between the work enveloped of a cartesian, cylindrical and polar robot?
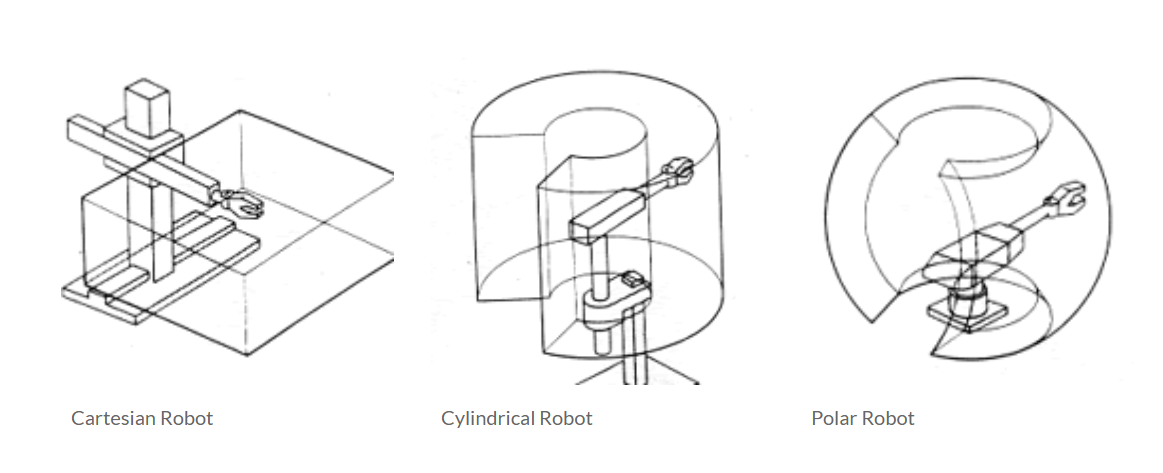
What is a single task robot?
Designed to do one task
Typically replacing skilled labour, such as welding or assembly line work
Their inputs and outputs are fixed, they cannot change their outcomes without being reprogrammed
1st generation robot, one task, no sensors
What is a multi task robot?
Can carry out more than one task at a time.
Flexible inputs and outputs, making use of sensors to respond to their environment.
Second generation robots
How do production lines make use of robots teams?
Multiple 1st generation robots working together
Hive robot systems: numerous robots, under control of a central system, cooperate to accomplish a task. The individual robots lack any form of Ai but the controller uses Ai to control the group.
What does Machine to Machine (M2M) refer to? What are the benefits of it?
Networking of robots together to share information and instructions. Common applications involve remote monitoring of worksites and product restocking.
Improves efficiency, accuracy and security of the sorting process and saves 70% of manual work, decreasing labour costs.
what is craft production?
small scale production centred around manual skills - made by a person with a deep set of manual skills where only rudimentary machinery is used. products such as wedding dresses, jewellery and ceramics use this scale of production.
what is one off production?
where only one or a few specialist items are required - would include a prototype before batch or volume production.
what are some noticeable features of one-off production?
designed and made to a client’s exact specification
labour and material costs are high
a high level of design and manufacturing skills are needed
what is vernacular design?
when traditional crafts are used to support local communities - local people, local materials, developing products for the local environment (e.g. inuit snow goggles). often an important part of the economy in developing countries.
what is batch production, and what are some characteristics of it?
when set quantities of a product are manufactured to order. requires a high level of design, pattern making, and sampling skills. materials are cost-effective and manufacturing costs are lower than one-off production.
what is mass production?
the production of large amounts of standardised products on production lines, permitting very high rates of production per worker.
what is continuous flow (CFM)?
a production method used to manufacture, produce or process materials without interruption (24/7). this eliminated the extra cost of starting and stopping the production process - highly automated with very few workers.
what is mass customisation?
a sophisticated CIM system that manufactures products to individual customer orders. the benefits of an economy of scale are gained whether the order is for a single item or for thousands. the basic form of the product is constant but using flexible CAM systems the product can be customised in terms of combinations, texture and patterns.
