Law of Persons: Key Concepts, Domicile, Birth, and End of Legal Subjectivity with 100% expert curated questions and answers (Guaranteed Pass)
1/269
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
270 Terms
What is the due date for the assignment in the Law of Persons module?
22 April 2025
What format must the assignment answers be typed in?
MS Word format and saved as a PDF document.
What information must be included on the cover page of the assignment?
Name, Surname, Student Number, and Module Code.
What is the naming convention for saving the assignment file?
[STUDENTNUMBER] [MODULECODE] [SURNAME].pdf
![<p>[STUDENTNUMBER] [MODULECODE] [SURNAME].pdf</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f8d4bdf5-0047-44b1-954e-5a2f1c673e62.jpg)
Where must the assignment be submitted?
Through Canvas, inside the corresponding Module Course site.
What is the total marks for the Law of Persons assignment?
50 marks
What should students do if they experience difficulties during the submission process?
Contact the office for assistance.
What does the term 'predeceases' refer to in the context of a will?
It refers to a beneficiary dying before the testator, affecting inheritance.
What is the role of the spokesperson of Wingtastic Airlines in the scenario?
To confirm that none of the passengers or crew aboard the flight survived the crash.
What happens to Rory's estate if Megan predeceases him?
The entire estate is bequeathed to his brother, Brandon.
What is the significance of Megan not having a valid will?
It means her estate will be distributed according to intestacy laws.
What is the purpose of the STADIO study guides and teaching documents?
To provide integral learning material for students.
What should students regularly access to ensure they have the latest material?
CANVAS@mySTADIO
What is the contact number for the South African office?
+27 (0) 11 662 1444
What is the contact number for the Namibian office?
+264 (0) 83 331 0080
What type of reading material is available for optional enhancement of understanding?
Additional recommended reading material.
What does the term 'assignment' refer to in the context of this module?
A compulsory task that must be submitted for evaluation.
What is the consequence of presenting AI-generated work as one's own?
It contravenes the STADIO Plagiarism policy.
What is the purpose of the STADIO Referencing Guide?
To provide guidance on how to reference materials correctly.
What must students do if they do not see their module class appear in Canvas?
Contact the office for assistance.
What is the importance of the Glossary of terms in the study guide?
To provide definitions and explanations of key concepts.
What does the term 'assignment submission' entail?
Logging into Canvas and submitting the completed assignment by the due date.
What is the significance of the artificial intelligence traffic light matrix (AIMat)?
It indicates when AI may or may not be used in answering questions.
What is the purpose of the 'Meet Your Lecturer' section on Canvas?
To provide students with lecturer details for academic inquiries.
What is the first step in completing the assignment?
Include a cover page with required information.
What is the significance of a valid will in estate distribution?
A valid will allows for the assets of the deceased to be divided according to their stipulations.
What is the term for when a person dies without a valid will?
Intestate succession, where assets are devolved according to the Intestate Succession Act.
What are the key headings required in a legal essay about a case?
Facts of the case, legal question and presumption, judgment, and good academic writing.
How is domicile determined for an adult woman who moves frequently?
Domicile is based on the place where she has established her permanent home.
Where is Thabiso, a nine-year-old extra-marital child, domiciled?
Thabiso is domiciled with his father, as he lives with him.
What does private law deal with?
Private law broadly deals with legal rules that apply to private individuals rather than the State.
Are animals regarded as legal subjects in South African law?
False, animals are not regarded as legal subjects in South African law.
What is the minimum age of criminal accountability according to the Child Justice Act?
12 years.
Can a married minor qualify as a guardian for their child?
False, a married parent who is still a minor does not qualify as their child's guardian.
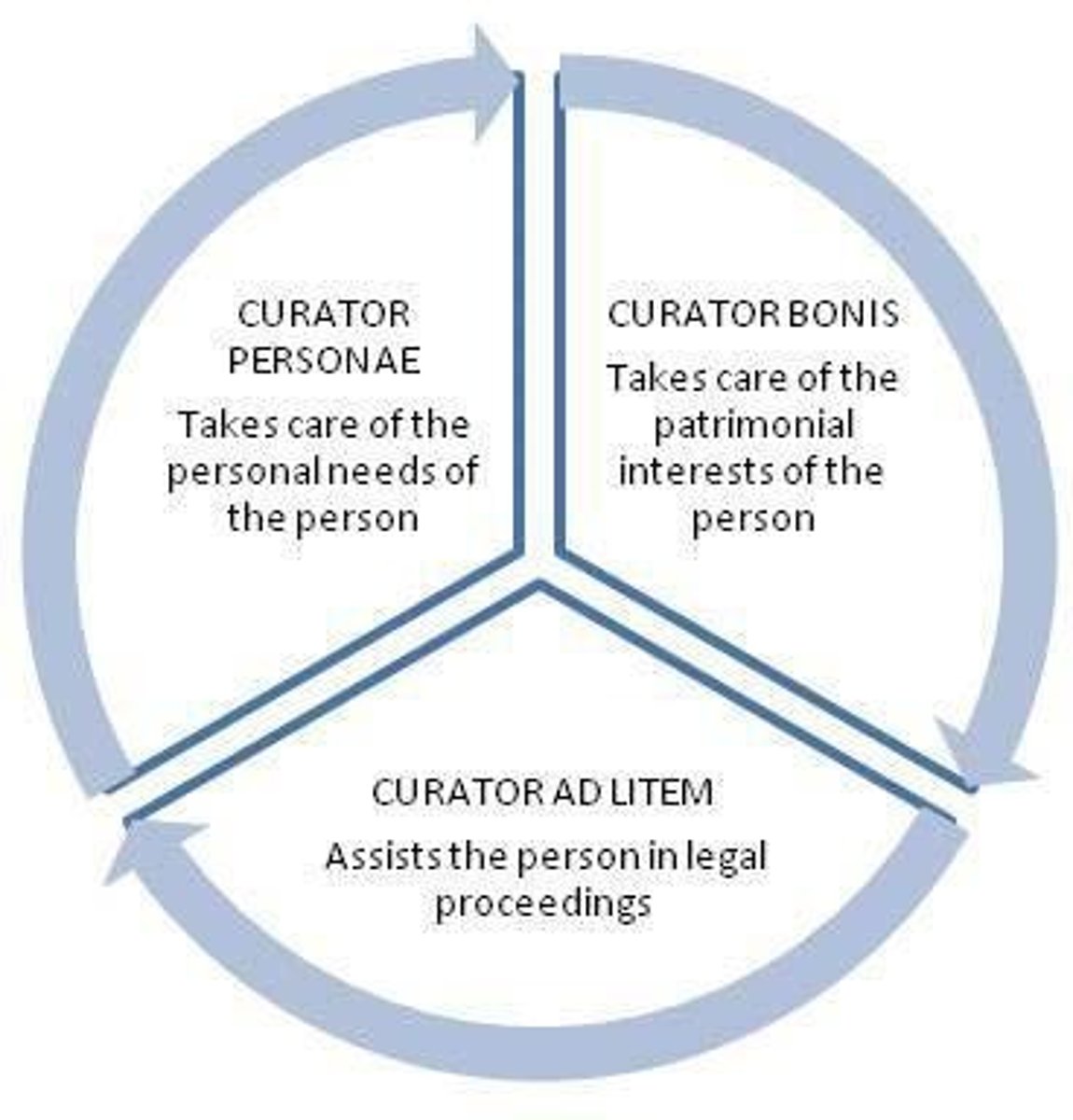
What is the role of a curator ad litem in legal proceedings involving minors?
A curator ad litem can be appointed to represent a minor's interests in legal proceedings.
What is the legal status of a child born to unmarried parents?
The legal status may differ based on the laws governing parental rights and responsibilities.
What is the purpose of the Intestate Succession Act?
To govern the distribution of assets when a person dies without a valid will.