how do you choose the right production method?
consider the product being made and the size of the market
one-off: small firms operating in the service sector to cater to individual needs
batch: group orders
flow or continuous: used to mass produce standardised items
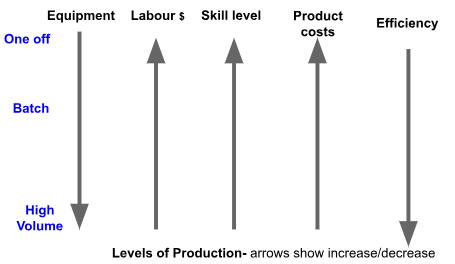
how do economies of scale work?
lead to lower unit costs and process - there is usually a trade off between unit costs and meeting specific customer needs
advantages and disadvantages of one off
advantages: unique, high-quality products; workers more motivated and take pride in their work
disadvantages: labour intensive (high selling prices); production can take a long time, cost a lot; economies of scale not possible
advantages and disadvantages of batch
advantages: lower unit costs; offers the customer some variety and choice; materials can be built in bulk (cheaper)
disadvantages: workers less motivated as work becomes repetitive; goods have to be stored until they are sold (expensive)
advantages and disadvantages of mass
advantages: lower labour costs; materials purchased in large quantities; large numbers of goods are produced
disadvantages: very expensive machinery; workers not motivated; production process has to stop for repairs; inflexible production processes
advantages and disadvantages of continuous
advantages: minimal labour costs, materials can be purchased in huge quantities, unlimited goods produced
disadvantages: very expensive machinery; inflexible production (which has to stop for repair)
what is a composite material?
a combination of two or more materials that are bonded together to improve their mechanical or physical properties. composites can be investigated as a whole but breaking them down into three key areas is most useful to achieve a detailed understanding - form, process and composition
how can textiles form part of a composite material?
fibres can be spun into filaments, string or rope, used as a component of a composite material or matted into sheets to make such products as fabrics, paper or felt. synthetic fibres can be produced very inexpensively and in large quantities, compared with natural fibres.
what can fabric fibres be combined with to form composite materials?
woven fabric fibres and other reinforcements are used in conjunction with resins (the matrix) to produce composite materials which combine the strengths and overcome the weaknesses of materials to produce very strong materials.
how can glass form part of a composite material? what can glass be combined with?
glass is generally made into sheets. when glass is laminated it becomes a composite because there is an interlayer between the glass sheets made from PVB (polyvinyl butyral). when the glass is shattered the interlayer keeps the glass layers bonded, preventing the glass breaking up/fragmenting.
how can metals form part of a composite material?
generally in particles. particle reinforced composites are less effective than fibre reinforcement. generally achieves gains in stiffness, strength and toughness.
what are the two categories of constituent materials?
matrix and reinforcement. the matrix for carbon fibre is an epoxy resin which surrounds and supports the reinforcement materials
how is carbon fibre produced industrially?
carbon fibre sheets and epoxy resin are cured in a moulding device called an autoclave with heat and pressure. this enables shapes to be made with very tight tolerances. on a more bespoke level, manufacturers use a hand-layup process - a mould is requires but the carbon fibre weave is layered between coats of epoxy resin.
what applications is woven carbon fibre useful for?
anything requiring a high strength-to-weight ratio
how is hand lay up different to spray lay up?
hand lay up is an open moulding method suitable for making a wide variety of composite products. production volume per mould is low and is feasible to produce substantial production quantities using multiple moulds.
spray lay up is an open mould similar to hand lay up, except it uses a chopped laminate with good conformability and is sometimes faster than hand lay-up in moulding complex shapes
what is pultrusion?
a continuous process for manufacture of composite materials with constant cross-section. the term combines pull and extrusion. the raw material is often a liquid resin mixture (fibres saturated with a liquid polymer), which is then pulled through a heated steel forming die using a continuous pulling device.