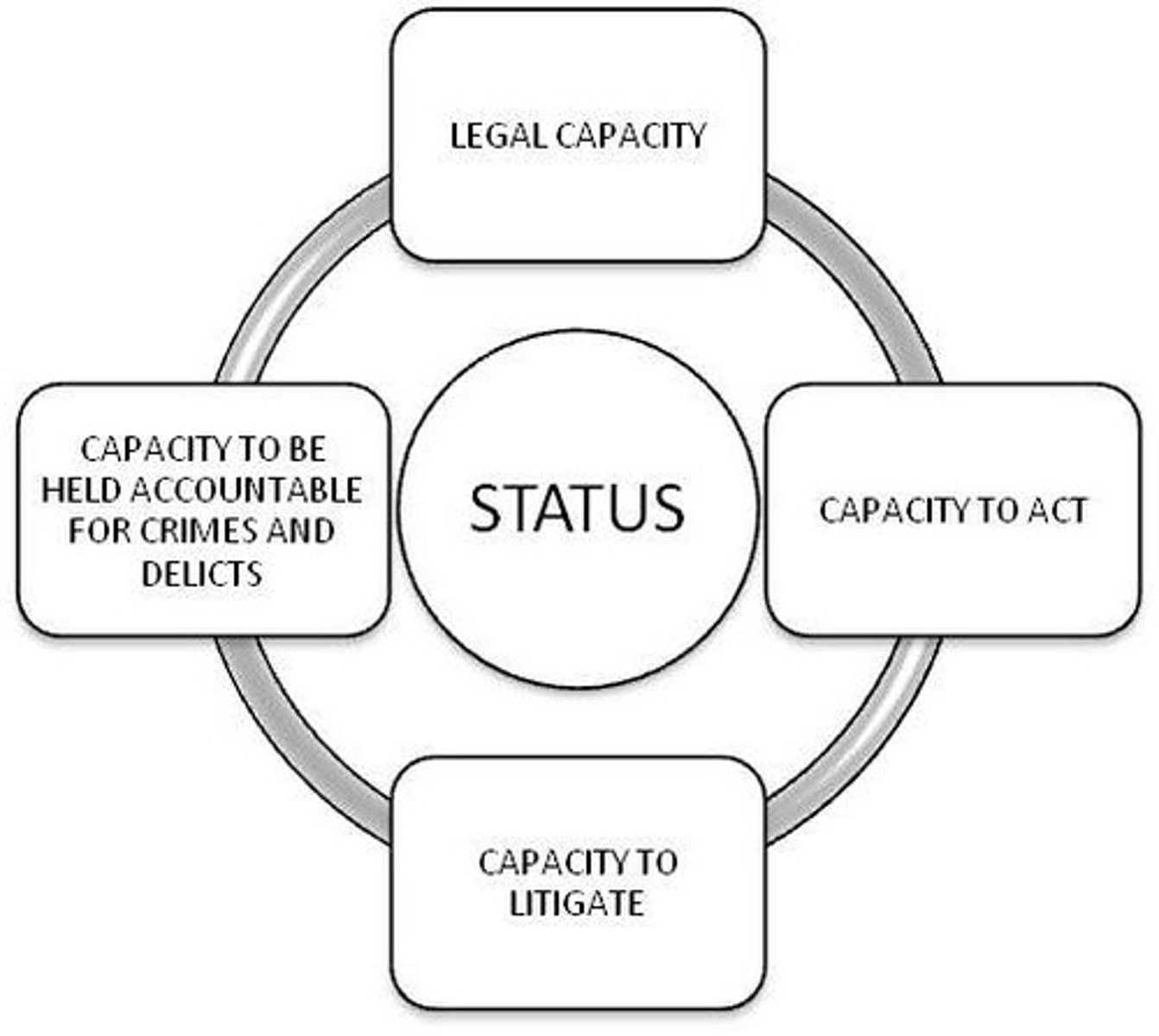
What is meant by 'legal subjectivity'?
Legal subjectivity refers to the capacity of a person to have legal rights and obligations.
What begins legal subjectivity?
Birth is recognized as the moment when legal subjectivity begins.
What is the significance of domicile in law?
Domicile determines a person's legal residence and jurisdiction for legal matters.
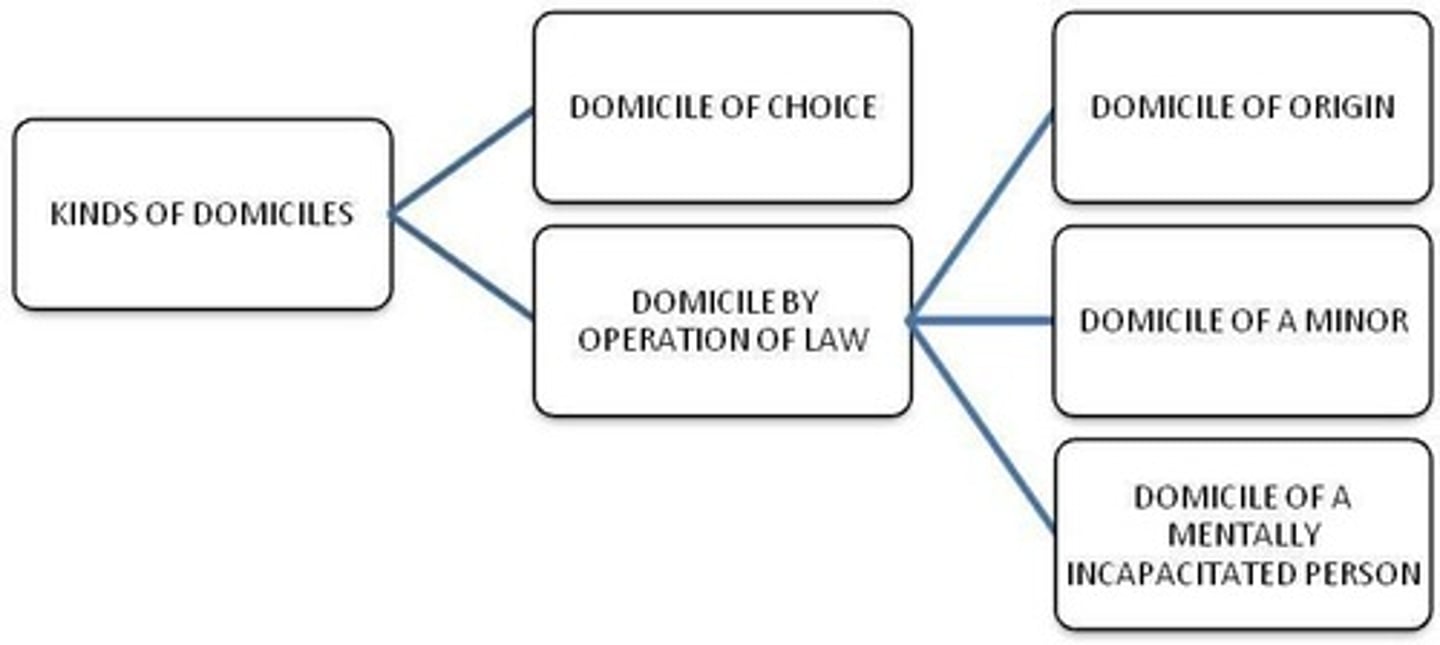
What are the different kinds of domiciles?
Domiciles can be classified as domicile of origin, domicile of choice, and domicile by operation of law.
What is the legal implication of a presumption of death?
It allows for the legal status of a person to be determined after a certain period of absence.
What is the duty to bury the deceased?
It is the legal obligation of the deceased's relatives or estate to arrange for their burial.
What is the impact of the Constitution of South Africa on the Law of Persons?
It influences legal principles and rights associated with personal status and legal identity.
What is the role of good academic writing (GAD) in legal essays?
GAD ensures clarity, coherence, and adherence to academic standards in legal writing.
What is the importance of understanding legal principles in the Law of Persons?
It enables individuals to analyze and apply relevant laws to factual situations.
What is the legal status of an infans (infant)?
An infans has limited legal capacity and is typically represented by guardians.
What factors can impact a person's legal status?
Factors include age, marital status, and adherence to customary law.
What is the significance of registration of births and deaths?
It provides legal recognition of a person's existence and status in society.
What is the primary focus of the Law of Persons in South Africa?
It provides an overview of the most important legal principles regarding legal subjects, recognizing all human beings as legal subjects with rights, duties, and capacities.
What significant change did the Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1996 bring to the Law of Persons?
It profoundly affected common law and legislation, including equal treatment of children born from artificial fertilization and same-sex adoption rights.
What was the outcome of the case J v Director-General, Department of Home Affairs (2003)?
A child born from artificial fertilization of a lesbian partner was placed on the same footing as a child born from a married woman for birth registration.
What did the case Du Toit v Minister of Welfare and Population Development (2003) establish?
It allowed same-sex partners to adopt jointly, granting legal recognition of guardianship and care for their children.
What was declared unconstitutional in Bhe v Magistrate, Khayelitsha (2005)?
The customary law rule of primogeniture, which favored male heirs, and the distinction between children born in and outside of marriage.
What key principle does Section 28(2) of the Constitution emphasize?
It states that a child's best interests are of paramount importance in all matters concerning the child.
How has the interpretation of the paramountcy principle evolved since the Constitution's commencement?
It has been refined to clarify that while the child's best interests are paramount, they are not absolute and can be limited.
What fundamental changes did the Children's Act 38 of 2005 introduce?
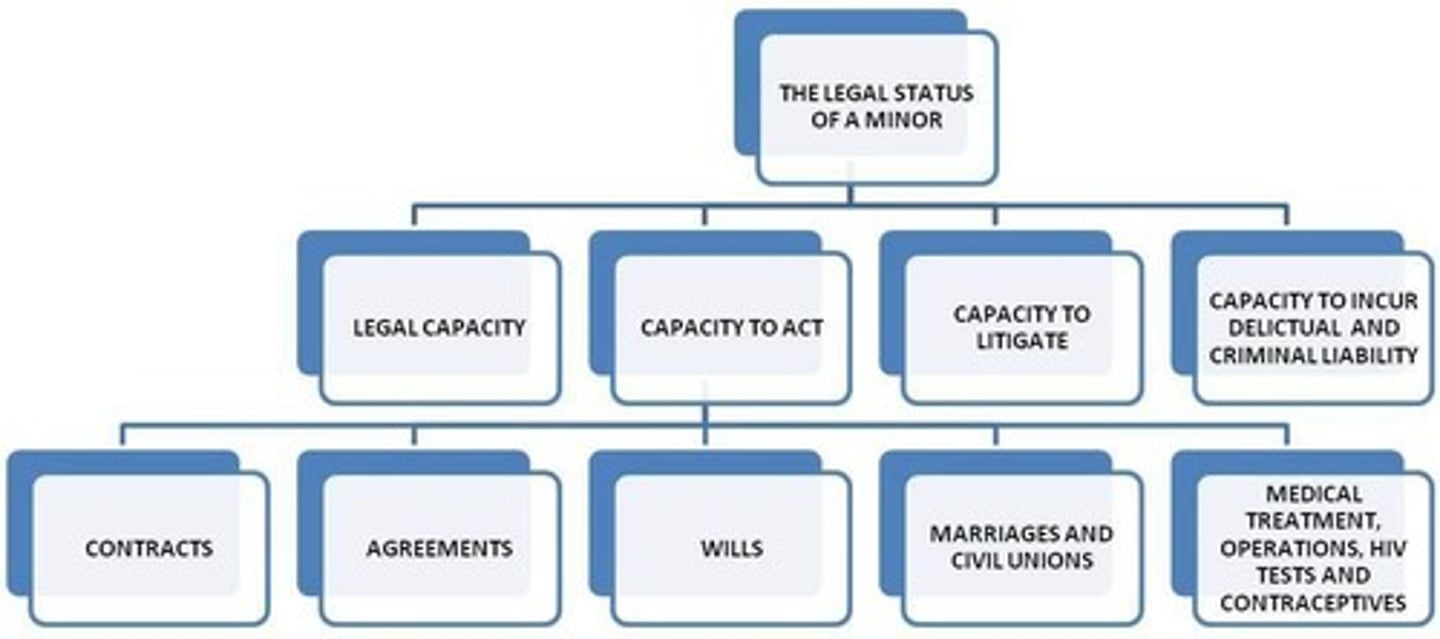
It enhanced the protection of children's best interests, replaced 'parental authority' with 'parental responsibilities and rights', and lowered the age of majority from 21 to 18.
What rights do unmarried fathers have under the Children's Act 38 of 2005?
They can acquire full parental responsibilities and rights under specified circumstances and can register agreements regarding these rights.
What provisions does the Children's Act 38 of 2005 include regarding medical consent for minors?
Minors over the age of 12 can consent to their own medical treatment if they are mature enough to understand the implications.
What is the minimum age of criminal accountability established by the Child Justice Act 75 of 2008?
The minimum age is now ten years, with children below this age being completely unaccountable for their crimes.
What change did the Child Justice Act 75 of 2008 make regarding children aged 7 to 14?
Children aged 7 to 14 are rebuttably presumed to lack criminal capacity, meaning they can be found responsible if the prosecution proves otherwise.
What does the term 'legal subject' refer to in the context of the Law of Persons?
It refers to all human beings recognized by law as having rights, duties, and capacities.
What is the impact of domicile on a person's legal rights and duties?
A person's age or domicile can affect the content of their legal rights, duties, and capacities.
What does the Children's Act 38 of 2005 say about consent to surgery for minors?
Minors over 12 can consent to their own surgery if they are mature enough, but must be assisted by a parent or guardian.
What new regulations regarding surrogacy were introduced by the Children's Act 38 of 2005?
It regulates surrogacy for the first time in South African law.
What does the Children's Act 38 of 2005 specify about access to contraceptives for minors?
Children aged 12 and older can access contraceptives without parental consent, although medical practitioners must be involved.
What is the significance of the Bill of Rights in the context of the Law of Persons?
It serves as a foundation for interpreting and applying legal principles regarding persons in South Africa.
What does the term 'parental responsibilities and rights' mean under the Children's Act?
It refers to the legal responsibilities and rights of parents regarding the care and well-being of their children.
How does the Law of Persons affect every human being?
It establishes that all human beings have legal subjectivity, which commences and ends at specific stages.
What is the role of the courts in interpreting the paramountcy principle for children's rights?
Courts refine the interpretation to balance children's best interests with other rights, ensuring no right is absolute.
What does the Children's Act 38 of 2005 state about consent for HIV testing?
It includes provisions similar to those for medical treatment consent, allowing minors to consent under certain conditions.
What is the minimum age of criminal capacity according to the Child Justice Amendment Act 28 of 2019?
The minimum age of criminal capacity will be raised to 12 years.
What presumption is made about children aged 12 to 14 under the Child Justice Amendment Act?
There will be a presumption that children between the ages of 12 and 14 are unaccountable.
What significant legal change was established in Road Accident Fund v Mtati 2005 regarding the nasciturus fiction?
The Supreme Court of Appeal decided it is unnecessary to extend the nasciturus fiction to the law of delict.
What does the law of persons regulate?
It regulates the coming into being and the coming to an end of a person (legal subject) and that person's private-law status.
What is the difference between objective law and subjective law?
Objective law refers to the system of laws and rules, while subjective law deals with the relationships and rights between legal subjects.
What is a legal subject?
A legal subject is an entity that can have rights, duties, and capacities.
What is a legal object?
A legal object refers to objects upon which the law has not conferred the capacity to have rights, duties, and capacities.
What are the four categories of legal objects?
The four categories are corporeal things, immaterial property, personality property, and performance.
What are the two categories of legal subjects?
Natural persons and juristic persons.
How is a juristic person defined?
A juristic person has a legal existence independent from its members and can acquire rights, duties, and capacities.
What are the three categories of juristic persons?
1. Associations established in separate legislation, 2. Associations incorporated in terms of enabling legislation, 3. Associations complying with common requirements for establishment.
What is the significance of birth in legal subjectivity?
Birth is recognized as the moment when legal subjectivity begins.
What legal protections are afforded to unborn children?
Unborn children may require legal protection, which is discussed under the nasciturus fiction.
What is the objective law also known as?
Positive law.
What is the relationship between a legal subject and a legal object?
A legal subject has claims over a legal object.
What is the role of subjective rights?
Subjective rights deal with the legal relationships between the bearer of the right and other legal subjects or objects.
What does the law of persons include regarding private law?
It includes rules that apply to legal relationships between legal subjects, such as contracts and family law.
What is the importance of the law of persons in South African law?
It defines who qualifies as a legal subject and what they are legally able to do.
How does the law of persons relate to the protection of interests?
It provides a framework for protecting the interests of both natural and juristic persons.
What is the significance of the term 'nasciturus fiction'?
It refers to the legal principle that an unborn child is considered a legal subject for certain protections.
What is the relationship between legal subjects and legal interaction?
Legal subjects participate in legal interactions and can possess rights and obligations.
What are the self-assessment questions related to the law of persons?
They include defining the law of persons, explaining legal subjects and objects, and discussing the beginning of legal subjectivity.
What does the nasciturus fiction provide for unborn children?
It allows an unborn child to be deemed as already born if it is to their advantage, keeping their interests open until live birth occurs.
In which area of law is the nasciturus fiction specifically applied?
The law of succession.
What is the legal significance of birth in relation to legal subjectivity?
Legal subjectivity begins at birth, which requires the fetus to be completely separate from the mother's body and to have lived independently.
What are the two requirements for a birth to be considered legally complete?
1. The fetus must be completely separate from the mother's body. 2. The fetus must have lived independently after separation.
What constitutes a sign of life for legal purposes?
Any sign of life, such as breathing, crying, or a detectable heartbeat.
What does Section 239(1) of the Criminal Procedure Act 51 of 1977 state regarding child murder?
A child is deemed to have been born alive if it is proved to have breathed, regardless of other conditions.
What obligation does the Births and Deaths Registration Act 51 of 1992 impose?
It creates an obligation to register the birth of a child born alive, based on any sign of life.